static_cast
Posted errorman
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了static_cast相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
static_cast 用于正常/普通类型转换。 这也是负责隐式类型强制的转换,也可以显式调用。 您应该在将 float 转换为 int、将 char 转换为 int 等情况下使用它。这可以转换相关的类型类。这是一个编译期间的转换操作。会进行类型检查。
1.隐式转换案例
int main()
float f = 3.5;
int a = f;
std::cout << "The Value of a: " << a <<std::endl; // a:3
int b = static_cast<int>(f);
std::cout << "\\nThe Value of b: " << b <<std::endl; // b: 3
return 0;
int main()
int a = 10;
char c = \'a\';
int* q = (int*)&c; //ok
int* p = static_cast<int*>(c); //非法
修改一下
int main()
int a = 10;
char c = \'a\';
int* q = (int*)&c;
void* m = static_cast<void*>(&c); //ok
int* p = static_cast<int*>(m); //ok
return 0;
2.使用用户定义的转换符转换对象
如果重载了运算符,那么static_cast可以调用。
// new class
class integer
int x;
public:
integer(int x_in = 0)
: x x_in
cout << "Constructor Called" << endl;
// 用户定义的转换运算符到字符串类型
operator string()
cout << "Conversion Operator Called" << endl;
return to_string(x);
;
int main()
integer obj(3); //调用构造函数:Constructor Called
string str = obj; //因为重载了运算法,所以编译器不会报错,string(obj):Conversion Operator Called
obj = 20; //调用构造函数:Constructor Called
string str2 = static_cast<string>(obj); //同上:Conversion Operator Called
obj = static_cast<integer>(30); //调用构造函数:Constructor Called
return 0;
3.用于继承
在继承的情况下,static_cast 可以提供向上转型和向下转型。
class Base ;
class Derived : public Base ;
int main()
Derived d1;
// 允许隐式转换
Base* b1 = (Base*)(&d1); //OK
// 使用static_cast向上转换
Base* b2 = static_cast<Base*>(&d1); //OK
return 0;
如果我们将public继承变为privat继承,会发生什么?
class Base ;
class Derived : private Base ;
int main()
Derived d1;
// 允许隐式转换
Base* b1 = (Base*)(&d1); //OK
Base* b2 = static_cast<Base*>(&d1); //error:\'Base\' is an inaccessible base of \'Derived\'
return 0;
即使使用protect继承也不可以。
因此,要在继承的情况下使用static_cast,基类必须是可访问的、non virtual 的和 unambiguous的。
class Base1
virtual void f1()
;
class Base2
virtual void f2()
;
class Derived: public Base1, public Base2
void f1()
void f2()
;
Base1 *pD = new Derived;
Derived *pD1 = dynamic_cast<Derived*>(pD); //OK
Derived *pD2 = static_cast<Derived*>(pD); //OK
Base2 *pB1 = dynamic_cast<Base2*>(pD); //OK,运行时会检查,pD实际指向Derived对象,可以转换为Base2
Base2 *pB2 = static_cast<Base2*>(pD); //error:Base1和Base2没有关系向下转换建议使用dynamic_cast,因为它会在运行时进行类型检查,更安全。
4.转换为void*指针
int main()
int i = 10;
void* v = static_cast<void*>(&i);
int* ip = static_cast<int*>(v);
cout << *ip; // 输出:10
return 0;
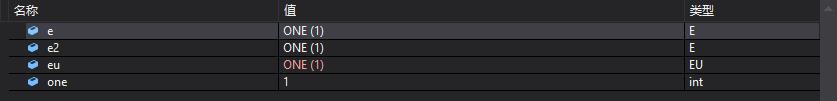
5.枚举和int互相转换,枚举到另一枚举
enum class E ONE = 1, TWO, THREE ;
enum EU ONE = 1, TWO, THREE ;
int main()
// 有作用域枚举到 int 或 float
E e = E::ONE; //0K
int one = static_cast<int>(e); //OK
// int 到枚举,枚举到另一枚举
E e2 = static_cast<E>(one); //OK
EU eu = static_cast<EU>(e2); //OK
本文来自博客园,原创作者:Clemens,转载请注明原文链接:https://www.cnblogs.com/errorman/p/17266658.html
以上是关于static_cast的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章