Linux06
Posted MyXjl
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了Linux06相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
Linux系统编程
文件
| 重要 | 难度 | |
|---|---|---|
| 目录流 | 3 | 4 |
| 无缓冲IO | 5 | 2 |
| IO多路复用 | 5 | 5 |
IO多路复用可用于制作即时聊天系统
进程
| 重要 | 难度 | |
|---|---|---|
| 虚拟 | 4 | 3 |
| CPU 进程调度 | 4 | 3 |
| 内存 虚拟内存 | 4 | 3 |
| 多进程 | 3 | 3 |
线程
| 重要 | 难度 | |
|---|---|---|
| 多线程 | 5 | 2 |
| 互斥 | 5 | 3 |
| 同步cond | 6 | 4 |
网络
| 重要 | 难度 | |
|---|---|---|
| 协议 | 4.5 | 3 |
| 编程 | 5 | 2 |
| IO多路复用 epoll | 5 | 5 |
服务器框架
| 重要 | 难度 | |
|---|---|---|
| 进程池 | 3 | 6 |
| 线程池 | 5 | 3 |
数据库
| 重要 | 难度 | |
|---|---|---|
| MySql | 2 | 3 |
Linux架构图
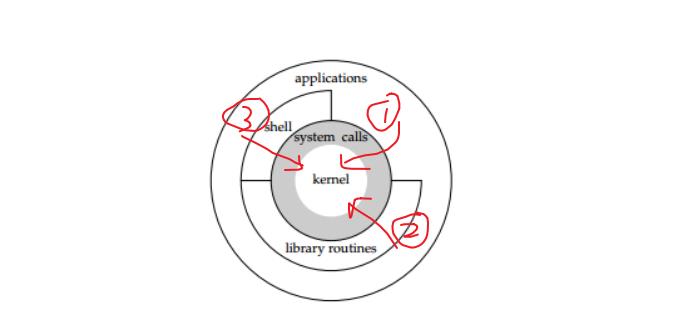
man手册
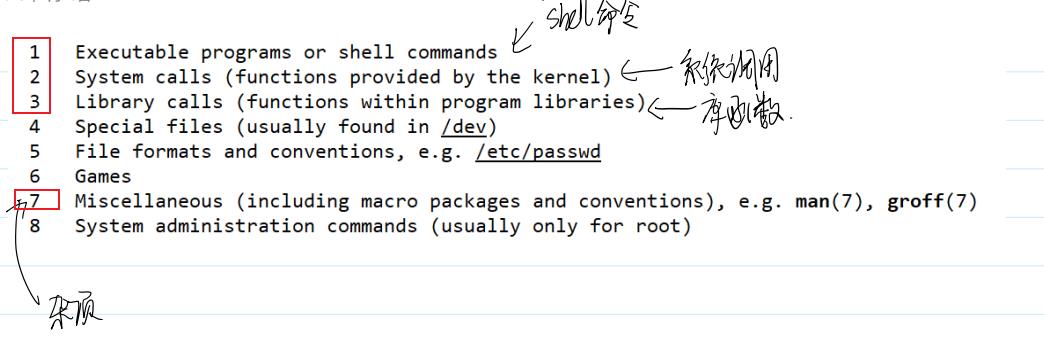
阅读手册的方法

在系统目录下的include文件夹中添加头文件简化代码
// 路径
/usr/include
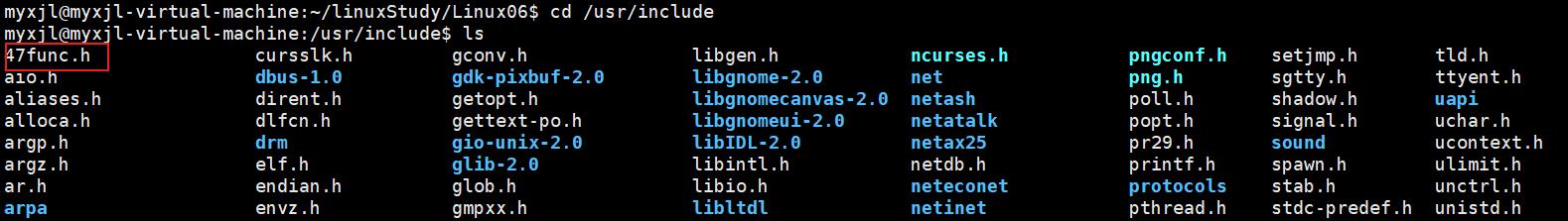
进入路径后,用touch命令新建文件,随后修改权限(修改为其他用户可写状态):
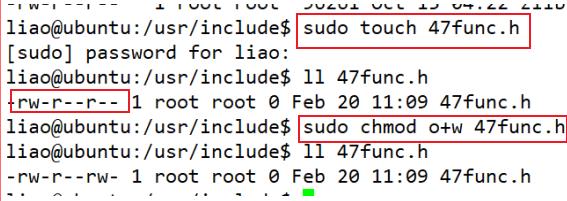
编写头文件(后续需要可继续往其中加代码):
// 47func.h
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <sys/stat.h>
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <unistd.h>
// 用于判断参数的个数是否准确
#define ARGS_CHECK(argc,num) if(argc != num)fprintf(stderr,"args error!\\n");return -1;
// 用于报错 ret是函数返回值
#define ERROR_CHECK(ret,num,msg) if(ret == num)perror(msg);return -1;
chmod函数
// 函数作用
change permissions of a file.
// 头文件
#include<sys/stat.h>
// 函数原型
int chmod(const char* pathname,mode_t mode);
// 返回值
On success, zero is returned. On error, -1 is returned, and errno is set appropriately.
#include <47func.h>
int main(int argc, char *argv[])
// ./chmod 777 file1
ARGS_CHECK(argc,3);
mode_t mode; // 实际是一个无符号整数
sscanf(argv[1],"%o",&mode); // 将第一个参数以八进制的形式写入mode
int ret = chmod(argv[2],mode);
ERROR_CHECK(ret,-1,"chmod");
return 0;
getcwd函数
// 函数作用
get current working directory.
// 头文件
#include <unistd.h>
// 函数原型
char *getcwd(char *buf, size_t size); // 无const,传入传出参数
// 返回值
On success, these functions return a pointer to a string containing the pathname of the current working directory.
On failure, these functions return NULL, and errno is set to indicate the error.
使用如下所示:
#include <47func.h>
int main(void)
// 方法一:在主调函数的栈帧中开辟一片内存空间,传入这片空间的指针buf,调用函数后,返回值实际上会指向buf这片内存区域
// 这样会将工作目录的绝对路径复制到buf所指向的空间中
char buf[1024]; // 比较浪费内存
char *p = getcwd(buf,sizeof(buf));
ERROR_CHECK(p,NULL,"getcwd"); // 当如果路径长度大于size,则会返回NULL
printf("p = %s , buf = %s.\\n",p,buf);
return 0;

#include <47func.h>
int main(void)
//方法二:函数在堆中动态分配一块内存存放路径,注意这样使用必须释放这片空间
char* p = getcwd(NULL,0);
// p指向堆空间
printf("p = %s.\\n",p);
free(p);
return 0;
chdir函数
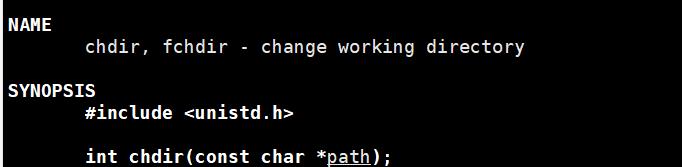


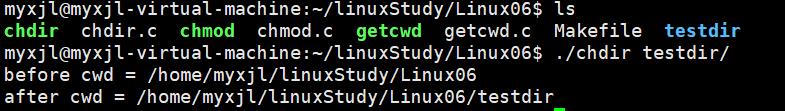
使用示例:
#include <47func.h>
int main(int argc,char*argv[])
// ./chdir dir1
ARGS_CHECK(argc,2);
printf("before cwd = %s\\n", getcwd(NULL,0));
int ret = chdir(argv[1]);
ERROR_CHECK(ret,-1,"chdir");
printf("after cwd = %s\\n", getcwd(NULL,0));
return 0;
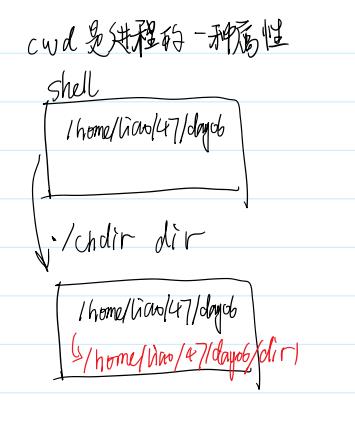
cwd(current working directory)是进程的一种属性
运行chdir这个可执行程序另起了一个进程,只是修改了在那个进程里的目录,并没有修改shell进程里的目录。
mkdir和rmdir函数
mkdir函数


新建的文件,其权限都会受到 umask 影响
#include<47func.h>
int main(int argc,char* argv[])
// ./mkdir filename
ARGS_CHECK(argc,2);
int ret = mkdir(argv[1],0777); // 新建的目录都会受掩码影响
ERROR_CHECK(ret,-1,"mkdir");
return 0;
rmdir函数
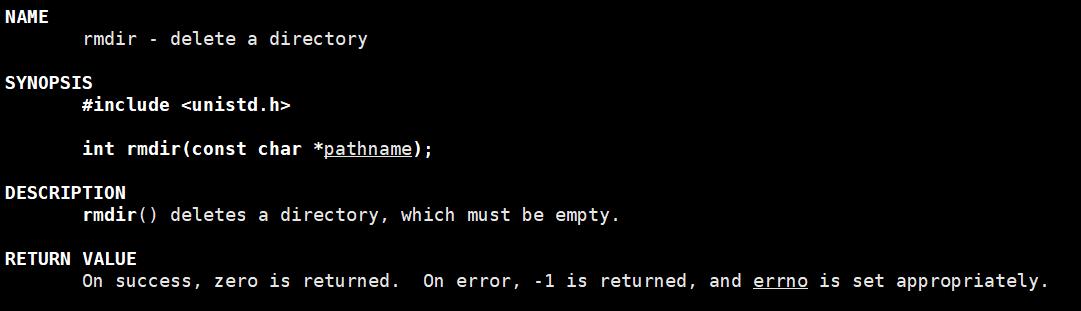
#include <47func.h>
int main(int argc,char* argv[])
// ./rmdir.c filename
ARGS_CHECK(argc,2);
int ret = rmdir(argv[1]);
ERROR_CHECK(ret,-1,"rmdir");
return 0;
目录流
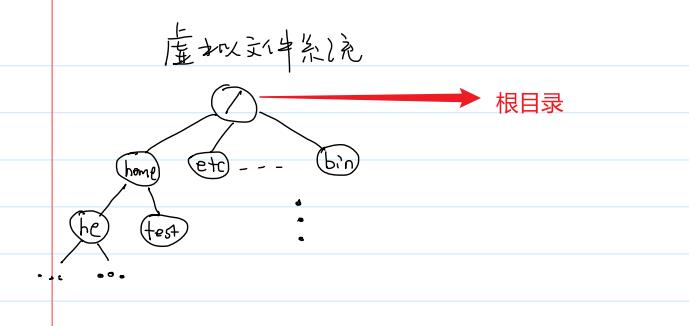
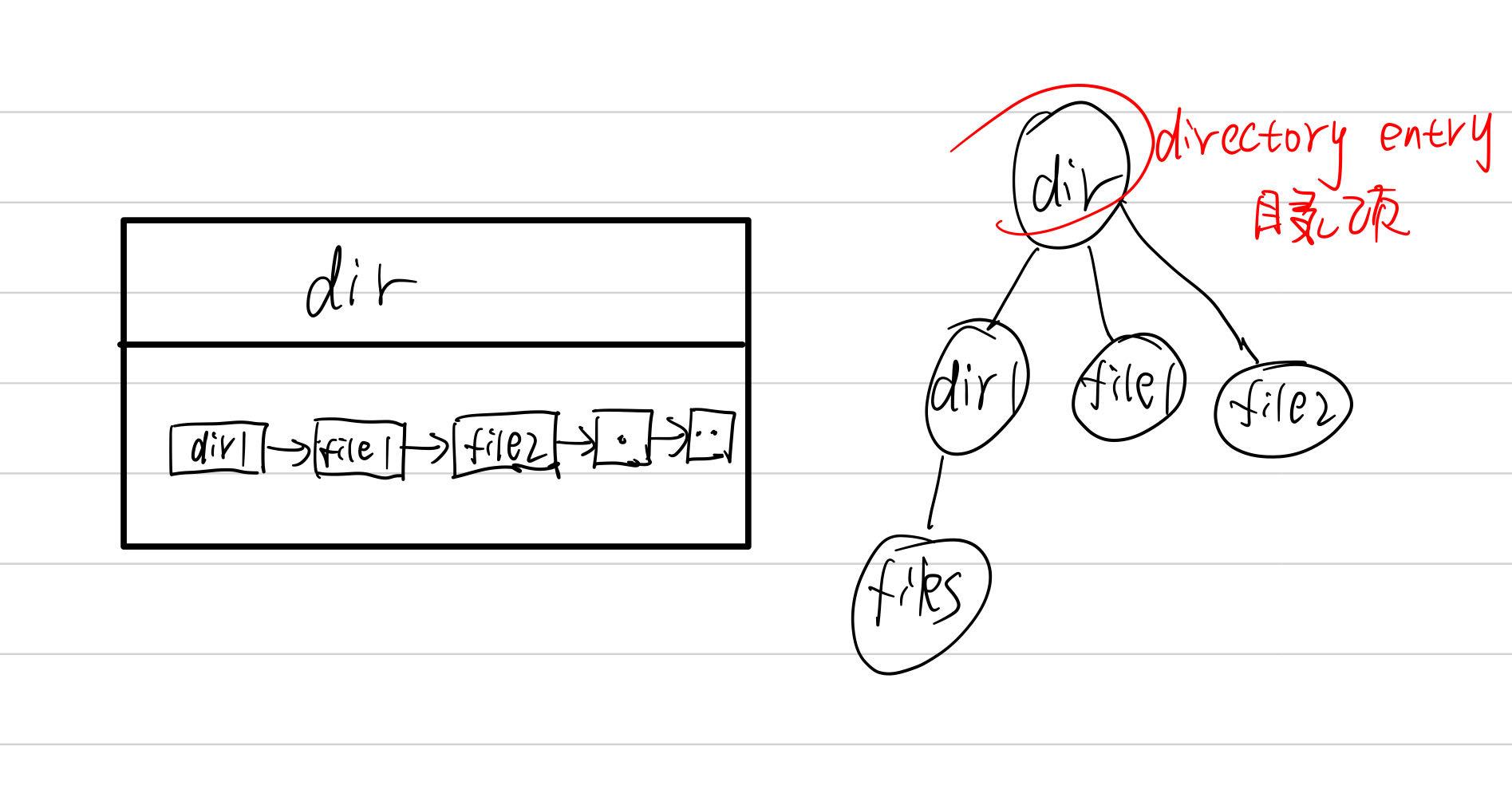
opendir函数和closedir函数
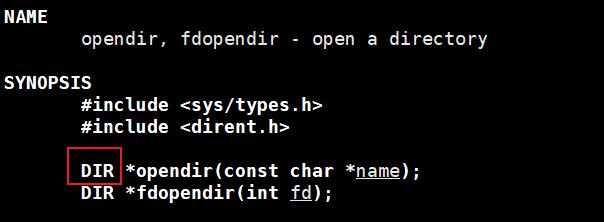
dirent:directory entry(目录项)
opendir函数:打开与目录名对应的目录流,并返回指向目录流的指针。指向位于目录流中的第一个目录项。
成功返回一个指针指向该目录流,失败返回空指针
DIR *opendir(const char *name); // DIR是目录流
int closedir(DIR *dirp);
readdir函数
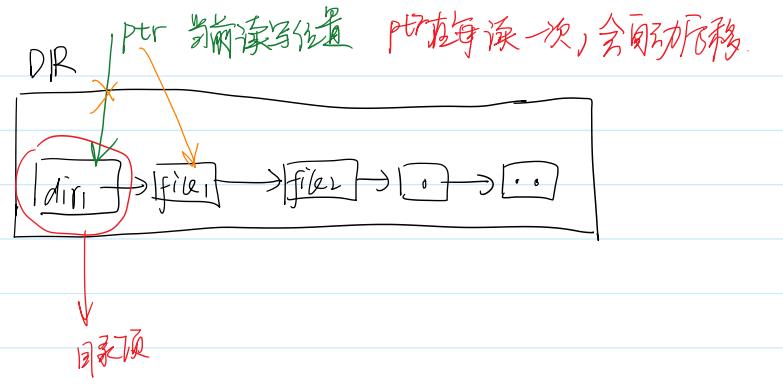
// 头文件
#include <dirent.h>
// 函数原型
struct dirent *readdir(DIR *dirp); // dirent是目录项
// 目录项结构体
// 目录项的长度与文件名有关
struct dirent
ino_t d_ino; // 磁盘地址
off_t d_off; // next指针
unsigned short d_reclen; // 单个dirent的长度
unsigned char d_type; // 文件类型
char d_name[256]; // 文件名
;
seekdir函数、telldir函数和telldir函数
void seekdir(DIR *dirp, long loc); // 回到某个位置,void说明此函数基本不会出错
long telldir(DIR *dirp); // 获取位置
void rewinddir(DIR *dirp); // 回到目录流的起点
stat函数
根据文件的路径获取详细信息
// 头文件
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <sys/stat.h>
#include <unistd.h>
// 函数原型
int stat(const char *pathname, struct stat *buf);
struct stat
dev_t st_dev; /* ID of device containing file */
ino_t st_ino; /* inode number 磁盘地址*/
mode_t st_mode; /* protection */
nlink_t st_nlink; /* number of hard links 硬链接数目*/
uid_t st_uid; /* user ID of owner */
gid_t st_gid; /* group ID of owner */
dev_t st_rdev; /* device ID (if special file) */
off_t st_size; /* total size, in bytes */
blksize_t st_blksize; /* blocksize for filesystem I/O */
blkcnt_t st_blocks; /* number of 512B blocks allocated */
/* Since Linux 2.6, the kernel supports nanosecond
precision for the following timestamp fields.
For the details before Linux 2.6, see NOTES. */
struct timespec st_atim; /* time of last access */
struct timespec st_mtim; /* time of last modification */
struct timespec st_ctim; /* time of last status change */
#define st_atime st_atim.tv_sec /* Backward compatibility */
#define st_mtime st_mtim.tv_sec
#define st_ctime st_ctim.tv_sec
;
//st_mtime是整数 ----->从1970年1月1日到现在多少秒
使用(实现ls -al命令):
#include<47func.h>
int main(int argc,char* argv[])
ARGS_CHECK(argc,2);
DIR* dirp = opendir(argv[1]);
ERROR_CHECK(dirp,NULL,"opendir");
struct dirent* direntp;
char path[1024];
const char * month[] = "Jan", "Feb", "Mar", "Apr", "May", "Jun", "Jul", "Aug", "Sep", "Oct","Nov","Dec";
while((direntp = readdir(dirp)) != NULL)
struct stat buf;
sprintf(path,"%s%s%s",argv[1],"/",direntp->d_name);
// 文件名不一定总是文件路径,只有在当前目录下才是
// int ret = stat(direntp->d_name,&buf);
int ret = stat(path,&buf); // 若出现dir//file的情况Linux会当做一个/
ERROR_CHECK(ret,-1,"stat");
//文件类型
if(S_ISLNK(buf.st_mode)) //符号链接
printf("l");
else if(S_ISREG(buf.st_mode)) //一般文件
printf("-");
else if(S_ISDIR(buf.st_mode)) //目录文件
printf("d");
else if(S_ISCHR(buf.st_mode)) //字符设备文件
printf("c");
else if(S_ISBLK(buf.st_mode)) //块设备文件
printf("b");
else if(S_ISFIFO(buf.st_mode)) //先进先出文件
printf("f");
else if(S_ISSOCK(buf.st_mode)) //socket文件
printf("s");
// 用户权限
if(buf.st_mode & S_IRUSR)
printf("r");
else
printf("-");
if(buf.st_mode & S_IWUSR)
printf("w");
else
printf("-");
if(buf.st_mode & S_IXUSR)
printf("x");
else
printf("-");
// 组权限
if(buf.st_mode & S_IRGRP)
printf("r");
else
printf("-");
if(buf.st_mode & S_IWGRP)
printf("w");
else
printf("-");
if(buf.st_mode & S_IXGRP)
printf("x");
else
printf("-");
// 其他用户权限
if(buf.st_mode & S_IROTH)
printf("r");
else
printf("-");
if(buf.st_mode & S_IWOTH)
printf("w");
else
printf("-");
if(buf.st_mode & S_IXOTH)
printf("x");
else
printf("-");
struct tm* ptm = localtime(&buf.st_mtime);
printf(" %ld %s %s %-6ld %s %02d %02d:%02d %s\\n",
buf.st_nlink,
getpwuid(buf.st_uid)->pw_name,
getgrgid(buf.st_gid)->gr_name,
buf.st_size,
month[ptm->tm_mon],ptm->tm_mday,ptm->tm_hour,ptm->tm_min,
direntp->d_name);
closedir(dirp);
return 0;
其他
sscanf函数
描述
C 库函数 int sscanf(const char *str, const char *format, ...) 从字符串读取格式化输入。
声明
下面是 sscanf() 函数的声明。
int sscanf(const char *str, const char *format, ...)
参数
- str -- 这是 C 字符串,是函数检索数据的源。
- format -- 这是 C 字符串,包含了以下各项中的一个或多个:空格字符、非空格字符 和 format 说明符。
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <string.h>
int main()
int day, year;
char weekday[20], month[20], dtm[100];
strcpy( dtm, "Saturday March 25 1989" );
sscanf( dtm, "%s %s %d %d", weekday, month, &day, &year );
printf("%s %d, %d = %s\\n", month, day, year, weekday );
return(0);
// 结果
March 25, 1989 = Saturday
sprintf函数
描述
C 库函数 int sprintf(char *str, const char *format, ...) 发送格式化输出到 str 所指向的字符串。
声明
下面是 sprintf() 函数的声明。
int sprintf(char *str, const char *format, ...)
参数
- str -- 这是指向一个字符数组的指针,该数组存储了 C 字符串。
- format -- 这是字符串,包含了要被写入到字符串 str 的文本。它可以包含嵌入的 format 标签,format 标签可被随后的附加参数中指定的值替换,并按需求进行格式化。
返回值
如果成功,则返回写入的字符总数,不包括字符串追加在字符串末尾的空字符。如果失败,则返回一个负数。
#include <stdio.h>
#include <math.h>
int main()
char str[80];
sprintf(str, "Pi 的值 = %f", M_PI);
puts(str);
return(0);
// 结果
Pi 的值 = 3.141593
一些概念
命令行参数
例:
./a.out aaa bbb ccc // argc = 4
// argv[0] = a.out argv[1] = aaa
#include <47func.h>
int main(int argc, char *argv[])
// ./chmod 777 file1
ARGS_CHECK(argc,3);
for(int i = 0;i < argc;i++)
printf("argv[%d] = %s\\n",i,argv[i]);
mode_t mode;
sscanf(argv[1],"%o",&mode);
int ret = chmod(argv[2],mode);
ERROR_CHECK(ret,-1,"chmod");
return 0;
路径
- 以 / 开头:绝对路径
- 不以 / 开头:相对路径,以当前工作目录为起点
以上是关于Linux06的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章