Linux:了解HTTP协议
Posted mbf330
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了Linux:了解HTTP协议相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
文章目录
HTTP 协议
1.概念
HTTP:默认端口号为80;是互联网上应用最为广泛的一种网络协议,是一个客户端和服务器端请求和应答的标准(TCP),用于从WWW服务器传输超文本到本地浏览器的传输协议,它可以使浏览器更加高效,使网络传输减少。
HTTPS:默认端口号为443;是以安全为目标的HTTP通道,简单讲是HTTP的安全版,即HTTP下加入SSL层,HTTPS的安全基础是SSL,因此加密的详细内容就需要SSL。
http与https在大多方面都相同,但是https协议更加私密,使用https协议传输数据多了一层加密过程。先以http为例来了解,后面会详谈二者的区别。
2.其他相关概念
(1)认识url
平时我们俗称的 “网址” 其实就是说的 URL

(2)urlencode和urldecode
urlencode是一个函数,可将字符串以URL编码,用于编码处理;
urldecode就是urlencode的逆过程。
像 ‘/ ? :’ 等这样的字符, 已经被url当做特殊意义理解了;因此这些字符不能随意出现;比如, 某个参数中需要带有这些特殊字符, 就必须先对特殊字符进行转义。
转义规则:将需要转码的字符转为16进制,然后从右到左,取4位(不足4位直接处理),每2位做一位,前面加上%,编码成%XY格式
下图中,c++中的“++”便被转码为“%2B%B”

3.HTTP协议格式

(1)HTTP请求
首行: [方法] + [url] + [版本];
Header: 请求的属性, 冒号分割的键值对;每组属性之间使用\\n分隔;遇到空行表示Header部分结束。
Body: 空行后面的内容都是Body. Body允许为空字符串. 如果Body存在, 则在Header中会有一个
Content-Length属性来标识Body的长度;

(2)HTTP相应
首行: [版本号] + [状态码] + [状态码解释];
Header: 请求的属性, 冒号分割的键值对;每组属性之间使用\\n分隔;遇到空行表示Header部分结束;
Body: 空行后面的内容都是Body.;Body允许为空字符串,如果Body存在, 则在Header中会有一个Content-Length属性来标识Body的长度; 如果服务器返回了一个html页面, 那么html页面内容就是在body中。

4.HTTP的方法
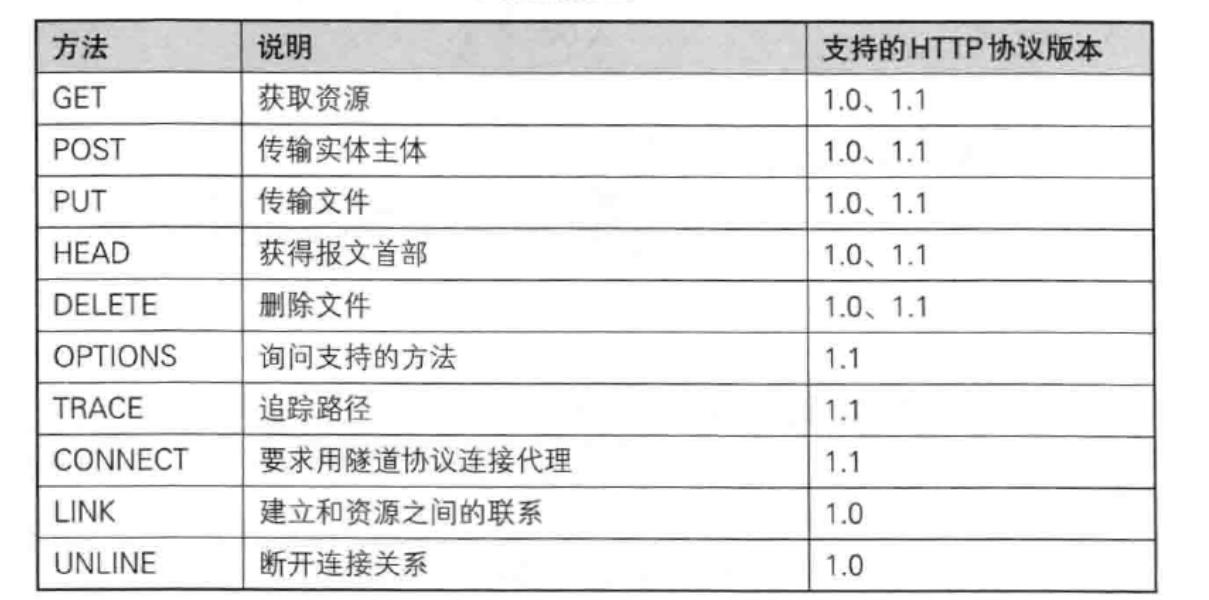
HTTP有多种方法;但是很多因为安全问题或者具有破坏性被服务器禁用;最常用的两种方法是GET和POST。
GET方法通过url传参;POST方法通过正文传参。POST方法更私密。
5.HTTP的状态码
最常见的状态码, 比如 200(OK), 404(Not Found), 403(Forbidden), 302(Redirect, 重定向), 504(Bad Gateway)。

6.HTTP常见Header
1.Content-Type: 数据类型(text/html等);
2.Content-Length: Body的长度;
3.Host: 客户端告知服务器, 所请求的资源是在哪个主机的哪个端口上;
4.User-Agent: 声明用户的操作系统和浏览器版本信息;
5.referer: 当前页面是从哪个页面跳转过来的;
6.location: 搭配3xx状态码使用, 告诉客户端接下来要去哪里访问;
7.Cookie: 用于在客户端存储少量信息. 通常用于实现会话(session)的功能。
cookie和session是http协议中很重要的功能,在后面会详谈
7.代码实现简单的HTTP服务器
#include<iostream>
#include<string>
#include<vector>
#include<stdlib.h>
#include<unistd.h>
#include<sys/types.h>
#include<sys/socket.h>
#include<netinet/in.h>
#include<string.h>
#include<signal.h>
#define BACKLOG 5
using namespace std;
class httpServer
private:
int port;
int lsock;
public:
httpServer(int _p):port(_p),lsock(-1)
void initServer()
signal(SIGCHLD,SIG_IGN);
lsock=socket(AF_INET,SOCK_STREAM,0);
if(lsock < 0)
cerr<<"socket init error"<<endl;
exit(2);
struct sockaddr_in local;
//对缓冲区进行清零
bzero(&local,sizeof(local));
local.sin_family=AF_INET;
local.sin_port=htons(port);
local.sin_addr.s_addr=INADDR_ANY;
if(bind(lsock,(struct sockaddr*)&local,sizeof(local)) < 0)
cerr<<"socker bind error"<<endl;
exit(3);
if(listen(lsock,BACKLOG) < 0)
cerr<<"listen error"<<endl;
exit(4);
void echoHTTP(int sock)
char request[2048];
size_t s=recv(sock,request,sizeof(request),0);
if(s > 0)
request[s]=0;
cout<<request<<endl;
string response="HTTP/1.0 200 OK\\r\\n";
response+="Content-Type:text/html\\r\\n";
response+="\\r\\n";
response+="<!DOCTYPE html>\\
<html>\\
<head>\\
<title>my http</title>\\
</head>\\
<body>\\
<h1>my http</h1>\\
<p>hello world</p>\\
</body>\\
</html>\\
";
send(sock,response.c_str(),response.size(),0);
void start()
struct sockaddr_in peer;
for(;;)
socklen_t len=sizeof(peer);
int sock=accept(lsock,(struct sockaddr*)&peer,&len);
if(sock < 0)
cerr<<"accept error"<<endl;
continue;
cout<<"get a new connect"<<endl;
if(fork() == 0)
close(lsock);
echoHTTP(sock);
exit(0);
close(sock);
~httpServer()
if(lsock!=-1)
close(lsock);
;
#include "http.h"
static void usage(string proc)
cout<<"usage:\\n\\t";
cout<<proc<<"port"<<endl;
int main(int argc,char*argv[])
if(argc != 2)
usage(argv[0]);
exit(1);
httpServer *hp=new httpServer(atoi(argv[1]));
hp->initServer();
hp->start();
return 0;
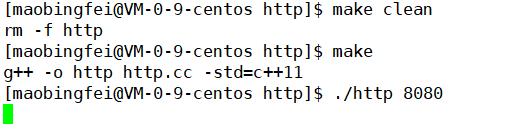
在浏览器进行访问
同时可以通过对其进行重定向来访问别的网页,修改respomse来使其访问B站主网页
void echoHTTP(int sock)
char request[2048];
size_t s=recv(sock,request,sizeof(request),0);
if(s > 0)
request[s]=0;
cout<<request<<endl;
string response="HTTP/1.0 302 FOUND\\r\\n";
response+="Content-Type:text/html\\r\\n";
response+="Location:https://www.bilibili.com/";
response+="\\r\\n";
response+="<!DOCTYPE html>\\
<html>\\
<head>\\
<title>my http</title>\\
</head>\\
<body>\\
<h1>my http</h1>\\
<p>hello world</p>\\
</body>\\
</html>\\
";
send(sock,response.c_str(),response.size(),0);
以上是关于Linux:了解HTTP协议的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章