2.自定义@Excel注解实现数据Excel形式导入导出
Posted 求知律己
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了2.自定义@Excel注解实现数据Excel形式导入导出相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
前言
这几天在学习如何使用自定义注解实现Excel格式数据导入导出,参考的还是若依框架里面的代码,由于是初学,所以照猫画虎呗,但是难受的是需要复制并根据自己项目修改作者自定义的工具类以及导入这些工具类的依赖包。由于吃了这个苦,我决定把这个艰辛的CV操作通过一张逻辑图来表达,方便我以后复用。下面证实开始介绍这个功能的实现,但是由于对项目中的只是很不了解,我这里简单实现,并简单讲解,深层次的代码我会给出,后续会继续运用讲解。整篇博客分为两个部分,一部分是数据的导出,一部分是数据的导入。本文项目链接:WomPlus: 结合若依项目对原始工单项目内容进行增强 (gitee.com)
1.所需要的依赖
在进行项目前,我们需要导入依赖才能引用具体的功能,因此第一步就是导入依赖了,这里除了Excel需要的依赖,一些工具类的依赖也需要导入,为什么呢?因为作者的项目写的很细致,比如在咋们的java中自带有StringUtils工具类,但是作者细致地自己写了一个,可见其基础功能之深呀!


<!--Excel工具类依赖--> <dependency> <groupId>org.apache.poi</groupId> <artifactId>poi-ooxml</artifactId> <version>4.1.2</version> </dependency> <!--常用工具类依赖--> <dependency> <groupId>org.apache.commons</groupId> <artifactId>commons-lang3</artifactId> </dependency> <!--io常用工具依赖--> <dependency> <groupId>commons-io</groupId> <artifactId>commons-io</artifactId> <version>2.11.0</version> </dependency> <!--解决@ConfigurationProperties(prefix = "wo")的 Springboot Configuration Annotation Processor not found in classPath问题依赖--> <dependency> <groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId> <artifactId>spring-boot-configuration-processor</artifactId> <optional>true</optional> </dependency>
2.修改配置文件
引入依赖是第一步,修改配置文件就是我们的第二步了,在这里修改配置文件是因为在该功能的数据导入,作者是在自己自定义的RuoYiConfig中通过
@ConfigurationProperties(prefix = "wo")注解获取配置文件中profile属性值,即我们上传下载文件的地址。我这里使用的是properties为后缀的文件,配置文件为yaml的请根据自己文件类型修改
//添加自己的项目配置类WoConfig需要配置的项目名和导出Excel形式数据下载路径
#项目相关配置
wo.name=WO
wo.profile=G:/Desktop/base_study/project/myself_springboot_project/wom-plus/uploadPath
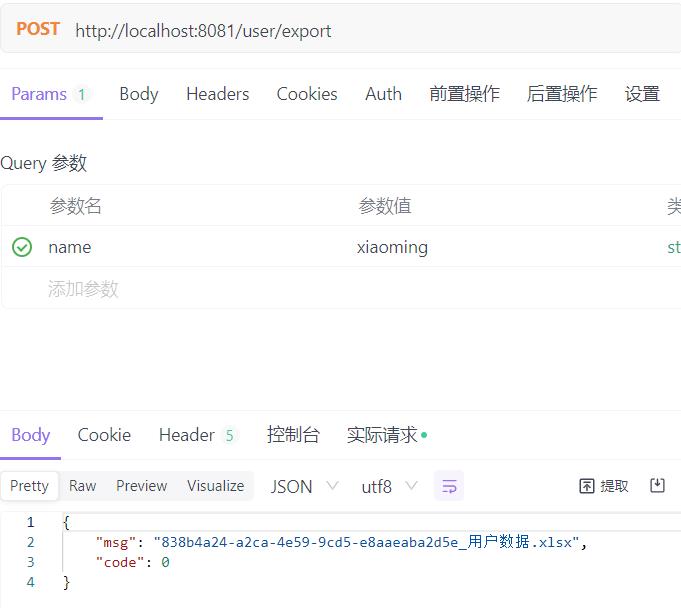
3.数据以Excel格式导出的Controller层
@PostMapping("/export")
@ResponseBody
public AjaxResult export(@RequestParam(value = "name", required = false) String username)
List<SysUser> list = userDetailsService.getUserListByUsername(username);
ExcelUtil<SysUser> util = new ExcelUtil<>(SysUser.class);
return util.exportExcel(list, "用户数据");
3.1 ExcelUtils的有参构造
//1.传入需要Excel导出类的Class.class,返回一个ExcelUtil<Class>对象 public ExcelUtil(Class<T> clazz) this.clazz = clazz;
这里就是传入一个Class类来创建该类的Excel对象,本篇博客围绕着SysUser类实现该功能的,因此这里传入SysUser.class
3.2 exportExcel(List<T>list, String sheetName)
public AjaxResult exportExcel(List<T> list, String sheetName) return exportExcel(list, sheetName, StringUtils.EMPTY);
在方法中,调用exportExcel(List<SysUser>list, String sheetName, String title)封装Excel格式数据导出
3.3 exportExcel(List<T> list, String sheetName, String title)
public AjaxResult exportExcel(List<T> list, String sheetName, String title) this.init(list, sheetName, title, Type.EXPORT); return exportExcel();
本文方法首先初始化要创建的Excel表格,然后返回exportExcel()方法来讲要导出的数据写进前面的profile路径中
3.3.1 init(list, sheetName, title, Type.EXPORT)
public void init(List<T> list, String sheetName, String title, Type type) if (list == null) list = new ArrayList<T>(); this.list = list; this.sheetName = sheetName; this.type = type; this.title = title; //根据要导出Excel的实体类的字段创建字段Class类所需要的Excel字段 createExcelField(); createWorkbook();//创建一个工作薄 createTitle();//创建Excel第一行标题 createSubHead();//创建对象子列表名称
3.3.2 exportExcel()


public AjaxResult exportExcel() OutputStream out = null; try writeSheet();//写入数据到Sheet String filename = encodingFilename(sheetName);//编辑文件名 //getAbsoluteFile(filename)根据文件名称获取下载路径 //创建一个输出流 out = new FileOutputStream(getAbsoluteFile(filename)); wb.write(out);//写入Excel信息到该路径 return AjaxResult.success(filename);//返回导出成功信息 catch (Exception e) log.error("导出Excel异常", e.getMessage()); throw new UtilException("导出Excel失败,请联系网站管理员!"); finally IOUtils.closeQuietly(wb);//关闭工作薄对象输出流 IOUtils.closeQuietly(out);//关闭输出流
3.4 @Excel和@Excels注解


package com.ku.wo.framework.aspectj.lang.annotation; import java.lang.annotation.ElementType; import java.lang.annotation.Retention; import java.lang.annotation.RetentionPolicy; import java.lang.annotation.Target; import java.math.BigDecimal; import org.apache.poi.ss.usermodel.HorizontalAlignment; import org.apache.poi.ss.usermodel.IndexedColors; import com.ku.wo.common.utils.poi.ExcelHandlerAdapter; /** * 自定义导出Excel数据注解 * * @author ruoyi */ @Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME) @Target(ElementType.FIELD)//作用在什么地方 public @interface Excel /** * 导出时在excel中排序 */ public int sort() default Integer.MAX_VALUE; /** * 导出到Excel中的名字. */ public String name() default ""; /** * 日期格式, 如: yyyy-MM-dd */ public String dateFormat() default ""; /** * 如果是字典类型,请设置字典的type值 (如: sys_user_sex) */ public String dictType() default ""; /** * 读取内容转表达式 (如: 0=男,1=女,2=未知) */ public String readConverterExp() default ""; /** * 分隔符,读取字符串组内容 */ public String separator() default ","; /** * BigDecimal 精度 默认:-1(默认不开启BigDecimal格式化) */ public int scale() default -1; /** * BigDecimal 舍入规则 默认:BigDecimal.ROUND_HALF_EVEN */ public int roundingMode() default BigDecimal.ROUND_HALF_EVEN; /** * 导出时在excel中每个列的高度 单位为字符 */ public double height() default 14; /** * 导出时在excel中每个列的宽 单位为字符 */ public double width() default 16; /** * 文字后缀,如% 90 变成90% */ public String suffix() default ""; /** * 当值为空时,字段的默认值 */ public String defaultValue() default ""; /** * 提示信息 */ public String prompt() default ""; /** * 设置只能选择不能输入的列内容. */ public String[] combo() default ; /** * 是否需要纵向合并单元格,应对需求:含有list集合单元格) */ public boolean needMerge() default false; /** * 是否导出数据,应对需求:有时我们需要导出一份模板,这是标题需要但内容需要用户手工填写. */ public boolean isExport() default true; /** * 另一个类中的属性名称,支持多级获取,以小数点隔开 */ public String targetAttr() default ""; /** * 是否自动统计数据,在最后追加一行统计数据总和 */ public boolean isStatistics() default false; /** * 导出类型(0数字 1字符串 2图片) */ public ColumnType cellType() default ColumnType.STRING; /** * 导出列头背景颜色 */ public IndexedColors headerBackgroundColor() default IndexedColors.GREY_50_PERCENT; /** * 导出列头字体颜色 */ public IndexedColors headerColor() default IndexedColors.WHITE; /** * 导出单元格背景颜色 */ public IndexedColors backgroundColor() default IndexedColors.WHITE; /** * 导出单元格字体颜色 */ public IndexedColors color() default IndexedColors.BLACK; /** * 导出字段对齐方式 */ public HorizontalAlignment align() default HorizontalAlignment.CENTER; /** * 自定义数据处理器 */ public Class<?> handler() default ExcelHandlerAdapter.class; /** * 自定义数据处理器参数 */ public String[] args() default ; /** * 字段类型(0:导出导入;1:仅导出;2:仅导入) */ Type type() default Type.ALL; public enum Type ALL(0), EXPORT(1), IMPORT(2); private final int value; Type(int value) this.value = value; public int value() return this.value; public enum ColumnType NUMERIC(0), STRING(1), IMAGE(2); private final int value; ColumnType(int value) this.value = value; public int value() return this.value; //@Excels package com.ku.wo.framework.aspectj.lang.annotation; import java.lang.annotation.ElementType; import java.lang.annotation.Retention; import java.lang.annotation.RetentionPolicy; import java.lang.annotation.Target; /** * Excel注解集 * * @author ruoyi */ @Target(ElementType.FIELD) @Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME) public @interface Excels Excel[] value();
3.5 运行结果
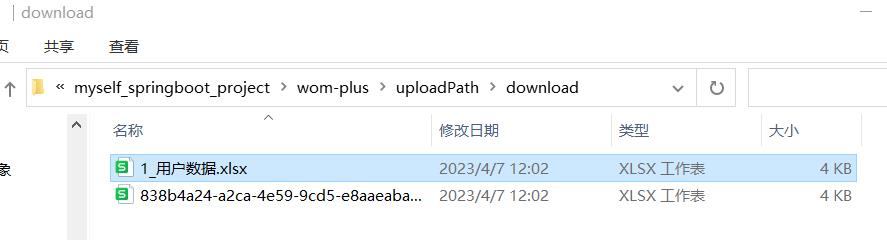
4.数据以Excel格式导出的Controller层
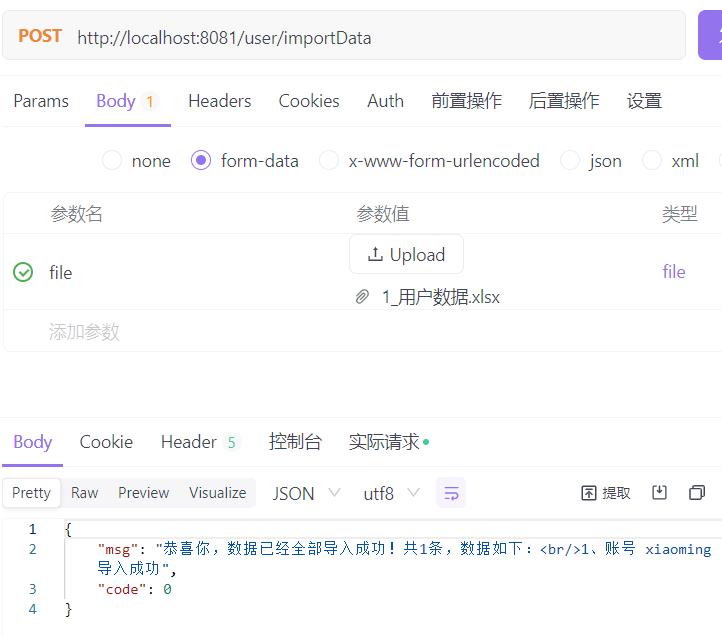
@PostMapping("/importData")
@ResponseBody
public AjaxResult importData(MultipartFile file) throws Exception
ExcelUtil<SysUser> util = new ExcelUtil<>(SysUser.class);
List<SysUser> userList = util.importExcel(file.getInputStream());
String message = userDetailsService.importUser(userList);
return AjaxResult.success(message);
4.1 importExcel(InputStream)


public List<T> importExcel(InputStream is) throws Exception return importExcel(is, 0); public List<T> importExcel(InputStream is, int titleNum) throws Exception return importExcel(StringUtils.EMPTY, is, titleNum); //核心实现代码 public List<T> importExcel(String sheetName, InputStream is, int titleNum) throws Exception this.type = Type.IMPORT; this.wb = WorkbookFactory.create(is); List<T> list = new ArrayList<T>(); // 如果指定sheet名,则取指定sheet中的内容 否则默认指向第1个sheet Sheet sheet = StringUtils.isNotEmpty(sheetName) ? wb.getSheet(sheetName) : wb.getSheetAt(0); if (sheet == null) throw new IOException("文件sheet不存在"); boolean isXSSFWorkbook = !(wb instanceof HSSFWorkbook); Map<String, PictureData> pictures; if (isXSSFWorkbook) pictures = getSheetPictures07((XSSFSheet) sheet, (XSSFWorkbook) wb); else pictures = getSheetPictures03((HSSFSheet) sheet, (HSSFWorkbook) wb); // 获取最后一个非空行的行下标,比如总行数为n,则返回的为n-1 int rows = sheet.getLastRowNum(); if (rows > 0) // 定义一个map用于存放excel列的序号和field. Map<String, Integer> cellMap = new HashMap<String, Integer>(); // 获取表头 Row heard = sheet.getRow(titleNum); for (int i = 0; i < heard.getPhysicalNumberOfCells(); i++) Cell cell = heard.getCell(i); if (StringUtils.isNotNull(cell)) String value = this.getCellValue(heard, i).toString(); cellMap.put(value, i); else cellMap.put(null, i); // 有数据时才处理 得到类的所有field. List<Object[]> fields = this.getFields(); Map<Integer, Object[]> fieldsMap = new HashMap<Integer, Object[]>(); for (Object[] objects : fields) Excel attr = (Excel) objects[1]; Integer column = cellMap.get(attr.name()); if (column != null) fieldsMap.put(column, objects); for (int i = titleNum + 1; i <= rows; i++) // 从第2行开始取数据,默认第一行是表头. Row row = sheet.getRow(i); // 判断当前行是否是空行 if (isRowEmpty(row)) continue; T entity = null; for (Map.Entry<Integer, Object[]> entry : fieldsMap.entrySet()) Object val = this.getCellValue(row, entry.getKey()); // 如果不存在实例则新建. entity = (entity == null ? clazz.newInstance() : entity); // 从map中得到对应列的field. Field field = (Field) entry.getValue()[0]; Excel attr = (Excel) entry.getValue()[1]; // 取得类型,并根据对象类型设置值. Class<?> fieldType = field.getType(); if (String.class == fieldType) String s = Convert.toStr(val); if (StringUtils.endsWith(s, ".0")) val = StringUtils.substringBefore(s, ".0"); else String dateFormat = field.getAnnotation(Excel.class).dateFormat(); if (StringUtils.isNotEmpty(dateFormat)) val = parseDateToStr(dateFormat, val); else val = Convert.toStr(val); else if ((Integer.TYPE == fieldType || Integer.class == fieldType) && StringUtils.isNumeric(Convert.toStr(val))) val = Convert.toInt(val); else if ((Long.TYPE == fieldType || Long.class == fieldType) && StringUtils.isNumeric(Convert.toStr(val))) val = Convert.toLong(val); else if (Double.TYPE == fieldType || Double.class == fieldType) val = Convert.toDouble(val); else if (Float.TYPE == fieldType || Float.class == fieldType) val = Convert.toFloat(val); else if (BigDecimal.class == fieldType) val = Convert.toBigDecimal(val); else if (Date.class == fieldType) if (val instanceof String) val = DateUtils.parseDate(val); else if (val instanceof Double) val = DateUtil.getJavaDate((Double) val); else if (Boolean.TYPE == fieldType || Boolean.class == fieldType) val = Convert.toBool(val, false); if (StringUtils.isNotNull(fieldType)) String propertyName = field.getName(); if (StringUtils.isNotEmpty(attr.targetAttr())) propertyName = field.getName() + "." + attr.targetAttr(); else if (StringUtils.isNotEmpty(attr.readConverterExp())) val = reverseByExp(Convert.toStr(val), attr.readConverterExp(), attr.separator()); else if (StringUtils.isNotEmpty(attr.dictType())) val = reverseDictByExp(Convert.toStr(val), attr.dictType(), attr.separator()); else if (!attr.handler().equals(ExcelHandlerAdapter.class)) val = dataFormatHandlerAdapter(val, attr); else if (ColumnType.IMAGE == attr.cellType() && StringUtils.isNotEmpty(pictures)) PictureData image = pictures.get(row.getRowNum() + "_" + entry.getKey()); if (image == null) val = ""; else byte[] data = image.getData(); val = FileUtils.writeImportBytes(data); ReflectUtils.invokeSetter(entity, propertyName, val); list.add(entity); return list;
该方法主要是通过传入的文件获取Excel表格中的数据,这里是真正导入数据的核心,我暂时还没想清楚。
4.2 importUser(InputStream)


String importUser(List<SysUser> userList); @Override public String importUser(List<SysUser> userList) //此处的isNull判断的是一个对象,此时我传入的是一个用户list对象 if (StringUtils.isNull(userList) || userList.size() == 0) throw new ServiceException("导入用户数据不能为空!"); int successNum = 0; //StringBuilder字符拼接工具类,是一个可变类不安全,StringBuffer是一个不可变的安全字符拼接工具类 StringBuilder successMsg = new StringBuilder(); for (SysUser user: userList) //因为前面验证了该list对象不为空,故直接插入 userMapper.insertUser(user); successNum++; successMsg.append("<br/>" + successNum + "、账号 " + user.getUsername() + " 导入成功"); successMsg.insert(0, "恭喜你,数据已经全部导入成功!共" + successNum + "条,数据如下:"); return successMsg.toString();
该方法实现将Excel中获取的数据导入到对应数据库的数据表中,并返回导入成功的响应信息。
4.3 运行结果
5.参考项目连链接
RuoYi: 反射+自定义注解---实现Excel数据列属性和JavaBean属性的自动映射
简单粗暴,直奔主题。
需求:通过自定义注解和反射技术,将Excel文件中的数据自动映射到pojo类中,最终返回一个List<pojo>集合?
今天我只是通过一位使用者的身份来给各位分享一套超级可以的POI“工具”,这套工具我只是第一个使用者,创作者是我的朋友,他喜好钻研底层和算法,擅长计算机软硬件,在我心里他一直是神一样的存在,每天晚上10点后我才能看到他,因为他每天需要加班,需要有更多时间能够学习,唉,这种毅力和耐力,我是真的羡慕,因为我也一直在努力,能够得到更多的东西。
首先关于jar的管理,我就不多说了,导入和POI相关的jar包即可。第一我给大家分享的是一个他封装好的工具类,原理是通过获取到Excel文件,然后通过你指定的pojo对象,他就会自动封装。这套代码也就400行左右,说真的用点心瞅瞅完全有必要看懂,不多说了,我看了半天,自己也能说得通他是怎么写的,更详细的我也想给各位补补,但是无能为力啊。

1 public class ExcelUtil { 2 3 public String defaultDateFormat = "yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss"; 4 5 /** 6 * 将excel表格中的信息设置进bean中 7 * 8 * @param file 9 * @param t 10 * @return 11 * @throws Exception 12 * @Date 2017年6月13日 13 */ 14 public <T> T setExcelInfo2Bean(File file, T t) { 15 // 获取工作簿类下的子类(表类) 16 Field[] declaredFields = t.getClass().getDeclaredFields(); 17 18 for (int i = 0; i < declaredFields.length; i++) { 19 Field sheetFiled = declaredFields[i]; 20 sheetFiled.setAccessible(true); 21 // 将子表的内容赋值到对象中 22 try { 23 sheetFiled.set(t, setSheetValue2Bean(sheetFiled, file)); 24 } catch (Exception e) { 25 e.printStackTrace(); 26 } 27 } 28 return t; 29 } 30 31 /** 32 * 校验参数的类中是否包含ExcelSheetName注解 33 * 34 * @param declaredFields 35 * @Date 2017年6月13日 36 */ 37 public <T extends Annotation> Field[] matchDeclaredFields(Field[] declaredFields, Class T) { 38 List<Field> matchedDeclaredFieldsList = new ArrayList<Field>(); 39 40 for (int i = 0; i < declaredFields.length; i++) { 41 42 Field sheetFiled = declaredFields[i]; 43 sheetFiled.setAccessible(true); 44 if (sheetFiled.getAnnotation(T) != null) { 45 matchedDeclaredFieldsList.add(sheetFiled); 46 } 47 } 48 Field[] matchedDeclaredFieldsArray = null; 49 50 if (matchedDeclaredFieldsList.size() > 0) { 51 matchedDeclaredFieldsArray = new Field[matchedDeclaredFieldsList.size()]; 52 53 for (int i = 0; i < matchedDeclaredFieldsArray.length; i++) { 54 matchedDeclaredFieldsArray[i] = matchedDeclaredFieldsList.get(i); 55 } 56 } 57 58 return matchedDeclaredFieldsArray; 59 60 } 61 62 /** 63 * 将子表的内容赋值到对象中 64 * 65 * @param sheetFiled 66 * @param file 67 * @return 68 * @throws Exception 69 * @Date 2017年6月8日 70 */ 71 private <T> Object setSheetValue2Bean(Field sheetFiled, File file) throws Exception { 72 // 薄类中所有参数均为list类型,不进行校验 73 Class sheetListClass = sheetFiled.getType(); 74 // 创建集合对象 75 // List sheetList = (List) sheetListClass.newInstance(); 76 // 获取参数的类型的参数化的类型 77 Type type = sheetFiled.getGenericType(); 78 // 将参数化的类型强转,获得类型中的参数(泛型中的类) 79 ParameterizedType pType = (ParameterizedType) type; 80 // 泛型中的参数,如果是map,数组长度就为2 81 Type[] listType = pType.getActualTypeArguments(); 82 // 获取list泛型中的子表class 83 Class sheetClass = (Class) listType[0]; 84 85 // 获取子类对应的sheet名 86 ExcelSheetName sheetNameAnno = (ExcelSheetName) sheetClass.getAnnotation(ExcelSheetName.class); 87 88 String sheetName = sheetNameAnno.value(); 89 90 // 获取文件后缀 91 String fileExt = file.getName().substring(file.getName().lastIndexOf(".") + 1); 92 // 创建流 93 InputStream input = new FileInputStream(file); 94 95 // 创建Workbook 96 Workbook wb = null; 97 98 // 创建sheet 99 Sheet sheet = null; 100 101 // 根据后缀判断excel 2003 or 2007+ 102 if (fileExt.equals("xls")) { 103 wb = (HSSFWorkbook) WorkbookFactory.create(input); 104 } else { 105 wb = new XSSFWorkbook(input); 106 } 107 108 // 获取表 109 sheet = wb.getSheet(sheetName); 110 // 获取行数 111 112 return getExcelInfo2Bean(sheetClass, sheet); 113 } 114 115 /** 116 * 将返回与sheet内容对应的class的实例的List集合 117 * 118 * @param sheetClass 119 * @param sheet 120 * @throws Exception 121 * @Date 2017年6月13日 122 */ 123 private <T extends ExcelCheckPropertie> List<T> getExcelInfo2Bean(Class T, Sheet sheet) throws Exception { 124 Map<String, Integer> cellNameMap = getCellNameMap(sheet); 125 126 // 获取行数 127 int rowNum = sheet.getLastRowNum(); 128 if (rowNum == 0) { 129 return new ArrayList<T>(); 130 } 131 132 List<T> tList = new ArrayList<T>(rowNum - 1); 133 134 // 获取子表类的属性(对应表中的列) 135 Field[] colFields = T.getDeclaredFields(); 136 Field[] excelCheckPropertiesDeclaredFields = T.getSuperclass().getDeclaredFields(); 137 // (获取只包含自定义注解的属性) 138 Field[] matchedColFields = matchDeclaredFields(colFields, ExcelColName.class); 139 // 如果包含自定义注解的参数 140 141 // 从第二行开始读取,并设置进实例 142 for (int j = 1; j <= rowNum; j++) { 143 Row row = sheet.getRow(j); 144 if (row == null) { 145 continue; 146 } 147 // 创建当前sheet类的实例 148 T sheetBean = (T) T.newInstance(); 149 150 // 遍历包含自定义注解的参数 151 if (matchedColFields != null && matchedColFields.length > 0) { 152 153 for (int i = 0; i < matchedColFields.length; i++) { 154 matchedColFields[i].setAccessible(true); 155 Field colField = matchedColFields[i]; 156 157 ExcelColName excelColNameAnno = colField.getAnnotation(ExcelColName.class); 158 String excelColName = excelColNameAnno.value().trim(); 159 // 判断该参数是否需要校验 160 boolean isRequired = excelColNameAnno.IsRequired(); 161 // 如果为必填字段 162 if (isRequired) { 163 // 遍历每行的每个参数,设置进bean 164 for (int k = 0; k < row.getPhysicalNumberOfCells(); k++) { 165 166 // 获取sheet类的属性对应的表中的列的cell对象 167 Cell cell = row.getCell(cellNameMap.get(excelColName)); 168 String cellValue = ""; 169 if (cell != null) { 170 cellValue = getCellValue(cell); 171 172 // 判断属性类型 173 if (matchedColFields[i].getType().isAssignableFrom(Integer.class)) { 174 matchedColFields[i].set(sheetBean, Integer.parseInt(getCellValue(cell))); 175 176 } else if (matchedColFields[i].getType().isAssignableFrom(Date.class)) { 177 matchedColFields[i].set(sheetBean, getDateCellValue(cell)); 178 179 } else if (matchedColFields[i].getType().isAssignableFrom(Double.class)) { 180 matchedColFields[i].set(sheetBean, Double.parseDouble(getCellValue(cell))); 181 182 } else if (matchedColFields[i].getType().isAssignableFrom(Float.class)) { 183 matchedColFields[i].set(sheetBean, Float.parseFloat(getCellValue(cell))); 184 185 } else { 186 matchedColFields[i].set(sheetBean, getCellValue(cell)); 187 } 188 } 189 190 // 设置父类属性 191 for (int l = 0; l < excelCheckPropertiesDeclaredFields.length; l++) { 192 Field superField = excelCheckPropertiesDeclaredFields[l]; 193 superField.setAccessible(true); 194 // 当前单元格所在表名 195 if (superField.getName().equals("sheetName")) { 196 superField.set(sheetBean, sheet.getSheetName()); 197 // 当前单元格所在行数 198 } else if (superField.getName().equals("rowNum")) { 199 superField.set(sheetBean, j); 200 // 当前单元格所在列名 201 } else if (superField.getName().equals("colName")) { 202 superField.set(sheetBean, excelColName); 203 // 非空校验结果 204 } else if (superField.getName().equals("isChecked")) { 205 if (cellValue == null || "".equals(cellValue.trim())) { 206 superField.set(sheetBean, false); 207 } 208 209 } 210 } 211 212 } 213 } else { 214 // 遍历每行的每个参数,设置进bean 215 for (int k = 0; k < row.getPhysicalNumberOfCells(); k++) { 216 217 // 获取sheet类的属性对应的表中的列的cell对象 218 if (excelColName.equals("上传时间")) { 219 System.out.println(); 220 } 221 Integer integer = cellNameMap.get(excelColName); 222 Cell cell = row.getCell(integer); 223 if (cell != null) { 224 // 设置父类属性 225 for (int l = 0; l < excelCheckPropertiesDeclaredFields.length; l++) { 226 Field superField = excelCheckPropertiesDeclaredFields[l]; 227 superField.setAccessible(true); 228 // 当前单元格所在表名 229 if (superField.getName().equals("sheetName")) { 230 superField.set(sheetBean, sheet.getSheetName()); 231 // 当前单元格所在行数 232 } else if (superField.getName().equals("rowNum")) { 233 superField.set(sheetBean, j); 234 // 当前单元格所在列名 235 } else if (superField.getName().equals("colName")) { 236 superField.set(sheetBean, excelColName); 237 } 238 } 239 // 判断属性类型 240 if (matchedColFields[i].getType().isAssignableFrom(Integer.class)) { 241 matchedColFields[i].set(sheetBean, Integer.parseInt(getCellValue(cell))); 242 243 } else if (matchedColFields[i].getType().isAssignableFrom(Date.class)) { 244 matchedColFields[i].set(sheetBean, getDateCellValue(cell)); 245 246 } else if (matchedColFields[i].getType().isAssignableFrom(Double.class)) { 247 matchedColFields[i].set(sheetBean, Double.parseDouble(getCellValue(cell))); 248 249 } else if (matchedColFields[i].getType().isAssignableFrom(Float.class)) { 250 matchedColFields[i].set(sheetBean, Float.parseFloat(getCellValue(cell))); 251 252 } else { 253 matchedColFields[i].set(sheetBean, getCellValue(cell)); 254 } 255 } 256 } 257 } 258 259 } 260 } 261 tList.add(sheetBean); 262 } 263 264 // 校验空值 265 ListIterator<T> listIterator = tList.listIterator(); 266 while (listIterator.hasNext()) { 267 T next = listIterator.next(); 268 int nullNum = 0; 269 for (int i = 0; i < matchedColFields.length; i++) { 270 if (matchedColFields[i].get(next) == null || matchedColFields[i].get(next).toString().equals("")) { 271 ++nullNum; 272 } 273 } 274 if (nullNum == matchedColFields.length) { 275 // System.out.println("已删除一个元素"); 276 listIterator.remove(); 277 } 278 } 279 280 return tList; 281 282 } 283 284 /** 285 * 获取时间类型数值 cell.getCellStyle().getDataFormat() 日期时间(yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss) - 286 * 22, 日期(yyyy-MM-dd) - 14, 时间(HH:mm:ss) - 21, 年月(yyyy-MM) - 17, 时分(HH:mm) - 287 * 20, 月日(MM-dd) - 58 288 * 289 * @param cell 290 * @return 291 * @Date 2017年6月13日 292 */ 293 private Date getDateCellValue(Cell cell) { 294 return cell.getDateCellValue(); 295 } 296 297 /** 298 * 获取第一行做标题存入列名与对应的列值 299 * 300 * @param sheet 301 * @return 302 * @Date 2017年6月13日 303 */ 304 public Map<String, Integer> getCellNameMap(Sheet sheet) { 305 // 获取第一行列的列名及列数存入map 306 Map<String, Integer> colNameMap = new HashMap<String, Integer>(); 307 Row firstRow = sheet.getRow(0); 308 // 列数 309 int cellNum = firstRow.getLastCellNum(); 310 // map赋值 311 for (int i = 0; i < cellNum; i++) { 312 colNameMap.put(getCellValue(firstRow.getCell(i)), i); 313 } 314 315 return colNameMap; 316 } 317 318 /** 319 * 对Excel的各个单元格的格式进行判断并转换 320 */ 321 private String getCellValue(Cell cell) { 322 String cellValue = ""; 323 DecimalFormat df = new DecimalFormat("####################.##########"); 324 switch (cell.getCellType()) { 325 case HSSFCell.CELL_TYPE_STRING: 326 cellValue = cell.getRichStringCellValue().getString().trim(); 327 break; 328 case HSSFCell.CELL_TYPE_NUMERIC: 329 if (HSSFDateUtil.isCellDateFormatted(cell)) { 330 Date date = cell.getDateCellValue(); 331 cellValue = new SimpleDateFormat(defaultDateFormat).format(date); 332 } else { 333 double dc = cell.getNumericCellValue(); 334 // cellValue = String.valueOf(dc); 335 cellValue = df.format(dc); 336 } 337 break; 338 case HSSFCell.CELL_TYPE_BOOLEAN: 339 cellValue = String.valueOf(cell.getBooleanCellValue()).trim(); 340 break; 341 case HSSFCell.CELL_TYPE_FORMULA: 342 cellValue = String.valueOf(cell.getNumericCellValue()); 343 break; 344 345 default: 346 cellValue = ""; 347 } 348 return cellValue; 349 } 350 351 }
接着就是俩个自定义注解分别是:@ExcelSheetName和@ExcelColName,这俩个注解都是放在pojo类上的。第一个主要是标注和Excel文件中那张sheet表,第二个主要是将Excel文件中的列名和pojo类的对应属性绑定,具体用法瞅瞅我下面贴的代码就OK。

1 /** 2 * 用于匹配Excel文件中的sheet表名(注解值必须是Excel文件中sheet表名) 3 * @author zxz 4 * 5 */ 6 @Documented 7 @Inherited 8 @Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME) 9 public @interface ExcelSheetName { 10 String value() default ""; 11 }

1 /** 2 * 用于匹配Excel表中的列(vlaue值必须是Excel文件中第一行的列名) 3 * @author zxz 4 * 5 */ 6 @Documented 7 @Target(ElementType.FIELD) 8 @Inherited 9 @Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME) 10 public @interface ExcelColName { 11 String value() default ""; 12 boolean IsRequired() default false; 13 }
具体是如何使用自定义注解将pojo类和Excel文件中的数据完成自动映射的,请参考下面pojo类代码。

1 /** 2 * 商品 3 * @author zxz 4 * 5 */ 6 @ExcelSheetName("商品信息") 7 public class Item extends ExcelCheckPropertie implements Serializable { 8 9 private String id; //主键 10 @ExcelColName(value="商品名称",IsRequired=true) //IsRequired=true表示非空 11 private String itemName; //商品名称 12 @ExcelColName(value="价格") 13 private Double price; //价格 14 @ExcelColName(value="描述") 15 private String itemDesc; //描述 16 @DateTimeFormat(pattern="yyyy-MM-dd") 17 @JsonFormat(pattern = "yyyy-MM-dd", timezone = "GMT+8") 18 @ExcelColName(value="上架时间") 19 private Date createTime; //添加时间
最后,我是将这套东西整合到我的一个数据录入小项目中,因为之前导入一张600条数据的文件时,速度就很慢,一直是我的心头病,不过这次杠杠的。那天下午我整合成功后,心里一直乐到下班,因为最后进行了一套小小的性能和速度测试,结果美滋滋。我调用工具类中的方法进行数据的自动映射,数据10000条,最终导入到数据库中全程使用了7分钟,各位是不是觉得时间还是有点长,但是这个过程我是即把这10000多条的数据封装进来了而且还成功插入到数据库中去了,我想这个结果应该能及格吧,如果各位还不能接受这个速度,那可以优化数据库的读写速度,效果可能会更好。需要特别说明一点的是:将Excel文件中的数据封装到数据集合中只需3秒多一点,我反正是够用了,哈哈~~
我的数据最后是封装到一个结果处理Vo类中。

1 import java.io.Serializable; 2 import java.util.List; 3 4 public class ItemVo implements Serializable { 5 6 private List<Item> listItem; 7 8 public List<Item> getListItem() { 9 return listItem; 10 } 11 12 public void setListItem(List<Item> listItem) { 13 this.listItem = listItem; 14 } 15 16 @Override 17 public String toString() { 18 return "ItemVo [listItem=" + listItem + "]"; 19 } 20 }

1 @Controller 2 @RequestMapping("/poi") 3 public class MainPOIAction { 4 5 @Autowired 6 private ItemService itemService; 7 8 /** 9 * 自动映射Excel文件和javaBean对象的属性封装 10 * @return 11 */ 12 @RequestMapping(value = "/autoMapping",produces = "text/plain;charset=UTF-8") 13 @ResponseBody 14 public String autoMapping(){ 15 ExcelUtil eu = new ExcelUtil(); 16 // 开始导入时间 17 long starTime=System.nanoTime(); 18 // 将指定路径下Excel文件中的数据自动封装到Bean对象中 19 ItemVo itemVo = eu.setExcelInfo2Bean(new File("H://POI开发//商品信息模板.xlsx"), new ItemVo()); 20 List<Item> listItem = itemVo.getListItem(); 21 /*for (Item item : listItem) { 22 int save = itemService.saveItem(item); 23 if(save != 1){ 24 System.out.println("商品ID"+item.getId()+"导入失败"); 25 continue; 26 } 27 }*/ 28 // 导入结束时间 29 long endTime=System.nanoTime(); 30 long time = endTime-starTime; 31 return JsonUtil.object2Json(time); 32 } 33 34 }
纯属抱大腿,但是也学到了不少东西,希望能给各位博友带来灵感。
以上是关于2.自定义@Excel注解实现数据Excel形式导入导出的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章
