day15 python-03 列表,元组,字典
Posted
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了day15 python-03 列表,元组,字典相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
Python之路,Day3 = Python基础3
模块的简单使用
sys模块
1 #!/usr/bin/env python #这句话的含义是,在linux上,默认以python执行该文件 2 # _*_ conding:utf-8 _*_ #这句的含义是,设置编码格式为utf_8 3 4 import sys #导入模块,模块名为 “sys” 5 6 print(sys.argv) #调用模块中的argv,这个是方法吗?怎么没有括号? 7 8 #当使用命令行cmd运行这个文件的时候,可以在命令行加入参数,这样可以获取参数,例如输入: python test.py 参数1 参数2 9 #得到的结果就是一个列表:[‘test.py‘, ‘hello‘, ‘word‘]
1 #!/usr/bin/env python 2 # _*_ coding:utf-8 _*_ 3 4 import sys 5 6 print(sys.path) #打印出python自有的环境变量的位置 7 8 #就是说,如果python需要import其它模块的时候,会从这里面搜索,如果没有,则提示找不到。通常自己在自定义模块的时候,可以把自己的模块放在这些路径下面,当然,也可以把自己写的模块的路劲添加进这个列表里面。
os模块
1 #!/usr/bin/env python 2 # _*_ coding:utf-8 _*_ 3 4 import os 5 6 os.system("dir .") 7 8 #调用系统命令“dir .”,这里的 “.”是当前目录的意思。整个命令就是,调用系统cmd命令中的显示当前文件夹下的所有文件。
list相关应用
1 #列表的创建 2 #方法一 3 test_list = ["zhang", 1, "String"] 4 5 #方法二 6 test_list = list(["zhang", 1, "String"]) 7 8 #注:列表中可以嵌套列表 9 #如:test_list = ["zhang", 1, "String", ["zhang", 1, "String"]]
基本操作
test_list = ["zhang", 1, "String", "admin", "username", "password"]
- 索引--> test_list.index("zhang") #返回结果为 0
- 从左往右找到括号中的元素第一次出现位置的下标,如果不存在,则返回错误。有多个时候,只返回第一个。
- 切片--> test_list[1:5] #结果为 [1, "String", "admin", "username"]
- 将下标为 >=1 且 <5 的所有元素取出来作为新的列表,如果,左右数字不写,则默认为从头开始,到末尾结束。此方法可以跳着切片 test_index[1:5:2] 意思为,距离为2.
- 追加--> test_list.append("people") #将字符串"people"添加到test_list最后面
- test_list.insert(1,"d") #将字符串"d",添加到下标为 1 的位置,其他内容顺序后移。
- test_list.extend(test_list) #将列表 test_list 本身添加到自己后面,这个方法通常用来将两个列表合并,括号中的列表,将会按顺序添加到前面列表的后面。
- 删除--> del test_list[0] #删除下标为0的元素
- test_list.pop() #删除最后一个元素,若果括号中加入下标,则删除,该下标位置
- test_list.remove("admin") #从左往右,删除第一个遇到的该元素
- test_list.clear() #清空 test_list。
- 长度--> len(test_list) #返回列表 test_list 的长度
- 循环-->
-
1 test_list = ["zhang", 1, "String", "admin", "username", "password"] 2 3 for i in test_list: 4 print(i) 5 6 #循环打印 test_list 中的所有元素
-
- 包含-->
- "zhang" in test_list #判断字符串 "zhang" 在 test_list 列表中,存在 True, 不存在 False
- "zhang" not in test_list #判断字符串 "zhang" 不在 test_list 列表中,不存在 True, 存在 False
- 计数--> test_list.count("user") #查看 test_list 列表中包含几个 "user" 字符串
元组(不可变的列表)
1 test_tuple = ("a", "b", "c", "d") #赋值方法1 2 test_tuple = tuple(("a", "b", "c", "d")) #赋值方法2
字典(无序)
1 test_dict = {"name": "zhang", "gender": "male", "age": 23} 2 test_dict = dict({"name": "zhang", "gender": "male", "age": 23})
- 索引
-
1 #!/usr/bin/env python 2 # _*_ coding:utf-8 _*_ 3 4 5 test_dict = {"name": "zhang", "gender": "male", "age": 23} 6 7 print(test_dict["name"]) 8 9 10 ==> zhang 11 12 #打印出 "name"对应的 值
索引用test_dict["name"]的时候,如果不存在,则会出错,所有一个更好的选择:
test_dict.get("name") 这样的话如果没有,则返回None,有的话返回值
- 新增
-
1 #!/usr/bin/env python 2 # _*_ coding:utf-8 _*_ 3 4 5 6 test_dict = {"name": "zhang", "gender": "male", "age": 23} 7 8 9 test_dict["salary"] = 3000 10 #添加新内容 "salary":3000, 如果 "salary" 已经存在,那么将修改它的值 11 12 print(test_dict)
dict1.update(dict2) 将dict2中不重复的元素添加到dict1中,如果存在,则将dict1中数值跟新进去
- 删除
1 test_dict = {"name": "zhang", "gender": "male", "age": 23} 2 3 4 test_dict.clear() #清空 test_claer 5 6 test_dict.pop("name") #删除 "name" 这一组数据; 7 8 test_dict.popitem() #随机删除一组数据。
- 键、值、键值对
- 循环
1 test_dict = {"name": "zhang", "gender": "male", "age": 23} 2 3 for k, v in test_dict.items(): 4 print(k,v) 5 6 """输出结果为 7 name zhang 8 gender male 9 age 23 10 """
- 长度
1 test_dict = {"name": "zhang", "gender": "male", "age": 23} 2 3 print(len(test_dict)) 4 5 ==> 3
字符串简单应用
1 test_String = " my name is bubblejia\\n" 2 3 print(test_String) #正常打印字符串,包括前面的空格和后面的换行 4 ==> my name is bubblejia 5 ==> 6 print(test_String.strip()) #去掉开头和结尾的空格及换行 7 ==>my name is bubblejia 8 print(test_String.split()) #以空格(默认的)为分界,将字符串转为列表 9 ==>[‘my‘, ‘name‘, ‘is‘, ‘bubblejia‘] 10 print(len(test_String)) #查看test_String长度 11 ==>22 12 print(test_String[:5]) #取test_String下标5之前的所有元素(不包含5) 13 ==> my n 14 print(test_String[5:]) #取test_String下标5之后的所有元素(包含5) 15 ==>ame is bubblejia 16 ==> 17 print(test_String.index("n")) #从左往右,找到第一个 "n" 所在位置的下标 18 ==>4
copy简单应用
1 import copy 2 a = [1, 2, 3, 4, [‘a‘, ‘b‘]] #原始对象 3 4 b = a #赋值,传对象的引用 5 c = copy.copy(a) #对象拷贝,浅拷贝,只拷贝第一层。 6 d = copy.deepcopy(a) #对象拷贝,深拷贝,拷贝所有层。
====================homework=====================

1 #! /usr/bin/env python 2 # -*- coding: utf-8 -*- 3 # __author__ = "Always" 4 # Date: 2017/6/8 5 6 """ 7 一、元素分类 8 9 有如下值集合 [11,22,33,44,55,66,77,88,99,90...],将所有大于 66 的值保存至字典的第一个key中,将小于 66 的值保存至第二个key的值中。 10 即: {‘k1‘: 大于66的所有值, ‘k2‘: 小于66的所有值} 11 12 """ 13 14 li = [11,22,33,44,55,66,77,88,99,90] 15 # print(li) 16 d = {‘k1‘:[], ‘k2‘:[]} 17 18 for i in li: 19 if type(i) is int: 20 if i > 66: 21 d[‘k1‘].append(i) 22 else: 23 d[‘k2‘].append(i) 24 25 print(‘k1:%s\\nk2:%s‘%(d[‘k1‘], d[‘k2‘]))

1 #! /usr/bin/env python 2 # -*- coding: utf-8 -*- 3 # __author__ = "Always" 4 # Date: 2017/6/8 5 6 """ 7 二、查找 8 查找列表中元素,移除每个元素的空格,并查找以 a或A开头 并且以 c 结尾的所有元素。 9 li = ["alec", " aric", "Alex", "Tony", "rain"] 10 tu = ("alec", " aric", "Alex", "Tony", "rain") 11 dic = {‘k1‘: "alex", ‘k2‘: ‘ aric‘, "k3": "Alex", "k4": "Tony"} 12 13 """ 14 15 li = ["alec", " aric", "Alex", "Tony", "rain"] 16 tu = ("alec", " aric", "Alex", "Tony", "rain") 17 dic = {‘k1‘: "alex", ‘k2‘: ‘ aric‘, "k3": "Alex", "k4": "Tony"} 18 19 new_d = {‘li‘:li, ‘tu‘:tu, ‘dic‘:dic} 20 21 for k in new_d: 22 print(‘%s中,以 a或A开头 并且以 c 结尾的所有元素有:‘%k, end=‘‘) 23 24 if type(new_d[k]) is list or type(new_d[k]) is tuple: 25 for v in new_d[k]: 26 new_v = v.strip() 27 s, *_, e = new_v 28 if e == ‘c‘ and (s == ‘a‘ or s == ‘A‘): 29 print(new_v, end=‘ ‘) 30 elif type(new_d[k]) is dict: 31 v2 = new_d[k] 32 for k2 in v2: 33 new_v = v2[k2].strip() 34 s, *_, e = new_v 35 if e == ‘c‘ and (s == ‘a‘ or s == ‘A‘): 36 print(k2+‘:‘+new_v, end=‘ ‘) 37 38 print()

1 #! /usr/bin/env python 2 # -*- coding: utf-8 -*- 3 # __author__ = "Always" 4 # Date: 2017/6/8 5 6 """ 7 三、输出商品列表,用户输入序号,显示用户选中的商品 8 商品 li = ["手机", "电脑", ‘鼠标垫‘, ‘游艇‘] 9 10 """ 11 import time 12 13 li = ["手机", "电脑", ‘鼠标垫‘, ‘游艇‘] 14 15 while True: 16 print("商品列表".center(15,‘=‘)) 17 for i in range(len(li)): 18 print("%s %s"%(i+1, li[i])) 19 choose = input(">>>") 20 if choose.isdigit() and 0 < int(choose) <= len(li): 21 print(‘你选择的是: %s %s‘%(choose, li[int(choose)-1])) 22 else: 23 print(‘没有这个选项。。。‘) 24 time.sleep(2)

1 #! /usr/bin/env python 2 # -*- coding: utf-8 -*- 3 # __author__ = "Always" 4 # Date: 2017/6/8 5 6 """ 7 四、购物车 8 功能要求: 9 10 要求用户输入总资产,例如:2000 11 显示商品列表,让用户根据序号选择商品,加入购物车 12 购买,如果商品总额大于总资产,提示账户余额不足,否则,购买成功。 13 附加:可充值、某商品移除购物车 14 goods = [ 15 {"name": "电脑", "price": 1999}, 16 {"name": "鼠标", "price": 10}, 17 {"name": "游艇", "price": 20}, 18 {"name": "美女", "price": 998}, 19 ] 20 """ 21 22 # ========= 23 import time 24 25 26 goods = [ 27 {"name": "电脑", "price": 1999}, 28 {"name": "鼠标", "price": 10}, 29 {"name": "游艇", "price": 20}, 30 {"name": "美女", "price": 998}, 31 ] 32 33 shopping_list = [] 34 # shopping_list = [ 35 # {‘name‘:‘电脑‘, ‘price‘:1999, ‘count‘:4} 36 # ] 37 38 39 """ 40 打印购物清单 41 print(‘ M E N U\\n序号 名称 \\t 价格‘) 42 for i, info in enumerate(goods, 1): 43 print(" %s %s \\t¥%s"%(i, info[‘name‘], info[‘price‘])) 44 buy_number = input("请输入需要购买的商品序号:") 45 """ 46 47 48 while True: 49 salary = input("请输如你的工资:") 50 if salary.isdigit(): 51 salary = int(salary) 52 break 53 54 while True: 55 print(‘ M E N U\\n序号 名称 \\t 价格‘) 56 for i, info in enumerate(goods, 1): 57 print(" %s %s \\t¥%s" % (i, info[‘name‘], info[‘price‘])) 58 buy_number = input("请输入需要购买的商品序号:") 59 if buy_number.isdigit() and int(buy_number) <= len(goods): 60 # 如果输入的序号信息没有问题,那么就加入购物车 61 append_flag = False 62 buy_number = int(buy_number) 63 goods_name = goods[buy_number - 1][‘name‘] 64 goods_price = goods[buy_number - 1][‘price‘] 65 for i_list, info_list in enumerate(shopping_list): 66 if goods_name in info_list[‘name‘]: 67 shopping_list[i_list][‘count‘] += 1 68 append_flag = True 69 break 70 if not append_flag: 71 shopping_list.append({‘name‘:goods_name, ‘price‘:goods_price, ‘count‘:1}) 72 print("%s已经加入了你的购物车。。"%goods_name) 73 time.sleep(1) 74 else: 75 print(‘那啥,东西不存在。。。‘) 76 time.sleep(1) 77 # print(shopping_list) 78 # 这个地方就用来打印是否继续购买,以及结算什么的 79 80 goahead_shopping = input("是否继续购买y/n:") 81 if goahead_shopping == ‘y‘: 82 continue 83 else: 84 take_the_bill = input("是否结账y/n:") 85 if take_the_bill == ‘y‘: 86 print(‘我要开始结账了‘) 87 88 # shopping_list = [ 89 # {‘name‘: ‘电脑‘, ‘price‘: 1999, ‘count‘: 10} 90 # ] 91 92 93 while True: 94 all_cost = 0 95 print(" 购物车列表\\n 序号 名称\\t 价格 \\t 数量") 96 for i, info_list in enumerate(shopping_list, 1): 97 print(" %s %s \\t ¥%s \\t %s" % (i, info_list[‘name‘], info_list[‘price‘], info_list[‘count‘])) 98 all_cost += info_list[‘price‘] * info_list[‘count‘] 99 print("合计:%s\\n" % all_cost) 100 input("回车键确定结账。。。") 101 102 if salary >= all_cost: 103 salary -= all_cost 104 print("结算成功,共消费%s元,还剩余%s元。。。" % (all_cost, salary)) 105 exit() 106 else: 107 deposit = input("钱不够,是否充值y/n:") # deposit 存款 108 if deposit == "y": 109 print(‘我要开始存钱了。。。‘) 110 deposit_number = input(‘你要存多少钱呢:‘) 111 if deposit_number.isdigit(): 112 salary += int(deposit_number) 113 print(‘OK了,你现在一共有%s元。。。‘ % salary) 114 time.sleep(1.2) 115 elif deposit == ‘q‘: 116 break 117 else: 118 del_shopping_list = input(‘是否删除购物车的物品y/n:‘) 119 if del_shopping_list == ‘y‘: 120 del_flag = True 121 while del_flag: 122 print(‘我要开始删除购物车的内容了。。。。‘) 123 all_cost = 0 124 for i, info_list in enumerate(shopping_list, 1): 125 print(" %s %s \\t ¥%s \\t %s" % ( 126 i, info_list[‘name‘], info_list[‘price‘], info_list[‘count‘])) 127 all_cost += info_list[‘price‘] * info_list[‘count‘] 128 print("合计:%s\\n" % all_cost) 129 del_choose = input(‘删除啥勒:‘) 130 if del_choose.isdigit() and int(del_choose) <= len(shopping_list): 131 del_choose = int(del_choose) 132 if shopping_list[del_choose - 1][‘count‘] == 1: 133 del_index = del_choose - 1 134 shopping_list.pop(del_index) 135 else: 136 shopping_list[del_choose - 1][‘count‘] -= 1 137 gohead_del = input(‘是否继续删除y/n:‘) 138 if gohead_del != ‘y‘: 139 del_flag = False 140 break 141 elif del_shopping_list == ‘q‘: 142 exit(‘谢谢使用。。。‘) 143 144 145 exit(‘谢谢使用。。。。‘) 146 else: 147 continue

1 #! /usr/bin/env python 2 # -*- coding: utf-8 -*- 3 # __author__ = "Always" 4 # Date: 2017/6/8 5 6 """ 7 选做题:用户交互,显示省市县三级联动的选择 8 dic = { 9 "河北": { 10 "石家庄": ["鹿泉", "藁城", "元氏"], 11 "邯郸": ["永年", "涉县", "磁县"], 12 } 13 "河南": { 14 ... 15 } 16 "山西": { 17 ... 18 } 19 20 } 21 """ 22 23 import sys 24 25 26 new_things = ["物体", ["金属物品",["铁","镁","铜"], "非金属物品", ["氢气", "空气" ,"氮气"]], "生物", ["人类",["男人", "女人"], "非人类", ["哺乳动物", "非哺乳动物"]]] 27 28 29 30 def get_things(new_things): 31 while True: #这里为了防止程序跑到末尾,进行死循环,除非遇到return,才终止程序 32 print("=======================================") 33 res = if_root(new_things) #判断列表中是否还包含列表,如果是,返回1,否返回0 34 if res == 1: 35 for i in range(int(len(new_things) / 2)): 36 print((i + 1), new_things[i * 2]) 37 print(int(len(new_things) / 2) + 1, "返回") 38 choose = input("Please input you choose:") 39 choose = int(choose) 40 if choose == int(len(new_things) / 2) + 1 : 41 return 42 elif choose == 1: 43 get_things(new_things[1]) 44 else: 45 get_things(new_things[choose * 2 - 1]) 46 else: 47 for i in range(len(new_things)): 48 print(i + 1, new_things[i]) 49 print(len(new_things) + 1, "返回") 50 choose = input("Please input you choose:") 51 choose = int(choose) 52 if choose == len(new_things) + 1: 53 return 54 else: 55 input("这个已经是最小的目录了。。。") 56 57 def if_root(new_things): 58 for i in new_things: 59 if type(i) is list: 60 return 1 61 else: 62 return 0 63 64 65 66 get_things(new_things)
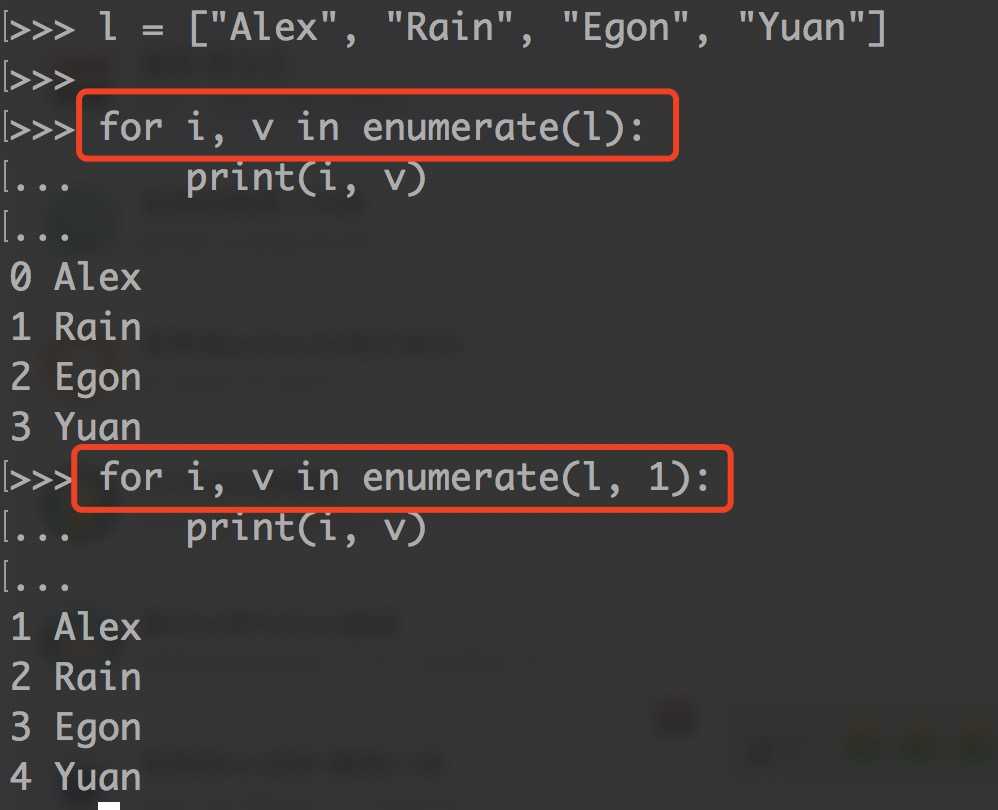
以上是关于day15 python-03 列表,元组,字典的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章
