笔记2. 堆(优先队列)
Posted 胖白白
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了笔记2. 堆(优先队列)相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
堆(优先队列)
堆的概念
- 堆是满二叉树:从左到右依次变满(一般用数组下标存储)

父节点和左右节点的位置
节点i位置对应的父子节点位置
父节点: (i - 1) / 2;
左子节点: 2 * i + 1
右子节点: 2 * i + 2
大根堆和小根堆
- 大根堆:每棵子树的头节点为当前树的最大值
- 小根堆:每棵子树的头节点为当前树的最小值
堆的行为:上浮(insert)、下沉(pop)
待刷的题

完全二叉树的高度
堆排序
需要两步:
- 数组array->大根堆。在这个过程中array也发生了变化,但是还未完成有序。但是大根堆的第1个元素就是array中最大的。
- 把大根堆第1个和最后一个做交换,然后heapSize--,直到heapSize为0,array中所有数据都处理完了,数组排序完成。
练习题
703. 数据流中的第 K 大元素
#define Parent(i) ((i - 1) / 2)
#define Left(i) ((i * 2) + 1)
#define Right(i) ((i * 2) + 2)
/* 小根堆 */
typedef struct
int *heap;
int heapSize;
int capacity;
KthLargest;
int Top(KthLargest *obj)
return obj->heap[0];
void Swap(int *a, int *b)
int tmp = *a;
*a = *b;
*b = tmp;
void Swim(KthLargest *obj, int index)
int cur = index;
while (cur >= 0 && obj->heap[Parent(cur)] > obj->heap[cur])
Swap(&obj->heap[Parent(cur)], &obj->heap[cur]);
cur = Parent(cur);
/* 下沉:从堆的指定位置(一般是顶部),开始下沉 */
void Sink(KthLargest *obj, int index)
int cur = index;
int reChild = cur;
while (cur < obj->capacity)
if (Left(cur) >= obj->capacity)
break;
if (obj->heap[Left(cur)] < obj->heap[cur])
reChild = Left(cur);
if (Right(cur) < obj->capacity && obj->heap[Right(cur)] < obj->heap[Left(cur)])
reChild = Right(cur);
if (obj->heap[reChild] < obj->heap[cur])
Swap(&obj->heap[reChild], &obj->heap[cur]);
cur = reChild;
else
break;
void HeapAdd(KthLargest *obj, int num)
// printf("add num = %d, Top(obj) = %d\\n", num, Top(obj));
if (obj->heapSize < obj->capacity)
obj->heap[obj->heapSize] = num;
++(obj->heapSize);
Swim(obj, obj->heapSize - 1);
else if (Top(obj) < num)
obj->heap[0] = num;
Sink(obj, 0);
KthLargest* kthLargestCreate(int k, int* nums, int numsSize)
KthLargest *obj = malloc(sizeof(KthLargest));
obj->heap = malloc(sizeof(int) * k);
obj->heapSize = 0;
obj->capacity = k;
for (int i = 0; i < numsSize; i++)
HeapAdd(obj, nums[i]);
return obj;
int kthLargestAdd(KthLargest* obj, int val)
HeapAdd(obj, val);
return Top(obj);
void kthLargestFree(KthLargest* obj)
free(obj->heap);
free(obj);
/**
* Your KthLargest struct will be instantiated and called as such:
* KthLargest* obj = kthLargestCreate(k, nums, numsSize);
* int param_1 = kthLargestAdd(obj, val);
* kthLargestFree(obj);
*/
347. 前 K 个高频元素
#define GetParent(i) ((i - 1) / 2)
#define GetLeftChid(i) ((2 * i) + 1)
#define GetRightChild(i) ((2 * i) + 2)
// #define TopCnt(Heap *heap) ((heap)->data[0].cnt)
typedef struct HashTable
int key; // num
int val; // 出现次数
UT_hash_handle hh;
HashTable;
HashTable *g_hash;
typedef struct Data
int num;
int cnt;
Data;
typedef struct Heap
Data *data;
int heapSize;
int capacity;
Heap; // 小根堆
void Swap(Data *a, Data *b)
Data tmp;
tmp.num = a->num;
tmp.cnt = a->cnt;
(*a).num = (*b).num;
(*a).cnt = (*b).cnt;
(*b).num = tmp.num;
(*b).cnt = tmp.cnt;
int TopCnt(Heap *heap)
return heap->data[0].cnt;
/* 上浮:添加到堆的指定位置(一般是尾巴),然后按照小根堆依次上浮上来 */
void Swim(Heap *heap, int index)
while (index >= 0 && heap->data[GetParent(index)].cnt < heap->data[index].cnt)
Swap(&heap->data[GetParent(index)], &heap->data[index]);
index = GetParent(index);
/* 下沉:从堆的指定位置(一般是顶部),开始下沉 */
void Sink(Heap *heap, int index)
int left, right;
int reChild;
while (index < heap->capacity)
left = GetLeftChid(index);
if (left >= heap->capacity)
break;
right = GetRightChild(index);
if (right < heap->capacity)
reChild = heap->data[left].cnt < heap->data[right].cnt ? left : right;
else
reChild = left;
if (heap->data[reChild].cnt < heap->data[index].cnt)
Swap(&heap->data[reChild], &heap->data[index]);
else
break;
index = reChild;
void HeapAdd(Heap *heap, int num, int cnt)
if (heap->heapSize >= heap->capacity) // 如果堆没有满则无脑添加
heap->data[heap->heapSize].num = num;
heap->data[heap->heapSize].cnt = cnt;
(heap->heapSize)++;
Swim(heap, heap->heapSize - 1);
else if (TopCnt(heap) < cnt) // 如果堆满了,则要在堆顶元素频次小于待添加元素频次,才添加
heap->data[0].num = num;
heap->data[0].cnt = cnt;
Sink(heap, 0);
int* topKFrequent(int* nums, int numsSize, int k, int* returnSize)
// 1. 遍历数组,将每个数出现的频次存到hash表中
g_hash = NULL;
HashTable *cur = NULL;
HashTable *tmp = NULL;
for (int i = 0; i < numsSize; i++)
HASH_FIND_INT(g_hash, &nums[i], cur);
if (cur == NULL)
cur = malloc(sizeof(HashTable));
cur->key = nums[i];
cur->val = 1;
HASH_ADD_INT(g_hash, key, cur);
else
++(cur->val);
// 2. 遍历hash表,开始往小根堆里push或pop节点
Heap *heap = malloc(sizeof(Heap));
heap->data = malloc(sizeof(Data) * k);
heap->heapSize = 0;
heap->capacity = k;
HASH_ITER(hh, g_hash, cur, tmp)
HeapAdd(heap, cur->key, cur->val);
HASH_DEL(g_hash, cur);
// 3. 取出小根堆的结果存到结果数组中
*returnSize = k;
int *res = malloc(sizeof(int) * k);
for (int i = 0; i < k; i++)
res[i] = heap->data[i].num;
return res;
优先队列及(二叉)堆
数据结构书籍与算法书(包括算法导论、算法设计)通常将优先队列(Priority Queue)与堆(Heap)放在一起讲,算法导论上先讲堆这个特殊的数据结构,后讲堆的两个应用,堆排序与优先队列。算法设计这本书先讲优先队列是个什么样的数据结构,有什么性质,为什么需要优先队列这种数据结构,然后讲实现优先队列有什么样的要求,而这些要求数组(Array)和链表(Linked List)都不能满足,所以我们需要设计一种新的数据结构来满足这些要求,那就是堆。个人更喜欢算法设计书上这种顺序。
某些特定的算法,只需要数据的一部分信息,而不需要全部的信息,这个时候为了提升算法的效率,可能需要设计某个特定的数据结构,这个特定的数据结构只保留了该算法需要的那部分信息,而舍弃了其余的信息,舍弃这部分信息换来了效率上的提升,这正是我们所需要的。举个例子直观一点,数组这种数据结构,你可以知道数组中每个元素(element)的值,这相当于知道所有信息,而堆这种数据结构,譬如最小堆,你只知道堆顶的元素是多少,而堆中其它的元素你是不知道的,相当于你只知道部分信息。而如果某个算法,你只关心一批数据中的最小值,而不关心具体每个数据的值,那最小堆就正能满足你的需求。效率方面而言,对于大小为n的数组,求最小值需要遍历整个数组,时间为(mathcal{O}(n)),而最小堆的堆顶元素即堆中数据的最小值,只需要(mathcal{O}(1))时间。
在【待填坑】稳定匹配问题中,需要维护一个集合S,对集合S的操作包括:插入元素、删除元素,访问最高优先级(优先级自己定义)的元素,而优先队列正是为此设计的。
优先队列
定义
优先队列是一种数据结构,其维护一个集合S,每一个元素(vin S)都有对应的键值(key(v))表示该元素的优先级,小键值对应高优先级。优先队列支持插入元素、删除元素、访问最小键值元素(^{[1]})。
优先队列的一个典型应用是简化的计算机进程调度(process scheduling)问题,每一个进程有一个优先级。每个进程的产生不是按照优先级顺序,我们维护一个进程的集合,每次我们在集合中选取一个最高优先级的进程去运行,同时从集合中删除该进程,另外我们还会往这个集合增加新的进程,这些正对应着优先队列的功能。
期望复杂度
那么我们期望大小为n的优先队列的时间复杂度达到多少呢?
我们知道基于比较的排序算法的时间复杂度的下界为(mathcal{O}(nlog n)),从这个下界出发,我们可以得出优先队列每次插入元素、删除元素、访问最小键值元素的期望时间复杂度。设想我们有一个大小为n的数组,我们依次将每个数组元素都加入到优先队列中,然后再将优先队列的元素依次都取出来,那么取出来元素就已经有顺序了,我们实现了对一个数组的排序。以上操作共有n次插入、n次取出、n次删除操作,那么可知,优先队列的这些基本操作的时间复杂度的(大概)下界应该是(mathcal{O}(log n))。但实际情况中,由于优先队列的实现方法不一样,基本操作的时间复杂度下界也不同(^{[3]}),但是对于数组排序这个问题而言,采用优先队列的方法进行排序(实际上就是堆排序)的时间复杂度下界是(mathcal{O}(nlog n))。
堆
数组和链表的局限
对于数组或者链表而言,基本操作能否达到(mathcal{O}(log n))?
答案是否定的。以进程调度问题举例,假如我们按照优先级顺序把进程放在不同的位置,那么访问操作和删除操作的时间都可以是(mathcal{O}(1))。但插入操作就不符合要求了,对于数组而言,找到要插入的位置可通过二分查找达到(mathcal{O}(log n))的时间,但插入元素的时间是(mathcal{O}(n)),而对于链表而言,插入元素的时间是(mathcal{O}(1)),但我们要找到插入的位置需要(mathcal{O}(n))的时间。综上,数组和链表都不符合我们的要求,需要设计新的数据结构——堆。
定义
堆有很多种类型,二叉堆、二项堆、斐波那契堆等,在这里讲的是二叉堆。二叉堆可以看作是平衡二叉树或近似的完全二叉树,平衡二叉树中任意一个节点的左右子树的深度之差不超过1,完全二叉树的叶节点的深度相同,内部节点的度(degree,孩子节点的数量)相同。
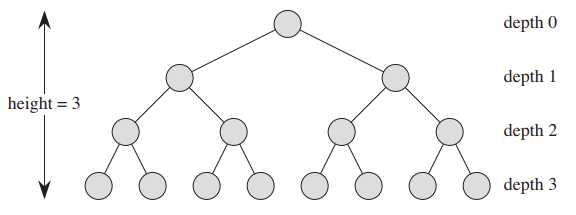
下图是一个堆的示意图,同时也是一个平衡二叉树,可以看出,堆之所以叫做近似的完全二叉树是因为不是所有内部节点的度都相同。
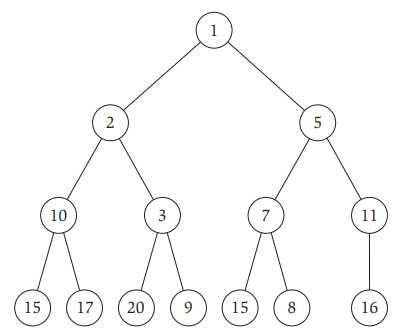
堆有一个性质,称作heap order, 对于最小堆而言,即树中任意一个节点的键值key要大于等于其父节点的键值key,最大堆反之。图2表示的是最小堆。
通常采用数组来存储堆,图2所示的最小堆可以存储如下图3所示:
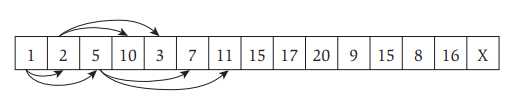
其中,数组A下标从1到N,N为堆的大小,A[1]是根节点,A[2]是根节点的左子孩节点,A[3]是根节点的右子孩节点。实际上,对于任何一个节点,若其在数组中的位置是i,则它的左子孩节点位置(left\\_child(i)=2i),右子孩节点位置(right\\_child=2i+1),它的父节点(假如有)的位置(parent(i)=lfloor i floor),(lfloor i floor)表示对i向下取整。图3中的箭头从父节点分别指向左右子孩节点。
用堆实现优先队列
基本操作
我们回顾优先队列的基本操作,并看看用数组表示的最小堆怎么实现这些操作。
- 访问优先级最高(键值key最小)的元素
由堆的heap order性质可以知道,A[1]即是键值最小的元素,所以只需要返回A[1]的值即可。
- 插入元素
我们维护一个变量(length)表示堆的大小,每次往堆里添加元素的时候,将(length)加1,然后将元素的值赋给数组A中(length)位置。
- 删除元素
优先队列的许多应用通常只会在访问优先级最高的元素后删除该元素。对于数组A而言,只需要把A[1]删除即可,具体实现时,我们将A[length]赋值给A[1],然后length减一。
我们需要注意一点,插入元素与删除元素会改变数组的值,而改变之后该数组是否还能表示一个堆呢?答案是不一定,因为数组值改变后不一定符合heap order,所以我们需要做一些操作,来维护堆的heap order性质。
维护堆的性质
以维护最大堆的heap order性质为例,插入元素后,A[length]的值有可能大于A[parent(length)]的值,所以需要将A[length]的值调整到合适的位置。需要heap_increase_key来实现插入操作,伪代码(^{[2]})如下:
heap_increase_key(A, i, key){
A[i] = key
while(i > 1 && A[parent(i)] < A[i]) {
exchange A[i] and A[parent(i)]
i = parent(i)
}
} 简单来说,就是若A[i]的值大于其父节点的值,则交换二者,直到A[i]的值小于等于父节点的值或已到达根节点。图4是heap_increase_key(A, 9, 15)的示意图:
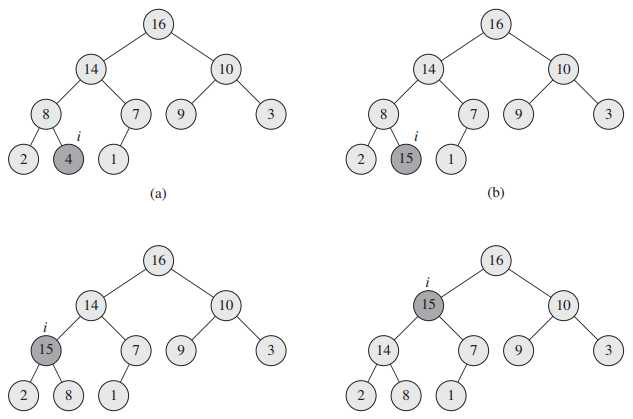
类似地,删除元素后,A[length]的值赋值给A[1],而此时A[1]可能小于A[left_child(1)]或A[right_child(1)],所以需要将A[1]的值调整到合适的位置。采用max_heapify函数来实现删除操作,输入数组A和下标i,我们假设A[i]是唯一违反堆性质的值,调用max_heapify(A, i)使得A[i]的值在最大堆中“逐级下降”,从而维护堆的性质。伪代码(^{[2]})如下:
max_heapify(A, i){
l = left_child(i)
r = right_child(i)
largest = i
if(l <= length && A[l] > A[i])
largest = l
if(r <= length && A[r] > A[largest])
largest = r
if(largest != i){
exchange A[i] and A[largest]
max_heapify(A, largest);
}
} 简单来说,就是在i节点及左右子孩节点中,选出键值最大的节点largest,若largest不是i,则交换A[i]和A[largest]的值,此时这三个节点是符合堆性质的,但A[largest]可能违反堆性质,所以我们递归调用max_heapify(A, largest)函数。图5是max_heapify(A, 2)的示意图。
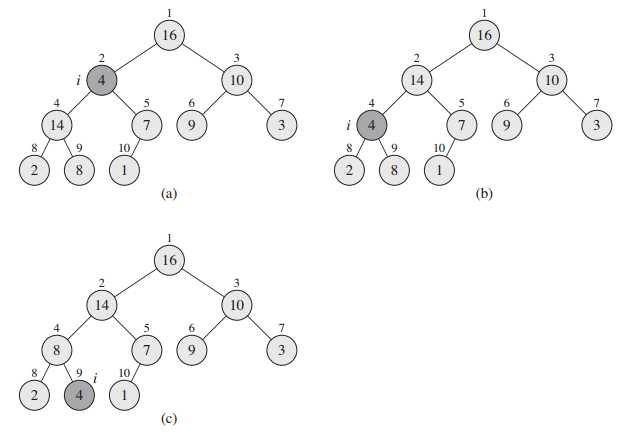
heap_increase_key和max_heapify都是沿着树的路径走,最坏情况下从叶节点走到根节点(max_heapify从根节点走到叶节点),则时间复杂度为(mathcal{O}(log n))。
类似heap_increase_key和max_heapify,不难得到heap_decrese_key和min_heapify,从而我们可以将优先队列的插入元素和删除元素操作完善如下:
- 插入元素
我们维护一个变量(length)表示堆的大小,每次往堆里添加元素的时候,将(length)加1,然后将INT_MIN赋给A[length],然后调用1次heap_decrease_key(A, length, key)。
- 删除元素
优先队列的许多应用通常只会在访问优先级最高的元素后删除该元素。对于数组A而言,只需要把A[1]删除即可,具体实现时,我们将A[length]赋值给A[1],然后length减一。然后调用1次min_heapify(A, 1)。
优先队列基本操作的时间复杂度
| 操作 | 时间复杂度 |
|---|---|
| 插入元素 | (mathcal{O}(log n)) |
| 删除元素 | (mathcal{O}(log n)) |
| 访问优先级最高的元素 | (mathcal{O}(1)) |
具体实现
根据上面的基本操作,给出基于最小堆的优先队列的伪代码如下:
- 访问最小键值元素
heap_minimum(A){
return A[1]
}- 插入操作
min_heap_insert(key){
length = length + 1
A[length] = INT_MAX
heap_decrease_key(length, key)
}- 访问键值最大元素后删除该元素
heap_extract_min(A){
min = A[1]
A[1] = A[length]
length = length - 1
min_heapify(A, 1)
return min
}例子
算法课的练习题:Dynamic Median
防止链接失效截一张图放这:

算法思路
分别实现一个最大堆、一个最小堆,最大堆中的所有元素小于等于最小堆中的任何元素。最大堆最小堆的大小相差不超过1,当最小堆的大小比最大堆的大小大1时,中位数为最小堆的堆顶元素,其余情况,中位数均为最大堆的堆顶元素(与题目要求一致)。插入新元素时,若元素值大于中位数则插入到最小堆,反之,插入到最大堆,同时应保持两个堆的大小相差不超过1。
自己编写堆实现
23596kB, 1084ms
代码比较长,因为为了与上文中伪代码的函数名对应,分开实现最大堆最小堆。
#include <stdio.h>
#include <math.h>
#include <limits.h>
#include <algorithm>
#include <iostream>
#define parent(i) (int)std::floor(i/2)
#define left(i) i * 2
#define right(i) i * 2 + 1
int A[5005], B[5005];//分别存储最大堆、最小堆
int max_heap_size, min_heap_size;
void exchange(int* array, int i, int j) {
int temp = array[i];
array[i] = array[j];
array[j] = temp;
}
//最大堆
void heap_increase_key(int i, int key) {
if (key < A[i])
printf("error: new key is smaller than current key.");
A[i] = key;
while (i > 1 && A[parent(i)] < A[i])
{
exchange(A, i, parent(i));
i = parent(i);
}
}
void max_heap_insert(int key) {
max_heap_size++;
A[max_heap_size] = INT_MIN;
heap_increase_key(max_heap_size, key);
}
int heap_maximum(void) {
return A[1];
}
void max_heapify(int i) {
int l = left(i), r = right(i);
int largest = i;
if (l <= max_heap_size && A[l] > A[i])
largest = l;
if (r <= max_heap_size && A[r] > A[largest])
largest = r;
if (largest != i) {
exchange(A, i, largest);
max_heapify(largest);
}
}
int heap_extract_max(void) {
int max = A[1];
A[1] = A[max_heap_size];
max_heap_size--;
max_heapify(1);
return max;
}
//最小堆
void heap_decrease_key(int i, int key) {
if (key > B[i])
printf("error: new key is bigger than current key.");
B[i] = key;
while (i > 1 && B[parent(i)] > B[i])
{
exchange(B, i, parent(i));
i = parent(i);
}
}
void min_heap_insert(int key) {
min_heap_size++;
B[min_heap_size] = INT_MAX;
heap_decrease_key(min_heap_size, key);
}
int heap_minimum(void) {
return B[1];
}
void min_heapify(int i) {
int l = left(i), r = right(i);
int smallest = i;
if (l <= min_heap_size && B[l] < B[i])
smallest = l;
if (r <= min_heap_size && B[r] < B[smallest])
smallest = r;
if (smallest != i) {
exchange(B, i, smallest);
min_heapify(smallest);
}
}
int heap_extract_min(void) {
int min = B[1];
B[1] = B[min_heap_size];
min_heap_size--;
min_heapify(1);
return min;
}
int quary(void) {
if (min_heap_size == max_heap_size + 1)
return heap_minimum();
else//max_heap_size = min_heap_size + 1或size相等
return heap_maximum();
}
void insert(int x) {
if ((!min_heap_size) && (!max_heap_size))//第一个数据
max_heap_insert(x);
else {
int median = quary();
if (x < median) {
max_heap_insert(x);
if (max_heap_size == min_heap_size + 2)//保持最大堆和最小堆的size相差不超过1
min_heap_insert(heap_extract_max());
}
else {
min_heap_insert(x);
if (min_heap_size == max_heap_size + 2)
max_heap_insert(heap_extract_min());
}
}
}
void del(void) {//del操作后,最大堆最小堆的size相差不超过1的性质不变
if (min_heap_size == max_heap_size + 1)
heap_extract_min();
else
heap_extract_max();
}
int main() {
int t, n, x;
char op;
scanf("%d", &t);
while (t--) {
max_heap_size = 0;
min_heap_size = 0;
scanf("%d", &n);
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
scanf(" %c", &op);
if (op == 'I') {
scanf("%d", &x);
insert(x);
}
else if (op == 'Q')
printf("%d
", quary());
else
del();
}
}
return 0;
}库函数实现
23724kB, 1288ms
#include <stdio.h>
#include <queue>
#include <functional>
std::priority_queue<int> max_heap;
std::priority_queue<int, std::vector<int>, std::greater<int>> min_heap;
int quary(void) {
if (min_heap.size() == max_heap.size() + 1)
return min_heap.top();
else//max_heap_size = min_heap_size + 1或size相等
return max_heap.top();
}
void insert(int x) {
if (min_heap.empty() && max_heap.empty())
max_heap.push(x);
else {
int median = quary();
if (x < median) {
max_heap.push(x);
if (max_heap.size() == min_heap.size() + 2) {
min_heap.push(max_heap.top());
max_heap.pop();
}
}
else {
min_heap.push(x);
if (min_heap.size() == max_heap.size() + 2) {
max_heap.push(min_heap.top());
min_heap.pop();
}
}
}
}
void del(void) {
if (min_heap.size() == max_heap.size() + 1)
min_heap.pop();
else
max_heap.pop();
}
int main() {
int t, n, x;
char op;
scanf("%d", &t);
while (t--) {
while (!min_heap.empty())
min_heap.pop();
while (!max_heap.empty())
max_heap.pop();
scanf("%d", &n);
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
scanf(" %c", &op);
if (op == 'I') {
scanf("%d", &x);
insert(x);
}
else if (op == 'Q')
printf("%d
", quary());
else
del();
}
}
return 0;
}
参考:
[1] 算法设计
[2] 算法导论
[3] Algorithm Design lecture slides: binary and binomial heaps
以上是关于笔记2. 堆(优先队列)的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章