多基因遗传简介
Posted
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了多基因遗传简介相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
参考技术A目录
- 1 拼音 2 英文参考 3 注解
1 拼音
duō jī yīn yí chuán
2 英文参考
polygenic inheritance
3 注解
多基因遗传(polygenic inheritance)是指生物和人类的许多表型性状由不同座位的较多基因协同决定,而非单一基因的作用,因而呈现数量变化的特征,故又称为数量性状遗传。多基因遗传时,每对基因的性状效应是微小的,故称微效基因(minor gene),但不同微效基因又称为累加基因(additive gene)。多基因遗传性状除受微效累加基因作用外,还受环境因素的影响,因而是两因素结合形成的一种性状,因此,这种遗传方式又称多因子遗传(multifactorical inheritance)
多基因遗传的数量性状(quantitative character)为连续变异的性状,可以正态分布曲线表示。人的身高、血压和智力都是多基因性状,而单基因的质量性状(qujalitatie character)则呈不连续变异。
多基因遗传具有3个特点:
①两个极端变异(纯种)个体杂交后,子1代大部分为中间型,具有一定变异范围,是环境影响。
②两个中间型子1代杂交后,子2代大部分为中间型,但其变异范围要比子1代广泛,也可出现极端的个体。这除环境因素外,基因的分离组合也有作用。
③在随机杂交的群体中,变异范围很广,然而大多数个体接近中间型极端个体很少,环境与遗传因素都起作用。
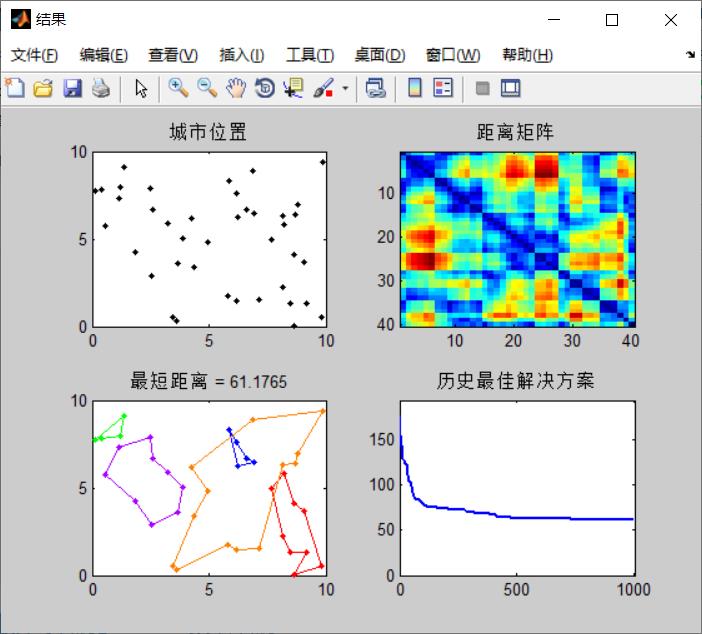
路径规划基于遗传算法求解多旅行商问题matlab
一.进化论知识
作为遗传算法生物背景的介绍,下面内容了解即可:
种群(Population):生物的进化以群体的形式进行,这样的一个群体称为种群。
个体:组成种群的单个生物。
基因 ( Gene ) :一个遗传因子。
染色体 ( Chromosome ) :包含一组的基因。
生存竞争,适者生存:对环境适应度高的、牛B的个体参与繁殖的机会比较多,后代就会越来越多。适应度低的个体参与繁殖的机会比较少,后代就会越来越少。
遗传与变异:新个体会遗传父母双方各一部分的基因,同时有一定的概率发生基因变异。
简单说来就是:繁殖过程,会发生基因交叉( Crossover ) ,基因突变 ( Mutation ) ,适应度( Fitness )低的个体会被逐步淘汰,而适应度高的个体会越来越多。那么经过N代的自然选择后,保存下来的个体都是适应度很高的,其中很可能包含史上产生的适应度最高的那个个体。
二.遗传算法思想
借鉴生物进化论,遗传算法将要解决的问题模拟成一个生物进化的过程,通过复制、交叉、突变等操作产生下一代的解,并逐步淘汰掉适应度函数值低的解,增加适应度函数值高的解。这样进化N代后就很有可能会进化出适应度函数值很高的个体。
举个例子,使用遗传算法解决“0-1背包问题”的思路:0-1背包的解可以编码为一串0-1字符串(0:不取,1:取) ;首先,随机产生M个0-1字符串,然后评价这些0-1字符串作为0-1背包问题的解的优劣;然后,随机选择一些字符串通过交叉、突变等操作产生下一代的M个字符串,而且较优的解被选中的概率要比较高。这样经过G代的进化后就可能会产生出0-1背包问题的一个“近似最优解”。
编码:需要将问题的解编码成字符串的形式才能使用遗传算法。最简单的一种编码方式是二进制编码,即将问题的解编码成二进制位数组的形式。例如,问题的解是整数,那么可以将其编码成二进制位数组的形式。将0-1字符串作为0-1背包问题的解就属于二进制编码。
遗传算法有3个最基本的操作:选择,交叉,变异。
选择:选择一些染色体来产生下一代。一种常用的选择策略是 “比例选择”,也就是个体被选中的概率与其适应度函数值成正比。假设群体的个体总数是M,那么那么一个体Xi被选中的概率为f(Xi)/( f(X1) + f(X2) + …….. + f(Xn) ) 。比例选择实现算法就是所谓的“轮盘赌算法”( Roulette Wheel Selection )
交叉(Crossover):2条染色体交换部分基因,来构造下一代的2条新的染色体。例如:
交叉前:
00000|011100000000|10000
11100|000001111110|00101
交叉后:
00000|000001111110|10000
11100|011100000000|00101
染色体交叉是以一定的概率发生的,这个概率记为Pc 。
变异(Mutation):在繁殖过程,新产生的染色体中的基因会以一定的概率出错,称为变异。变异发生的概率记为Pm 。例如:
变异前:
000001110000000010000
变异后:
000001110000100010000
适应度函数 ( Fitness Function ):用于评价某个染色体的适应度,用f(x)表示。有时需要区分染色体的适应度函数与问题的目标函数。例如:0-1背包问题的目标函数是所取得物品价值,但将物品价值作为染色体的适应度函数可能并不一定适合。适应度函数与目标函数是正相关的,可对目标函数作一些变形来得到适应度函数。
function varargout = guimtsp(varargin)
% GUIMTSP MATLAB code for guimtsp.fig
% GUIMTSP, by itself, creates a new GUIMTSP or raises the existing
% singleton*.
%
% H = GUIMTSP returns the handle to a new GUIMTSP or the handle to
% the existing singleton*.
%
% GUIMTSP('CALLBACK',hObject,eventData,handles,...) calls the local
% function named CALLBACK in GUIMTSP.M with the given input arguments.
%
% GUIMTSP('Property','Value',...) creates a new GUIMTSP or raises the
% existing singleton*. Starting from the left, property value pairs are
% applied to the GUI before guimtsp_OpeningFcn gets called. An
% unrecognized property name or invalid value makes property application
% stop. All inputs are passed to guimtsp_OpeningFcn via varargin.
%
% *See GUI Options on GUIDE's Tools menu. Choose "GUI allows only one
% instance to run (singleton)".
%
% See also: GUIDE, GUIDATA, GUIHANDLES
% Edit the above text to modify the response to help guimtsp
% Last Modified by GUIDE v2.5 28-Dec-2019 12:21:56
% Begin initialization code - DO NOT EDIT
gui_Singleton = 1;
gui_State = struct('gui_Name', mfilename, ...
'gui_Singleton', gui_Singleton, ...
'gui_OpeningFcn', @guimtsp_OpeningFcn, ...
'gui_OutputFcn', @guimtsp_OutputFcn, ...
'gui_LayoutFcn', [] , ...
'gui_Callback', []);
if nargin && ischar(varargin{1})
gui_State.gui_Callback = str2func(varargin{1});
end
if nargout
[varargout{1:nargout}] = gui_mainfcn(gui_State, varargin{:});
else
gui_mainfcn(gui_State, varargin{:});
end
% End initialization code - DO NOT EDIT
% --- Executes just before guimtsp is made visible.
function guimtsp_OpeningFcn(hObject, eventdata, handles, varargin)
% This function has no output args, see OutputFcn.
% hObject handle to figure
% eventdata reserved - to be defined in a future version of MATLAB
% handles structure with handles and user data (see GUIDATA)
% varargin command line arguments to guimtsp (see VARARGIN)
% Choose default command line output for guimtsp
handles.output = hObject;
% Update handles structure
guidata(hObject, handles);
% UIWAIT makes guimtsp wait for user response (see UIRESUME)
% uiwait(handles.figure1);
% --- Outputs from this function are returned to the command line.
function varargout = guimtsp_OutputFcn(hObject, eventdata, handles)
% varargout cell array for returning output args (see VARARGOUT);
% hObject handle to figure
% eventdata reserved - to be defined in a future version of MATLAB
% handles structure with handles and user data (see GUIDATA)
% Get default command line output from handles structure
varargout{1} = handles.output;
function edit1_Callback(hObject, eventdata, handles)
% hObject handle to edit1 (see GCBO)
% eventdata reserved - to be defined in a future version of MATLAB
% handles structure with handles and user data (see GUIDATA)
% Hints: get(hObject,'String') returns contents of edit1 as text
% str2double(get(hObject,'String')) returns contents of edit1 as a double
% --- Executes during object creation, after setting all properties.
function edit1_CreateFcn(hObject, eventdata, handles)
% hObject handle to edit1 (see GCBO)
% eventdata reserved - to be defined in a future version of MATLAB
% handles empty - handles not created until after all CreateFcns called
% Hint: edit controls usually have a white background on Windows.
% See ISPC and COMPUTER.
if ispc && isequal(get(hObject,'BackgroundColor'), get(0,'defaultUicontrolBackgroundColor'))
set(hObject,'BackgroundColor','white');
end
function edit2_Callback(hObject, eventdata, handles)
% hObject handle to edit2 (see GCBO)
% eventdata reserved - to be defined in a future version of MATLAB
% handles structure with handles and user data (see GUIDATA)
% Hints: get(hObject,'String') returns contents of edit2 as text
% str2double(get(hObject,'String')) returns contents of edit2 as a double
% --- Executes during object creation, after setting all properties.
function edit2_CreateFcn(hObject, eventdata, handles)
% hObject handle to edit2 (see GCBO)
% eventdata reserved - to be defined in a future version of MATLAB
% handles empty - handles not created until after all CreateFcns called
% Hint: edit controls usually have a white background on Windows.
% See ISPC and COMPUTER.
if ispc && isequal(get(hObject,'BackgroundColor'), get(0,'defaultUicontrolBackgroundColor'))
set(hObject,'BackgroundColor','white');
end
function edit3_Callback(hObject, eventdata, handles)
% hObject handle to edit3 (see GCBO)
% eventdata reserved - to be defined in a future version of MATLAB
% handles structure with handles and user data (see GUIDATA)
% Hints: get(hObject,'String') returns contents of edit3 as text
% str2double(get(hObject,'String')) returns contents of edit3 as a double
% --- Executes during object creation, after setting all properties.
function edit3_CreateFcn(hObject, eventdata, handles)
% hObject handle to edit3 (see GCBO)
% eventdata reserved - to be defined in a future version of MATLAB
% handles empty - handles not created until after all CreateFcns called
% Hint: edit controls usually have a white background on Windows.
% See ISPC and COMPUTER.
if ispc && isequal(get(hObject,'BackgroundColor'), get(0,'defaultUicontrolBackgroundColor'))
set(hObject,'BackgroundColor','white');
end
function edit4_Callback(hObject, eventdata, handles)
% hObject handle to edit4 (see GCBO)
% eventdata reserved - to be defined in a future version of MATLAB
% handles structure with handles and user data (see GUIDATA)
% Hints: get(hObject,'String') returns contents of edit4 as text
% str2double(get(hObject,'String')) returns contents of edit4 as a double
% --- Executes during object creation, after setting all properties.
function edit4_CreateFcn(hObject, eventdata, handles)
% hObject handle to edit4 (see GCBO)
% eventdata reserved - to be defined in a future version of MATLAB
% handles empty - handles not created until after all CreateFcns called
% Hint: edit controls usually have a white background on Windows.
% See ISPC and COMPUTER.
if ispc && isequal(get(hObject,'BackgroundColor'), get(0,'defaultUicontrolBackgroundColor'))
set(hObject,'BackgroundColor','white');
end
function edit5_Callback(hObject, eventdata, handles)
% hObject handle to edit5 (see GCBO)
% eventdata reserved - to be defined in a future version of MATLAB
% handles structure with handles and user data (see GUIDATA)
% Hints: get(hObject,'String') returns contents of edit5 as text
% str2double(get(hObject,'String')) returns contents of edit5 as a double
% --- Executes during object creation, after setting all properties.
function edit5_CreateFcn(hObject, eventdata, handles)
% hObject handle to edit5 (see GCBO)
% eventdata reserved - to be defined in a future version of MATLAB
% handles empty - handles not created until after all CreateFcns called
% Hint: edit controls usually have a white background on Windows.
% See ISPC and COMPUTER.
if ispc && isequal(get(hObject,'BackgroundColor'), get(0,'defaultUicontrolBackgroundColor'))
set(hObject,'BackgroundColor','white');
end
% --- Executes on button press in pushbutton1.
function pushbutton1_Callback(hObject, eventdata, handles)
% hObject handle to pushbutton1 (see GCBO)
% eventdata reserved - to be defined in a future version of MATLAB
% handles structure with handles and user data (see GUIDATA)
% 主函数
% 输入:
% XY:各个城市坐标的 N*2 矩阵,N 为城市的个数
% DMAT:各个城市之间的距离矩阵
% SALESMEN :旅行商人数
% MIN_TOUR:每个人所经过的最少城市点
% POP_SIZE:种群大小
% NUM_ITER:迭代次数
% 输出:
% 最优路线
% 总距离
global n;
% 初始化
a=get(handles.edit1,'String');%城市个数
num=str2num(a);
xy = 10*rand(num,2);
N = size(xy,1);
a = meshgrid(1:N);
dmat = reshape(sqrt(sum((xy(a,:)-xy(a',:)).^2,2)),N,N);
b=get(handles.edit2,'String');%旅行商人数
salesmen=str2num(b);
c=get(handles.edit3,'String');%每个人所经过的最少城市点
min_tour=str2num(c);
d=get(handles.edit4,'String');%种群大小
pop_size=str2num(d);
e=get(handles.edit5,'String');%迭代次数
num_iter=str2num(e);
show_prog = 1;
show_res = 1;
%调整输入数据
[nr,nc] = size(dmat);
if N ~= nr || N ~= nc
error('Invalid XY or DMAT inputs!')
end
n = N;
mtsp_ga(xy,dmat,salesmen,min_tour,pop_size,num_iter,1,1)
% set(handles.edit6,'String',num2str(min_dist));
function edit6_Callback(hObject, eventdata, handles)
% hObject handle to edit6 (see GCBO)
% eventdata reserved - to be defined in a future version of MATLAB
% handles structure with handles and user data (see GUIDATA)
% Hints: get(hObject,'String') returns contents of edit6 as text
% str2double(get(hObject,'String')) returns contents of edit6 as a double
% --- Executes during object creation, after setting all properties.
function edit6_CreateFcn(hObject, eventdata, handles)
% hObject handle to edit6 (see GCBO)
% eventdata reserved - to be defined in a future version of MATLAB
% handles empty - handles not created until after all CreateFcns called
% Hint: edit controls usually have a white background on Windows.
% See ISPC and COMPUTER.
if ispc && isequal(get(hObject,'BackgroundColor'), get(0,'defaultUicontrolBackgroundColor'))
set(hObject,'BackgroundColor','white');
end
完整代码添加QQ1575304183
以上是关于多基因遗传简介的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章
