问下matlab里image和imagesc有啥相同处和区别啊,使用时应该如何选择?
Posted
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了问下matlab里image和imagesc有啥相同处和区别啊,使用时应该如何选择?相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
参考技术A MATLAB图像处理之imshow和imagesc inshow主要用于调用图像索引,比如:imshow(X,map)其功能等同于:image(X)colormap(map)但是,inshow的功能要强大一些,比如用于灰度图像,RGB图像,二进制图像,都可以应用。imagesc属于图像缩放函数具体说一些例子:要显示一副灰度图像,可以调用函数imshow或imagesc(即imagescale,图像缩放函数) (1)imshow函数显示灰度图像使用imshow(I)或使用明确指定的灰度级书目:imshow(I,32)由于Matlab自动对灰度图像进行标度以适合调色板的范围,因而可以使用自定义大小的调色板。其调用格式如下:imshow(I,[low,high])其中,low和high分别为数据数组的最小值和最大值。 (2)imagesc函数显示灰度图像下面的代码是具有两个输入参数的imagesc函数显示一副灰度图像imagesc(1,[0,1]);colormap(gray);imagesc函数中的第二个参数确定灰度范围。灰度范围中的第一个值(通常是0),对应于颜色映象表中的第一个值(颜色),第二个值(通常是1)则对应与颜色映象表中的最后一个值(颜色)。灰度范围中间的值则线型对应与颜色映象表中剩余的值(颜色)。在调用imagesc函数时,若只使用一个参数,可以用任意灰度范围显示图像。在该调用方式下,数据矩阵中的最小值对应于颜色映象表中的第一个颜色值,数据矩阵中的最大值对应于颜色映象表中的最后一个颜色值。 5.3RGB图像及其显示(1)image(RGB)不管RGB图像的类型是double浮点型,还是uint8或uint16无符号整数型,Matlab都能通过image函数将其正确显示出来。RGB8=uint8(round(RGB64×255));%将double浮点型转换为uint8无符号整型RGB64=double(RGB8)/255;%将uint8无符号整型转换为double浮点型RGB16=uint16(round(RGB64×65535));%将double浮点型转换为uint16无符号整型RGB64=double(RGB16)/65535;%将uint16无符号整型转换为double浮点型(2)imshow(RGB)参数是一个m×n×3的数组 5.4二进制图像及其显示 (1)imshow(BW)在Matlab7.0中,二进制图像是一个逻辑类,仅包括0和1两个数值。像素0显示为黑色,像素1显示为白色。显示时,也可通过NOT(~)命令,对二进制图象进行取反,使数值0显示为白色;1显示为黑色。例如:imshow(~BW) (2)此外,还可以使用一个调色板显示一副二进制图像。如果图形是uint8数据类型,则数值0显示为调色板的第一个颜色,数值1显示为第二个颜色。例如:imshow(BW,[100;001])MATLAB 颜色图函数(imagesc/scatter/polarPcolor/pcolor)
2维的热度图 imagesc
imagesc(x, y, z),x和y分别是横纵坐标,z为值,表示颜色
1 imagesc(theta,phi,slc); colorbar 2 xlabel(‘theta(°)‘,‘fontname‘,‘Times New Roman‘,‘FontSize‘,14); 3 ylabel(‘phi(°)‘,‘fontname‘,‘Times New Roman‘,‘FontSize‘,14); 4 sta = ‘3 objects at (θ,φ,r) : (-30,30,1) (0,0,2) (60,-60,0.5)‘; 5 str=sprintf(strcat(‘3D Imaging Slice at :‘, num2str(d_max*D/N), ‘(m)‘, ‘ ‘,sta)); 6 title(str, ‘fontname‘,‘Times New Roman‘,‘Color‘,‘k‘,‘FontSize‘,13); 7 grid on
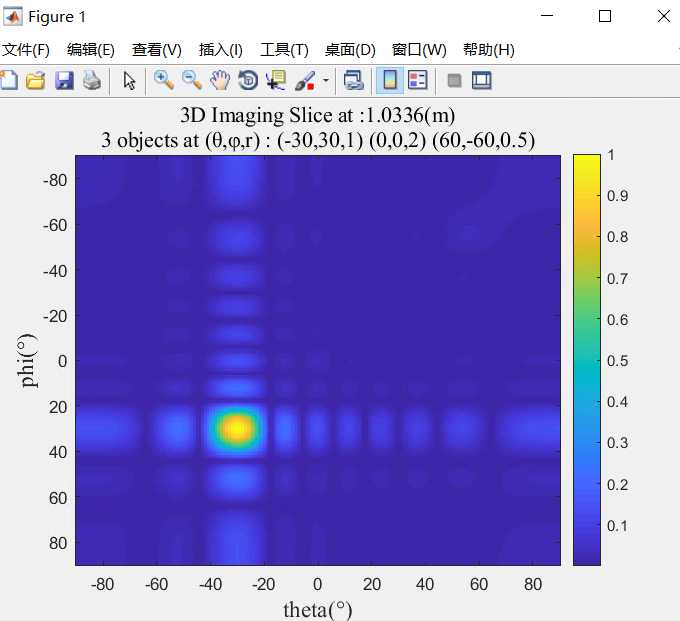
其中,colorbar的坐标值调整:caxis([0 1]);
colormap的色系调整:colormap hot
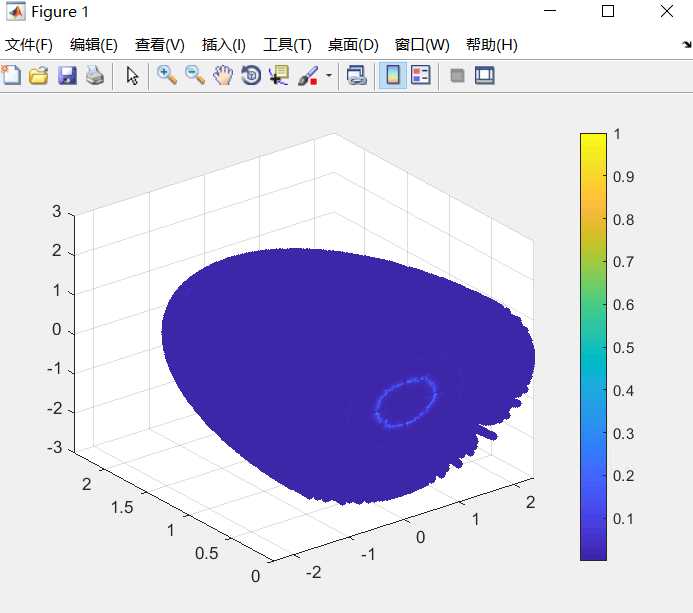
3维散点图 scatter
1 scatter3(x,y,z,24,c,‘filled‘); 2 % axis([-(R+2) (R+2) -(R+2) (R+2) 0 (h+2)]); 3 colorbar
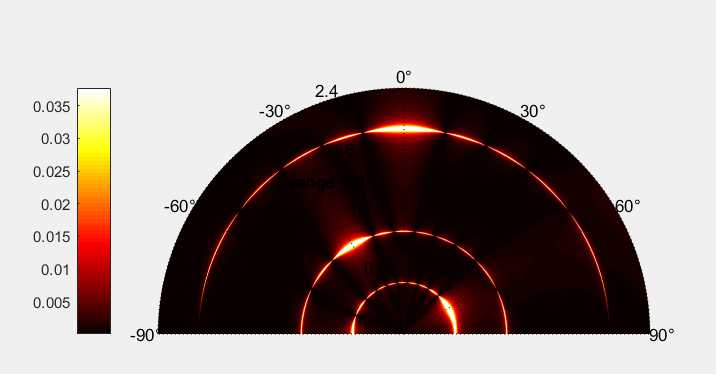
2维 极坐标热度图 polarPcolor
polarPcolor(R_axis, theta, value),前两个为半径方向坐标轴和圆心角坐标轴,value为值,用颜色表示
1 [fig, clr] = polarPcolor(R_axis, theta, x_d_th, ‘labelR‘,‘range (m)‘,‘Ncircles‘, 5,‘Nspokes‘,7); 2 colormap hot 3 % caxis([0 1]);
其中polarPcolor代码如下:

1 function [varargout] = polarPcolor(R,theta,Z,varargin) 2 % [h,c] = polarPcolor1(R,theta,Z,varargin) is a pseudocolor plot of matrix 3 % Z for a vector radius R and a vector angle theta. 4 % The elements of Z specify the color in each cell of the 5 % plot. The goal is to apply pcolor function with a polar grid, which 6 % provides a better visualization than a cartesian grid. 7 % 8 %% Syntax 9 % 10 % [h,c] = polarPcolor(R,theta,Z) 11 % [h,c] = polarPcolor(R,theta,Z,‘Ncircles‘,10) 12 % [h,c] = polarPcolor(R,theta,Z,‘Nspokes‘,5) 13 % [h,c] = polarPcolor(R,theta,Z,‘Nspokes‘,5,‘colBar‘,0) 14 % [h,c] = polarPcolor(R,theta,Z,‘Nspokes‘,5,‘labelR‘,‘r (km)‘) 15 % 16 % INPUT 17 % * R : 18 % - type: float 19 % - size: [1 x Nrr ] where Nrr = numel(R). 20 % - dimension: radial distance. 21 % * theta : 22 % - type: float 23 % - size: [1 x Ntheta ] where Ntheta = numel(theta). 24 % - dimension: azimuth or elevation angle (deg). 25 % - N.B.: The zero is defined with respect to the North. 26 % * Z : 27 % - type: float 28 % - size: [Ntheta x Nrr] 29 % - dimension: user‘s defined . 30 % * varargin: 31 % - Ncircles: number of circles for the grid definition. 32 % - Nspokes: number of spokes for the grid definition. 33 % - colBar: display the colorbar or not. 34 % - labelR: legend for R. 35 % 36 % 37 % OUTPUT 38 % h: returns a handle to a SURFACE object. 39 % c: returns a handle to a COLORBAR object. 40 % 41 %% Examples 42 % R = linspace(3,10,100); 43 % theta = linspace(0,180,360); 44 % Z = linspace(0,10,360)‘*linspace(0,10,100); 45 % figure 46 % polarPcolor(R,theta,Z,‘Ncircles‘,3) 47 % 48 %% Author 49 % Etienne Cheynet, University of Stavanger, Norway. 28/05/2016 50 % see also pcolor 51 % 52 53 %% InputParseer 54 p = inputParser(); 55 p.CaseSensitive = false; 56 p.addOptional(‘Ncircles‘,5); 57 p.addOptional(‘Nspokes‘,8); 58 p.addOptional(‘labelR‘,‘‘); 59 p.addOptional(‘colBar‘,1); 60 p.parse(varargin{:}); 61 62 Ncircles = p.Results.Ncircles ; 63 Nspokes = p.Results.Nspokes ; 64 labelR = p.Results.labelR ; 65 colBar = p.Results.colBar ; 66 %% Preliminary checks 67 % case where dimension is reversed 68 Nrr = numel(R); 69 Noo = numel(theta); 70 if isequal(size(Z),[Noo,Nrr]), 71 Z=Z‘; 72 end 73 74 % case where dimension of Z is not compatible with theta and R 75 if ~isequal(size(Z),[Nrr,Noo]) 76 fprintf(‘ ‘) 77 fprintf([ ‘Size of Z is : [‘,num2str(size(Z)),‘] ‘]); 78 fprintf([ ‘Size of R is : [‘,num2str(size(R)),‘] ‘]); 79 fprintf([ ‘Size of theta is : [‘,num2str(size(theta)),‘] ‘]); 80 error(‘ dimension of Z does not agree with dimension of R and Theta‘) 81 end 82 %% data plot 83 rMin = min(R); 84 rMax = max(R); 85 thetaMin=min(theta); 86 thetaMax =max(theta); 87 % Definition of the mesh 88 Rrange = rMax - rMin; % get the range for the radius 89 rNorm = R/Rrange; %normalized radius [0,1] 90 % get hold state 91 cax = newplot; 92 % transform data in polar coordinates to Cartesian coordinates. 93 YY = (rNorm)‘*cosd(theta); 94 XX = (rNorm)‘*sind(theta); 95 % plot data on top of grid 96 h = pcolor(XX,YY,Z,‘parent‘,cax); 97 shading flat 98 set(cax,‘dataaspectratio‘,[1 1 1]);axis off; 99 if ~ishold(cax); 100 % make a radial grid 101 hold(cax,‘on‘) 102 % Draw circles and spokes 103 createSpokes(thetaMin,thetaMax,Ncircles,Nspokes); 104 createCircles(rMin,rMax,thetaMin,thetaMax,Ncircles,Nspokes) 105 end 106 107 %% PLot colorbar if specified 108 if colBar==1, 109 c =colorbar(‘location‘,‘WestOutside‘); 110 caxis([quantile(Z(:),0.01),quantile(Z(:),0.99)]) 111 else 112 c = []; 113 end 114 115 %% Outputs 116 nargoutchk(0,2) 117 if nargout==1, 118 varargout{1}=h; 119 elseif nargout==2, 120 varargout{1}=h; 121 varargout{2}=c; 122 end 123 124 %%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%% 125 % Nested functions 126 %%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%% 127 function createSpokes(thetaMin,thetaMax,Ncircles,Nspokes) 128 129 circleMesh = linspace(rMin,rMax,Ncircles); 130 spokeMesh = linspace(thetaMin,thetaMax,Nspokes); 131 contour = abs((circleMesh - circleMesh(1))/Rrange+R(1)/Rrange); 132 cost = cosd(90-spokeMesh); % the zero angle is aligned with North 133 sint = sind(90-spokeMesh); % the zero angle is aligned with North 134 for kk = 1:Nspokes 135 plot(cost(kk)*contour,sint(kk)*contour,‘k:‘,... 136 ‘handlevisibility‘,‘off‘); 137 % plot graduations of angles 138 % avoid superimposition of 0 and 360 139 if and(thetaMin==0,thetaMax == 360), 140 if spokeMesh(kk)<360, 141 142 text(1.05.*contour(end).*cost(kk),... 143 1.05.*contour(end).*sint(kk),... 144 [num2str(spokeMesh(kk),3),char(176)],... 145 ‘horiz‘, ‘center‘, ‘vert‘, ‘middle‘); 146 end 147 else 148 text(1.05.*contour(end).*cost(kk),... 149 1.05.*contour(end).*sint(kk),... 150 [num2str(spokeMesh(kk),3),char(176)],... 151 ‘horiz‘, ‘center‘, ‘vert‘, ‘middle‘); 152 end 153 154 end 155 end 156 function createCircles(rMin,rMax,thetaMin,thetaMax,Ncircles,Nspokes) 157 158 % define the grid in polar coordinates 159 angleGrid = linspace(90-thetaMin,90-thetaMax,100); 160 xGrid = cosd(angleGrid); 161 yGrid = sind(angleGrid); 162 circleMesh = linspace(rMin,rMax,Ncircles); 163 spokeMesh = linspace(thetaMin,thetaMax,Nspokes); 164 contour = abs((circleMesh - circleMesh(1))/Rrange+R(1)/Rrange); 165 % plot circles 166 for kk=1:length(contour) 167 plot(xGrid*contour(kk), yGrid*contour(kk),‘k:‘); 168 end 169 % radius tick label 170 for kk=1:Ncircles 171 172 position = 0.51.*(spokeMesh(min(Nspokes,round(Ncircles/2)))+... 173 spokeMesh(min(Nspokes,1+round(Ncircles/2)))); 174 175 if abs(round(position)) ==90, 176 % radial graduations 177 text((contour(kk)).*cosd(90-position),... 178 (0.1+contour(kk)).*sind(86-position),... 179 num2str(circleMesh(kk),2),‘verticalalignment‘,‘BaseLine‘,... 180 ‘horizontalAlignment‘, ‘center‘,... 181 ‘handlevisibility‘,‘off‘,‘parent‘,cax); 182 183 % annotate spokes 184 text(contour(end).*0.6.*cosd(90-position),... 185 0.07+contour(end).*0.6.*sind(90-position),... 186 [labelR],‘verticalalignment‘,‘bottom‘,... 187 ‘horizontalAlignment‘, ‘right‘,... 188 ‘handlevisibility‘,‘off‘,‘parent‘,cax); 189 else 190 % radial graduations 191 text((contour(kk)).*cosd(90-position),... 192 (contour(kk)).*sind(90-position),... 193 num2str(circleMesh(kk),2),‘verticalalignment‘,‘BaseLine‘,... 194 ‘horizontalAlignment‘, ‘right‘,... 195 ‘handlevisibility‘,‘off‘,‘parent‘,cax); 196 197 % annotate spokes 198 text(contour(end).*0.6.*cosd(90-position),... 199 contour(end).*0.6.*sind(90-position),... 200 [labelR],‘verticalalignment‘,‘bottom‘,... 201 ‘horizontalAlignment‘, ‘right‘,... 202 ‘handlevisibility‘,‘off‘,‘parent‘,cax); 203 end 204 end 205 206 end 207 end
再贴一个示例代码:

1 %% Examples 2 % The following examples illustrate the application of the function 3 % polarPcolor 4 clearvars;close all;clc; 5 6 %% Minimalist example 7 % Assuming that a remote sensor is measuring the wind field for a radial 8 % distance ranging from 50 to 1000 m. The scanning azimuth is oriented from 9 % North (0 deg) to North-North-East ( 80 deg): 10 R = linspace(50,1000,100)./1000; % (distance in km) 11 Az = linspace(0,80,100); % in degrees 12 [~,~,windSpeed] = peaks(100); % radial wind speed 13 figure(1) 14 [h,c]=polarPcolor(R,Az,windSpeed); 15 16 %% Example with options 17 % We want to have 4 circles and 7 spokes, and to give a label to the 18 % radial coordinate 19 20 figure(2) 21 [~,c]=polarPcolor(R,Az,windSpeed,‘labelR‘,‘r (km)‘,‘Ncircles‘,7,‘Nspokes‘,7); 22 ylabel(c,‘ radial wind speed (m/s)‘); 23 set(gcf,‘color‘,‘w‘) 24 %% Dealing with outliers 25 % We introduce outliers in the wind velocity data. These outliers 26 % are represented as wind speed sample with a value of 100 m/s. These 27 % corresponds to unrealistic data that need to be ignored. To avoid bad 28 % scaling of the colorbar, the function polarPcolor uses the function caxis 29 % combined to the function quantile to keep the colorbar properly scaled: 30 % caxis([quantile(Z(:),0.01),quantile(Z(:),0.99)]) 31 32 windSpeed(1:10:end,1:20:end)=100; 33 34 figure(3) 35 [~,c]=polarPcolor(R,Az,windSpeed); 36 ylabel(c,‘ radial wind speed (m/s)‘); 37 set(gcf,‘color‘,‘w‘) 38 39 %% polarPcolor without colorbar 40 % The colorbar is activated by default. It is possible to remove it by 41 % using the option ‘colBar‘. When the colorbar is desactivated, the 42 % outliers are not "removed" and bad scaling is clearly visible: 43 44 figure(4) 45 polarPcolor(R,Az,windSpeed,‘colBar‘,0) ; 46 47 48 %% Different geometry 1 49 N = 360; 50 R = linspace(0,1000,N)./1000; % (distance in km) 51 Az = linspace(0,360,N); % in degrees 52 [~,~,windSpeed] = peaks(N); % radial wind speed 53 figure(5) 54 [~,c]= polarPcolor(R,Az,windSpeed); 55 ylabel(c,‘ radial wind speed (m/s)‘); 56 set(gcf,‘color‘,‘w‘) 57 %% Different geometry 2 58 N = 360; 59 R = linspace(500,1000,N)./1000; % (distance in km) 60 Az = linspace(0,270,N); % in degrees 61 [~,~,windSpeed] = peaks(N); % radial wind speed 62 figure(6) 63 [~,c]= polarPcolor(R,Az,windSpeed,‘Ncircles‘,3); 64 location = ‘NorthOutside‘; 65 ylabel(c,‘ radial wind speed (m/s)‘); 66 set(c,‘location‘,location); 67 set(gcf,‘color‘,‘w‘)
以上是关于问下matlab里image和imagesc有啥相同处和区别啊,使用时应该如何选择?的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章
