Python-WXPY实现微信监控报警
Posted
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了Python-WXPY实现微信监控报警相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
概述:
本文主要分享一下博主在学习wxpy 的过程中开发的一个小程序。博主在最近有一个监控报警的需求需要完成,然后刚好在学习wxpy 这个东西,因此很巧妙的将工作和学习联系在一起。
博文中主要使用到的技术设计到Python,Redis,以及Java。涉及到的技术看似很多,但是主要的语言是基于Python进行开发的。
架构涉及主要采用了 生产者消费者的涉及模式,使用Redis作为消息队列进行解耦操作。
主要架构涉及如下:
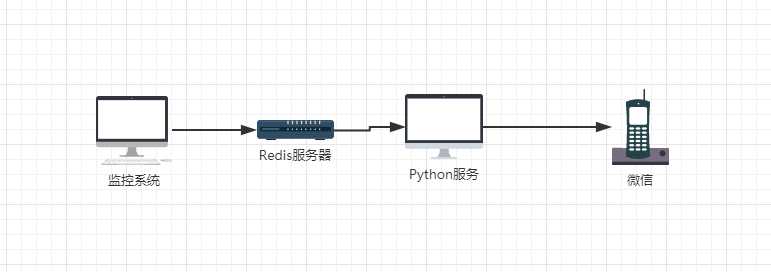
接下来开始介绍一下程序的实现过程,主要讲解wxpy -> python.redis -> Java.redis
1、Wxpy初体验
项目使用的python 是3.5版本的,因此语法会和2.x版本有所区别,wxpy 支持python3.4-3.6 以及python2.7版本 ,因此在python版本上不用太过于纠结
1.1 安装wxpy
在这里默认大家以及安装好了pip,我们需要安装wxpy 以及wechat_sender 两个包,这里推荐使用国内的豆瓣源,如果大家网速过硬 请忽略。。。。
pip install wxpy -i "https://pypi.doubanio.com/simple/" pip install wechat_sender -i "https://pypi.doubanio.com/simple/"
1.2 wxpy 登陆
wxpy 使用起来非常简单,我们只需要创建一个bot 对象,程序运行后,会弹出二维码,扫描二维码后显示登陆成功。
下述代码在登陆完成后,会向我们的文件传输助手发送一个“hello world!”。(每个程序都需要一个hello world)
from wxpy import * bot = Bot() bot.file_helper.send(‘hello world!‘) print("ending")
关于Bot()对象的相关参数说明,我们可以在源码中的注释中看到:
"""
:param cache_path:
* 设置当前会话的缓存路径,并开启缓存功能;为 `None` (默认) 则不开启缓存功能。
* 开启缓存后可在短时间内避免重复扫码,缓存失效时会重新要求登陆。
* 设为 `True` 时,使用默认的缓存路径 ‘wxpy.pkl‘。
:param console_qr:
* 在终端中显示登陆二维码,需要安装 pillow 模块 (`pip3 install pillow`)。
* 可为整数(int),表示二维码单元格的宽度,通常为 2 (当被设为 `True` 时,也将在内部当作 2)。
* 也可为负数,表示以反色显示二维码,适用于浅底深字的命令行界面。
* 例如: 在大部分 Linux 系统中可设为 `True` 或 2,而在 macOS Terminal 的默认白底配色中,应设为 -2。
:param qr_path: 保存二维码的路径
:param qr_callback: 获得二维码后的回调,可以用来定义二维码的处理方式,接收参数: uuid, status, qrcode
:param login_callback: 登陆成功后的回调,若不指定,将进行清屏操作,并删除二维码文件
:param logout_callback: 登出时的回调
"""
这里介绍一下两个主要使用到的参数:
cache_path: 在开发过程中可以设置为True 避免每次登陆都需要重新扫描,具有缓存的作用。
qr_path:用于保存二维码生成图片,主要解决服务器图片展示不方便的问题
1.3 wxpy 好友与聊天群
如代码所示,我们可以通过Bot.friends 以及Bot.groups 来获取到所有的好友以及聊天群,这里需要注意的是,聊天群需要保存到通讯录中,不然可能会出现找不到聊天群的情况。
在搜索方法中,可以提供的参数有:姓名,city,province,sex 等相关变量。
关于好友的详细API文档,可以参考---》 微信好友API
from wxpy import * bot = Bot() # 获取所有好友 friends = bot.friends() # 遍历输出好友名称 for friend in friends: print(friend) # 找到好友 friend = bot.friends.search(‘被单‘)[0] print(friend) friend.send("hello world!") # 获取所有聊天群 groups = bot.groups() for group in groups: print(group) # 找到目标群 group = groups.search("409")[0] group.send("hello world!")
1.4 wxpy 消息处理
接下来主要介绍一下用户发送消息的类型,目前wxpy 支持发送文本,图片,视频以及文件。主要的发送方式如代码所示:
这里比较重要的就是关于 @bot.register() 的使用,该注释主要用于注册消息接收器,我们可以根据特定的需求,配置不一样的消息接收器。
Bot.register(chats=None, msg_types=None, except_self=True, run_async=True, enabled=True) 详情可以查看源码中的介绍
关于消息处理API,读者可以在该地址下查看详细的配置,这里不做过多的描述。
代码中有使用到:embed() 这个方法, 主要用于阻塞进程,避免由于程序运行结束导致无法接收消息。
from wxpy import * bot = Bot() # 获取好友 my_friend = bot.friends().search(‘被单‘)[0] # 搜索信息 messages = bot.messages.search(keywords=‘测试‘, sender=bot.self) for message in messages: print(message) # 发送文本 my_friend.send(‘Hello, WeChat!‘) # 发送图片 my_friend.send_image(‘my_picture.png‘) # 发送视频 my_friend.send_video(‘my_video.mov‘) # 发送文件 my_friend.send_file(‘my_file.zip‘) # 以动态的方式发送图片 my_friend.send(‘@[email protected]_picture.png‘) # 发送公众号 my_friend.send_raw_msg( # 名片的原始消息类型 raw_type=42, # 注意 `username` 在这里应为微信 ID,且被发送的名片必须为自己的好友 raw_content=‘<msg username="wxpy_bot" nickname="wxpy 机器人"/>‘ ) # 消息接收监听器 @bot.register() def print_others(msg): # 输出监听到的消息 print(msg) # 回复消息 msg.reply("hello world") embed()
1.4 wxpy 图灵机器人
wxpy 接入图灵机器人相当方便,我们首先需要到图灵近期人官网进行注册,哆啦A梦的任意门。
通过注册Tuling 对象,当我们接收到消息的时候,可以直接使用tuling机器人来帮我们进行答复。其他的业务需求各位可以根据自己的需求来完成相应的逻辑。
from wxpy import * bot = Bot() # 获取好友 dear = bot.friends().search(‘被单‘)[0] # 注册获得个人的图灵机器人key 填入 tuling = Tuling(api_key=‘******‘) # 使用图灵机器人自动与指定好友聊天 @bot.register(dear) def reply_my_friend(msg): print(msg) tuling.do_reply(msg) embed()
1.5 wechat_sender
在熟悉了wxpy 的相关操作后,我们接下来介绍一下一个主要使用到的工具。由于wxpy 的设计,导致了一些业务操作并不好进行实现。因此我们在这里引入一个工具类:wechat_sender 。
首先我们需要像往常一样进行微信登陆,然后使用 listen() 进行对我们的 bot() 对象进行监听。
在这里我们可以看到了和上面代码的区别,这里使用的是listen(),上面是使用embed()进行监听。 我们再这里使用listen 进行监听对象后,可以设置相应的配置。监听默认设置的接收对象为self.file_helper,通过设置receivers 可以配置消息的接收者。
# login.py
from wxpy import * from wechat_sender import * bot = Bot() friend = bot.friends().search(‘被单‘)[0] listen(bot, token=‘test‘, receivers=[friend])
# sender.py coding: utf-8 from wechat_sender import Sender sender = Sender(token=‘test‘) sender.send(‘hello world!‘)
在别的python 文件中,我们只需要创建一个Sender() 对象,然后调用Sender.send()方法,即可对我们设定好的消息接收者发送消息。
Sender()在创建的时候可以通过特定的参数设定,比如这里使用了 token 用于避免多个listen 导致sender 混淆。还可以在sender中设置receiver 从listen 中选取需要接收消息的对象。
1.6 wxpy 在监控模块的代码实现
微信登陆模块:
from wechat_sender import * from wxpy import * bot = Bot(qr_path="qr.png") group = bot.groups().search(‘监控报警‘)[0] print("微信登陆成功!进行监控报警功能!") print(group) # listen(bot, token=‘test‘, receivers=[group])
业务处理模块:
import redis from wechat_sender import * sender = Sender(token=‘test‘, receivers=‘监控报警‘)
while true: # do anything sender.send(message=data) # do anything
p.unsubscribe(‘cardniu-monitor‘) print(‘取消订阅‘)
2、Python-Redis
这一模块我们将简单描述一下python 对于Redis 的支持,首先我们需要安装python-redis相关模块:
2.1 Python-redis安装
- 下载压缩包:哆啦A梦的任意门
- 解压进入 Redis 目录
- 命令行执行: python setup.py install
2.2 Python 简单操作Redis
由于Python 操作Redis 并不是我们这里的主要内容,所以这里简单的过一下Python 对Redis 的支持。
import redis r = redis.Redis(host=‘ip‘, port=6379, db=15, password=‘****‘) r.set(‘name‘, ‘Jaycekon‘) value = r.get(‘name‘) print(value)
2.3 Redis的发布订阅模式
在为大家讲解Redis 的发布订阅模式前,先为大家科普一下生产者消费者模式:
大家来领略一下我的灵魂画图,生产者消费者的核心思想是通过一个冰箱来进行解耦,就是我们的厨师不需要出厨房,顾客也不需要去厨房拿饭吃。通过一个冰箱来进行中间的解耦合。
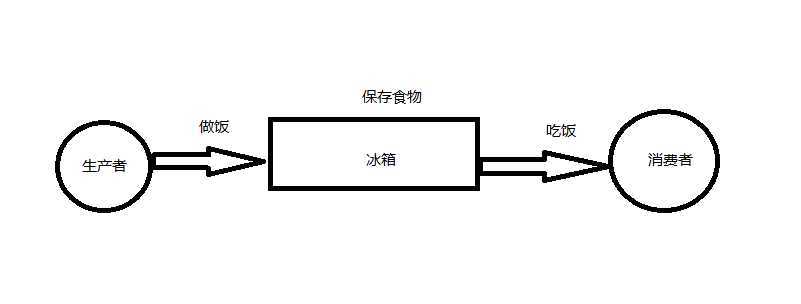
下面是我们通过python 实现的一个生产者消费者模式,厨师不停的做饭,顾客不停的吃。。大家相互不影响。
from threading import Thread queues = queue.Queue(10) class Producer(Thread): def run(self): while True: elem = random.randrange(9) queues.put(elem) print("厨师 {} 做了 {} 饭 --- 还剩 {} 饭没卖完".format(self.name, elem, queues.qsize())) time.sleep(random.random()) class Consumer(Thread): def run(self): while True: elem = queues.get() print("吃货{} 吃了 {} 饭 --- 还有 {} 饭可以吃".format(self.name, elem, queues.qsize())) time.sleep(random.random()) def main(): for i in range(3): p = Producer() p.start() for i in range(2): c = Consumer() c.start() if __name__ == ‘__main__‘: main()
再来说一下为什么使用到Redis 的发布订阅模式。
Redis在当前程序中,主要担当了一个消息队列的角色,我们并没有使用目前较为热门的RabbitMq,ActiveMq来消息队列进行解耦。主要原因在于我们的服务不大,消息量也比较小,因此在不影响程序的架构基础上,采用了Redis 作为消息队列。
消息队列的关键点在于,当生产者发布消息后,要确保消费者能够快速的接收消息。发布订阅模式能够很好的帮我们解决,当有消息到达的时候,程序马上能够做出响应操作。
Redis消息发布:
import redis pool = redis.ConnectionPool(host=‘ip‘, port=6379, db=4, password=‘****‘) r = redis.StrictRedis(connection_pool=pool) while True: inputs = input("publish:") r.publish(‘spub‘, inputs) if inputs == ‘over‘: print(‘停止发布‘) break
Redis消息订阅:
import redis pool = redis.ConnectionPool(host=‘ip‘, port=6379, db=4, password=‘***‘) r = redis.StrictRedis(connection_pool=pool) p = r.pubsub() p.subscribe(‘cardniu-monitor‘) for item in p.listen(): print(item) if item[‘type‘] == ‘message‘: data = item[‘data‘] print("消息队列中接收到信息:", data)if item[‘data‘] == ‘over‘: break p.unsubscribe(‘cardniu-monitor‘) print(‘取消订阅‘)
2.4 wxpy+Redis 实现监控系统的消费者
最终,在python 这边实现的监控系统消费者如下:
微信登陆模块:
from wechat_sender import * from wxpy import * bot = Bot(qr_path="qr.png") group = bot.groups().search(‘监控报警‘)[0] print("微信登陆成功!进行监控报警功能!") print(group) # listen(bot, token=‘test‘, receivers=[group])
Redis消息订阅模块:
import redis from wechat_sender import * sender = Sender(token=‘test‘, receivers=‘监控报警‘) pool = redis.ConnectionPool(host=‘10.201.3.18‘, port=6379, db=4, password=‘kntest%[email protected]‘) r = redis.StrictRedis(connection_pool=pool) p = r.pubsub() p.subscribe(‘cardniu-monitor‘) for item in p.listen(): print(item) if item[‘type‘] == ‘message‘: data = item[‘data‘] print("消息队列中接收到信息:", data)
sender.send(message=data) if item[‘data‘] == ‘over‘: break p.unsubscribe(‘cardniu-monitor‘) print(‘取消订阅‘)
3、Java-Redis
最后,在生产者这块,即是我们监控系统的核心部分,当我们的Java系统出现异常时,我们即可向Redis发送消息,最后由消费者那一边完成消息的发送。
在下面会跟大家简单讲解一下生产者这边的代码,但是由于代码设计公司内容,因此不做过多的描述。
Spring-redis.xml

<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context" xmlns:util="http://www.springframework.org/schema/util" xmlns:aop="http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop" xsi:schemaLocation=" http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans-3.1.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/context http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context-3.1.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/util http://www.springframework.org/schema/util/spring-util-3.1.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop/spring-aop-3.1.xsd"> <!-- redis连接池的配置 --> <bean id="jedisPoolConfig" class="redis.clients.jedis.JedisPoolConfig"> <property name="maxTotal" value="${redis.pool.maxTotal}" /> <property name="maxIdle" value="${redis.pool.maxIdle}" /> <property name="minIdle" value="${redis.pool.minIdle}" /> <property name="maxWaitMillis" value="${redis.pool.maxWaitMillis}" /> <property name="testOnBorrow" value="${redis.pool.testOnBorrow}" /> <property name="testOnReturn" value="${redis.pool.testOnReturn}" /> </bean> <bean id="sentinelJedisPool" class="redis.clients.jedis.JedisSentinelPool"> <constructor-arg index="0" value="${redis.sentinel.masterName}" /> <constructor-arg index="1" value="#{‘${redis.sentinels}‘.split(‘,‘)}" /> <constructor-arg index="2" ref="jedisPoolConfig" /> <constructor-arg index="3" value="${redis.sentinel.timeout}" type="int" /> <constructor-arg index="4" value="${redis.sentinel.password}" /> <constructor-arg index="5" value="${redis.sentinel.database}" type="int" /> </bean> </beans>
JedisUtils.java

@Autowired private JedisSentinelPool jedisPool; @PostConstruct private void init() throws Exception { /* 缓存初始化 */ JedisUtils.setJedisPool(jedisPool); } public static void setJedisPool(Pool<Jedis> jedisPool) throws Exception { JedisCache.jedisPool = jedisPool; Jedis jedis = null; try { jedis = jedisPool.getResource(); isInitSuc = true; logger.info("redis start success!"); } catch (Exception e) { if (null != jedis) jedisPool.returnBrokenResource(jedis); logger.error("redis start exception!!!error:{}", e.getMessage(), e); if (e instanceof redis.clients.jedis.exceptions.JedisConnectionException) { throw e; } } finally { if (null != jedis) jedisPool.returnResource(jedis); } } public static Long publish(String chanel, String value) { Jedis jedis = null; try { jedis = jedisPool.getResource(); return jedis.publish(chanel,value); } catch (Exception e) { if (null != jedis) { jedisPool.returnBrokenResource(jedis); jedis = null; } logger.error("redis exception:{}", e.getMessage(), e); return 0L; } finally { if (null != jedis) jedisPool.returnResource(jedis); } }
NoticeTask.java
@Scheduled(cron = "*/5 * * * * ? ") public void runMonitor() { try { List<T> notices; List<EbankNotice> result; while ((notices = QueueHolder.noticeBlockingQueue.take()) != null) { //消费 if (notices.isEmpty()) { continue; } result = service.calculateNotice(notices); result.forEach(notice -> { JedisUtils.publish("cardniu-monitor", notice.getTitle() + "," + DateUtils.format(notice.getPostTime(), "yyyy-MM-dd hh:mm:ss") + "," + notice.getLinkAddress()); }); } } catch (InterruptedException e) { logger.error("发送邮件定时任务异常,{}", e.getMessage(), e); } }
4、总结
这个项目的核心在于wxpy 的运用,以及生产者消费者的设计思想。语言的话,核心的python这一块的wxpy,在生产者这边,无论是其他的什么语言,都可以作为我们的生产者。
项目github地址:https://github.com/jaycekon/WxpyDemo
希望各位喜欢的朋友可以fork 或者start一下~~~~~
参考:
wxpy API:http://wxpy.readthedocs.io/zh/latest/messages.html
wechat_sender Api:https://pypi.python.org/pypi/wechat-sender/0.1.3
python-redis :https://pypi.python.org/pypi/redis
Java-Redis:http://docs.spring.io/spring-data/redis/docs/2.0.0.M4/reference/html/
以上是关于Python-WXPY实现微信监控报警的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章
