怎么用5v的arduino控制12v的共阴rgb灯带,用9014三极管
Posted
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了怎么用5v的arduino控制12v的共阴rgb灯带,用9014三极管相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
怎么用5v的arduino控制12v的共阴rgb灯带,用9014三极管大概如图,补全基极
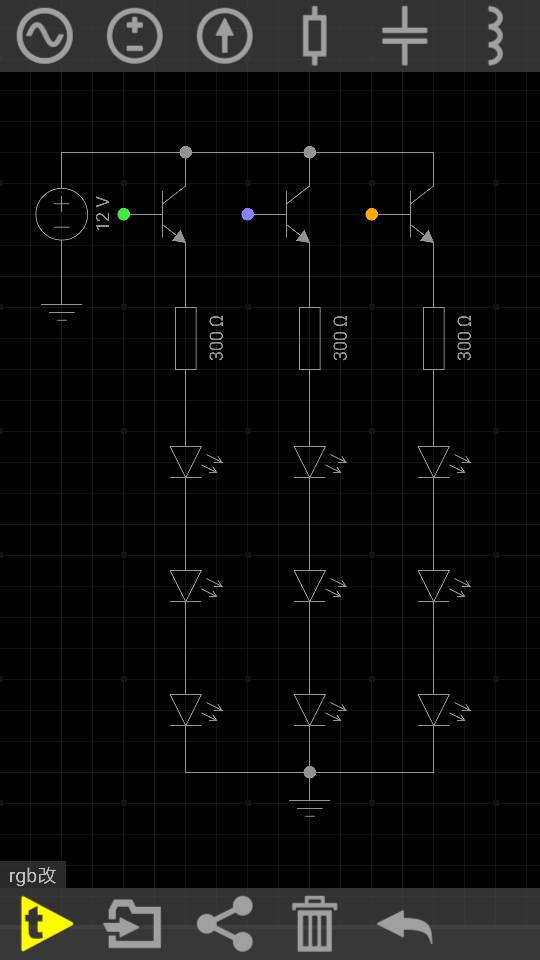
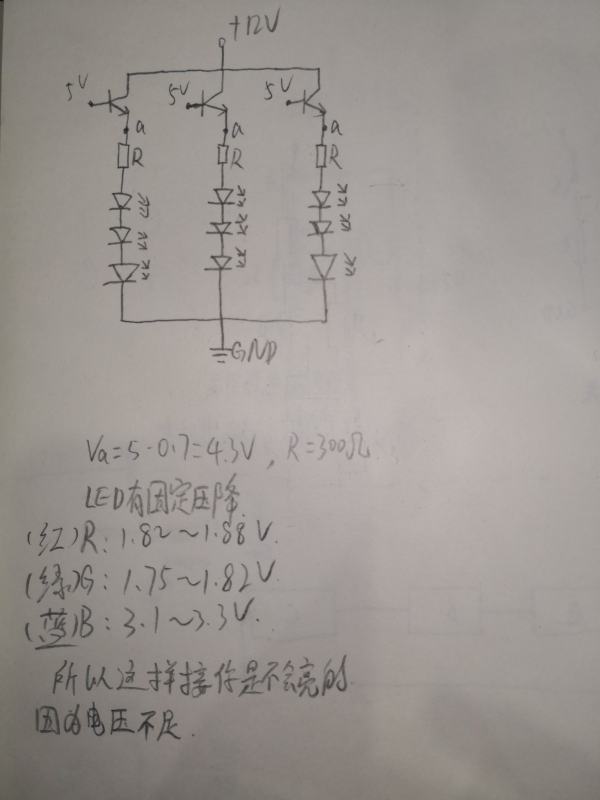
因为LED有固定压降,你这种接法,在a点处的电压是固定4.3V,所以导致,每个LED上的分压根本不够,导致要不不亮,要不就是很微弱的亮。
建议把所有LED的阴极接到三极管的集电极,阳极接12V电源,取消电阻R,然后通过调整三极管基极处的电阻大小,来调节三极管Ic的电流就可以了,因为只要电流恒定在LED的工作电流上就可以正常工作,至于多出去的电压在哪,在三极管ce结上。
追问灯改不了,是灯带,如果用pnp三极管或者mos可以吗?
追答PNP可以,用P-mos也可以,不可以用NPN和N-mos
追问能不能帮忙画个图
追答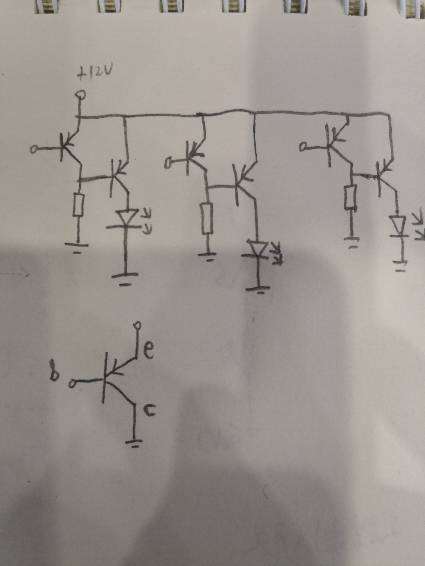
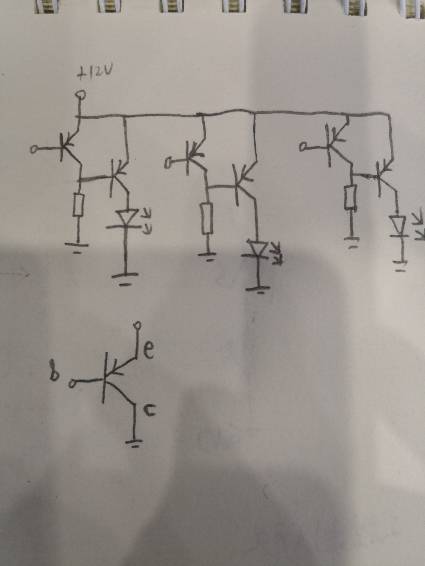
借LED的三极管,基极需要串入一个电阻
电阻的大小你应该会算吧
追问谢谢
追答上面的电路有一个缺点,我把它修改以后的电路发给你
出现一种特殊情况会无法关断
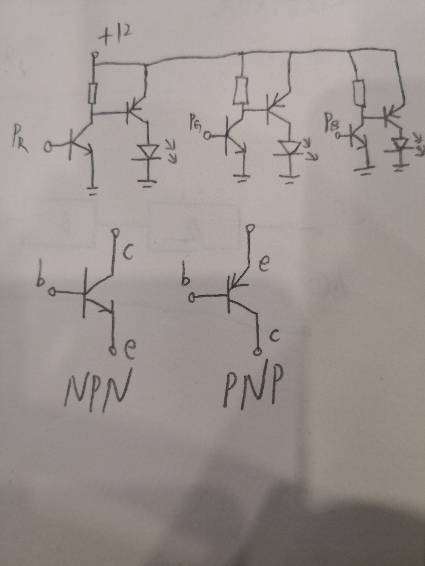
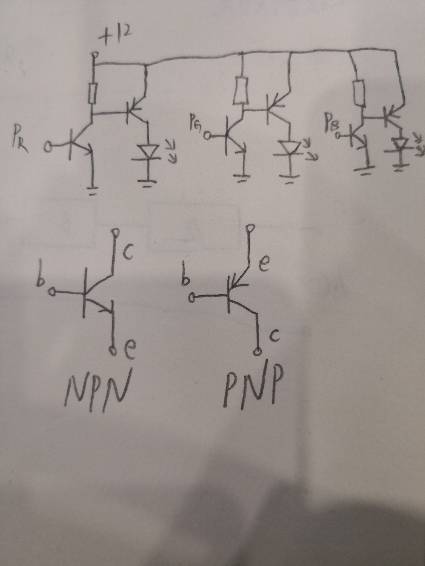
这个图就不会出现无法关断的情况。
参考技术A 每个基极串电阻,电阻阻值Rb=Vcc-Ube/(lc/β)Arduino ESP32 Web网页控制RGB灯
Arduino ESP32 Web网页控制RGB灯
ESP32 LED PWM控制器具有16个独立通道,可配置为生成具有不同属性的PWM信号。 我们可以使用ESP32的LED PWM控制器和零知开发工具对LED进行调光。
- 连线:
1、红色引脚连接到ESP32的GPIO25
2、绿色引脚连接到ESP32的GPIO26
3、蓝色引脚连接到ESP32的GPIO27
实例代码
#include <WiFi.h>
// 填写wifi信息
const char* ssid = "";
const char* password = "";
// Set web server port number to 80
WiFiServer server(80);
// Decode HTTP GET value
String redString = "0";
String greenString = "0";
String blueString = "0";
int pos1 = 0;
int pos2 = 0;
int pos3 = 0;
int pos4 = 0;
// Variable to store the HTTP req uest
String header;
// Red, green, and blue pins for PWM control
const int redPin = 25; // 13 corresponds to GPIO13
const int greenPin = 26; // 12 corresponds to GPIO12
const int bluePin = 27; // 14 corresponds to GPIO14
// Setting PWM frequency, channels and bit resolution
const int freq = 5000;
const int redChannel = 0;
const int greenChannel = 1;
const int blueChannel = 2;
// Bit resolution 2^8 = 256
const int resolution = 8;
// Current time
unsigned long currentTime = millis();
// Previous time
unsigned long previousTime = 0;
// Define timeout time in milliseconds (example: 2000ms = 2s)
const long timeoutTime = 2000;
void setup() {
Serial.begin(115200);
// configure LED PWM functionalitites
ledcSetup(redChannel, freq, resolution);
ledcSetup(greenChannel, freq, resolution);
ledcSetup(blueChannel, freq, resolution);
// attach the channel to the GPIO to be controlled
ledcAttachPin(redPin, redChannel);
ledcAttachPin(greenPin, greenChannel);
ledcAttachPin(bluePin, blueChannel);
// Connect to Wi-Fi network with SSID and password
Serial.println();
Serial.print("Connecting to ");
Serial.println(ssid);
WiFi.begin(ssid, password);
while (WiFi.status() != WL_CONNECTED) {
delay(500);
Serial.print(".");
}
// Print local IP address and start web server
Serial.println("");
Serial.println("WiFi connected.");
Serial.println("IP address: ");
Serial.println(WiFi.localIP());
server.begin();
}
void loop() {
WiFiClient client = server.available(); // Listen for incoming clients
if (client) { // If a new client connects,
currentTime = millis();
previousTime = currentTime;
Serial.println("New Client."); // print a message out in the serial port
String currentLine = ""; // make a String to hold incoming data from the client
while (client.connected() && currentTime - previousTime <= timeoutTime) { // loop while the client's connected
currentTime = millis();
if (client.available()) { // if there's bytes to read from the client,
char c = client.read(); // read a byte, then
Serial.write(c); // print it out the serial monitor
header += c;
if (c == '\\n') { // if the byte is a newline character
// if the current line is blank, you got two newline characters in a row.
// that's the end of the client HTTP request, so send a response:
if (currentLine.length() == 0) {
// HTTP headers always start with a response code (e.g. HTTP/1.1 200 OK)
// and a content-type so the client knows what's coming, then a blank line:
client.println("HTTP/1.1 200 OK");
client.println("Content-type:text/html");
client.println("Connection: close");
client.println();
// Display the HTML web page
client.println("<!DOCTYPE html><html>");
client.println("<head><meta name=\\"viewport\\" content=\\"width=device-width, initial-scale=1\\">");
client.println("<link rel=\\"icon\\" href=\\"data:,\\">");
client.println("<link rel=\\"stylesheet\\" href=\\"https://stackpath.bootstrapcdn.com/bootstrap/4.3.1/css/bootstrap.min.css\\">");
client.println("<script src=\\"https://cdnjs.cloudflare.com/ajax/libs/jscolor/2.0.4/jscolor.min.js\\"></script>");
client.println("</head><body><div class=\\"container\\"><div class=\\"row\\"><h1>ESP Color Picker</h1></div>");
client.println("<a class=\\"btn btn-primary btn-lg\\" href=\\"#\\" id=\\"change_color\\" role=\\"button\\">Change Color</a> ");
client.println("<input class=\\"jscolor {onFineChange:'update(this)'}\\" id=\\"rgb\\"></div>");
client.println("<script>function update(picker) {document.getElementById('rgb').innerHTML = Math.round(picker.rgb[0]) + ', ' + Math.round(picker.rgb[1]) + ', ' + Math.round(picker.rgb[2]);");
client.println("document.getElementById(\\"change_color\\").href=\\"?r\\" + Math.round(picker.rgb[0]) + \\"g\\" + Math.round(picker.rgb[1]) + \\"b\\" + Math.round(picker.rgb[2]) + \\"&\\";}</script></body></html>");
// The HTTP response ends with another blank line
client.println();
// Request sample: /?r201g32b255&
// Red = 201 | Green = 32 | Blue = 255
if (header.indexOf("GET /?r") >= 0) {
pos1 = header.indexOf('r');
pos2 = header.indexOf('g');
pos3 = header.indexOf('b');
pos4 = header.indexOf('&');
redString = header.substring(pos1 + 1, pos2);
greenString = header.substring(pos2 + 1, pos3);
blueString = header.substring(pos3 + 1, pos4);
/*Serial.println(redString.toInt());
Serial.println(greenString.toInt());
Serial.println(blueString.toInt());*/
ledcWrite(redChannel, abs(255 - redString.toInt()));
ledcWrite(greenChannel, abs(255 - greenString.toInt()));
ledcWrite(blueChannel, abs(255 - blueString.toInt()));
}
// Break out of the while loop
break;
} else { // if you got a newline, then clear currentLine
currentLine = "";
}
} else if (c != '\\r') { // if you got anything else but a carriage return character,
currentLine += c; // add it to the end of the currentLine
}
}
}
// Clear the header variable
header = "";
// Close the connection
client.stop();
Serial.println("Client disconnected.");
Serial.println("");
}
}
以上是关于怎么用5v的arduino控制12v的共阴rgb灯带,用9014三极管的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章