并查集介绍及实现以及相关例题
Posted 遥远的歌s
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了并查集介绍及实现以及相关例题相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
并查集的原理和使用背景
在一些应用问题中,需要将n个不同的元素划分成一些不相交的集合。开始时,每个元素自成一个 单元素集合,然后按一定的规律将归于同一组元素的集合合并。在此过程中要反复用到查询某一 个元素归属于那个集合的运算。适合于描述这类问题的抽象数据类型称为并查集(union-find set)。
比如:
某个公司的新员工有10人(这里给他们编号0,1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9),其中4人(0,1,2,3)来自A城市,3人(4,5,6)来自B城市,3人(7,8,9)来自C城市,刚开始他们都不认识。当加入该公式的新职工群时,来自相同城市的人都互相认识了,他们约定一起去公司上班。
每个城市的人组成一个团队,约定每一个城市的第一号人当队长,那么可以表现如下图
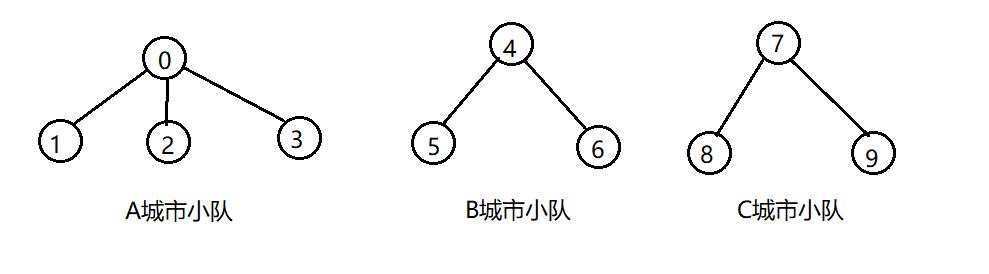
当他们一起到公司后,就熟悉了很多,就形成一个朋友圈,这里就可以用一个数组来表示。
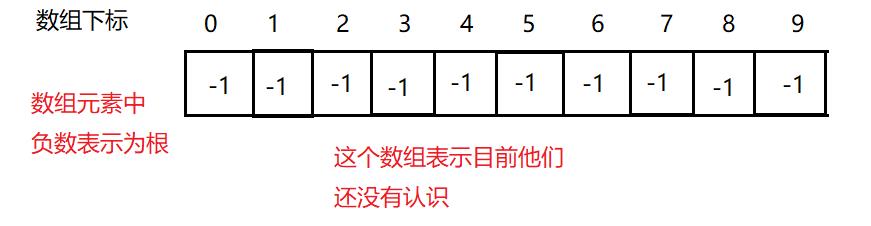
当他们认识后,相同城市的就可以合并
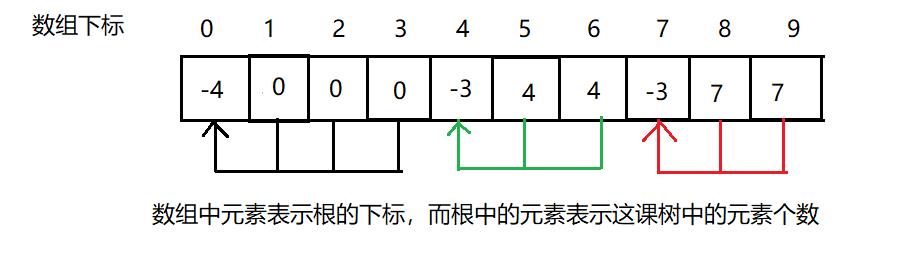
不难得出一些结论
1. 数组的下标对应集合中元素的编号
2. 数组中如果为负数,负号代表根,数字代表该集合中元素个数
3. 数组中如果为非负数,代表该元素双亲在数组中的下标
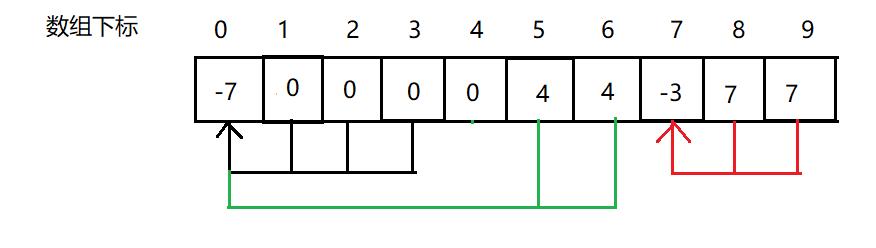
当经过一段时间,A城市小队和B城市小队走到了一起,他们形成了一个朋友圈。如下图
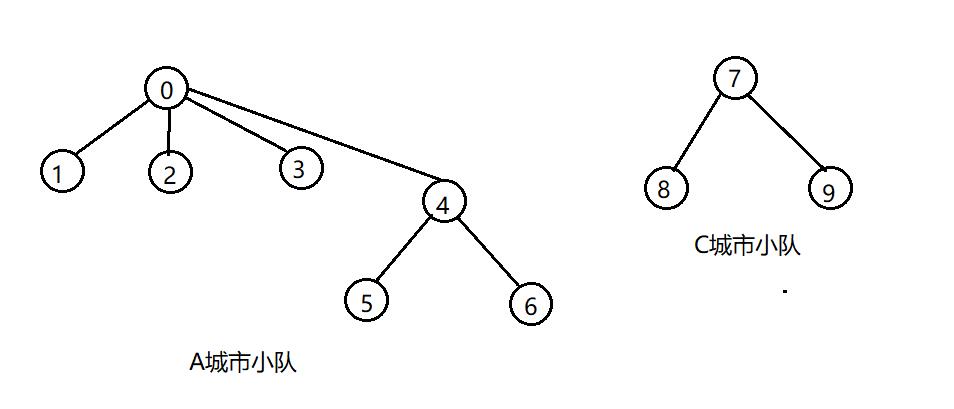
那么数组的表示如下图
并查集实现
#include<iostream>
#include<vector>
using namespace std;
class uninfindset//并查集
public:
uninfindset(size_t n)
_v.resize(n,-1);
int find_root(int x)//找根,x是下标
while(_v[x] >= 0)
int tmp = _v[x];
x = tmp;
//x = _v[x];
return x;
bool Union(int x1,int x2)
int root1 = find_root(x1);
int root2 = find_root(x2);
//如果两个已经再同一个集合则返回false
if(root1 == root2) return false;
_v[root1]+=_v[root2];//合并
_v[root2] = root1;//改变x2的根
return true;
//返回根的个数
size_t count() const
size_t num = 0;
for(auto& ch:_v)
if(ch<0)
num++;
return num;
private:
vector<int> _v;
;
例题
1.朋友圈
参考代码
class uninfindset
public:
uninfindset(size_t n)
_v.resize(n,-1);
int find_root(int x)
while(_v[x] >= 0)
int tmp = _v[x];
x = tmp;
return x;
bool Union(int x1,int x2)
int root1 = find_root(x1);
int root2 = find_root(x2);
if(root1 == root2) return false;
_v[root1]+=_v[root2];
_v[root2] = root1;
return true;
size_t count() const
size_t num = 0;
for(auto& ch:_v)
if(ch<0)
num++;
return num;
private:
vector<int> _v;
;
class Solution
public:
int findCircleNum(vector<vector<int>>& M)
uninfindset ufs(M.size());
for(int i = 0;i<M.size();i++)
for(int j = 0;j<M[i].size();j++)
if(i == j) continue;//自己一样跳过不合并
//如果等于1则表示有关系进行合并
if(M[i][j] == 1)
ufs.Union(i,j);
return ufs.count();
;
2.等式方程的可满足行性
参考代码
class uninfindset
public:
uninfindset(size_t n)
_v.resize(n,-1);
int find_root(int x)
while(_v[x] >= 0)
int tmp = _v[x];
x = tmp;
return x;
bool Union(int x1,int x2)
int root1 = find_root(x1);
int root2 = find_root(x2);
if(root1 == root2) return false;
_v[root1]+=_v[root2];
_v[root2] = root1;
return true;
size_t count()
size_t num = 0;
for(auto& ch:_v)
if(ch<0)
num++;
return num;
private:
vector<int> _v;
;
class Solution
public:
bool equationsPossible(vector<string>& equations)
uninfindset ufs(26);
//先将等于的都合并
for(int i = 0;i<equations.size();i++)
if(equations[i][1] == '=')
ufs.Union(equations[i][0] - 'a',equations[i][3] - 'a');
//查看不等于的是否再合并的集合中
for(auto& str:equations)
if(str[1] == '!')
if(ufs.find_root(str[0]-'a') == ufs.find_root(str[3]-'a'))
return false;
return true;
;
以上是关于并查集介绍及实现以及相关例题的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章