Linux 进程控制
Posted mfcheer
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了Linux 进程控制相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
进程
1 进程创建
fork()函数创建子进程。
“调用一次,返回两次”
#include <stdio.h>
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
int main()
pid_t pid;
if ((pid = fork())<0)
printf("error\\n");
exit(0);
else if (pid == 0)
printf("in fork\\n");
else
printf("father\\n");
return 0;
代码打印结果为:
father
in fork
vfork()函数,与父进程共享地址空间,使用vfork时父进程会被堵塞,使用_exit()退出子进程。
#include <stdio.h>
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
int main()
pid_t pid;
int var = 5;
printf("process id %ld\\n",(long)getpid());
if ((pid = vfork())<0)
printf("error\\n");
return 1;
else if (pid == 0)
var++;
printf("in fork\\n");
_exit(0);
else
printf("father\\n");
return 0;
return 0;
运行结果:
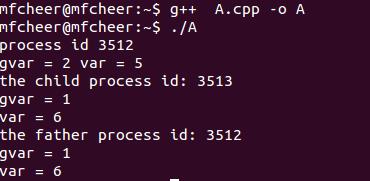
execve()函数创建子进程,在另外一个文件执行。
new.cpp文件
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <unistd.h>
int main()
puts("hello");
return 0;
A.cpp
#include <stdio.h>
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
extern char **environ;
int main(int argc,char *argv[])
pid_t pid;
if ((pid =fork()) < 0)
puts("error!\\n");
if (pid == 0)
execve("new",argv,environ);
else
puts("ok");
return 0;
执行A.cpp运行结果:
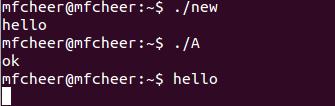
2 进程等待
wait()函数,挂起父进程,等待子进程运行结束。
#include <stdio.h>
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <sys/wait.h>
void exit_s(int status)
if (WIFEXITED(status))
printf("normal exit,status = %d\\n",WEXITSTATUS(status));
else
printf("single exit!,status = %d\\n",WTERMSIG(status));
int main(void)
pid_t pid,pid1;
int status;
if ((pid = fork()) < 0)
puts("error");
exit(0);
else if (pid == 0)
printf("child process\\n");
exit(2);
else
printf("father process\\nwait error!\\n");
exit(1);
exit_s(status);
if ((pid = fork()) < 0)
puts("error");
exit(1);
else if (pid == 0)
printf("child process\\n");
pid1 = getpid();
kill(pid1,14);
exit(2);
if (wait(&status) != pid)
printf("father process\\nwait error!\\n");
exit(0);
exit_s(status);
exit(0);
运行结果:
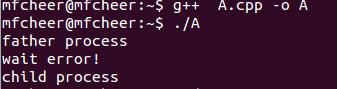
3 进程结束
exit和_exit
区别:exit退出时释放占用的资源及清空缓冲区。_exit则不具备这个功能。
4 进程组
setpgid创建新的进程组
#include <stdio.h>
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <sys/wait.h>
int main(void)
int a;
pid_t pgid,pid;
pid = getpid();
pgid = getpgrp();
a = setpgid(pid,pgid);
printf("a = %d , pid = %d ,pgid = %d \\n",a,pid,pgid);
return 0;
运行结果:
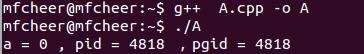
5 时间片的分配
进程优先级:
头文件
#include <sched.h>setpriority()和getpriority()设置和获取线程的优先级。
6 进程的操作
getpid()进程id
getppid()父进程id
getuid()用户id
geteuid()有效用户id
getgid()用户组id
getegid()有效用户组id
setuid()设置用户标识
setgid()设置用户组标识#include <stdio.h>
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <sys/wait.h>
#include <sched.h>
#include <pthread.h>
int main(void)
int a1,a2;
a1 = setuid(0);
a2 = setgid(100);
printf("a1 = %d a2 = %d\\n",a1,a2);
return 0;
以上是关于Linux 进程控制的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章