logback的使用和原理
Posted 永恒&
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了logback的使用和原理相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
logback的使用和原理
1 依赖关系
在pom文件中引入springboot starter依赖,自动引入了这三个依赖,而这三个依赖,就是logback日志框架进行日志操作的。
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter</artifactId>
</dependency>
</dependencies>

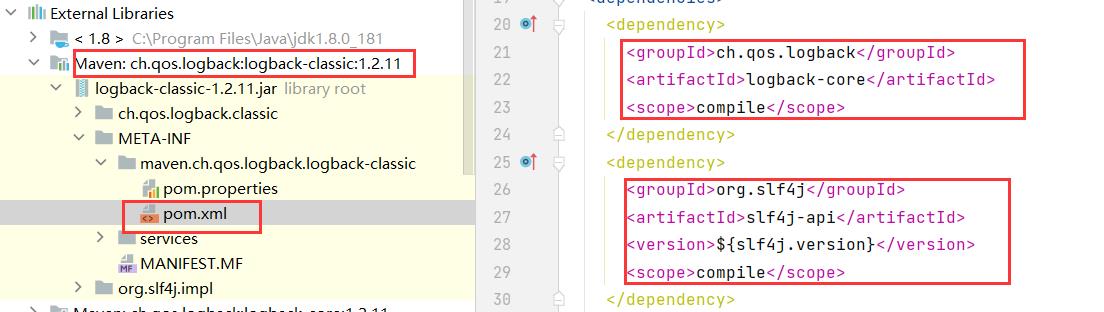
可以看到,logback-classic依赖于logback-core和slf4j-api。
2 执行流程
当我们在一个类中,使用 LoggerFactory.getLogger(xxx.class) 获取一个类的 Logger 对象时,发生了什么事,是在什么时候加载的logback.xml文件中的配置的,这是本文要解决的问题。
package org.example;
import org.slf4j.Logger;
import org.slf4j.LoggerFactory;
import java.util.Date;
import java.util.UUID;
public class LogPathOnLinuxApp
private static final Logger logger = LoggerFactory.getLogger(LogPathOnLinuxApp.class);
public static void main(String[] args)
logger.info(new Date().toString() + "生成了 UUID: " + UUID.randomUUID());
单独的 T 代表一个类型 ,而 Class<T>代表这个类型所对应的类, Class<?>表示类型不确定的类,Class<?extends A>表示类型不确定的类是A的子类
常见的调用方式,使用 LoggerFactory.getLogger(LogPathOnLinuxApp.class) 获取 Logger 对象,然后使用 logger.info() 使用日志框架,输出日志信息。
首先,从 LoggerFactory.getLogger入手,他位于 org.slf4j 包中
LoggerFactory 类中,
// 1.1 使用时传入的class对象,调用的是这个方法
public static Logger getLogger(Class<?> clazz)
// 1.2 调用上面的方法,传入一个String类型的class的名字,返回一个Logger对象,这个就是最终返回的Logger对象,ctrl+鼠标左键,点进去
Logger logger = getLogger(clazz.getName());
if (DETECT_LOGGER_NAME_MISMATCH)
Class<?> autoComputedCallingClass = Util.getCallingClass();
if (autoComputedCallingClass != null && nonMatchingClasses(clazz, autoComputedCallingClass))
Util.report(String.format("Detected logger name mismatch. Given name: \\"%s\\"; computed name: \\"%s\\".", logger.getName(), autoComputedCallingClass.getName()));
Util.report("See http://www.slf4j.org/codes.html#loggerNameMismatch for an explanation");
// 最终返回给调用者的logger
return logger;
// 1.2
public static Logger getLogger(String name)
// 1.3 调用getILoggerFactory方法,返回一个ILoggerFactory对象,点进去
ILoggerFactory iLoggerFactory = getILoggerFactory();
// 最终返回iLoggerFactory.getLogger(name)的Logger对象
return iLoggerFactory.getLogger(name);
// 这是类中的静态变量,在类加载的时候初始化
static final int UNINITIALIZED = 0; // 未初始化
static final int ONGOING_INITIALIZATION = 1; // 正在初始化
static final int FAILED_INITIALIZATION = 2; // 初始化失败
static final int SUCCESSFUL_INITIALIZATION = 3; // 初始化成功
static final int NOP_FALLBACK_INITIALIZATION = 4; // 无回退初始化
static volatile int INITIALIZATION_STATE = 0; // 初始化状态
// 1.3
public static ILoggerFactory getILoggerFactory()
// 如果未初始化,就进行初始化操作
if (INITIALIZATION_STATE == 0)
Class var0 = LoggerFactory.class;
// 对LoggerFactory类加锁
synchronized(LoggerFactory.class)
// 如果未初始化,将状态设置为正在初始化,执行performInitialization()
if (INITIALIZATION_STATE == 0)
INITIALIZATION_STATE = 1;
// 执行初始化
performInitialization();
// 判断初始化状态
switch (INITIALIZATION_STATE)
case 1:
return SUBST_FACTORY;
case 2:
throw new IllegalStateException("org.slf4j.LoggerFactory in failed state. Original exception was thrown EARLIER. See also http://www.slf4j.org/codes.html#unsuccessfulInit");
// 如果初始化成功,返回 StaticLoggerBinder.getSingleton().getLoggerFactory();
case 3:
// 1.4 看这个方法 getLoggerFactory
return StaticLoggerBinder.getSingleton().getLoggerFactory();
case 4:
return NOP_FALLBACK_FACTORY;
default:
throw new IllegalStateException("Unreachable code");
StaticLoggerBinder 类中,
private static StaticLoggerBinder SINGLETON = new StaticLoggerBinder();
private LoggerContext defaultLoggerContext = new LoggerContext();
static
SINGLETON.init();
void init()
try
try
// 自动配置,autoConfig 点进去
(new ContextInitializer(this.defaultLoggerContext)).autoConfig();
catch (JoranException var2)
Util.report("Failed to auto configure default logger context", var2);
if (!StatusUtil.contextHasStatusListener(this.defaultLoggerContext))
StatusPrinter.printInCaseOfErrorsOrWarnings(this.defaultLoggerContext);
this.contextSelectorBinder.init(this.defaultLoggerContext, KEY);
this.initialized = true;
catch (Exception var3)
Util.report("Failed to instantiate [" + LoggerContext.class.getName() + "]", var3);
ContextInitializer 类中,
// 此处的静态常量,表示的是logback的配置文件名
public static final String AUTOCONFIG_FILE = "logback.xml";
public static final String TEST_AUTOCONFIG_FILE = "logback-test.xml";
public static final String CONFIG_FILE_PROPERTY = "logback.configurationFile";
final LoggerContext loggerContext;
//
public void autoConfig() throws JoranException
StatusListenerConfigHelper.installIfAsked(this.loggerContext);
// 没有任何配置文件时url为null
URL url = this.findURLOfDefaultConfigurationFile(true);
if (url != null)
// 读取自定义的配置文件,logback.xml文件配置生效
this.configureByResource(url);
else
Configurator c = (Configurator)EnvUtil.loadFromServiceLoader(Configurator.class);
if (c != null)
try
c.setContext(this.loggerContext);
c.configure(this.loggerContext);
catch (Exception var4)
throw new LogbackException(String.format("Failed to initialize Configurator: %s using ServiceLoader", c != null ? c.getClass().getCanonicalName() : "null"), var4);
else
// 这一段代码保证了,没有任何配置文件时,也可以进行基础的自动配置,进行日志输出
BasicConfigurator basicConfigurator = new BasicConfigurator();
basicConfigurator.setContext(this.loggerContext);
basicConfigurator.configure(this.loggerContext);
3 日志滚动配置
需要注意在linux下执行的路径问题
<configuration>
<!-- 加入监听器,可以在监听器中设置 $LOG_PATH和$PROJECT_NAME 的值,从而实现指定日志输出路径的效果 -->
<!-- 也可以使用 $user.dir:-./logs/xxxx.log, user.dir 表示执行运行jar包命令时所在的路径 -->
<contextListener class="org.example.com.smy.CustomLogContextListener" />
<appender name="dailyRollingFileAppender" class="ch.qos.logback.core.rolling.RollingFileAppender">
<File>$LOG_PATH/$PROJECT_NAME/logs/LogsPathTest.log</File>
<rollingPolicy class="ch.qos.logback.core.rolling.SizeAndTimeBasedRollingPolicy">
<!--日志文件输出的文件名,.gz 表示开启文件压缩-->
<FileNamePattern>$LOG_PATH/$PROJECT_NAME/logs/LogsPathTest.%dyyyy-MM-dd.%i.log.gz</FileNamePattern>
<!--日志文件保留天数-->
<MaxHistory>15</MaxHistory>
<!--日志文件最大的大小-->
<MaxFileSize>2MB</MaxFileSize>
</rollingPolicy>
<encoder>
<Pattern>%dateyyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss\\t%level\\t%logger96\\t%msg%n</Pattern>
</encoder>
<filter class="ch.qos.logback.classic.filter.ThresholdFilter">
<level>INFO</level>
</filter>
</appender>
<!-- Console output -->
<appender name="STDOUT" class="ch.qos.logback.core.ConsoleAppender">
<!-- encoder defaults to ch.qos.logback.classic.encoder.PatternLayoutEncoder -->
<encoder>
<Pattern>%dateyyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss\\t%level\\t%logger96\\t%msg%n</Pattern>
</encoder>
<filter class="ch.qos.logback.classic.filter.ThresholdFilter">
<level>INFO</level>
</filter>
</appender>
<root level="INFO">
<appender-ref ref="dailyRollingFileAppender"/>
<appender-ref ref="STDOUT"/>
</root>
</configuration>
本文来自博客园,作者:永恒&,转载请注明原文链接:https://www.cnblogs.com/Sun-yuan/p/17258439.html
以上是关于logback的使用和原理的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章