python学习第二周 购物车
Posted
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了python学习第二周 购物车相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
shopping_mall.py
1. 介绍
这是一个简单的购物车软件,模拟用户登陆、购买、重置等操作。
2. 环境需求
python 3.0 及以上版本。
3. 移植问题
windows 下运行,linux上没有做测试。
4. 特性
1)执行程序,提示用户输入用户名、密码
2)密码文件 pass.txt 测试账户:admin 密码 admin
3)输入错误超过3次,锁定账户。
4)账户信息存储在pass.txt。格式:用户名 密码 锁定状态。
5)锁定状态=0,表示用户没有锁定。锁定状态=1,表示该用户已被锁定。
6) 可以显示2层菜单,可以返回和退出。
7) 用户退出后,下次登陆余额不变。
8)用户购买时,可以选择买几件。
9)可以随时显示已购买信息。
10)用户可以查看购买的历史记录。
11) 退出及购买成功,提示用户,并显示余额。
12)用户购买记录保存在username_file.txt对应用户名。
5. 重要文件
主程序shopping_mall.py;账户文件: pass.txt
6. 执行方式
python shopping_mall.py
7. 博客地址
http://www.cnblogs.com/lzf8989/p/6096919.html
8. Author
sunny [email protected]
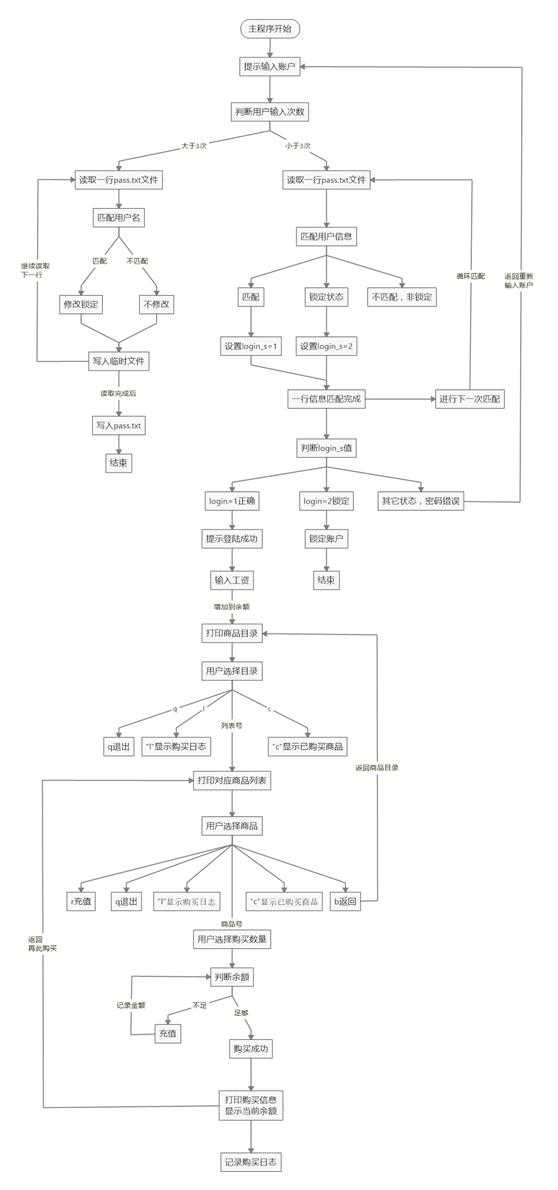
#!/usr/bin/env python # -*- coding: utf-8 -*- ## Author:lzf8989 #引入os,time模块 import os import time #用户账户文件,密码本+余额 file = "pass.txt" #定义时间格式,获取当前时间 ISOTIMEFORMAT = ‘%Y-%m-%d %X‘ this_time = time.strftime(ISOTIMEFORMAT, time.localtime()) print ("当前时间:",this_time) #设置商品字典 product_dict = { "手机":[(‘iphone‘,5888),(‘ipad‘,6888),(‘xiaomi2‘,2000),(‘锤子‘,4000)], "汽车":[(‘特斯拉‘,888880),("哈佛 H6",140000),("高尔夫",150000),("奔驰S400",170000)], "家居用品":[(‘桌子‘,2000),(‘椅子‘,500),(‘电视‘,3000),(‘音响‘,5000)] } #定义购物车列表 shop_car = [] #设置登陆出事计数器=0 user_login_count = 0 #设置用户登录缓存字典 user_login_cache ={} #计数器初始值 counter = 1 #登陆状态初始值 login_status = 0 #定义密码文件修改函数,方便调用。 def pass_file_change (username_input,salary,change): pass_file = open(file,‘r‘) line = pass_file.readline() new_pass_file = open("pass_new.txt",‘w‘) #匹配账户,修改文件。 while line: #整理用户名、密码、状态字段,清理字符串前后的空字符。 username_new_file = line.split()[0].strip() userpass_file = line.split()[1].strip() userstatus_file = line.split()[2].strip() usersalary_file = line.split()[3].strip() #判断用户名是否匹配,写入用户数据到临时文件。 if username_new_file == username_input and change == 1 : lock_user_info = username_new_file + " "+userpass_file+" 1"+ " " + str(usersalary_file) +‘\\n‘ new_pass_file.write(lock_user_info) elif username_new_file == username_input and change == 0 : lock_user_info = username_new_file + " "+userpass_file+" " +userstatus_file+" "+ str(salary) +‘\\n‘ new_pass_file.write(lock_user_info) else: other_user_info = username_new_file+" "+userpass_file+" "+userstatus_file+" "+usersalary_file+‘\\n‘ new_pass_file.write(other_user_info) line = pass_file.readline() pass_file.close() #从临时文件读取信息,写入pass.txt文件。 new_pass_file = open("pass_new.txt") read_new_pass_file = new_pass_file.read() old_pass_file = open(file,‘w‘) old_pass_file.write(read_new_pass_file) new_pass_file.close() #删除临时文件 os.unlink("pass_new.txt") #定义查看用户购买日志函数。 def look_user_log (user_log_file): file = open(user_log_file,"r") for line in file: print (line.strip("/n")) file.close() welcome_msg = ‘Welcome to SUNNY Shopping Mall‘.center(50,‘-‘) print (welcome_msg) #主程序开始,循环提示用户输入账户。 while 1: #获取用户输入信息。去掉空字符。 username_input = input("username:").strip() password_input = input("pasword:").strip() if username_input in user_login_cache.keys(): user_login_cache[username_input] += 1 else: user_login_cache[username_input] = user_login_count #判断用户输入次数 if user_login_cache[username_input] < 2: #计数器小于3次,开始逐行读取密码文件。 pass_file = open(file,‘r‘) line = pass_file.readline() while line: #切割字符串,获取密码文件中的账户信息。 username_file = line.split()[0].strip() userpass_file = line.split()[1].strip() lock_status = int(line.split()[2]) #print (lock_status) #匹配用户名、密码如果相同,标记login_status=1 if username_input == username_file and password_input == userpass_file: login_status = 1 username_ok = username_input user_salary = line.split()[3].strip() #print (user_salary) #匹配用户名相同,lock_status=1,标记login_status=2. elif username_input == username_file and lock_status == 1: login_status = 2 elif username_input == username_file and password_input != userpass_file: login_status = 0 #读取下一行 line = pass_file.readline() #判断login_status值,输出结果。 if login_status == 1: welcome_login = ‘登陆成功‘.center(40,‘-‘) print (welcome_login) recharge_flag = True salary = int(user_salary) print ("账户余额:",user_salary) while recharge_flag: salary_input = input("输入工资:") salary_input = salary_input.strip() if salary_input.isdigit() : salary = int(user_salary) recharge_flag = False else: continue salary = int(salary_input) + int(user_salary) pass_file_change (username_input,salary,0) #设置退出标志位 exit_flag = False #打印商品列表,于用户交互,实现购买。 while not exit_flag: print ("商品列表".center(50,‘-‘)) for shop_key_item in enumerate(product_dict.keys()): print (shop_key_item[0],". ",shop_key_item[1]) user_choice_mulu = input("请选择商品类别(q退出,l购买日志,c已买物品):") if user_choice_mulu.isdigit(): product_dict_keys = list(product_dict.keys()) #定义菜单标志位 caidan_2_flag = True #循环控制用户购买商品。 while caidan_2_flag: if int(user_choice_mulu) < int(len(product_dict_keys)): user_choice_mulu_name = product_dict_keys[int(user_choice_mulu)] print (user_choice_mulu_name.center(50,‘-‘)) user_choice_mulu_name_list = product_dict[user_choice_mulu_name.strip()] for user_choice_item in enumerate(user_choice_mulu_name_list): user_choice_item_index = user_choice_item[0] user_choice_item_name = user_choice_item[1][0] user_choice_item_jiage = user_choice_item[1][1] print(user_choice_item_index,".",user_choice_item_name," ",user_choice_item_jiage) user_choice_commodity = input("请选择需要购买的商品(b返回,q退出,l购买日志,c已买物品):") #对用户输入字符进行判断,控制购买流程。 if user_choice_commodity.isdigit(): if int(user_choice_commodity) < int(len(user_choice_mulu_name_list)): p_item = user_choice_mulu_name_list[int(user_choice_commodity)] num_exit_flag = True while num_exit_flag: if int(salary) < int(p_item[1]): print ("您的余额不足以支付一件该商品") user_choice = input ("余额不足(r充值,b返回:)") user_choice = user_choice.strip() #输入r开始充值,并写入pass.txt文件 if user_choice == "r": recharge_flag = True while recharge_flag: user_choice_recharge = input("输入充值金额:") user_choice_recharge = user_choice_recharge.strip() if user_choice_recharge.isdigit(): salary += int(user_choice_recharge) recharge_flag = False num_exit_flag = True #输入b返回长层菜单。 elif user_choice == "b": num_exit_flag = False else: user_choice_num = input("请选择购买数量:") #print ("OK",int(salary),p_item[1]) if user_choice_num.isdigit(): p_zongjia = int(user_choice_num) * p_item[1] #判断用户余额是否充足。 if p_zongjia <= salary: this_time = time.strftime(ISOTIMEFORMAT, time.localtime()) for i in range(int(user_choice_num)): shop_car.append(p_item) salary -= p_zongjia print ("购买成功:",p_item[0],"总售价:",p_zongjia,"购买时间:",this_time) #设置用户购买日志文件 user_log_file = username_input + ".txt" user_log = open(user_log_file,‘a‘) print (user_choice_num) mai_log = this_time+" "+p_item[0]+" Number:"+ user_choice_num +"price:"+str(p_item[1])+"\\n" #写入日志 user_log.write(mai_log) user_log.close() print ("账户余额:",salary) pass_file_change (username_input,salary,0) num_exit_flag = False continue else: #print ("钱不够,输入b重新输入购买数量") user_choice = input ("余额不足(r充值,c继续购买:)") user_choice = user_choice.strip() #提示用户充值或者重新选择熟练。 if user_choice == "r": user_choice_recharge = input("输入充值金额:") user_choice_recharge = user_choice_recharge.strip() if user_choice_recharge.isdigit(): salary += int(user_choice_recharge) pass_file_change (username_input,salary,0) num_exit_flag = True elif user_choice == "c": continue elif user_choice_commodity == ‘b‘: caidan_2_flag = False else: #用户输入q,退出 if user_choice_commodity == ‘q‘ or user_choice_commodity == ‘quit‘: print("已购买物品".center(40,"*")) print("%3s %7s %3s %7s"%("ID","商品","数量","单价")) #print("ID"," ","p_name"," ","num"," ","total_price") shop_car_single = set(shop_car) count = 1 for shop_car_item in (shop_car_single): shop_car_count = shop_car.count(shop_car_item) print ("%3d %7s %3s %10s"%(count,shop_car_item[0],shop_car_count,shop_car_item[1])) #print (count,shop_car_item[0],shop_car_count,shop_car_item[1]) count += 1 print("完成".center(50,"*")) print("账户余额\\033[41;1m[%s]\\033[0m" % salary) exit() #用户选择c,输出已购买列表。 elif user_choice_commodity == ‘c‘ or user_choice_commodity == ‘check‘: print("已购买物品".center(40,"*")) print("%3s %7s %3s %7s"%("ID","商品","数量","单价")) shop_car_single = set(shop_car) count = 1 for shop_car_item in (shop_car_single): shop_car_count = shop_car.count(shop_car_item) print ("%3d %7s %3s %10s"%(count,shop_car_item[0],shop_car_count,shop_car_item[1])) count += 1 print("完成".center(50,"*")) print("账户余额\\033[41;1m[%s]\\033[0m" % salary) #exit_flag = True #输入l,查看购买日志。 elif user_choice_commodity == ‘l‘or user_choice_commodity == ‘look‘: user_log_file = username_input + ".txt" look_user_log (user_log_file) else: caidan_2_flag = False else: #输入q退出并显示余额 if user_choice_mulu == ‘q‘ or user_choice_mulu == ‘quit‘: print("已购买物品".center(50,"*")) print("%3s %7s %3s %7s"%("ID","商品","数量","单价")) shop_car_single = set(shop_car) count = 1 for shop_car_item in (shop_car_single): shop_car_count = shop_car.count(shop_car_item) print ("%3d %7s %3s %10s"%(count,shop_car_item[0],shop_car_count,shop_car_item[1])) count += 1 print("完成".center(50,"*")) print("账户余额\\033[41;1m[%s]\\033[0m" % salary) exit() #查看购买记录 elif user_choice_mulu == ‘l‘or user_choice_mulu == ‘look‘: user_log_file = username_input + ".txt" look_user_log (user_log_file) #输入c查看已购买物品,显示余额。 elif user_choice_mulu == ‘c‘ or user_choice_mulu == ‘check‘: print("已购买物品".center(50,"*")) print("%3s %7s %3s %7s"%("ID","商品","数量","单价")) shop_car_single = set(shop_car) count = 1 for shop_car_item in (shop_car_single): shop_car_count = shop_car.count(shop_car_item) print ("%3d %7s %3s %10s"%(count,shop_car_item[0],shop_car_count,shop_car_item[1])) count += 1 print("完成".center(40,"*")) print("账户剩余\\033[41;1m[%s]\\033[0m" % salary) #exit_flag = True continue #用户已被锁定,提示用户。 elif login_status == 2: print ("账户锁定中!!!") counter += 1 #计数器+1,开始下一次循环。 #用户密码错误,提示。 else: print ("用户名或密码错误,请重新输入") counter += 1 #计数器+1,开始下一次循环。 else: #计数器大于3次,输出提示,锁定账户。 print ("输入次数过多,锁定账户",username_input) #逐行读取,并设置临时文件 pass_file_change (username_input,salary,1) break pass_file.close()
以上是关于python学习第二周 购物车的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章