dubbo整体架构
Posted
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了dubbo整体架构相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
参考技术A 一、dubbo 核心调用链路 消费者、生产者、注册中心、监控中心二、dubbo详细流程调用图
三、dubbo 分层架构图
Dubbo框架设计一共划分了10个层,而最上面的Service层是留给实际想要使用Dubbo开发分布式服务的开发者实现业务逻辑的接口层。图中左边淡蓝背景的为服务消费方使用的接口,右边淡绿色背景的为服务提供方使用的接口, 位于中轴线上的为双方都用到的接口。
下面,结合Dubbo官方文档,我们分别理解一下框架分层架构中,各个层次的设计要点:
服务接口层(Service):该层是与实际业务逻辑相关的,根据服务提供方和服务消费方的业务设计对应的接口和实现。
配置层(Config):对外配置接口,以ServiceConfig和ReferenceConfig为中心,可以直接new配置类,也可以通过spring解析配置生成配置类。
服务代理层(Proxy):服务接口透明代理,生成服务的客户端Stub和服务器端Skeleton,以ServiceProxy为中心,扩展接口为ProxyFactory。
服务注册层(Registry):封装服务地址的注册与发现,以服务URL为中心,扩展接口为RegistryFactory、Registry和RegistryService。可能没有服务注册中心,此时服务提供方直接暴露服务。
集群层(Cluster):封装多个提供者的路由及负载均衡,并桥接注册中心,以Invoker为中心,扩展接口为Cluster、Directory、Router和LoadBalance。将多个服务提供方组合为一个服务提供方,实现对服务消费方来透明,只需要与一个服务提供方进行交互。
监控层(Monitor):RPC调用次数和调用时间监控,以Statistics为中心,扩展接口为MonitorFactory、Monitor和MonitorService。
远程调用层(Protocol):封将RPC调用,以Invocation和Result为中心,扩展接口为Protocol、Invoker和Exporter。Protocol是服务域,它是Invoker暴露和引用的主功能入口,它负责Invoker的生命周期管理。Invoker是实体域,它是Dubbo的核心模型,其它模型都向它靠扰,或转换成它,它代表一个可执行体,可向它发起invoke调用,它有可能是一个本地的实现,也可能是一个远程的实现,也可能一个集群实现。
信息交换层(Exchange):封装请求响应模式,同步转异步,以Request和Response为中心,扩展接口为Exchanger、ExchangeChannel、ExchangeClient和ExchangeServer。
网络传输层(Transport):抽象mina和NETty为统一接口,以Message为中心,扩展接口为Channel、Transporter、Client、Server和Codec。
数据序列化层(Serialize):可复用的一些工具,扩展接口为Serialization、 ObjectInput、ObjectOutput和ThreadPool。
从上图可以看出,Dubbo对于服务提供方和服务消费方,从框架的10层中分别提供了各自需要关心和扩展的接口,构建整个服务生态系统(服务提供方和服务消费方本身就是一个以服务为中心的)
后续我们将从这10个模块去分析dubbo源码。源码版本基于dubbo 2.7.9
Dubbo原理和源码解析之服务暴露
github新增仓库 "dubbo-read"(点此查看),集合所有《Dubbo原理和源码解析》系列文章,后续将继续补充该系列,同时将针对Dubbo所做的功能扩展也进行分享。不定期更新,欢迎Follow。
一、框架设计
在官方《Dubbo 用户指南》架构部分,给出了服务调用的整体架构和流程:
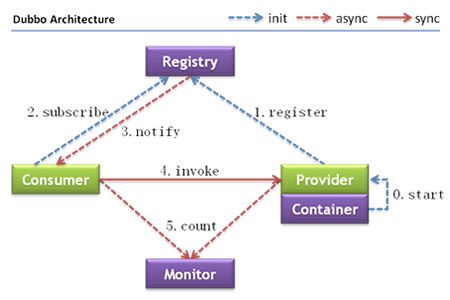
另外,在官方《Dubbo 开发指南》框架设计部分,给出了整体设计:

以及暴露服务时序图:

本文将根据以上几张图,分析服务暴露的实现原理,并进行详细的代码跟踪与解析。
二、原理和源码解析
2.1 标签解析
从文章《Dubbo原理和源码解析之标签解析》中我们知道,<dubbo:service> 标签会被解析成 ServiceBean。
ServiceBean 实现了 InitializingBean,在类加载完成之后会调用 afterPropertiesSet() 方法。在 afterPropertiesSet() 方法中,依次解析以下标签信息:
- <dubbo:provider>
- <dubbo:application>
- <dubbo:module>
- <dubbo:registry>
- <dubbo:monitor>
- <dubbo:protocol>
ServiceBean 还实现了 ApplicationListener,在 Spring 容器初始化的时候会调用 onApplicationEvent 方法。ServiceBean 重写了 onApplicationEvent 方法,实现了服务暴露的功能。
ServiceBean.java
public void onApplicationEvent(ApplicationEvent event) { if (ContextRefreshedEvent.class.getName().equals(event.getClass().getName())) { if (isDelay() && ! isExported() && ! isUnexported()) { if (logger.isInfoEnabled()) { logger.info("The service ready on spring started. service: " + getInterface()); } export(); } } }
2.2 延迟暴露
ServiceBean 扩展了 ServiceConfig,调用 export() 方法时由 ServiceConfig 完成服务暴露的功能实现。
ServiceConfig.java
public synchronized void export() { if (provider != null) { if (export == null) { export = provider.getExport(); } if (delay == null) { delay = provider.getDelay(); } } if (export != null && ! export.booleanValue()) { return; } if (delay != null && delay > 0) { Thread thread = new Thread(new Runnable() { public void run() { try { Thread.sleep(delay); } catch (Throwable e) { } doExport(); } }); thread.setDaemon(true); thread.setName("DelayExportServiceThread"); thread.start(); } else { doExport(); } }
由上面代码可知,如果设置了 delay 参数,Dubbo 的处理方式是启动一个守护线程在 sleep 指定时间后再 doExport。
2.3 参数检查
在 ServiceConfig 的 doExport() 方法中会进行参数检查和设置,包括:
- 泛化调用
- 本地实现
- 本地存根
- 本地伪装
- 配置(application、registry、protocol等)
ServiceConfig.java
protected synchronized void doExport() { if (unexported) { throw new IllegalStateException("Already unexported!"); } if (exported) { return; } exported = true; if (interfaceName == null || interfaceName.length() == 0) { throw new IllegalStateException("<dubbo:service interface=\\"\\" /> interface not allow null!"); } checkDefault(); //省略 if (ref instanceof GenericService) { interfaceClass = GenericService.class; generic = true; } else { try { interfaceClass = Class.forName(interfaceName, true, Thread.currentThread() .getContextClassLoader()); } catch (ClassNotFoundException e) { throw new IllegalStateException(e.getMessage(), e); } checkInterfaceAndMethods(interfaceClass, methods); checkRef(); generic = false; } if(local !=null){ if(local=="true"){ local=interfaceName+"Local"; } Class<?> localClass; try { localClass = ClassHelper.forNameWithThreadContextClassLoader(local); } catch (ClassNotFoundException e) { throw new IllegalStateException(e.getMessage(), e); } if(!interfaceClass.isAssignableFrom(localClass)){ throw new IllegalStateException("The local implemention class " + localClass.getName() + " not implement interface " + interfaceName); } } if(stub !=null){ if(stub=="true"){ stub=interfaceName+"Stub"; } Class<?> stubClass; try { stubClass = ClassHelper.forNameWithThreadContextClassLoader(stub); } catch (ClassNotFoundException e) { throw new IllegalStateException(e.getMessage(), e); } if(!interfaceClass.isAssignableFrom(stubClass)){ throw new IllegalStateException("The stub implemention class " + stubClass.getName() + " not implement interface " + interfaceName); } } //此处省略:检查并设置相关参数 doExportUrls(); }
2.4 多协议、多注册中心
在检查完参数之后,开始暴露服务。Dubbo 支持多协议和多注册中心:
ServiceConfig.java
private void doExportUrls() { List<URL> registryURLs = loadRegistries(true); for (ProtocolConfig protocolConfig : protocols) { doExportUrlsFor1Protocol(protocolConfig, registryURLs); } }
2.5 组装URL
针对每个协议、每个注册中心,开始组装 URL。
ServiceConfig.java
private void doExportUrlsFor1Protocol(ProtocolConfig protocolConfig, List<URL> registryURLs) { String name = protocolConfig.getName(); if (name == null || name.length() == 0) { name = "dubbo"; } //处理host //处理port Map<String, String> map = new HashMap<String, String>(); //设置参数到map // 导出服务 String contextPath = protocolConfig.getContextpath(); if ((contextPath == null || contextPath.length() == 0) && provider != null) { contextPath = provider.getContextpath(); } URL url = new URL(name, host, port, (contextPath == null || contextPath.length() == 0 ? "" : contextPath + "/") + path, map); if (ExtensionLoader.getExtensionLoader(ConfiguratorFactory.class) .hasExtension(url.getProtocol())) { url = ExtensionLoader.getExtensionLoader(ConfiguratorFactory.class) .getExtension(url.getProtocol()).getConfigurator(url).configure(url); } //此处省略:服务暴露(详见 2.6 和 2.7) this.urls.add(url); }
2.6 本地暴露
如果配置 scope=none, 则不会进行服务暴露;如果没有配置 scope 或者 scope=local,则会进行本地暴露。
ServiceConfig.java
//public static final String LOCAL_PROTOCOL = "injvm"; //public static final String LOCALHOST = "127.0.0.1"; private void doExportUrlsFor1Protocol(ProtocolConfig protocolConfig, List<URL> registryURLs) { //...... String scope = url.getParameter(Constants.SCOPE_KEY); //配置为none不暴露 if (! Constants.SCOPE_NONE.toString().equalsIgnoreCase(scope)) { //配置不是remote的情况下做本地暴露 (配置为remote,则表示只暴露远程服务) if (!Constants.SCOPE_REMOTE.toString().equalsIgnoreCase(scope)) { exportLocal(url); } //...... } //...... } private void exportLocal(URL url) { if (!Constants.LOCAL_PROTOCOL.equalsIgnoreCase(url.getProtocol())) { URL local = URL.valueOf(url.toFullString()) .setProtocol(Constants.LOCAL_PROTOCOL) .setHost(NetUtils.LOCALHOST) .setPort(0); Exporter<?> exporter = protocol.export( proxyFactory.getInvoker(ref, (Class) interfaceClass, local)); exporters.add(exporter); logger.info("Export dubbo service " + interfaceClass.getName() +" to local registry"); } }
1. 暴露服务的时候,会通过代理创建 Invoker;
2. 本地暴露时使用 injvm 协议,injvm 协议是一个伪协议,它不开启端口,不能被远程调用,只在 JVM 内直接关联,但执行 Dubbo 的 Filter 链。