Python初识-day1
Posted
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了Python初识-day1相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
1.第一个python程序(在pycharm中运行的,感觉还不错)

注释:
当行注释:#被注释内容
多行注释:‘‘‘ 被注释内容 ‘‘‘
2.变量
(1) 自己理解的定义(仅供参考): 为了存储数据以便反复调用的自定义合法标识符(存于内存中)。
比如:name = “congcong” #name即为一个变量。
(2) 变量定义的规则:
<1>变量名只能是字母、数字、或下划线的任意组合。
<2>变量名的第一个字符不能是数字。
<3>关键字不能声明为变量名。
包括[‘and’,‘as‘,‘assert‘(宣称),‘break‘,‘class‘,‘continue‘,‘def‘,‘if‘,‘elif‘,‘else‘,‘for‘,‘except‘,‘finaly‘,
‘exec‘(执行程序),‘form‘,‘global‘,‘import‘,‘in‘,‘is‘,‘lambda‘(匿名程序),‘not‘,‘or‘,‘pass‘,‘print‘,‘raise‘(增加),
‘return‘,‘try‘,‘while‘,‘with‘,‘yield‘(收率)]。
3.常量的表示
字母必须大写,且不能修改,否则会出错。
例如: PHR = 3
4.字符编码
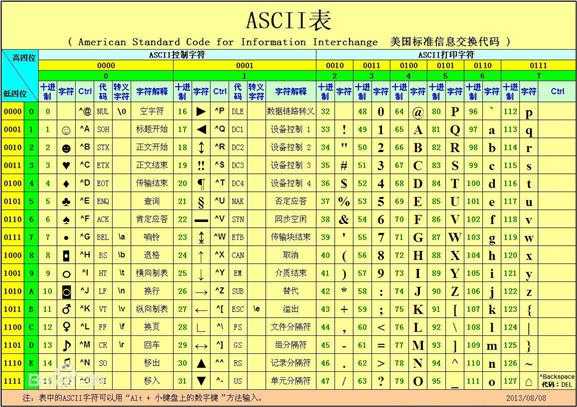
(1) python解释器在加载 .py文件中的代码时,会对内容进行编码(默认是ASCII码)
(2) ASCII码(美国标准信息交换代码)是基于拉丁字母的一套电脑编码系统,主要用于显示现代英语和其他西欧语言,
其最多只能用8位来表示(即一个字节,2**8=256),所以,ASCII码最多只能表示255个字符。如下图(素材来源于网上):
(3)字符编码发展史:
ASCII码 ——1980年,GB2312,支持7千多汉字——1995年,GBK1.0,支持2万多汉字——2000年,GB18030,支持2万7千多汉字
—— Unicode,统一为2bytes(字节),由于有争议,接着另开发了utf-8——utf-8,支持中英文,英文1个字母为1byte,而中文一个汉字为3bytes。
5.用户交互程序(如无特殊说明,以下python代码均是在pycharm中运行过的,可用的)
1 #congcong for huangYuTing
2 import getpass #导入getpass模块,将密码设为不可见
3 _usename = ‘congcong‘ #预存用户名
4 _password = ‘huangyuting‘ #预存用户名密码
5 usename = input("usename:") #用户输入用户名
6 password = input("password:") #用户输入密码
7 if _usename == usename and _password == password: #表判断,两个条件均成立时继续
8 print(‘Welcome user {name} login...‘.format(name = usename)) #.format()获取用户名
9 else:
10 print(‘Invalid usename or password‘)
6.if...else判断结构(含while)

1 #congcong for huangYuTing 2 age_of_erha = 21 3 4 count = 0 5 while count < 3: 6 guess_age = int(input(‘Guess age:‘)) 7 if guess_age == age_of_erha: 8 print(‘You are right!‘) 9 break 10 elif guess_age > age_of_erha: 11 print(‘Think smaller.‘) 12 else : 13 print(‘Think bigger...‘) 14 count += 1 15 if count == 3: 16 print(‘Do you want to continue....‘) 17 Is_continue = input(‘continue:‘) 18 if Is_continue != ‘n‘: 19 count = 0 20 #else:
7.while and for 循环
1 #congcong for huangYuTing 2 ‘‘‘ 3 for i in range(0,15,2):#从 0 开始,15结束,每次相差 2 4 print(‘number‘,i) 5 ‘‘‘ 6 7 ‘‘‘ 8 age_of_erha = 21 9 for i in range(4): 10 guess_age = int(input(‘Guess age:‘)) 11 if guess_age == age_of_erha: 12 print(‘You are right!‘) 13 break 14 elif guess_age > age_of_erha: 15 print(‘Think smaller.‘) 16 else : 17 print(‘Think bigger...‘) 18 else: 19 print(‘You have tried too many times....‘) 20 ‘‘‘ 21 22 # continue的使用 23 ‘‘‘ 24 for i in range(0,20,2): 25 if(i > 7): 26 print(‘congcong‘,i) 27 else: 28 continue #跳出本次循环,继续下次循环,而break是结束循环 29 print(‘Hello‘) 30 ‘‘‘ 31 #多重for循环 32 for i in range(0,8,1):#小于8,不包含8 33 print(‘hello...........‘,i) 34 for n in range(0,6,1): 35 print(‘world‘,n) 36 if n > 3: 37 break #结束最近的循环 38 #多重循环打印结果如下:

1 hello........... 0 2 world 0 3 world 1 4 world 2 5 world 3 6 world 4 7 hello........... 1 8 world 0 9 world 1 10 world 2 11 world 3 12 world 4 13 hello........... 2 14 world 0 15 world 1 16 world 2 17 world 3 18 world 4 19 hello........... 3 20 world 0 21 world 1 22 world 2 23 world 3 24 world 4 25 hello........... 4 26 world 0 27 world 1 28 world 2 29 world 3 30 world 4 31 hello........... 5 32 world 0 33 world 1 34 world 2 35 world 3 36 world 4 37 hello........... 6 38 world 0 39 world 1 40 world 2 41 world 3 42 world 4 43 hello........... 7 44 world 0 45 world 1 46 world 2 47 world 3 48 world 4
以上是关于Python初识-day1的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章
