Redis 源码解析之通用双向链表(adlist)
Posted 杨领well的博客
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了Redis 源码解析之通用双向链表(adlist)相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
Redis 源码解析之通用双向链表(adlist)
概述
Redis源码中广泛使用 adlist(A generic doubly linked list),作为一种通用的双向链表,用于简单的数据集合操作。adlist提供了基本的增删改查能力,并支持用户自定义深拷贝、释放和匹配操作来维护数据集合中的泛化数据 value。
adlist 的数据结构
- 链表节点
listNode, 作为双向链表,prev,next指针分别指向前序和后序节点。void*指针类型的value用于存放泛化的数据类型(如果数据类型的 size 小于sizeof(void*), 则可直接存放在value中。 否则value存放指向该泛化类型的指针)。
// in adlist.h
typedef struct listNode
struct listNode *prev;
struct listNode *next;
void *value;
listNode;
- 链表迭代器
listIter, 其中next指针指向下一次访问的链表节点。direction标识当前迭代器的方向是AL_START_HEAD(从头到尾遍历)还是AL_START_TAIL(从尾到头遍历)。
// in adlist.h
typedef struct listIter
listNode *next;
int direction;
listIter;
/* Directions for iterators */
#define AL_START_HEAD 0
#define AL_START_TAIL 1
- 双向链表结构
list。 其中,head和tail指针分别指向链表的首节点和尾节点。len记录当前链表的长度。函数指针dup,free和match分别代表业务注册的对泛化类型value进行深拷贝,释放和匹配操作的函数。(如果没有注册dup, 则默认进行浅拷贝。 如果没有注册free, 则不对value进行释放。如果没有注册match则直接比较value的字面值)
// in adlist.h
typedef struct list
listNode *head;
listNode *tail;
void *(*dup)(void *ptr);
void (*free)(void *ptr);
int (*match)(void *ptr, void *key);
unsigned long len;
list;
adlist 的基本操作
- 创建:
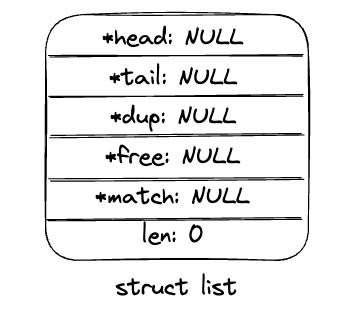
listCreate初始化相关字段为零值。可以通过listSetDupMethod,listSetFreeMethod,listSetMatchMethod来注册该链表泛化类型value的dup,free和match函数。
/* Create a new list. The created list can be freed with
* listRelease(), but private value of every node need to be freed
* by the user before to call listRelease(), or by setting a free method using
* listSetFreeMethod.
*
* On error, NULL is returned. Otherwise the pointer to the new list. */
list *listCreate(void)
struct list *list;
if ((list = zmalloc(sizeof(*list))) == NULL)
return NULL;
list->head = list->tail = NULL;
list->len = 0;
list->dup = NULL;
list->free = NULL;
list->match = NULL;
return list;
#define listSetDupMethod(l,m) ((l)->dup = (m))
#define listSetFreeMethod(l,m) ((l)->free = (m))
#define listSetMatchMethod(l,m) ((l)->match = (m))
- 在链表首插入新节点:
listAddNodeHead
-
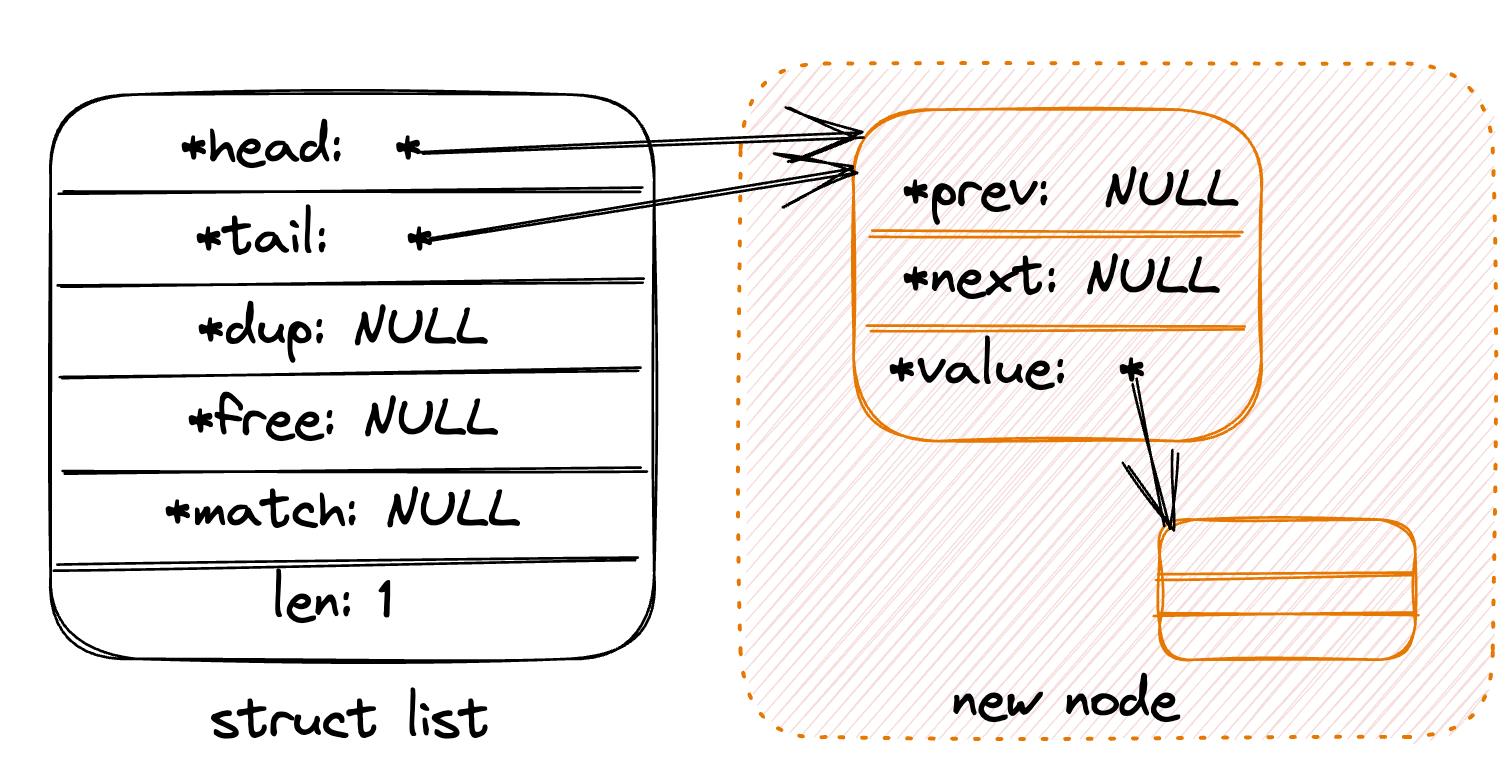
在空链表插入新节点: 为
value创建新节点,并让list的head和tail都指向新节点。
-
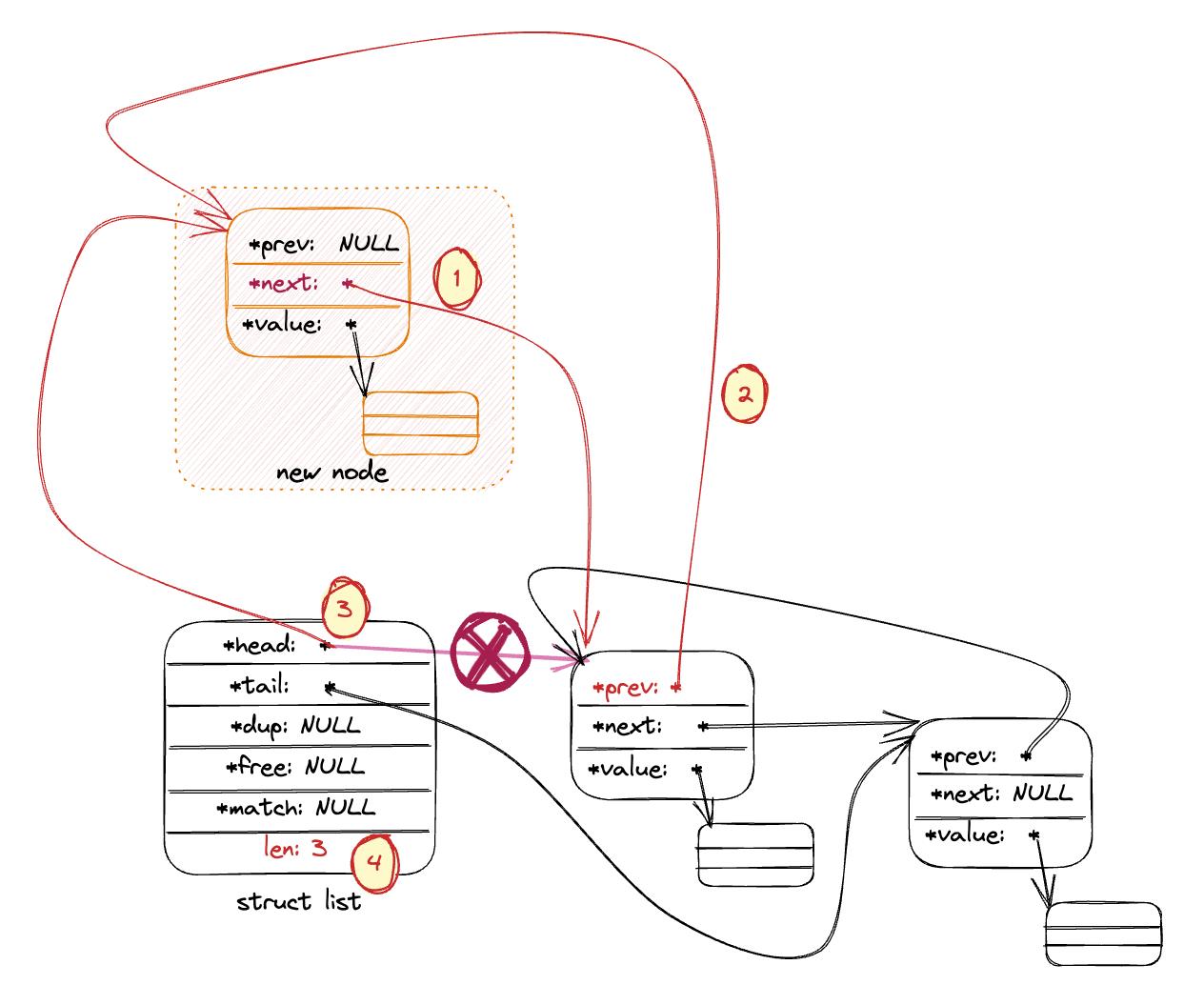
在非空链表插入新节点:
(1) 将新节点的next指向当前首节点(当前首节点将成为第二节点, 将会是新节点的后继节点)
(2) 将当前节点的prev指向新节点, 新节点作为新的首节点将成为原首节点的前驱节点。
(3) 将head从原本指向旧的首节点改为指向新节点, 将新节点作为链表首。
(4) 链表总计数加一
/* Add a new node to the list, to head, containing the specified \'value\'
* pointer as value.
*
* On error, NULL is returned and no operation is performed (i.e. the
* list remains unaltered).
* On success the \'list\' pointer you pass to the function is returned. */
list *listAddNodeHead(list *list, void *value)
listNode *node;
if ((node = zmalloc(sizeof(*node))) == NULL)
return NULL;
node->value = value;
listLinkNodeHead(list, node);
return list;
/*
* Add a node that has already been allocated to the head of list
*/
void listLinkNodeHead(list* list, listNode *node)
if (list->len == 0)
list->head = list->tail = node;
node->prev = node->next = NULL;
else
node->prev = NULL;
node->next = list->head;
list->head->prev = node;
list->head = node;
list->len++;
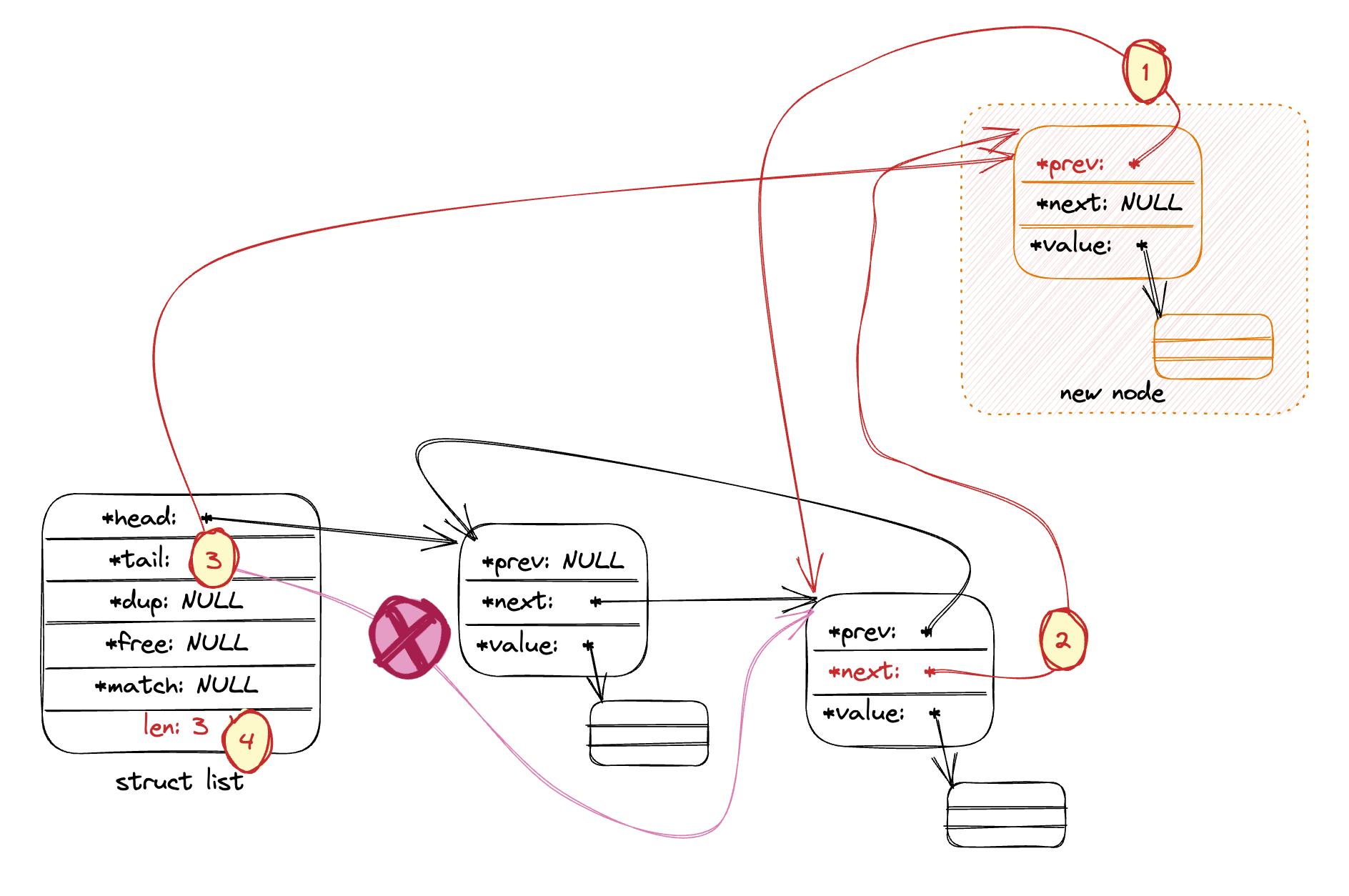
- 在链表尾插入新节点:
listAddNodeTail
- 在空链表插入新节点: 逻辑与
listAddNodeHead实现一致。 - 在非空链表插入新节点:
(1) 将新节点的prev指向当前首节点(当前尾节点将成为倒数第二节点, 将会是新节点的前驱节点)
(2) 将当前节点的next指向新节点, 新节点作为新的尾节点将成为原尾节点的后继节点。
(3) 将tail从原本指向旧的尾节点改为指向新节点, 将新节点作为链表尾。
(4) 链表总计数加一
/* Add a new node to the list, to tail, containing the specified \'value\'
* pointer as value.
*
* On error, NULL is returned and no operation is performed (i.e. the
* list remains unaltered).
* On success the \'list\' pointer you pass to the function is returned. */
list *listAddNodeTail(list *list, void *value)
listNode *node;
if ((node = zmalloc(sizeof(*node))) == NULL)
return NULL;
node->value = value;
listLinkNodeTail(list, node);
return list;
/*
* Add a node that has already been allocated to the tail of list
*/
void listLinkNodeTail(list *list, listNode *node)
if (list->len == 0)
list->head = list->tail = node;
node->prev = node->next = NULL;
else
node->prev = list->tail;
node->next = NULL;
list->tail->next = node;
list->tail = node;
list->len++;
- 在链表指定位置插入
value:listInsertNode。如果after为非零, 则将新节点作为old_node后继节点。否则,新节点作为old_node前驱节点。下图以after为非零作为例子, 描述了这部分的代码逻辑。
(1) 将新节点的prev指向old_node(新节点插入在old_node之后);
(2) 将新节点的next指向old_node的后继节点(old_node的后继节点将成为新节点的后继节点);
(3) 将old_node的next指向新节点;
(4) 将新节点的后继节点的prev指向新节点(old_node的原后继节点现在成为了新节点的后继节点) 。
(5) 链表总计数加一
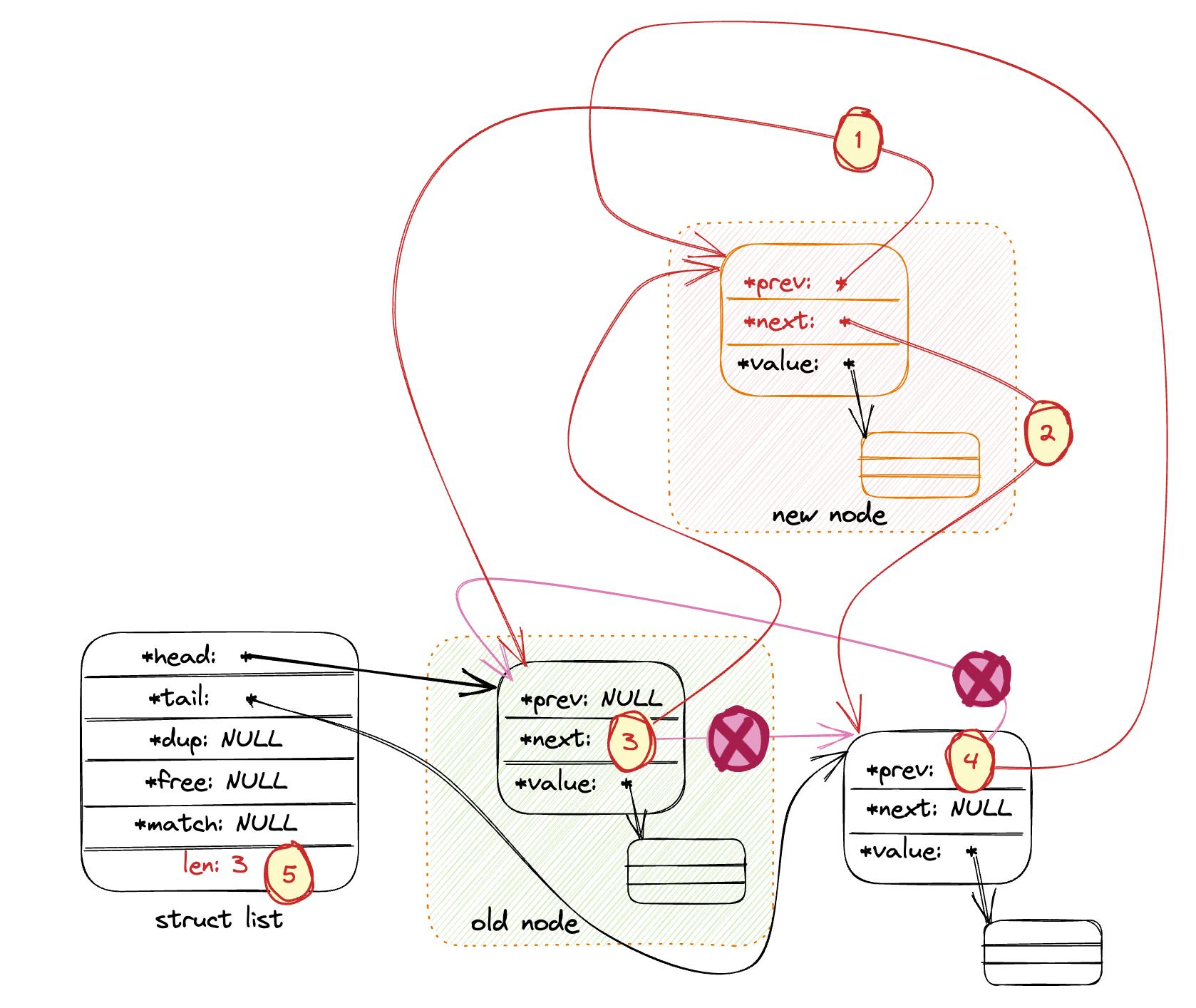
list *listInsertNode(list *list, listNode *old_node, void *value, int after)
listNode *node;
if ((node = zmalloc(sizeof(*node))) == NULL)
return NULL;
node->value = value;
if (after)
node->prev = old_node;
node->next = old_node->next;
if (list->tail == old_node)
list->tail = node;
else
node->next = old_node;
node->prev = old_node->prev;
if (list->head == old_node)
list->head = node;
if (node->prev != NULL)
node->prev->next = node;
if (node->next != NULL)
node->next->prev = node;
list->len++;
return list;
- 删除链表指定节点:
listDelNode。 下图以删除中间节点为例,展示了删除的流程。
(1) 待删除节点的前驱节点的next指向待删除节点的后继节点;
(2) 待删除节点的后继节点的prev指向待删除节点的前驱节点;
(3) 待删除节点的next和prev都置为NULL;
(4) 链表总计数减一
(5) 如果有注册free函数,则用free函数释放待删除节点的value。然后释放待删除节点。
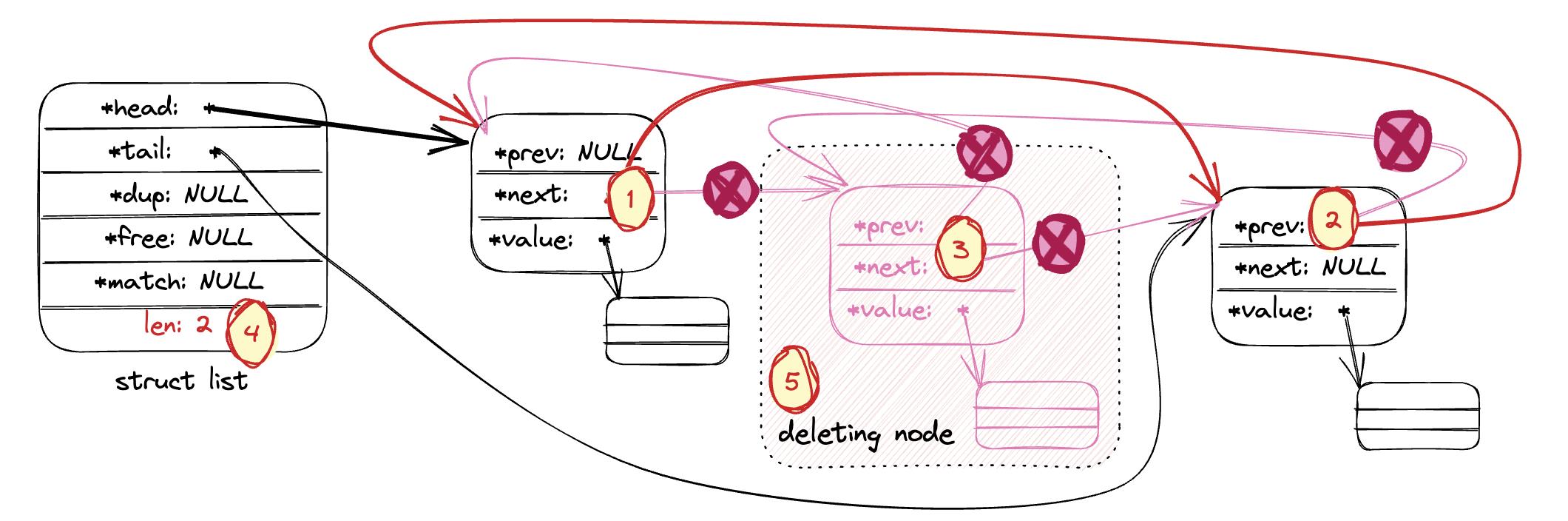
/* Remove the specified node from the specified list.
* The node is freed. If free callback is provided the value is freed as well.
*
* This function can\'t fail. */
void listDelNode(list *list, listNode *node)
listUnlinkNode(list, node);
if (list->free) list->free(node->value);
zfree(node);
/*
* Remove the specified node from the list without freeing it.
*/
void listUnlinkNode(list *list, listNode *node)
if (node->prev)
node->prev->next = node->next;
else
list->head = node->next;
if (node->next)
node->next->prev = node->prev;
else
list->tail = node->prev;
node->next = NULL;
node->prev = NULL;
list->len--;
5.链表的 Join 操作: listJoin 在链表l的末尾添加列表o的所有元素。 下图以两个链表都不为 NULL 的场景为例。
(1) o 的首部节点的 prev 指向 l 的尾部节点;
(2) l 的尾部节点的 next 指向 o 的首部节点(1,2 步将两个链表链接起来);
(3) l 的 tail 指向 o 的 tail(o 的 tail作为新链表的尾部);
(4) l 链表总计数加一;
(5) (6) 清空 o 链表的信息;
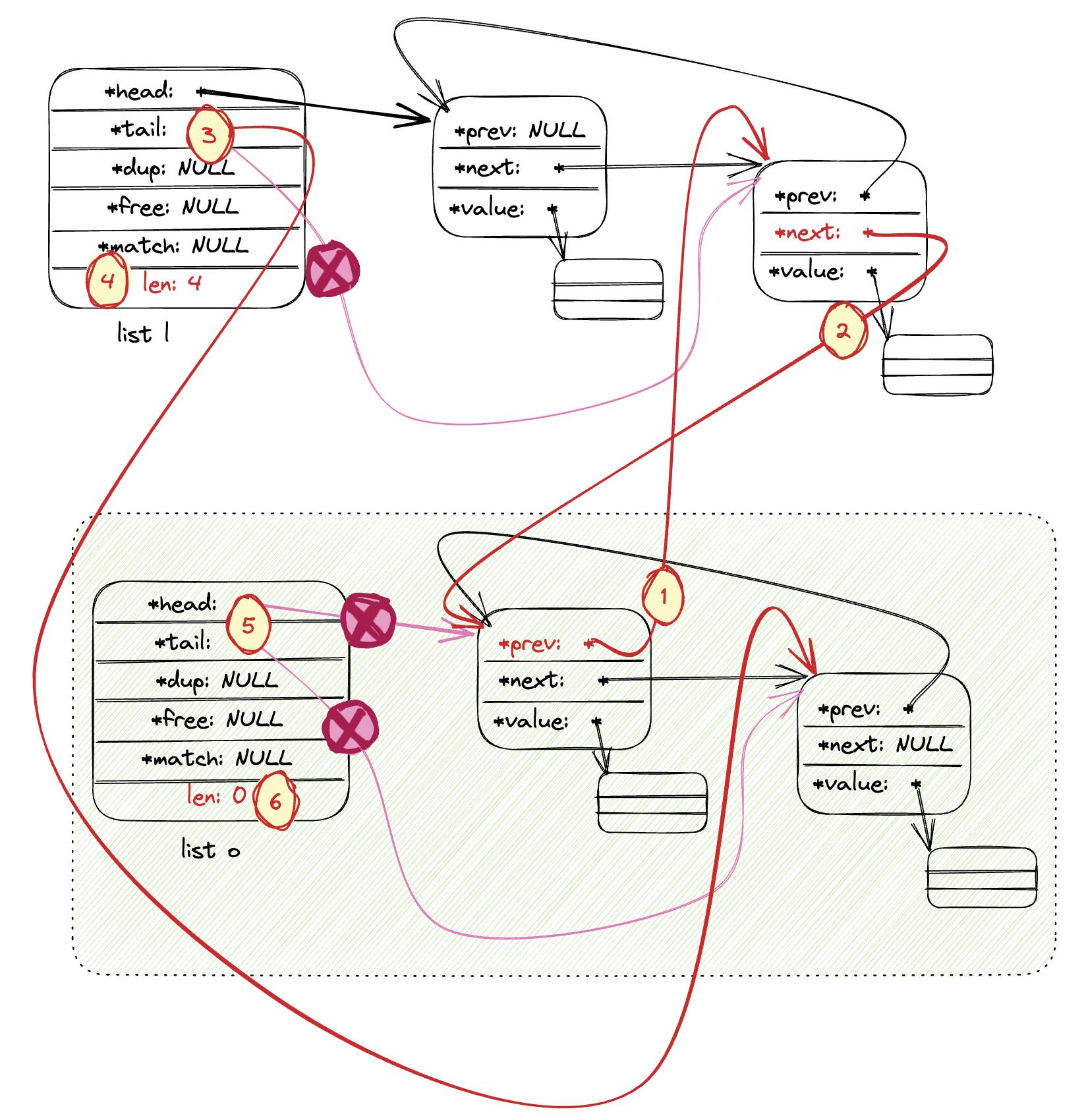
/* Add all the elements of the list \'o\' at the end of the
* list \'l\'. The list \'other\' remains empty but otherwise valid. */
void listJoin(list *l, list *o)
if (o->len == 0) return;
o->head->prev = l->tail;
if (l->tail)
l->tail->next = o->head;
else
l->head = o->head;
l->tail = o->tail;
l->len += o->len;
/* Setup other as an empty list. */
o->head = o->tail = NULL;
o->len = 0;
- 其他函数: 其他函数实现较为简单,这里简单罗列一下,感兴趣的可以去看下源码。
// 获取 list 的迭代器
listIter *listGetIterator(list *list, int direction);
// 返回迭代器的下一个元素,并将迭代器移动一位。如果已遍历完成, 则返回 NULL
listNode *listNext(listIter *iter);
// 释放迭代器资源
void listReleaseIterator(listIter *iter);
// 拷贝链表
list *listDup(list *orig);
// 在链表中查找与 key 匹配的 value 所在的第一个节点。
// 如果不存在,则返回 NULL。
// 匹配操作由 list->match 函数提供。
// 如果没有注册 match 函数, 则直接比较 key 是否与 value 相等。
listNode *listSearchKey(list *list, void *key);
// 返回指定的索引的元素。 如果超过了链表范围, 则返回 NULL。
// 正整数表示从首部开始计算。
// 0 表示第一个元素, 1 表示第二个元素, 以此类推。
// 负整数表示从尾部开始计算。
// -1 表示倒数第一个元素, -2 表示倒数第二个元素,以此类推。
listNode *listIndex(list *list, long index);
// 返回链表初始化的正向迭代器
void listRewind(list *list, listIter *li);
// 返回链表初始化的反向迭代器
void listRewindTail(list *list, listIter *li);
// 将链表尾部节点移到首部
void listRotateTailToHead(list *list);
// 将链表首部节点移到尾部
void listRotateHeadToTail(list *list);
// 用 value 初始化节点
void listInitNode(listNode *node, void *value);
adlist 的使用 demo
git@github.com:younglionwell/redis-adlist-example.git
关注公众号了解更多 redis 源码细节和其他技术内容。 你的关注是我最大的动力。

redis 5.0.7 源码阅读——双向链表
redis中动态字符串sds相关的文件为:adlist.h与adlist.c
一、数据结构
redis里定义的双向链表,与普通双向链表大致相同
单个节点:
1 typedef struct listNode { 2 struct listNode *prev; 3 struct listNode *next; 4 void *value; 5 } listNode;
链表:
1 typedef struct list { 2 listNode *head; 3 listNode *tail; 4 void *(*dup)(void *ptr); 5 void (*free)(void *ptr); 6 int (*match)(void *ptr, void *key); 7 unsigned long len; 8 } list;
链表以函数指针的方式,实现了复制、销毁与比较的方法的多态。
迭代器:
1 typedef struct listIter { 2 listNode *next; 3 int direction; 4 } listIter;
迭代器中有个成员变量direction,用于表示当前遍历的方向。
大致结构:
1 /* 2 +-------------------+ +----------------> +--------------+ <-------+ 3 |listNode *head |--------+ |listNode *prev|-->NULL | 4 +-------------------+ +--------------+ | 5 |listNode *tail |--------+ |listNode *next|----+ | 6 +-------------------+ | +--------------+ | | 7 |void *(*dup)(...) | | |void *value | | | 8 +-------------------+ | +--------------+ | | 9 |void (*free)(...) | | | | 10 +-------------------+ | | | 11 |int (*match)(...) | | | | 12 +-------------------+ +----------------> +--------------+ <--+ | 13 |unsigned long len | |listNode *prev|---------+ 14 +-------------------+ +--------------+ 15 |listNode *next|-->NULL 16 +--------------+ 17 |void *value | 18 +--------------+ 19 */
二、创建
redis中创建一个初始双向链表比较简单,只要分配好内存,并给成员变量赋初值就可以了
1 list *listCreate(void) 2 { 3 struct list *list; 4 5 if ((list = zmalloc(sizeof(*list))) == NULL) 6 return NULL; 7 list->head = list->tail = NULL; 8 list->len = 0; 9 list->dup = NULL; 10 list->free = NULL; 11 list->match = NULL; 12 return list; 13 }
redis中提供了头插法、尾插法以及指定位置插入节点三种方式向链表中添加节点,与普通双向链表无异,此处不做详细叙述。
三、销毁
因链表中每个节点的value可能指向堆空间,故不能直接把list结构体free,这样会造成内存泄露。需要先将每个节点的value释放,才可以free结构体
清空所有节点:
1 void listEmpty(list *list) 2 { 3 unsigned long len; 4 listNode *current, *next; 5 6 current = list->head; 7 len = list->len; 8 while(len--) { 9 next = current->next; 10 //若指定了销毁的函数,则使用指定的函数进行销毁value 11 if (list->free) list->free(current->value); 12 zfree(current); 13 current = next; 14 } 15 list->head = list->tail = NULL; 16 list->len = 0; 17 }
销毁链表:
1 void listRelease(list *list) 2 { 3 listEmpty(list); 4 zfree(list); 5 }
同样,redis的链表提供了与普通链表相同的删除单个节点的操作,此处也不做叙述。
四、迭代器操作
redis中提供了获取迭代器的接口
1 listIter *listGetIterator(list *list, int direction) 2 { 3 listIter *iter; 4 5 if ((iter = zmalloc(sizeof(*iter))) == NULL) return NULL; 6 if (direction == AL_START_HEAD) 7 iter->next = list->head; 8 else 9 iter->next = list->tail; 10 iter->direction = direction; 11 return iter; 12 }
以AL_START_HEAD为例,生成好的迭代器结构如下:
1 /* 2 +-------------------+ +---> +--------------+ <-------+----+ 3 |listNode *head |----+ |listNode *prev|-->NULL | | 4 +-------------------+ +--------------+ | | +--------------+ 5 |listNode *tail |----+ |listNode *next|----+ | +--|listNode *next| 6 +-------------------+ | +--------------+ | | +--------------+ 7 |void *(*dup)(...) | | |void *value | | | |int direction | 8 +-------------------+ | +--------------+ | | +--------------+ 9 |void (*free)(...) | | | | 10 +-------------------+ | | | 11 |int (*match)(...) | | | | 12 +-------------------+ +---> +--------------+ <--+ | 13 |unsigned long len | |listNode *prev|---------+ 14 +-------------------+ +--------------+ 15 |listNode *next|-->NULL 16 +--------------+ 17 |void *value | 18 +--------------+ 19 */
迭代器的next方法:
1 listNode *listNext(listIter *iter) 2 { 3 listNode *current = iter->next; 4 5 if (current != NULL) { 6 if (iter->direction == AL_START_HEAD) 7 iter->next = current->next; 8 else 9 iter->next = current->prev; 10 } 11 return current; 12 }
调用一次之后的结构:
1 /* 2 +-------------------+ +---> +--------------+ <-------+ 3 |listNode *head |----+ |listNode *prev|-->NULL | 4 +-------------------+ +--------------+ | +--------------+ 5 |listNode *tail |----+ |listNode *next|----+ | +--|listNode *next| 6 +-------------------+ | +--------------+ | | | +--------------+ 7 |void *(*dup)(...) | | |void *value | | | | |int direction | 8 +-------------------+ | +--------------+ | | | +--------------+ 9 |void (*free)(...) | | | | | 10 +-------------------+ | | | | 11 |int (*match)(...) | | | | | 12 +-------------------+ +---> +--------------+ <--+----|----+ 13 |unsigned long len | |listNode *prev|---------+ 14 +-------------------+ +--------------+ 15 |listNode *next|-->NULL 16 +--------------+ 17 |void *value | 18 +--------------+ 19 */
再次调用:
1 /* 2 +-------------------+ +---> +--------------+ <-------+ 3 |listNode *head |----+ |listNode *prev|-->NULL | 4 +-------------------+ +--------------+ | +--------------+ 5 |listNode *tail |----+ |listNode *next|----+ | +--|listNode *next| 6 +-------------------+ | +--------------+ | | | +--------------+ 7 |void *(*dup)(...) | | |void *value | | | | |int direction | 8 +-------------------+ | +--------------+ | | | +--------------+ 9 |void (*free)(...) | | | | | 10 +-------------------+ | | | | 11 |int (*match)(...) | | | | | 12 +-------------------+ +---> +--------------+ <--+ | +-->NULL 13 |unsigned long len | |listNode *prev|---------+ 14 +-------------------+ +--------------+ 15 |listNode *next|-->NULL 16 +--------------+ 17 |void *value | 18 +--------------+ 19 */
调用next函数的返回值为调用之前的listNode首地址
五、其它操作
redis的双向链表还提供了其它操作。其中,查找指定的key与复制整个list依赖于迭代器的使用,并使用到自定义的比较/复制方法。
除此之外,还提供了类似随机读取的方式,其内部实现为遍历,且“越界”时返回NULL。同时,它支持index为负数,表示从尾开始。类似旋转的操作,把尾节点移至原头节点之前,成为新的头节点。当然,还有拼接两个链表的操作。
redis 5.0.7 下载链接
http://download.redis.io/releases/redis-5.0.7.tar.gz
源码阅读顺序参考:
https://github.com/huangz1990/blog/blob/master/diary/2014/how-to-read-redis-source-code.rst
以上是关于Redis 源码解析之通用双向链表(adlist)的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章