python web.py
Posted cxscode
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了python web.py相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
浅谈五大Python Web框架:https://www.cnblogs.com/suzhigang/p/6208244.html
web.py 0.3 新手指南:http://webpy.org/docs/0.3/tutorial.zh-cn
webpy框架:https://www.cnblogs.com/xiaowuyi/archive/2012/11/15/2771099.html
web.py 教程:http://blog.sina.com.cn/s/blog_69812f770100xrk6.html
在windows下nginx+django+flup python3:https://www.cnblogs.com/to-creat/p/6543525.html
Windows系统下使用flup搭建Nginx和Python环境的方法:http://www.jb51.net/article/77006.htm
一、安装与开发
web.py下载地址:http://webpy.org/static/web.py-0.33.tar.gz。解压并拷贝web文件夹到你的应用程序目录下。或者,为了让所有的应用程序都可以使用,运行:
python setup.py install
注意: 在某些类unix系统上你可能需要切换到root用户或者运行:
sudo python setup.py install
也可以直接把里面的WEB文件夹放site-packages 。
web.py 内置了web服务器,代码写完后,将其保存,例如文件名为mywebpy.py,可以用下面的方法来启动服务器:
python mywebpy.py
打开你的浏览器输入 http://localhost:8080/ 查看页面。 若要制定另外的端口,使用 python mywebpy.py 1234。
二、URL 处理
任何网站最重要的部分就是它的URL结构。你的URL并不仅仅只是访问者所能看到并且能发给朋友的。它还规定了你网站运行的心智模型。在一些类似del.icio.us的流行网站 , URL甚至是UI的一部分。 web.py使这类强大的URL成为可能。
urls = ( \'/\', \'index\' )
第一部分是匹配URL的正则表达式,像/、/help/faq、/item/(\\d+)等(\\d+将匹配数字)。圆括号表示捕捉对应的数据以便后面使用。第二部分是接受请求的类名称,像index、view、welcomes.hello (welcomes模块的hello类),或者get_\\1。\\1 会被正则表达式捕捉到的内容替换,剩下来捕捉的的内容将被传递到你的函数中去。这行表示我们要URL/(首页)被一个叫index的类处理。现在我们需要创建一个列举这些url的application。
app = web.application(urls, globals())
这会告诉web.py去创建一个基于我们刚提交的URL列表的application。这个application会在这个文件的全局命名空间中查找对应类。
一般来说,在每个应用的最顶部,你通常会看到整个URL调度模式被定义在元组中:
urls = (
"/tasks/?", "signin",
"/tasks/list", "listing",
"/tasks/post", "post",
"/tasks/chgpass", "chgpass",
"/tasks/act", "actions",
"/tasks/logout", "logout",
"/tasks/signup", "signup"
)
这些元组的格式是: URL路径, 处理类 。
你可以利用强大的正则表达式去设计更灵活的URL路径。比如 /(test1|test2) 可以捕捉 /test1 或 /test2。要理解这里的关键,匹配是依据URL路径的。比如下面的URL:
http://localhost/myapp/greetings/hello?name=Joe
这个URL的路径是 /myapp/greetings/hello。web.py会在内部给URL路径加上和$ ,这样 /tasks/ 不会匹配 /tasks/addnew。URL匹配依赖于“路径”,所以不能这样使用,如: /tasks/delete?name=(.+) ,?之后部分表示是“查询”,并不会被匹配。阅读URL组件的更多细节,请访问web.ctx。
你可以捕捉URL的参数,然后用在处理类中:
/users/list/(.+), "list_users"
在 list/后面的这块会被捕捉,然后作为参数被用在GET或POST:
class list_users:
def GET(self, name):
return "Listing info about user: {0}".format(name)
你可以根据需要定义更多参数。同时要注意URL查询的参数(?后面的内容)也可以用web.input()取得。
三、hello world
现在我们需要来写index类。虽然大多数人只会看看,并不会注意你的浏览器在使用用于与万维网通信的HTTP语言。具体的细节并不重要,但是要理解web访问者请求web服务器去根据URL(像/、/foo?f=1)执行一个合适的函数(像GET、POST)的基本思想。GET用于请求网页文本。当你在浏览器输入harvard.edu,它会直接访问Harvard的web服务器,去GET /。 POST经常被用在提交form,比如请求买什么东西。每当提交一个去做什么事情(像使用信用卡处理一笔交易)的请求时,你可以使用POST。这是关键,因为GET的URL可以被搜索引擎索引,并通过搜索引擎访问。虽然大部分页面你希望被索引,但是少数类似订单处理的页面你是不希望被索引的。
在我们web.py的代码中,我们将这两个方法明确区分:
class index:
def GET(self):
return "Hello, world!"
当有人用GET请求/时,这个GET函数随时会被web.py调用。
好了,限制我们只需要最后一句就写完了。这行会告诉web.py开始提供web页面:
if __name__ == "__main__": app.run()
这会告诉web.py为我们启动上面我们写的应用。
于是将上面的代码完整列出如下:
import web
urls = (
\'/\', \'index\'
)
class index:
def GET(self):
return "Hello, world!"
if __name__ == "__main__":
app = web.application(urls, globals())
app.run()
保存为hello.py,运行后显示:
http://0.0.0.0:8080/
在浏览器中输入http://127.0.0.1:8080,就会出现hello world!页面。
四、模板
给模板新建一个目录(命名为 templates),在该目录下新建一个以 .html 结尾的文件,这里存为index.html,内容如下:
<em>Hello</em>, world!
你也可以在模板中使用 web.py 模板支持代码:
$def with (name)
$if name:
I just wanted to say <em>hello</em> to $name.
$else:
<em>Hello</em>, world!
如上,该模板看起来就像 python 文件一样,除了顶部的 def with (表示从模板将从这后面取值)和总是位于代码段之前的$。当前,template.py 首先请求模板文件的首行 $def 。当然,你要注意 web.py 将会转义任何用到的变量,所以当你将name的值设为是一段HTML时,它会被转义显示成纯文本。如果要关闭该选项,可以写成 $:name 来代替 $name。
在code.py第一行之下添加:
render = web.template.render(\'templates/\')
这会告诉web.py到你的模板目录中去查找模板。然后把 index.GET改成: 告诉 web.py 在你的模板目录下查找模板文件。修改 index.GET :
name = \'Bob\' return render.index(name)
完整代码为:
##@小五义http://www.cnblogs.com/xiaowuyi
import web
render = web.template.render(\'templates/\')
urls = (
\'/\', \'index\'
)
class index:
def GET(self):
name=\'Bob\'
return render.index(name)
#return "Hello, world!"
if __name__ == "__main__":
app = web.application(urls, globals())
app.run()
访问站点它将显示 I just wanted to say hello to Bob。
但是如果我们想让用户自行输入他的名字,如下:
i = web.input(name=None) return render.index(i.name)
访问 / 将显示 hello world,访问 /?name=Joe 将显示 I just wanted to say hello to Joe。
URL 的后面的 ? 看起来不好看,修改下 URL 配置:
\'/(.*)\', \'index\'
然后修改下 GET:
def GET(self, name):
return render.index(name)
完整代码为:
##@小五义http://www.cnblogs.com/xiaowuyi
import web
render = web.template.render(\'templates/\')
urls = (
\'/(.*)\', \'index\'
)
class index:
def GET(self,name):
i=web.input(name=None)
return render.index(name)
#return "Hello, world!"
if __name__ == "__main__":
app = web.application(urls, globals())
app.run()
现在访问http://127.0.0.1:8080/TOM ,它会显示I just wanted to say hello to TOM. 如果访问http://127.0.0.1:8080/,它会显示Hello, world!
五、表单
1、简介
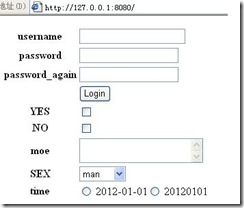
表单包括Textbox、Password 、Textarea 、Dropdown、Radio、Checkbox、Button具体使用及样式如下:
login = form.Form(
form.Textbox(\'username\'),
form.Password(\'password\'),
form.Password(\'password_again\'),
form.Button(\'Login\'),
form.Checkbox(\'YES\'),
form.Checkbox(\'NO\'),
form.Textarea(\'moe\'),
form.Dropdown(\'SEX\', [\'man\', \'woman\']),
form.Radio(\'time\',[\'2012-01-01\',\'20120101\']),
validators = [form.Validator("Passwords didn\'t match.", lambda i: i.password == i.password_again)]
)
显现在页面中:
2、输入属性
如:
form.textbox("firstname",
form.notnull, #put validators first followed by optional attributes
class_="textEntry", #gives a class name to the text box -- note the underscore
pre="pre", #directly before the text box
post="post", #directly after the text box
description="please enter your name", #describes field, defaults to form name ("firstname")
value="bob", #default value
id="nameid", #specify the id
)
3、例子:
##code.py
##@小五义http://www.cnblogs.com/xiaowuyi
import web,os
from web import form
render = web.template.render("d:/webpy/templates")##这里仿照http://webpy.org/form#example最初使用了相对路径templates/,但总是发生找不到formtest的错误,于是搜索后,发现换成绝对路径可以解决这一问题。
urls = (
\'/\', \'index\',
)
app = web.application(urls, globals())
login = form.Form(
form.Textbox(\'username\'),
form.Password(\'password\'),
form.Password(\'password_again\'),
form.Button(\'Login\'),
form.Checkbox(\'YES\'),
form.Checkbox(\'NO\'),
form.Textarea(\'moe\'),
form.Dropdown(\'SEX\', [\'man\', \'woman\']),
form.Radio(\'time\',[\'2012-01-01\',\'20120101\']),
validators = [form.Validator("Passwords didn\'t match.", lambda i: i.password == i.password_again)]
)
class index:
def GET(self):
f=login()
return render.formtest(f)
def POST(self):
f=login()
if not f.validates():
return render.formtest(f)
else:
return "HAHA!"
if __name__ == "__main__":
web.internalerror = web.debugerror
app.run()
d:/webpy/templates文件夹下存放formtest.html文件,文件代码如下:
$def with (form) <form name="main" method="post"> $if not form.valid: <p class="error">Try again,Passwords didn\'t match:</p> $:form.render() <input type="submit" /> </form>
运行code.py,然后在浏览器中浏览页面如下:
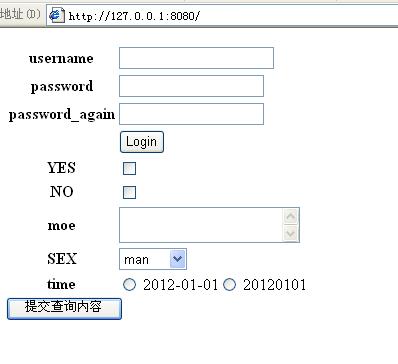
填写表格后,如果两次password相同,那么会显示HAHA!,否则显示Try again, Passwords didn\'t match:。
六、数据库
1、数据库的连接
在开始使用数据库之前,确保已经安装了合适的数据库访问库。比如对于MySQL数据库,使用 MySQLdb ,对于Postgres数据库使用psycopg2。
创建一个数据库对象:db = web.database(dbn=\'postgres\', user=\'username\', pw=\'password\', db=\'dbname\')
2、数据库读取
例,在数据库test中有一个表testtable,字段是name,在上面code.py中进行修改,如果login成功,那么列出test表中的内容。
|
1
|
#code.py |
##@小五义http://www.cnblogs.com/xiaowuyi
import web,os
from web import form
db = web.database(dbn=\'postgres\', user=\'postgres\', pw=\'password\', db=\'test\')
render = web.template.render("d:/webpy/templates")
urls = (
\'/\', \'index\',
)
app = web.application(urls, globals())
login = form.Form(
form.Textbox(\'username\'),
form.Password(\'password\'),
form.Password(\'password_again\'),
form.Button(\'Login\'),
form.Checkbox(\'YES\'),
form.Checkbox(\'NO\'),
form.Textarea(\'moe\'),
form.Dropdown(\'SEX\', [\'man\', \'woman\']),
form.Radio(\'time\',[\'2012-01-01\',\'20120101\']),
validators = [form.Validator("Passwords didn\'t match.", lambda i: i.password == i.password_again)]
)
class index:
def GET(self):
f=login()
return render.formtest(f)
def POST(self):
f=login()
if not f.validates():
return render.formtest(f)
else:
testtables = db.select(\'testtable\')
return render.index(testtables)
if __name__ == "__main__":
web.internalerror = web.debugerror
app.run()
|
1
|
##index.html |
$def with (testtables)
<ul>
$for testtable in testtables:
<li id="t$testtable.name">$testtable.name</li>
</ul>
当login正确后,会列出testtable表中name字段的值。
3、数据库写入
如将上面的FORM表中的user加入到testtable表name字段中,很简单,只需要在上面的代码中加入一句:n=db.insert(\'voa\',filename=f[\'username\'].value)。
现在,对code.py代码进行修改后,当表单填写正确后,会将username加入到testtable表中,完整代码如下:
##@小五义http://www.cnblogs.com/xiaowuyi
import web,os
from web import form
db = web.database(dbn=\'postgres\', user=\'postgres\', pw=\'password\', db=\'bbstime\')
render = web.template.render("d:/webpy/templates")
urls = (
\'/\', \'index\',
)
app = web.application(urls, globals())
login = form.Form(
form.Textbox(\'username\'),
form.Password(\'password\'),
form.Password(\'password_again\'),
form.Button(\'Login\'),
form.Checkbox(\'YES\'),
form.Checkbox(\'NO\'),
form.Textarea(\'moe\'),
form.Dropdown(\'SEX\', [\'man\', \'woman\']),
form.Radio(\'time\',[\'2012-01-01\',\'20120101\']),
validators = [form.Validator("Passwords didn\'t match.", lambda i: i.password == i.password_again)]
)
class index:
def GET(self):
f=login()
return render.formtest(f)
def POST(self):
f=login()
if not f.validates():
return render.formtest(f)
else:
n=db.insert(\'voa\',filename=f[\'username\'].value)
voas = db.select(\'voa\')
return render.index(voas)
if __name__ == "__main__":
web.internalerror = web.debugerror
app.run()
以上是关于python web.py的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章
Python简单Web框架web.py实例hello world