nacos源码分析-心跳检测(服务端)
Posted 墨家巨子@俏如来
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了nacos源码分析-心跳检测(服务端)相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
前言
前面我们讲了《nacos源码分析-服务注册(客户端)》 和 《nacos源码分析-服务注册(服务端)》,主要是讲的服务注册流程,本章节我们来讲服务心跳检测机制。
心跳续约客户端
其实我们在讲 nacos服务注册客户端的时候顺带就说了心跳,服务注册流程是:
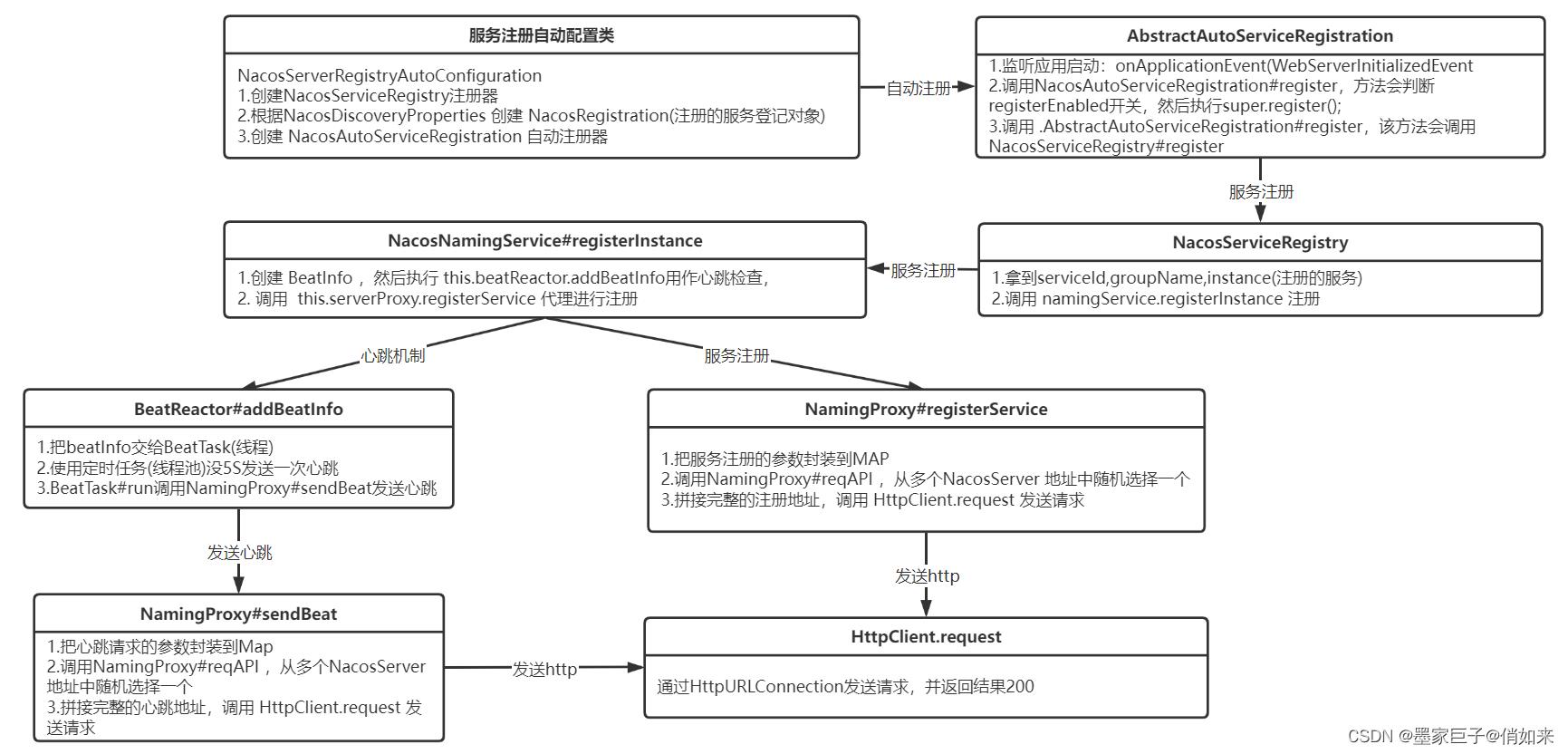
nacos客户端服务心跳在服务注册的流程中触发,这里我再贴一下源码, NacosNamingService#registerInstance的源码:
public void registerInstance(String serviceName, String groupName, Instance instance) throws NacosException
if (instance.isEphemeral())
BeatInfo beatInfo = new BeatInfo();
beatInfo.setServiceName(NamingUtils.getGroupedName(serviceName, groupName));
beatInfo.setIp(instance.getIp());
beatInfo.setPort(instance.getPort());
beatInfo.setCluster(instance.getClusterName());
beatInfo.setWeight(instance.getWeight());
beatInfo.setMetadata(instance.getMetadata());
beatInfo.setScheduled(false);
beatInfo.setPeriod(instance.getInstanceHeartBeatInterval());
//添加心跳
this.beatReactor.addBeatInfo(NamingUtils.getGroupedName(serviceName, groupName), beatInfo);
this.serverProxy.registerService(NamingUtils.getGroupedName(serviceName, groupName), groupName, instance);
这里就看的比较清楚了,这里会把服务的ip,端口,服务名等信息封装到 BeatInfo 对象中,beatReactor.addBeatInfo是把当前服务实例加入心跳机制(心跳续约),然后通过serverProxy.registerService注册
代码在 BeatReactor#addBeatInfo中添加的心跳续约,在 NacosNamingService#registerInstance方法中把服务信息封装为一个 BeatInfo ,然后加入this.beatReactor.addBeatInfo 心跳机制。我们来看一下心跳是如何做的,下面是beatReactor.addBeatInfo的源码
public void addBeatInfo(String serviceName, BeatInfo beatInfo)
LogUtils.NAMING_LOGGER.info("[BEAT] adding beat: to beat map.", beatInfo);
String key = this.buildKey(serviceName, beatInfo.getIp(), beatInfo.getPort());
BeatInfo existBeat = null;
if ((existBeat = (BeatInfo)this.dom2Beat.remove(key)) != null)
existBeat.setStopped(true);
this.dom2Beat.put(key, beatInfo);
//线程池,定时任务,5000毫秒发送一次心跳。beatInfo.getPeriod()是定时任务执行的频率
this.executorService.schedule(new BeatTask(beatInfo), beatInfo.getPeriod(), TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS);
MetricsMonitor.getDom2BeatSizeMonitor().set((double)this.dom2Beat.size());
//心跳任务
class BeatTask implements Runnable
BeatInfo beatInfo;
public BeatTask(BeatInfo beatInfo)
this.beatInfo = beatInfo;
public void run()
if (!this.beatInfo.isStopped())
long nextTime = this.beatInfo.getPeriod();
try
//发送心跳请求,拿到结果
JSONObject result = BeatReactor.this.serverProxy.sendBeat(this.beatInfo, BeatReactor.this.lightBeatEnabled);
long interval = (long)result.getIntValue("clientBeatInterval");
boolean lightBeatEnabled = false;
if (result.containsKey("lightBeatEnabled"))
lightBeatEnabled = result.getBooleanValue("lightBeatEnabled");
BeatReactor.this.lightBeatEnabled = lightBeatEnabled;
if (interval > 0L)
nextTime = interval;
int code = 10200;
if (result.containsKey("code"))
code = result.getIntValue("code");
if (code == 20404)
//实例不存在就创建
Instance instance = new Instance();
instance.setPort(this.beatInfo.getPort());
instance.setIp(this.beatInfo.getIp());
instance.setWeight(this.beatInfo.getWeight());
instance.setMetadata(this.beatInfo.getMetadata());
instance.setClusterName(this.beatInfo.getCluster());
instance.setServiceName(this.beatInfo.getServiceName());
instance.setInstanceId(instance.getInstanceId());
instance.setEphemeral(true);
try
//注册服务
BeatReactor.this.serverProxy.registerService(this.beatInfo.getServiceName(), NamingUtils.getGroupName(this.beatInfo.getServiceName()), instance);
catch (Exception var10)
catch (NacosException var11)
LogUtils.NAMING_LOGGER.error("[CLIENT-BEAT] failed to send beat: , code: , msg: ", new Object[]JSON.toJSONString(this.beatInfo), var11.getErrCode(), var11.getErrMsg());
//定时任务:5s一次执行心跳任务
BeatReactor.this.executorService.schedule(BeatReactor.this.new BeatTask(this.beatInfo), nextTime, TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS);
和Eureka一样,心跳也是通过线程池 ScheduledExecutorService 来实现的,时间频率默认是5秒一次。
- BeatInfo : 心跳续约的对象,其中包括服务的IP,端口,服务名,权重等
- executorService.schedule :定时任务,beatInfo.getPeriod()是定时任务执行频率,默认是5000 毫秒发送一次心跳续约请求到NacosServer
- BeatTask :是一个Runnable线程,run方法中会调用 BeatReactor.this.serverProxy.sendBeat 发送心跳请求。
BeatTask作为心跳续约的线程对象,他的run方法中 通过 BeatReactor.this.serverProxy.sendBeat发送心跳,如果发现服务未注册会通过 BeatReactor.this.serverProxy.registerService 注册服务。
下面是 com.alibaba.nacos.client.naming.net.NamingProxy#sendBeat 发送心跳的方法
public JSONObject sendBeat(BeatInfo beatInfo, boolean lightBeatEnabled) throws NacosException
if (LogUtils.NAMING_LOGGER.isDebugEnabled())
LogUtils.NAMING_LOGGER.debug("[BEAT] sending beat to server: ", this.namespaceId, beatInfo.toString());
Map<String, String> params = new HashMap(8);
String body = "";
if (!lightBeatEnabled)
try
body = "beat=" + URLEncoder.encode(JSON.toJSONString(beatInfo), "UTF-8");
catch (UnsupportedEncodingException var6)
throw new NacosException(500, "encode beatInfo error", var6);
params.put("namespaceId", this.namespaceId);
params.put("serviceName", beatInfo.getServiceName());
params.put("clusterName", beatInfo.getCluster());
params.put("ip", beatInfo.getIp());
params.put("port", String.valueOf(beatInfo.getPort()));
String result = this.reqAPI(UtilAndComs.NACOS_URL_BASE + "/instance/beat", params, body, "PUT");
return JSON.parseObject(result);
这里也是会拼接好心跳的地址 :127.0.0.1:8848/nacos/v1/ns/instance/beat ,参数包括namespaceId命名空间ID;serviceName 服务名;clusterName 集群名;ip 服务的IP;port 端口。然后发送一个PUT请求。底层依然是从多个NacosServer随机选择一个发起心跳请求。底层交给httpClient去执行
心跳续约服务端
服务端还是在InstanceController中,其中提供了一个beat方法,我们出了要考虑他是如何处理心跳请求外,还要考虑他是如何做心跳过期检查的。源码如下
/**
* Create a beat for instance.
* 心跳检测
* @param request http request
* @return detail information of instance
* @throws Exception any error during handle
*/
@CanDistro
@PutMapping("/beat")
@Secured(parser = NamingResourceParser.class, action = ActionTypes.WRITE)
public ObjectNode beat(HttpServletRequest request) throws Exception
//客户端心跳频率 5s/次
ObjectNode result = JacksonUtils.createEmptyJsonNode();
result.put(SwitchEntry.CLIENT_BEAT_INTERVAL, switchDomain.getClientBeatInterval());
//拿到请求中的beat数据,转成clientBeat对象
String beat = WebUtils.optional(request, "beat", StringUtils.EMPTY);
RsInfo clientBeat = null;
if (StringUtils.isNotBlank(beat))
clientBeat = JacksonUtils.toObj(beat, RsInfo.class);
//集群名
String clusterName = WebUtils
.optional(request, CommonParams.CLUSTER_NAME, UtilsAndCommons.DEFAULT_CLUSTER_NAME);
//拿到客户端IP,端口
String ip = WebUtils.optional(request, "ip", StringUtils.EMPTY);
int port = Integer.parseInt(WebUtils.optional(request, "port", "0"));
if (clientBeat != null)
if (StringUtils.isNotBlank(clientBeat.getCluster()))
clusterName = clientBeat.getCluster();
else
// fix #2533
clientBeat.setCluster(clusterName);
ip = clientBeat.getIp();
port = clientBeat.getPort();
//拿到命名空间ID和服务名
String namespaceId = WebUtils.optional(request, CommonParams.NAMESPACE_ID, Constants.DEFAULT_NAMESPACE_ID);
String serviceName = WebUtils.required(request, CommonParams.SERVICE_NAME);
//检查服务名
NamingUtils.checkServiceNameFormat(serviceName);
Loggers.SRV_LOG.debug("[CLIENT-BEAT] full arguments: beat: , serviceName: ", clientBeat, serviceName);
//拿到服务表中的服务实例
Instance instance = serviceManager.getInstance(namespaceId, serviceName, clusterName, ip, port);
// 如果获取失败,说明心跳失败,实例尚未注册
if (instance == null)
if (clientBeat == null) //如果客户端心跳出现为空(请求参数中没beat),返回资源没找到
result.put(CommonParams.CODE, NamingResponseCode.RESOURCE_NOT_FOUND);
return result;
Loggers.SRV_LOG.warn("[CLIENT-BEAT] The instance has been removed for health mechanism, "
+ "perform data compensation operations, beat: , serviceName: ", clientBeat, serviceName);
//创建一个实例
instance = new Instance();
instance.setPort(clientBeat.getPort());
instance.setIp(clientBeat.getIp());
instance.setWeight(clientBeat.getWeight());
instance.setMetadata(clientBeat.getMetadata());
instance.setClusterName(clusterName);
instance.setServiceName(serviceName);
instance.setInstanceId(instance.getInstanceId());
instance.setEphemeral(clientBeat.isEphemeral());
//注册实例
serviceManager.registerInstance(namespaceId, serviceName, instance);
//获取服务
Service service = serviceManager.getService(namespaceId, serviceName);
if (service == null)
//服务为空
throw new NacosException(NacosException.SERVER_ERROR,
"service not found: " + serviceName + "@" + namespaceId);
if (clientBeat == null)
clientBeat = new RsInfo();
clientBeat.setIp(ip);
clientBeat.setPort(port);
clientBeat.setCluster(clusterName);
//处理心跳请求
service.processClientBeat(clientBeat);
result.put(CommonParams.CODE, NamingResponseCode.OK);
if (instance.containsMetadata(PreservedMetadataKeys.HEART_BEAT_INTERVAL))
result.put(SwitchEntry.CLIENT_BEAT_INTERVAL, instance.getInstanceHeartBeatInterval());
result.put(SwitchEntry.LIGHT_BEAT_ENABLED, switchDomain.isLightBeatEnabled());
return result;
方法大致逻辑如下
- 拿到心跳请求参数,beat,其中包括客户端服务的IP,端口,服务名,命名空间等
- 通过serviceManager 从服务端服务注册表中拿到当前心跳请求的服务实例
- 如果实例为空会创建新的instance,通过serviceManager注册实例
- 然后拿到当前服务的service对象,调用 service.processClientBeat 方法处理心跳
- 最后返回OK
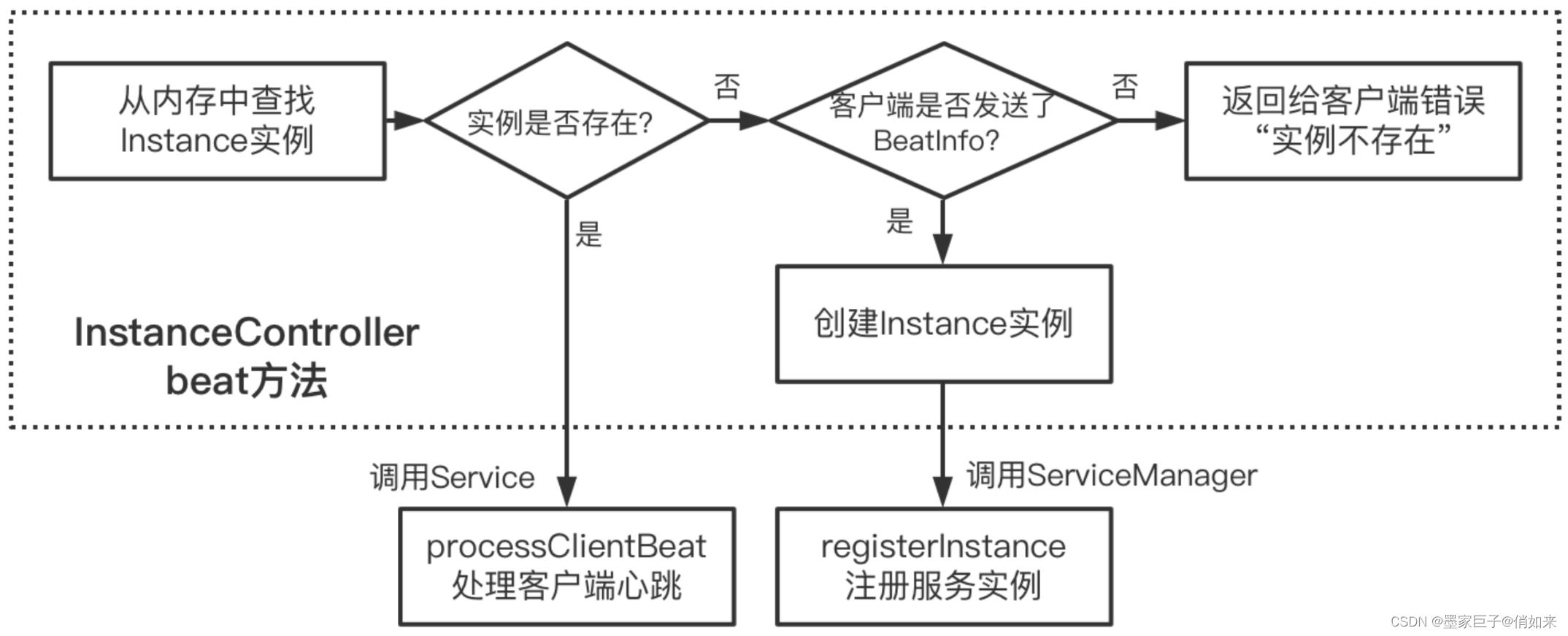
下面是 service#processClientBeat方法源码
public void processClientBeat(final RsInfo rsInfo)
//心跳处理器,runnable对象
ClientBeatProcessor clientBeatProcessor = new ClientBeatProcessor();
clientBeatProcessor.setService(this);
clientBeatProcessor.setRsInfo(rsInfo);
//这里HealthCheckReactor.scheduleNow(clientBeatProcessor);
// 开启一个没有延迟的任务,可以理解为这里就是开启了一个异步线程处理心跳续约逻辑
HealthCheckReactor.scheduleNow(clientBeatProcessor);
/** 没有延迟的任务
* Schedule client beat check task without a delay.
*
* @param task health check task
* @return scheduled future
*/
public static ScheduledFuture<?> scheduleNow(Runnable task)
return GlobalExecutor.scheduleNamingHealth(task, 0, TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS);
看得出来,心跳是通过 ClientBeatProcessor去处理的。通过定时任务去执行。ClientBeatProcessor是一个线程对象