MPU6050陀螺仪与Processing和上位机飞控联动实录
Posted 旁观者-郑昀
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了MPU6050陀螺仪与Processing和上位机飞控联动实录相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
一,MPU6050简介
二,MUP6050特点
三,原理说明
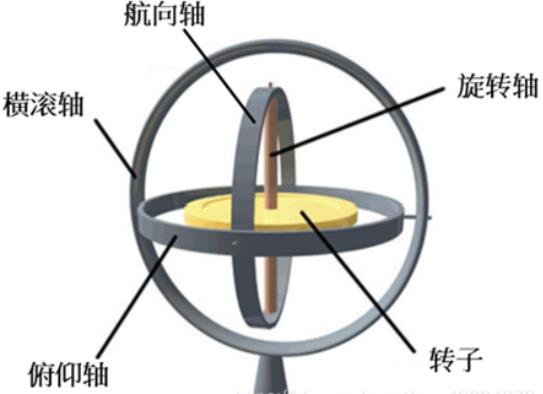
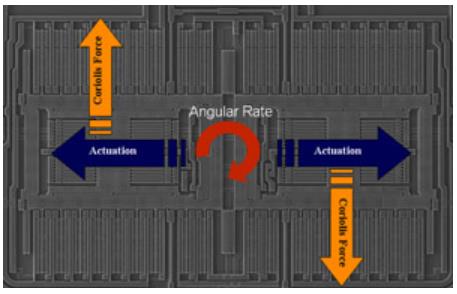
3.1.MEMS陀螺仪
3.2.MEMS加速度计
四,模块初始化工作
4.1.初始化 IIC 接口
4.2.复位 MPU6050
const uint8_t MPU6050_REGISTER_PWR_MGMT_1 = 0x6B;
I2C_Write(MPU6050SlaveAddress, MPU6050_REGISTER_PWR_MGMT_1, 0x01);4.3.设置角速度传感器(陀螺仪)和加速度传感器的满量程范围
4.4.设置其他参数
- 关闭中断
- 关闭 AUX IIC 接口
- 禁止 FIFO
- 设置陀螺仪采样率
- 设置数字低通滤波器(DLPF)等。
const uint8_t MPU6050_REGISTER_INT_ENABLE = 0x38;
I2C_Write(MPU6050SlaveAddress, MPU6050_REGISTER_INT_ENABLE, 0x01);
const uint8_t MPU6050_REGISTER_USER_CTRL = 0x6A;
I2C_Write(MPU6050SlaveAddress, MPU6050_REGISTER_USER_CTRL, 0x00);const uint8_t MPU6050_REGISTER_FIFO_EN = 0x23;
I2C_Write(MPU6050SlaveAddress, MPU6050_REGISTER_FIFO_EN, 0x00);const uint8_t MPU6050_REGISTER_SMPLRT_DIV = 0x19;
I2C_Write(MPU6050SlaveAddress, MPU6050_REGISTER_SMPLRT_DIV, 0x07);const uint8_t MPU6050_REGISTER_CONFIG = 0x1A;
I2C_Write(MPU6050SlaveAddress, MPU6050_REGISTER_CONFIG, 0x00);4.5.配置系统时钟源并使能角速度传感器和加速度传感器
const uint8_t MPU6050_REGISTER_PWR_MGMT_2 = 0x6C;
I2C_Write(MPU6050SlaveAddress, MPU6050_REGISTER_PWR_MGMT_2, 0x00);五,数据处理
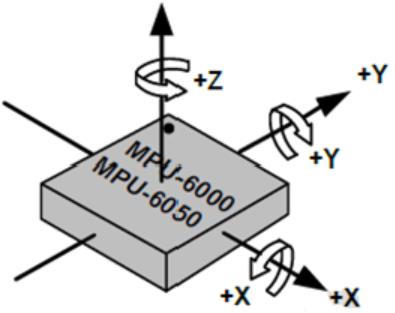
5.1.原始数据格式
5.2.DMP处理成欧拉角
q0=quat[0] / q30;//q30格式转换为浮点数
q1=quat[1] / q30;
q2=quat[2] / q30;
q3=quat[3] / q30; //计算得到ypr:pitch俯仰角/roll横滚角/yaw航向角
pitch=asin(-2 * q1 * q3 + 2 * q0* q2)* 57.3;//俯仰角
roll=atan2(2 * q2 * q3 + 2 * q0 * q1, -2 * q1 * q1 - 2 * q2* q2 + 1)* 57.3;//横滚角
yaw=atan2(2*(q1q2 + q0q3),q0q0+q1q1-q2q2-q3q3) * 57.3;//航向角5.3.Yaw角的问题
5.4.数据校准和滤波
float valSums[7] = 0.0f, 0.0f, 0.0f, 0.0f, 0.0f, 0.0f, 0.0;
//先求和
for (int i = 0; i < nCalibTimes; ++i)
int mpuVals[nValCnt];
ReadAccGyr(mpuVals);
for (int j = 0; j < nValCnt; ++j)
valSums[j] += mpuVals[j];
//再求平均
for (int i = 0; i < nValCnt; ++i)
calibData[i] = int(valSums[i] / nCalibTimes);
calibData[2] += 16384;六、接线方式
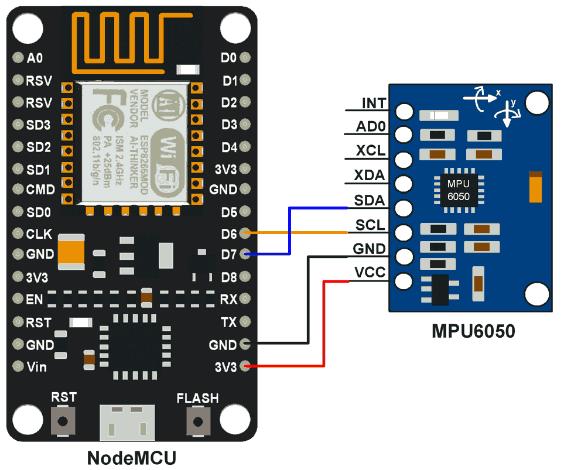
#include <Wire.h>
// MPU6050 Slave Device Address
const uint8_t MPU6050SlaveAddress = 0x68;//MPU6050的I2C地址
// Select SDA and SCL pins for I2C communication
const uint8_t scl = D6;
const uint8_t sda = D7;
// sensitivity scale factor respective to full scale setting provided in datasheet
const uint16_t AccelScaleFactor = 16384;
const uint16_t GyroScaleFactor = 131;
// MPU6050 few configuration register addresses
const uint8_t MPU6050_REGISTER_SMPLRT_DIV = 0x19;
const uint8_t MPU6050_REGISTER_USER_CTRL = 0x6A;
const uint8_t MPU6050_REGISTER_PWR_MGMT_1 = 0x6B;
const uint8_t MPU6050_REGISTER_PWR_MGMT_2 = 0x6C;
const uint8_t MPU6050_REGISTER_CONFIG = 0x1A;
const uint8_t MPU6050_REGISTER_GYRO_CONFIG = 0x1B;
const uint8_t MPU6050_REGISTER_ACCEL_CONFIG = 0x1C;
const uint8_t MPU6050_REGISTER_FIFO_EN = 0x23;
const uint8_t MPU6050_REGISTER_INT_ENABLE = 0x38;
const uint8_t MPU6050_REGISTER_ACCEL_XOUT_H = 0x3B;//我们感兴趣的数据位于 0X3B 到 0X48 这14个字节的寄存器当中
const uint8_t MPU6050_REGISTER_SIGNAL_PATH_RESET = 0x68;
int16_t AccelX, AccelY, AccelZ, Temperature, GyroX, GyroY, GyroZ;
void setup()
Serial.begin(115200);
Wire.begin(sda, scl);
MPU6050_Init();
void loop()
double Ax, Ay, Az, T, Gx, Gy, Gz;
Read_RawValue(MPU6050SlaveAddress, MPU6050_REGISTER_ACCEL_XOUT_H);
//divide each with their sensitivity scale factor
Ax = (double)AccelX/AccelScaleFactor;
Ay = (double)AccelY/AccelScaleFactor;
Az = (double)AccelZ/AccelScaleFactor;
T = (double)Temperature/340+36.53; //temperature formula
Gx = (double)GyroX/GyroScaleFactor;
Gy = (double)GyroY/GyroScaleFactor;
Gz = (double)GyroZ/GyroScaleFactor;
Serial.print("Ax: "); Serial.print(Ax);
Serial.print(";Ay: "); Serial.print(Ay);
Serial.print(";Az: "); Serial.print(Az);
Serial.print(";T: "); Serial.print(T);
Serial.print(";Gx: "); Serial.print(Gx);
Serial.print(";Gy: "); Serial.print(Gy);
Serial.print(";Gz: "); Serial.println(Gz);
delay(100);
void I2C_Write(uint8_t deviceAddress, uint8_t regAddress, uint8_t data)
Wire.beginTransmission(deviceAddress);
Wire.write(regAddress);
Wire.write(data);
Wire.endTransmission();
// read all 14 register
void Read_RawValue(uint8_t deviceAddress, uint8_t regAddress)
Wire.beginTransmission(deviceAddress);
Wire.write(regAddress);
Wire.endTransmission();
Wire.requestFrom(deviceAddress, (uint8_t)14);
AccelX = (((int16_t)Wire.read()<<8) | Wire.read());
AccelY = (((int16_t)Wire.read()<<8) | Wire.read());
AccelZ = (((int16_t)Wire.read()<<8) | Wire.read());
Temperature = (((int16_t)Wire.read()<<8) | Wire.read());
GyroX = (((int16_t)Wire.read()<<8) | Wire.read());
GyroY = (((int16_t)Wire.read()<<8) | Wire.read());
GyroZ = (((int16_t)Wire.read()<<8) | Wire.read());
//configure MPU6050
void MPU6050_Init()
delay(150);
I2C_Write(MPU6050SlaveAddress, MPU6050_REGISTER_SMPLRT_DIV, 0x07);
I2C_Write(MPU6050SlaveAddress, MPU6050_REGISTER_PWR_MGMT_1, 0x01);
I2C_Write(MPU6050SlaveAddress, MPU6050_REGISTER_PWR_MGMT_2, 0x00);
I2C_Write(MPU6050SlaveAddress, MPU6050_REGISTER_CONFIG, 0x00);
I2C_Write(MPU6050SlaveAddress, MPU6050_REGISTER_GYRO_CONFIG, 0x00);//set +/-250 degree/second full scale
I2C_Write(MPU6050SlaveAddress, MPU6050_REGISTER_ACCEL_CONFIG, 0x00);// set +/- 2g full scale
I2C_Write(MPU6050SlaveAddress, MPU6050_REGISTER_FIFO_EN, 0x00);
I2C_Write(MPU6050SlaveAddress, MPU6050_REGISTER_INT_ENABLE, 0x01);
I2C_Write(MPU6050SlaveAddress, MPU6050_REGISTER_SIGNAL_PATH_RESET, 0x00);
I2C_Write(MPU6050SlaveAddress, MPU6050_REGISTER_USER_CTRL, 0x00);
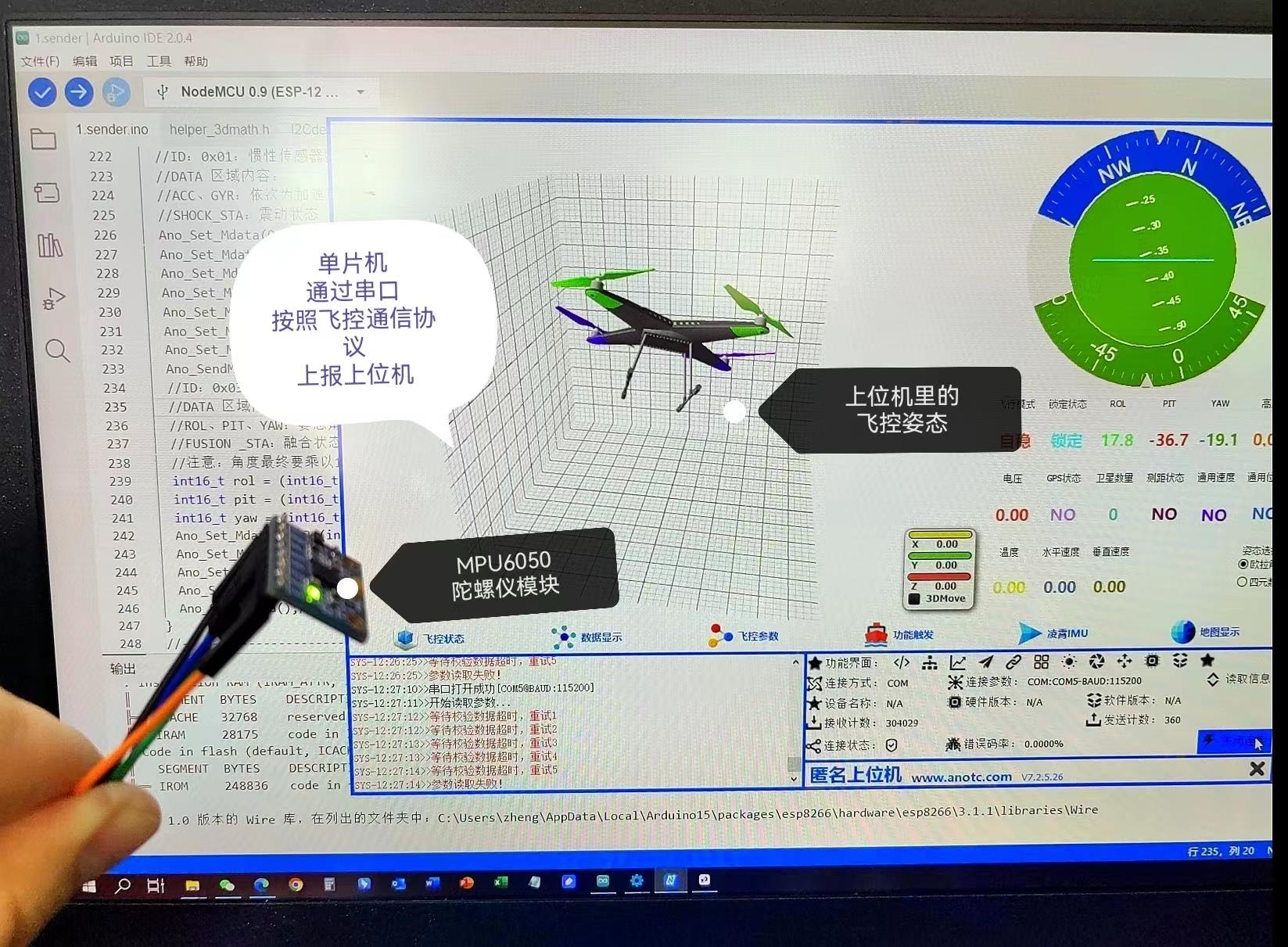
七,外接Processing实验
#define OUTPUT_READABLE_YAWPITCHROLL#define OUTPUT_TEAPOT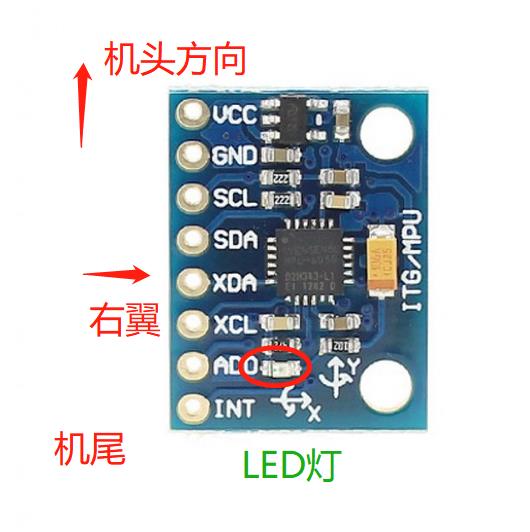
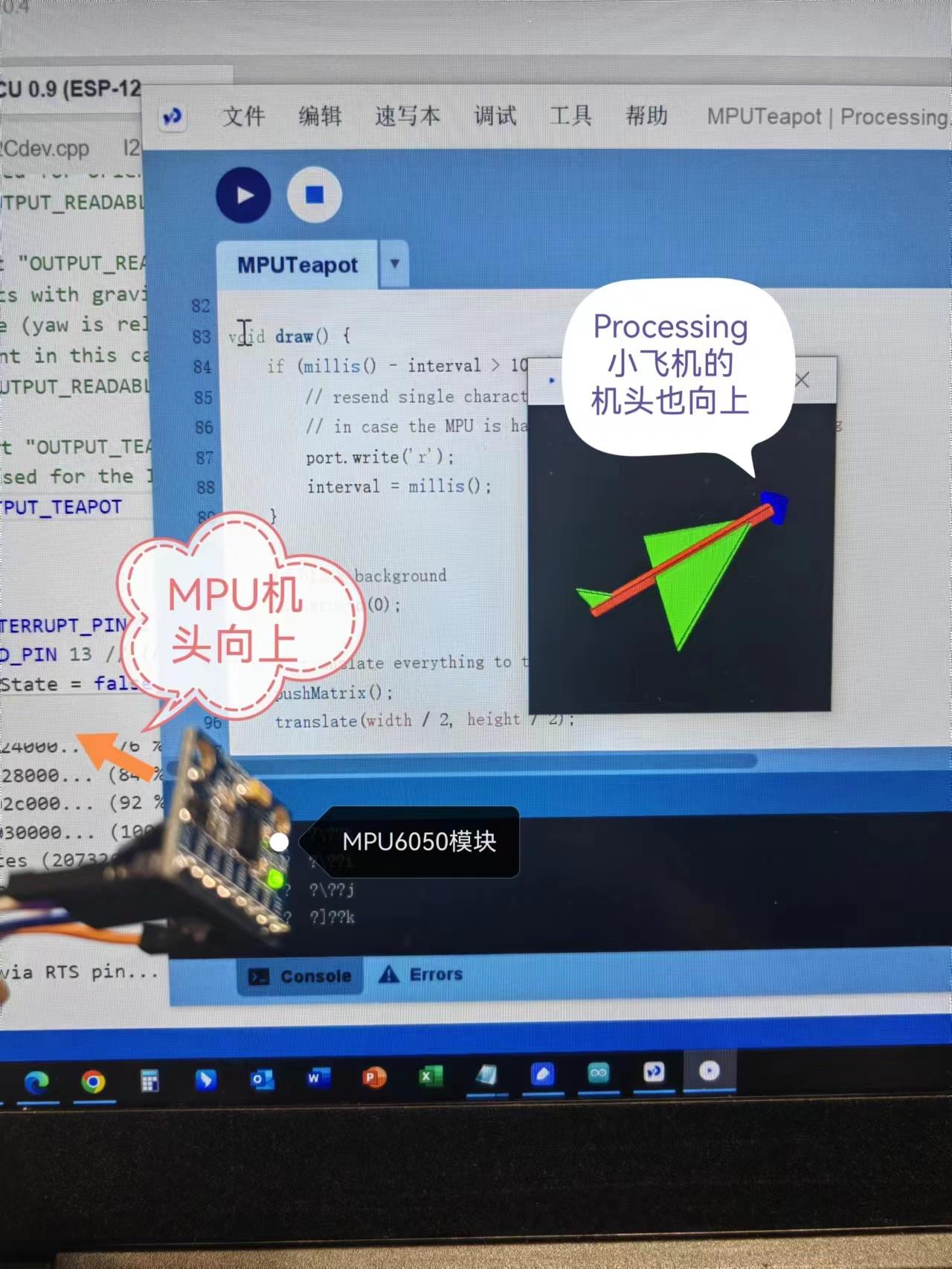
attachInterrupt(digitalPinToInterrupt(INTERRUPT_PIN), dmpDataReady, RISING);
mpuIntStatus = mpu.getIntStatus();八,外接匿名上位机(V7)
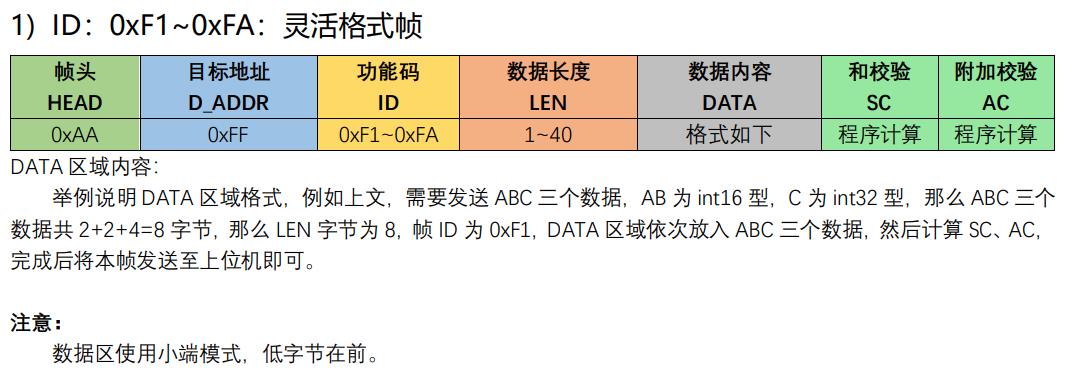
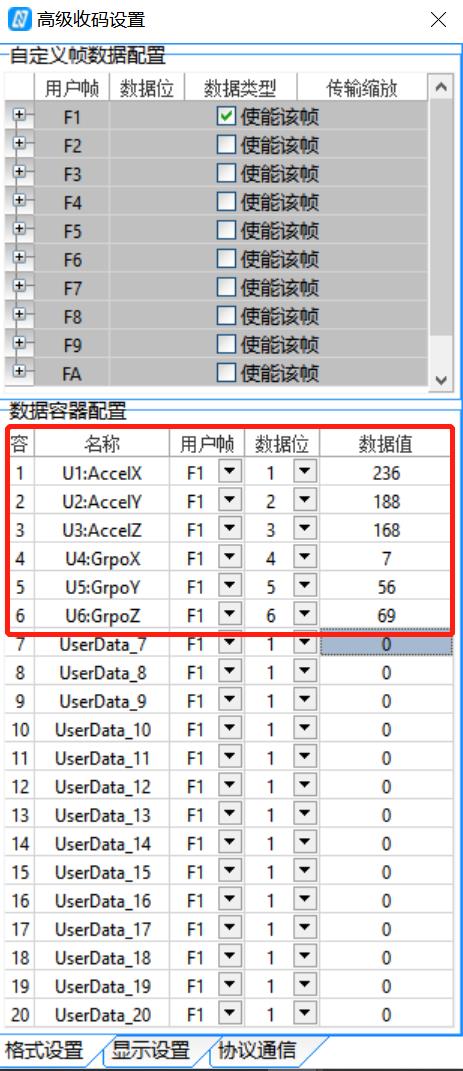
8.1.单片机上报灵活格式帧给上位机
void Ano_Init(void)
MyAno.Head = FRAME_HEADER;//0XAA是帧头
MyAno.Addr = GENERAL_OUTPUT_ADDR;//地址码为0xFF,指的是无特定目标,用于数据广播型输出
MyAno.Lenth = 0;
//-----------------与匿名上位机通讯-----------------------------
/** 发送灵活格式帧,帧ID为0xF1~0xFA
* 功能:发送加速度传感器和陀螺仪传感器数据给匿名上位机(V7)
* 入口参数:第一个参数accel,它的三个元素是xyz三个方向的加速度值
* 第二个参数gyro,它的三个元素是xyz三个方向的陀螺仪值
* 返回值:无
* 注:数据格式:帧头0xAA+目标地址0xFF+功能码0xF1+数据长度LEN+DATA+和校验SC+附加校验AC
*/
void mpu6050_send_data2ano(VectorInt16 *accel,VectorInt16 *gyro)
uint8_t nul = 0;
Ano_Set_Mdata(0xF1,(int16_t*)&accel->x,sizeof(accel->x),1);
Ano_Set_Mdata(0xF1,(int16_t*)&accel->y,sizeof(accel->y),2);
Ano_Set_Mdata(0xF1,(int16_t*)&accel->z,sizeof(accel->z),3);
Ano_Set_Mdata(0xF1,(int16_t*)&gyro->x,sizeof(gyro->x),4);
Ano_Set_Mdata(0xF1,(int16_t*)&gyro->y,sizeof(gyro->y),5);
Ano_Set_Mdata(0xF1,(int16_t*)&gyro->z,sizeof(gyro->z),6);
Ano_Set_Mdata(0xF1,(uint8_t*)&nul,sizeof(nul),7);//加载数据到对应的数据位
Ano_SendMdata();//发送数据
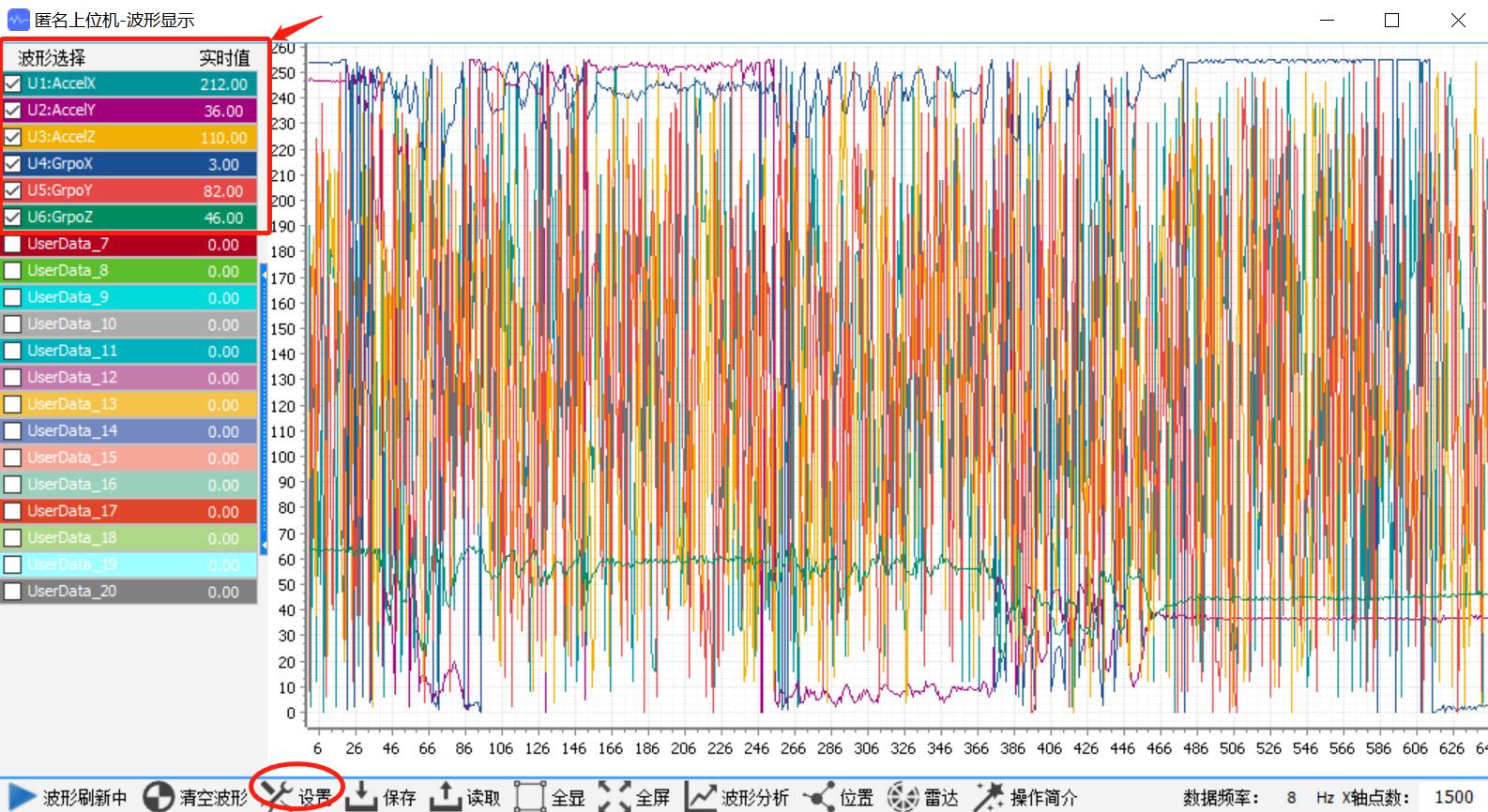
8.2.单片机上报飞行状态数据给上位机
//-----------------与匿名上位机通讯-----------------------------
/** 发送基本信息类帧,功能码ID为0x01~0x04之间,在飞控通信协议里属于飞控相关信息类
* 功能:发送惯性传感器、欧拉角等数据给匿名上位机(V7)
* 入口参数:第一个参数accel,它的三个元素是xyz三个方向的加速度值
* 第二个参数gyro,它的三个元素是xyz三个方向的陀螺仪值
* 第三个参数ypr,这是一个float[]数组,分别是yaw/pitch/roll angles原始值
* 返回值:无
* 注:数据格式:帧头0xAA+目标地址0xFF+功能码+数据长度LEN+DATA+和校验SC+附加校验AC
* 注:为了提高数据传输的效率,当有浮点数类型数据需要传输时,根据数据类型的特点,适当截取小数点后固定几
位,比如飞控姿态数据,保留角度的小数点后两位即可(即乘以100)。
将浮点数转化成整数类型进行传输,可缩短数据长度,并且避免浮点数传输时发生异
常,解析成非法浮点数。
*/
void mpu6050_send_flydata2ano(VectorInt16 *accel,VectorInt16 *gyro,float *ypr)
uint8_t nul = 0;
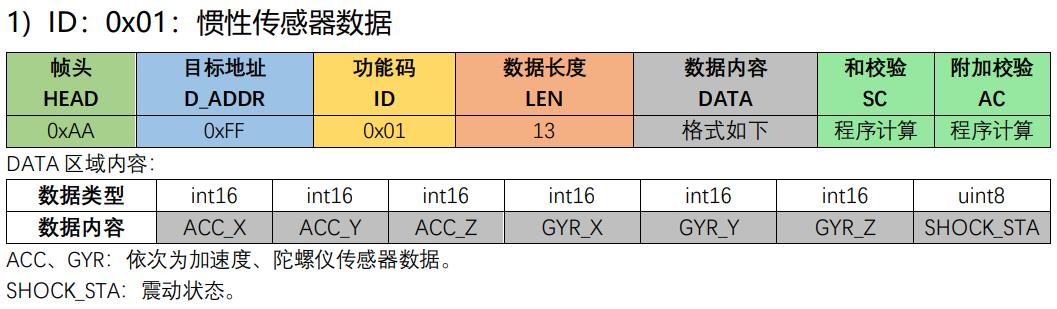
//ID:0x01:惯性传感器数据
//DATA 区域内容:
//ACC、GYR:依次为加速度、陀螺仪传感器数据。
//SHOCK_STA:震动状态
Ano_Set_Mdata(0x01,(int16_t*)&accel->x,sizeof(accel->x),1);
Ano_Set_Mdata(0x01,(int16_t*)&accel->y,sizeof(accel->y),2);
Ano_Set_Mdata(0x01,(int16_t*)&accel->z,sizeof(accel->z),3);
Ano_Set_Mdata(0x01,(int16_t*)&gyro->x,sizeof(gyro->x),4);
Ano_Set_Mdata(0x01,(int16_t*)&gyro->y,sizeof(gyro->y),5);
Ano_Set_Mdata(0x01,(int16_t*)&gyro->z,sizeof(gyro->z),6);
Ano_Set_Mdata(0x01,(uint8_t*)&nul,sizeof(nul),7);
Ano_SendMdata();//发送数据
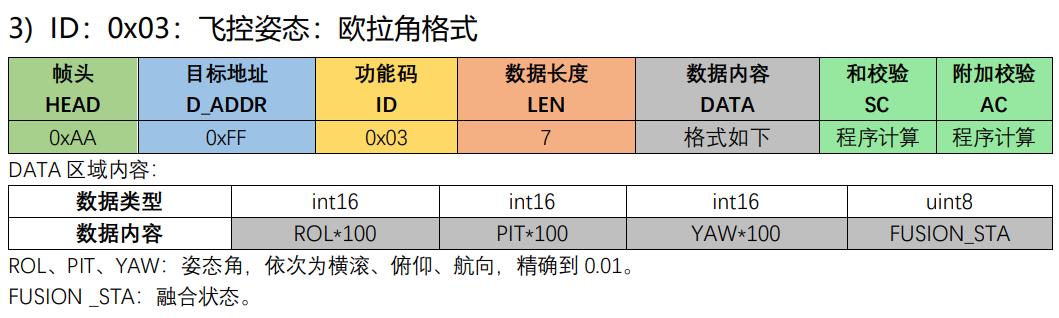
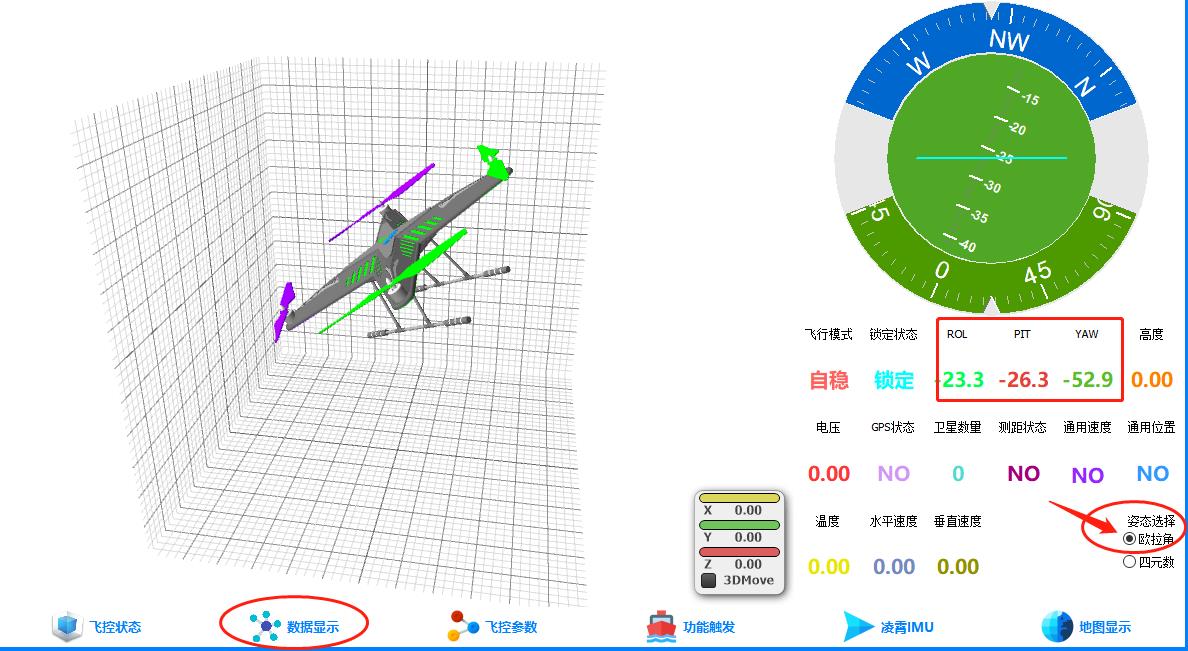
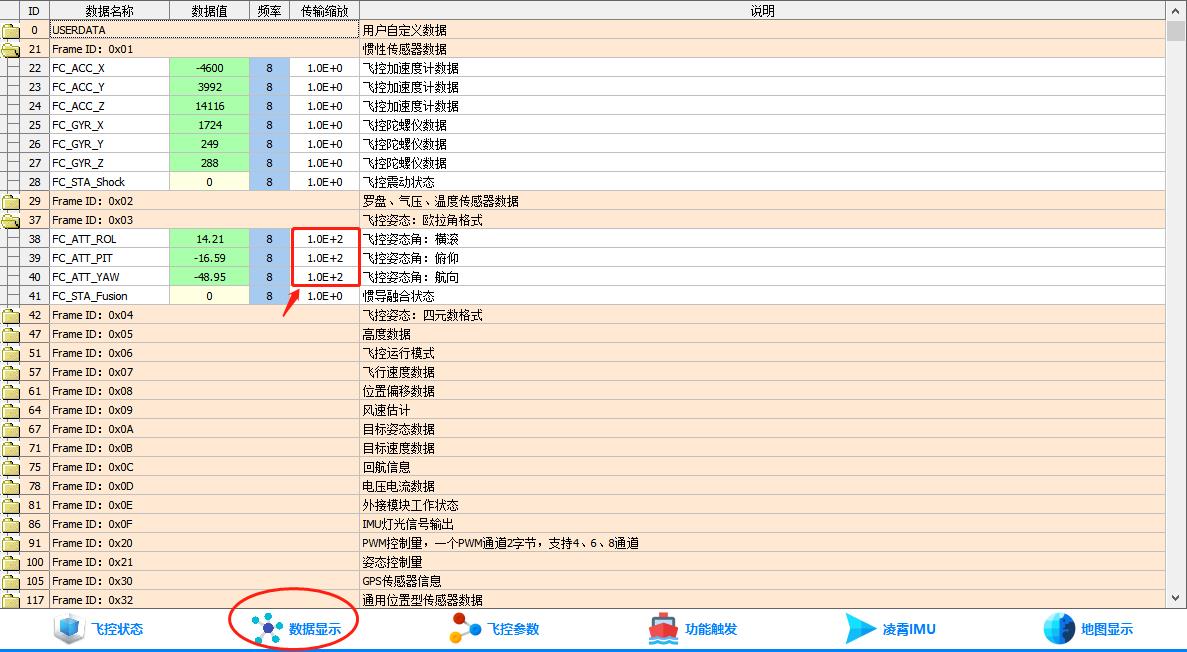
//ID:0x03:飞控姿态:欧拉角格式
//DATA 区域内容:
//ROL、PIT、YAW:姿态角,依次为横滚、俯仰、航向,精确到 0.01。
//FUSION _STA:融合状态
//注意:角度最终要乘以100,上位机那边会除以100做展示
int16_t rol = (int16_t)(ypr[2] * 180 * 100.00 / M_PI);
int16_t pit = (int16_t)(ypr[1] * 180 * 100.00 / M_PI);
int16_t yaw = (int16_t)(ypr[0] * 180 * 100.00 / M_PI);
Ano_Set_Mdata(0x03,(int16_t*)&rol,sizeof(rol),1);
Ano_Set_Mdata(0x03,(int16_t*)&pit,sizeof(pit),2);
Ano_Set_Mdata(0x03,(int16_t*)&yaw,sizeof(yaw),3);
Ano_Set_Mdata(0x03,(uint8_t*)&nul,sizeof(nul),4);
Ano_SendMdata();//发送数据

ESP32上手笔记 | 05 - 获取MPU6050数据进行姿态解算和展示(I2Cdev+MPU6050+Processing)
一、MPU6050陀螺仪加速度计传感器
1. 介绍
MPU6050是一个带有3轴加速度计和3轴陀螺仪的传感器,也称之为惯性测量单元(IMU)传感器:
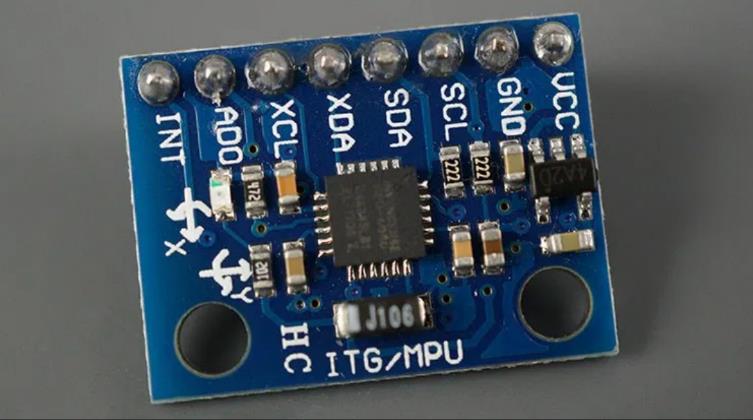
陀螺仪测量回转的速度(rad/s),是在X、Y、Z三个轴的角位置变化,分别称为roll、pitch、yaw,这可以使我们判断物体的朝向:
加速度计用来测量加速度,也就是物体速度的变化率。
2. 模块引脚说明
- VCC:3.3V
- GND
- SCL:用于I2C通信
- SDA:用于I2C通信
- XDA:用来连接其它的I2C传感器到MPU6050
- XCL:用来连接其它的I2C传感器到MPU6050
- AD0:用来设置I2C从机地址
- INT:中断引脚,用来表示有新的测量数据可用
3. I2C通信协议
MPU6050的I2C从机地址是110100X,7bit长度,最低位X由AD0引脚来控制。
MPU6050支持的最大I2C速度为400kHz。
二、i2cdevlib
I2C Device Library(i2cdevlib)是一组基本统一且文档良好的类的集合,为I2C设备提供简单直观的接口。
1. 安装库
Github仓库地址:https://github.com/jrowberg/i2cdevlib
拉取到之后,将其中Arduino下的I2Cdev文件夹和MPU6050文件夹复制到platformIO工程的lib路径中。
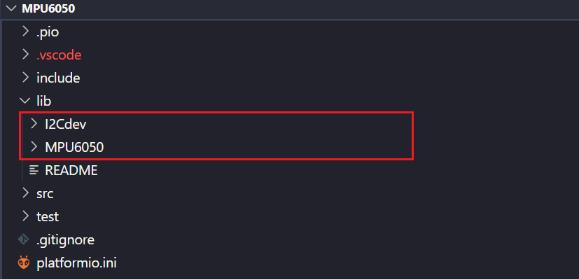
2. 使用库
包含头文件:
#include "I2Cdev.h"
#include "MPU6050.h"
2.1. 创建MPU6050对象
MPU6050_Base(uint8_t address=MPU6050_DEFAULT_ADDRESS, void *wireObj=0);
构造函数中address参数是指MPU6050的从机地址,
默认是0x68(AD0引脚为低电平),如果AD0引脚接为高电平,可以指定地址为0x69。
2.2. 初始化
/** Power on and prepare for general usage.
* This will activate the device and take it out of sleep mode (which must be done
* after start-up). This function also sets both the accelerometer and the gyroscope
* to their most sensitive settings, namely +/- 2g and +/- 250 degrees/sec, and sets
* the clock source to use the X Gyro for reference, which is slightly better than
* the default internal clock source.
*/
void MPU6050_Base::initialize();
2.3. 测试通信是否正常
/** Verify the I2C connection.
* Make sure the device is connected and responds as expected.
* @return True if connection is valid, false otherwise
*/
bool MPU6050_Base::testConnection()
return getDeviceID() == 0x34;
2.4. 获取六轴数据
/** Get raw 6-axis motion sensor readings (accel/gyro).
* Retrieves all currently available motion sensor values.
* @param ax 16-bit signed integer container for accelerometer X-axis value
* @param ay 16-bit signed integer container for accelerometer Y-axis value
* @param az 16-bit signed integer container for accelerometer Z-axis value
* @param gx 16-bit signed integer container for gyroscope X-axis value
* @param gy 16-bit signed integer container for gyroscope Y-axis value
* @param gz 16-bit signed integer container for gyroscope Z-axis value
* @see getAcceleration()
* @see getRotation()
* @see MPU6050_RA_ACCEL_XOUT_H
*/
void MPU6050_Base::getMotion6(int16_t* ax, int16_t* ay, int16_t* az, int16_t* gx, int16_t* gy, int16_t* gz);
三、获取MPU6050原始数据
1. 硬件连接

2. 代码编写
#include <Arduino.h>
#include "I2Cdev.h"
#include "MPU6050.h"
#include "Wire.h"
class IMU
private:
MPU6050 imu;
int16_t ax, ay, az;
int16_t gx, gy, gz;
int16_t temperature;
public:
int init();
void update();
int16_t getAccelX();
int16_t getAccelY();
int16_t getAccelZ();
int16_t getGyroX();
int16_t getGyroY();
int16_t getGyroZ();
int16_t getTemperature();
;
IMU imu;
void setup()
Serial.begin(115200);
imu.init();
void loop()
imu.update();
// display tab-separated accel/gyro x/y/z values
Serial.print("a/g/t:\\t");
Serial.print(imu.getAccelX()); Serial.print("\\t");
Serial.print(imu.getAccelY()); Serial.print("\\t");
Serial.print(imu.getAccelZ()); Serial.print("\\t");
Serial.print(imu.getGyroX()); Serial.print("\\t");
Serial.print(imu.getGyroY()); Serial.print("\\t");
Serial.print(imu.getGyroZ()); Serial.print("\\t");
Serial.println(imu.getTemperature());
delay(100);
int IMU::init()
// initialize i2c
Wire.begin();
Wire.setClock(400000);
// initialize device
Serial.println("Initializing I2C devices...");
imu.initialize();
// verify connection
Serial.println("Testing device connections...");
if (imu.testConnection())
Serial.println("MPU6050 connection successful");
return 0;
else
Serial.println("MPU6050 connection failed");
return -1;
void IMU::update()
// read raw accel/gyro measurements from device
imu.getMotion6(&ax, &ay, &az, &gx, &gy, &gz);
// read temperature
temperature = imu.getTemperature();
int16_t IMU::getAccelX()
return ax;
int16_t IMU::getAccelY()
return ay;
int16_t IMU::getAccelZ()
return az;
int16_t IMU::getGyroX()
return gx;
int16_t IMU::getGyroY()
return gy;
int16_t IMU::getGyroZ()
return gz;
int16_t IMU::getTemperature()
return temperature;
3. 测试结果

四、获取MPU6050 DMP姿态解算数据
1. 姿态解算
2. 硬件连接
添加 引脚GPIO16用来连接MPU6050中断引脚:

3. 代码编写
#include <Arduino.h>
#include "I2Cdev.h"
#include "MPU6050_6Axis_MotionApps20.h"
#include "Wire.h"
#define INTERRUPT_PIN 16
class IMU
private:
MPU6050 imu;
float euler[3]; // [psi, theta, phi] Euler angle container
float ypr[3]; // [yaw, pitch, roll] yaw/pitch/roll container and gravity vector
int16_t temperature;
// MPU control/status vars
bool dmpReady = false; // set true if DMP init was successful
public:
int init(uint8_t pin);
void update();
float getYaw();
float getPitch();
float getRoll();
int16_t getTemperature();
;
IMU imu;
volatile bool mpuInterrupt = false; // indicates whether MPU interrupt pin has gone high
void dmpDataReady()
mpuInterrupt = true;
void setup()
Serial.begin(115200);
imu.init(INTERRUPT_PIN);
void loop()
imu.update();
Serial.print("ypr\\t");
Serial.print(imu.getYaw());
Serial.print("\\t");
Serial.print(imu.getPitch());
Serial.print("\\t");
Serial.println(imu.getRoll());
delay(100);
int IMU::init(uint8_t pin)
uint8_t mpuIntStatus; // holds actual interrupt status byte from MPU
uint8_t devStatus; // return status after each device operation (0 = success, !0 = error)
uint16_t packetSize; // expected DMP packet size (default is 42 bytes)
// initialize i2c
Wire.begin();
Wire.setClock(400000);
// initialize device
Serial.println("Initializing I2C devices...");
imu.initialize();
// verify connection
Serial.println("Testing device connections...");
if (imu.testConnection())
Serial.println("MPU6050 connection successful");
else
Serial.println("MPU6050 connection failed");
return -1;
pinMode(pin, INPUT);
// load and configure the DMP
devStatus = imu.dmpInitialize();
// supply your own gyro offsets here, scaled for min sensitivity
imu.setXGyroOffset(220);
imu.setYGyroOffset(76);
imu.setZGyroOffset(-85);
imu.setZAccelOffset(1788); // 1688 factory default for my test chip
// make sure it worked (returns 0 if so)
if (devStatus == 0)
// Calibration Time: generate offsets and calibrate our MPU6050
imu.CalibrateAccel(6);
imu.CalibrateGyro(6);
imu.PrintActiveOffsets();
// turn on the DMP, now that it's ready
Serial.println(F("Enabling DMP..."));
imu.setDMPEnabled(true);
// enable Arduino interrupt detection
Serial.print(F("Enabling interrupt detection (Arduino external interrupt "));
Serial.print(digitalPinToInterrupt(INTERRUPT_PIN));
Serial.println(F(")..."));
attachInterrupt(digitalPinToInterrupt(INTERRUPT_PIN), dmpDataReady, RISING);
mpuIntStatus = imu.getIntStatus();
// set our DMP Ready flag so the main loop() function knows it's okay to use it
Serial.println(F("DMP ready! Waiting for first interrupt..."));
dmpReady = true;
// get expected DMP packet size for later comparison
packetSize = imu.dmpGetFIFOPacketSize();
else
// ERROR!
// 1 = initial memory load failed
// 2 = DMP configuration updates failed
// (if it's going to break, usually the code will be 1)
Serial.print(F("DMP Initialization failed (code "));
Serial.print(devStatus);
Serial.println(F(")"));
void IMU::update()
// orientation/motion vars
Quaternion q; // [w, x, y, z] quaternion container
VectorInt16 aa; // [x, y, z] accel sensor measurements
VectorInt16 aaReal; // [x, y, z] gravity-free accel sensor measurements
VectorInt16 aaWorld; // [x, y, z] world-frame accel sensor measurements
VectorFloat gravity; // [x, y, z] gravity vector
// MPU control/status vars
uint8_t fifoBuffer[64]; // FIFO storage buffer
// if programming failed, don't try to do anything
if (!dmpReady) return;
// read a packet from FIFO
if (imu.dmpGetCurrentFIFOPacket(fifoBuffer)) // Get the Latest packet
// display Euler angles in degrees
imu.dmpGetQuaternion(&q, fifoBuffer);
imu.dmpGetGravity(&gravity, &q);
imu.dmpGetYawPitchRoll(ypr, &q, &gravity);
// read temperature
temperature = imu.getTemperature();
float IMU::getYaw()
return ypr[0] * 180/M_PI;
float IMU::getPitch()
return ypr[1] * 180/M_PI;
float IMU::getRoll()
return ypr[2] * 180/M_PI;
int16_t IMU::getTemperature()
return temperature;
4. 测试结果

五、使用Processing进行姿态可视化
1. 安装Processing
下载地址:https://processing.org/download。
2. 安装toxiclibs库

3. 修改数据打印格式
添加格式定义:
// packet structure for InvenSense teapot demo
uint8_t teapotPacket[14] = '$', 0x02, 0,0, 0,0, 0,0, 0,0, 0x00, 0x00, '\\r', '\\n' ;
删除之前的打印格式:
Serial.print("ypr\\t");
Serial.print(imu.getYaw());
Serial.print("\\t");
Serial.print(imu.getPitch());
Serial.print("\\t");
Serial.println(imu.getRoll());
新增一个IMU类的发送数据函数:
void IMU::sendDataToProcessing()
// display quaternion values in InvenSense Teapot demo format:
teapotPacket[2] = fifoBuffer[0];
teapotPacket[3] = fifoBuffer[1];
teapotPacket[4] = fifoBuffer[4];
teapotPacket[5] = fifoBuffer[5];
teapotPacket[6] = fifoBuffer[8];
teapotPacket[7] = fifoBuffer[9];
teapotPacket[8] = fifoBuffer[12];
teapotPacket[9] = fifoBuffer[13];
Serial.write(teapotPacket, 14);
teapotPacket[11]++; // packetCount, loops at 0xFF on purpose
在update函数调用之后,调用该函数发送数据到上位机。
修改完毕,烧录代码。
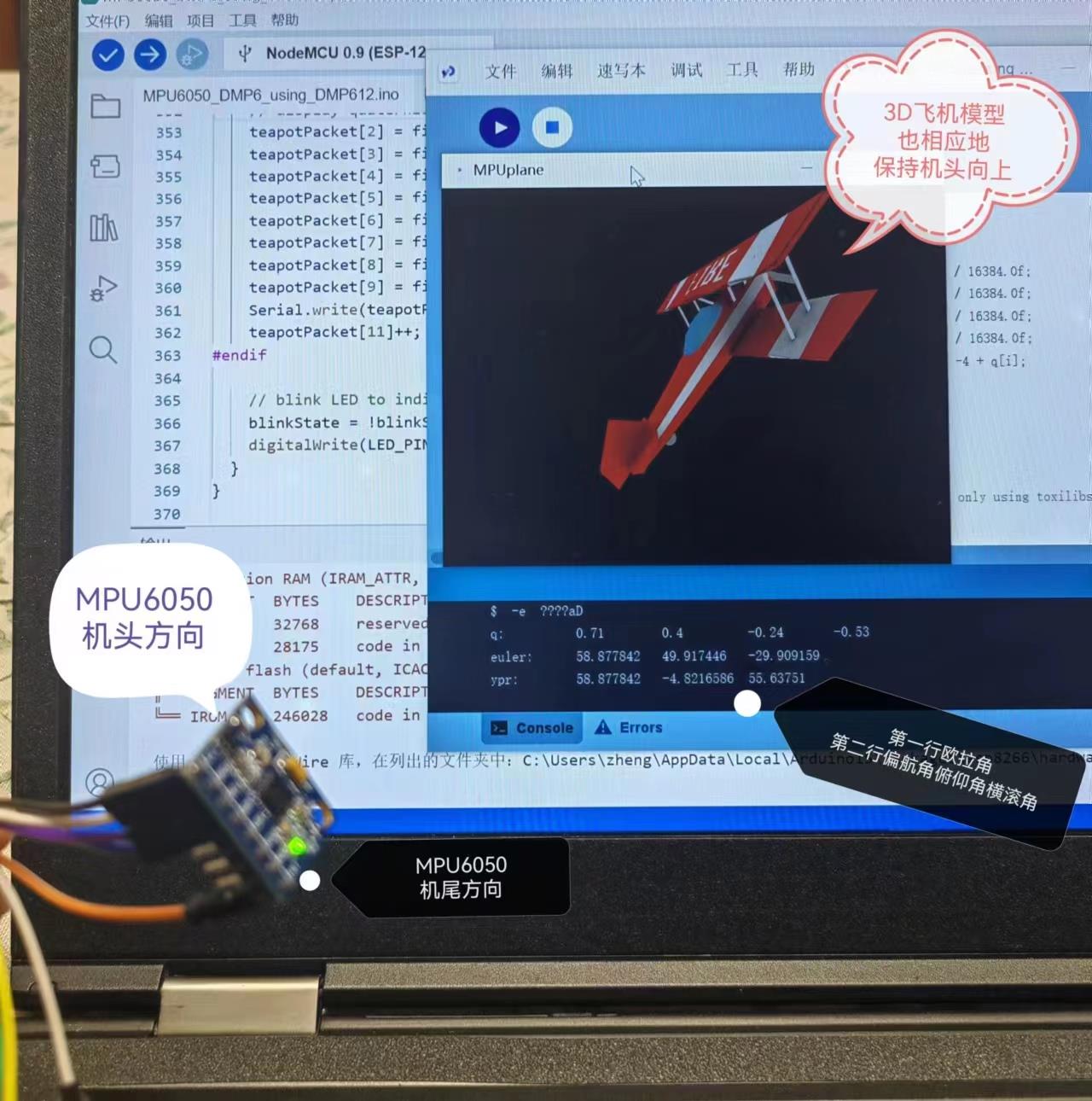
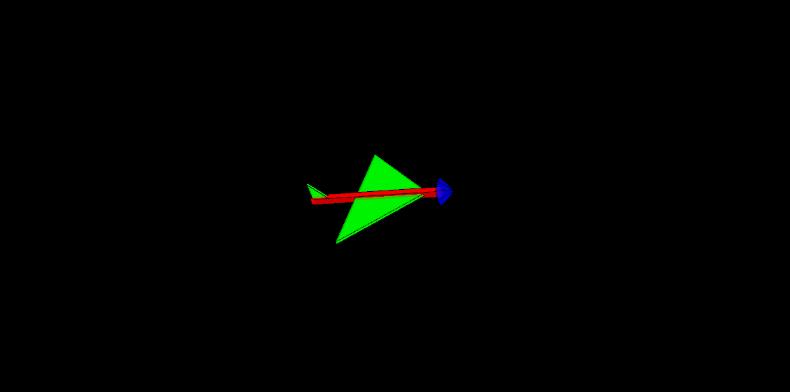
4. 运行processing上位机
上位机为lib\\MPU6050\\examples\\MPU6050_DMP6\\Processing\\MPUTeapot\\MPUTeapot.pde,使用processing打开。
修改连接ESP32的串口:

以上是关于MPU6050陀螺仪与Processing和上位机飞控联动实录的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章