如何找出数组中出现次数超过长度一半的元素
Posted
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了如何找出数组中出现次数超过长度一半的元素相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
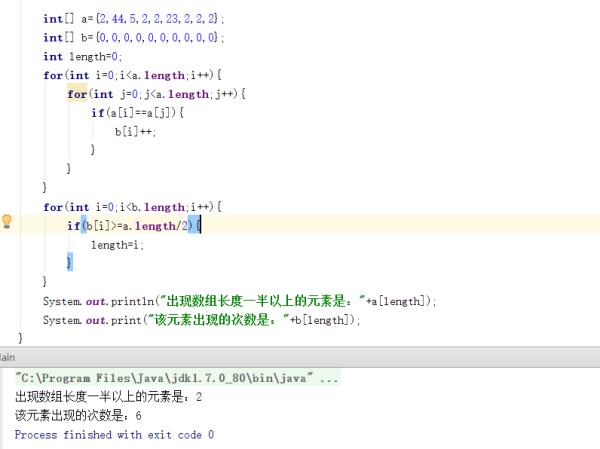
利用另一个数组,初始化为0(数组b),用来记录对应数组a中每个元素出现的次数,然后再循环数组b判断哪个元素的次数大于一半,记录当时的b的下标给length,那么a[length]就是出现次数超过长一半的元素,b[length]是该元素一共出现了多少次
参考技术A #include <iostream>using namespace std;
/*
两种思想:第一种想到统计上的中位数定义如果存在满足条件的数,则肯定该数为数组的中位数,找到中位数
没必要对整个数组进行排序,只需要利用快速排序中的Partition方法找到某个元素应该在middle位置,
然后检查是否满足次数超过数组大小的一半。
*/
int Partition(int *A,int low,int high)
int pivotkey=A[low];
while (low<high)
while (low<high&&A[high]>=pivotkey)
high--;
A[low]=A[high];
while (low<high&&A[low]<=pivotkey)
low++;
A[high]=A[low];
A[low]=pivotkey;
return low;
bool confirmNum(int *array,int number,int len)
int time=0,i;
for (i=0;i<len;i++)
if (array[i]==number)
time++;
if (time*2>len)
return true;
else
return false;
void MoreThanHalfArray(int *array,int len)
int middle=len/2;
int index,start=0,end=len-1;
index=Partition(array,start,end);
while (index!=middle)
if (index>middle)
end=index-1;
index=Partition(array,start,end);
else
start=index+1;
index=Partition(array,start,end);
int result=array[middle];
if (confirmNum(array,result,len))
cout<<"exsit this element is "<<result<<endl;
else
cout<<"not found this element\n";
/*
另外一种就是进行标号的遍历数组,因为某个元素超过一半,保存数组中的数字和其出现次数
如果下一个相同则次数加1,不同减1,如果次数变为0则保存数字为下一个数,最终情况是出现次数最多的元素
最终保存下来,然后检查是否超过半数
*/
void MoreThanHalf(int *array,int len)
int i;
int result,time=0;
for (i=0;i<len;i++)
if (time==0)
result=array[i];
time=1;
else if (array[i]==result)
time++;
else
time--;
if (confirmNum(array,result,len))
cout<<"exsit this element is "<<result<<endl;
else
cout<<"not found this element\n";
int main()
int array[]=1,2,3,2,2,2,5,4,2;
MoreThanHalfArray(array,9);
MoreThanHalf(array,9);
return 0;
这两种实现都能在O(n)时间内完成,要优于先排序然后找数组元素的方法。
数组中出现次数超过一半的数字
题目描述
数组中有一个数字出现的次数超过数组长度的一半,请找出这个数字。例如输入一个长度为9的数组{1,2,3,2,2,2,5,4,2}。由于数字2在数组中出现了5次,超过数组长度的一半,因此输出2。如果不存在则输出0。
开始的思路:思路很简单,申请一个map。将所有元素作为下标,value值为出现的次数。
代码如下:
int MoreThanHalfNum_Solution(vector<int> numbers) { int length = numbers.size(); if(length == 1) return numbers[0]; map<int,int> m; for(int i = 0; i < length; i++) { m[numbers[i]] += 1; } int len = m.size(); for(int i = 0; i < len; i++) { if(m[i] > length/2) return i; } return 0; }
但是map浪费空间和时间。
思路二:我们要找的数字出现的次数超过一半,所以它比其他变量加起来都多。设两个变量,一个记录数字,一个记录次数,遍历数组,当前数字不等于记录的数字,则次数--,如果当前数字==记录的数字,则次数++。如果有满足条件的数字,即为变量的数字。需要注意的是最后的得到的数字,要进行验证。
只有当有数字出现一半时,计数为零。所以不能通过此条件判断是否有符合条件的值。如果没有符合条件的点,那么变量记录的为最后一个值。
例如样例:1 2 3 2 4 2 5 2 3 没有符合的数字,则最后num存的为3
代码:
int MoreThanHalfNum_Solution(vector<int> numbers) { int length = numbers.size(); int nCount = 1; int num = numbers[0]; for(int i = 1; i < length; i++) { if(nCount == 0) { num = numbers[i] ; nCount++; } else if(numbers[i] == num) { nCount++; } else { nCount--; } } nCount = 0; for(int i = 0 ; i < length;i++) { if(numbers[i] == num) nCount++; } if(nCount > length/2) return num; else return 0; }
思路三:数组排序后,如果符合条件的数存在,则一定是数组中间那个数。(比如:1,2,2,2,3;或2,2,2,3,4;或2,3,4,4,4等等)
这种方法虽然容易理解,但由于涉及到快排sort,其时间复杂度为O(NlogN)并非最优;
参考代码:
class Solution { public: int MoreThanHalfNum_Solution(vector<int> numbers) { // 因为用到了sort,时间复杂度O(NlogN),并非最优 if(numbers.empty()) return 0; sort(numbers.begin(),numbers.end()); // 排序,取数组中间那个数 int middle = numbers[numbers.size()/2]; int count=0; // 出现次数 for(int i=0;i<numbers.size();++i) { if(numbers[i]==middle) ++count; } return (count>numbers.size()/2) ? middle : 0; } };
以上是关于如何找出数组中出现次数超过长度一半的元素的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章