netty之io模型
Posted better_hui
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了netty之io模型相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
目录
前言
所有的IO的前戏都是这三部曲
1、new socket()
2、bind 端口
3、监听 端口
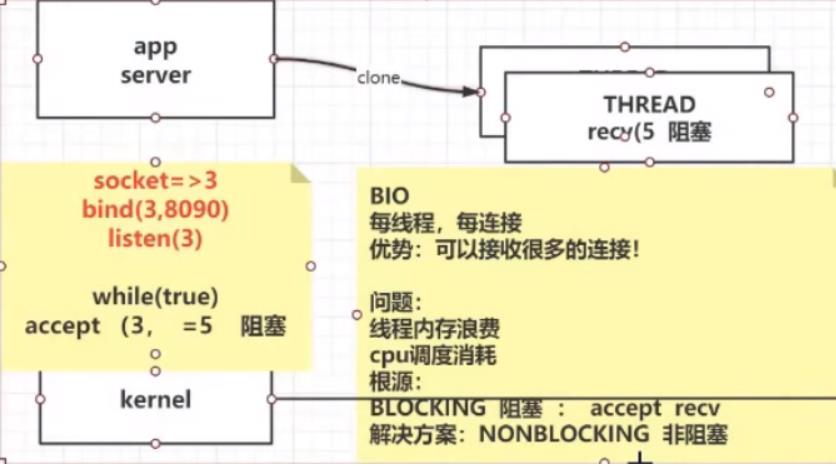
一、BIO
package netty.bio;
import java.io.InputStream;
import java.net.InetSocketAddress;
import java.net.ServerSocket;
import java.net.Socket;
import java.util.concurrent.TimeUnit;
/**
* @author hee.wong
* @version 1.0.0
* BIO 阻塞IO模型
* serverSocket.accept inputStream.read 都是阻塞的 , 未获取到数据是不返回的。
* BIO为了能够支持多个连接 , 只能是以多线程的方式 , 下面有多线程的代码
* 特点 : 一个链接一个线程
* 优点 : 简单、可以接受多个链接
* 缺点 : 线程内存损耗、cpu调度损耗
*/
public class Bioserver
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception
//1、打开一个socket
ServerSocket server = new ServerSocket();
//2、绑定一个端口 bind
server.bind(new InetSocketAddress(8081));
while (true)
TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(1);
System.out.println("监听中");
//3、监听并接收
Socket socket = server.accept();
System.out.println(socket.getPort()+"-----请求进来了");
handleInThread(socket);
private static void handleInThread(final Socket socket) throws Exception
new Thread(new Runnable()
@Override
public void run()
try
System.out.println("开始读取数据");
InputStream inputStream = socket.getInputStream();
byte[] data = new byte[1024];
while (true)
int read = inputStream.read(data);
if(read>0)
System.out.println("读取客户端数据"+new String(data,0,read));
else
break;
catch (Exception e)
e.printStackTrace();
).start();
二、NIO
BIO的缺点是非常明显的,大量的请求链接会耗费服务器的大量线程资源,因此无法支持海量的链接请求。NIO应运而生,nio的accept和 recv 都可以设置为非阻塞 , 即没有事件时,直接返回,基于这一点,我们就可以实现在一个线程内,接收处理N个链接。

package netty.nio;
import java.net.InetSocketAddress;
import java.nio.ByteBuffer;
import java.nio.channels.ServerSocketChannel;
import java.nio.channels.SocketChannel;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.concurrent.TimeUnit;
/**
* @author hee.wong
* @version 1.0.0
* NIO 针对java而言就是nio下的api接口 ,针对linux而言就是非阻塞IO ,
* 非阻塞IO的允许调用方发起一个内核调用,然后轮询是否有自己感兴趣的事件发生
* 特点:单线程可以处理多个链接请求
* 优点:规避了BIO多线程的问题
* 缺点:C10K的问题,我们假设有10000个链接 , 但是只有1个连接有数据可以读取,但是我们每次都要循环尝试读取这10000
* 个链接,那么9999个请求是无效的,浪费时间和系统资源的。
* NIO的缺点简单来讲就是 循环调用
*/
public class NioServer
public static void main(String[]args) throws Exception
//打开一个socket
ServerSocketChannel channel = ServerSocketChannel.open();
//绑定一个端口
channel.bind(new InetSocketAddress(8082));
//设置为非阻塞
channel.configureBlocking(false);
List<SocketChannel> sockets = new ArrayList<>();
while (true)
TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(1);
//接受请求 , 请注意这里是非阻塞的,非阻塞的
SocketChannel socket = channel.accept();
if(socket==null)
System.out.println("没有链接");
else
System.out.println(socket.getRemoteAddress()+"-----链接来了");
//设置这个链接为非阻塞 , 意思是没有数据时直接返回
socket.configureBlocking(false);
sockets.add(socket);
for (SocketChannel socketChannel : sockets)
ByteBuffer buffer = ByteBuffer.allocateDirect(1024);
int read = socketChannel.read(buffer);
if(read < 0)
continue;
else
System.out.println("开始读取数据");
buffer.flip();
byte[] data = new byte[read];
buffer.get(data);
System.out.println(new String(data));
buffer.clear();
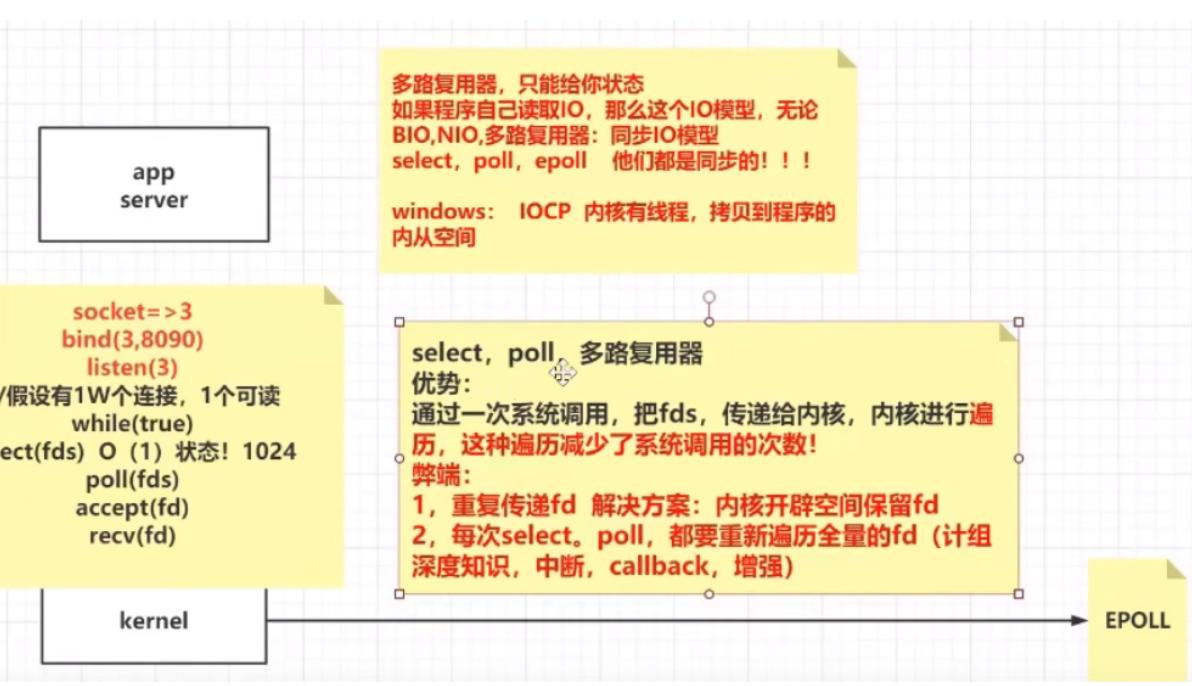
三、IO多路复用
非阻塞的IO模型 , 有循环系统调用的问题 , 而每一次系统调用都会发生软中断 , 涉及到系统执行现场的保存,是很损耗性能的。我们是否可用将这循环调用 , 优化为一次批量调用,答案是肯定的 , 这就是IO多路复用,简单来讲就是我们发起一次系统调用,询问内核有哪些链接有可读的事件。
代码
package netty.nio2;
import java.net.InetSocketAddress;
import java.nio.ByteBuffer;
import java.nio.channels.*;
import java.util.Iterator;
import java.util.Set;
/**
* @author hee.wong
* @version 1.0.0
* IO多路复用 , 是针对NIO循环系统调用的缺点而来的,这里有了复用器selector的概念,
* 我们只需要发起一次系统调用,把所有的fds 传递给内核,让内核循环遍历 ,然后把有事件的fd, 告诉我就可以了
* select poll弊端:
* 1、重复传递fd
* 2、每次select / poll , 都需要遍历全脸的fd数组
*
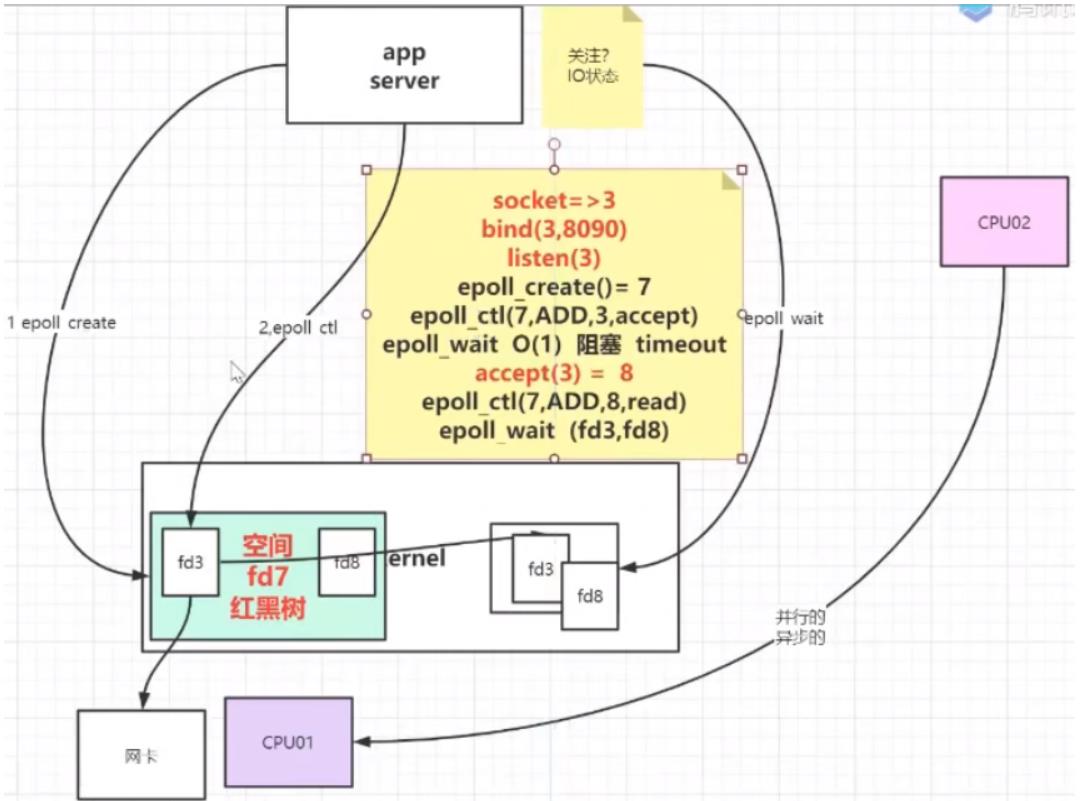
* 对此epoll有了优化:
* 1、应用程序不用传递fds给我了 , 我在内核帮你记录着
* 2、另外我还开辟了另外一块空间 , 专门保存有事件的fd ,
* 至于如何从复用的fd空间 , 将有事件的fd 移动到另外一块空间 , 是系统内核另起线程 帮我们搞定的, 我们可以漠不关心
*/
public class Nio2Server
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception
//打开一个通道channel
ServerSocketChannel server = ServerSocketChannel.open();
//设置为非阻塞
server.configureBlocking(false);
//绑定端口
server.bind(new InetSocketAddress(8083));
//打开一个selector
//epoll模型下 , oepn -> epoll_create = fd3 , 返回一个文件描述符
Selector selector = Selector.open();
//注册 将我们打开的socket 注册到多路复用器上 , 由复用器负责监听事件, 注意这里关心的事件是连接时间
// select 、 poll : jvm 会开辟一个数组 , 存放监听的文件描述 fd4
// epoll : epoll_ctl(fd3 , ADD , fd4 ,ACCEPT) , 在selector对应的文件描述符空间内,添加一个fd4 , 关心的是链接请求
server.register(selector , SelectionKey.OP_ACCEPT);
// select / poll , 调用的是内核 select(fd4) poll(fd4)
// epoll 是调用的 epoll_wait() , 这一步是阻塞的 , 等待关心的事件发生。
System.out.println("多路复用的服务器起来了");
while (true)
while (selector.select(500) > 0)
//
Set<SelectionKey> selectionKeys = selector.selectedKeys();
if(selectionKeys.size()>0)
Iterator<SelectionKey> iterator = selectionKeys.iterator();
while (iterator.hasNext())
SelectionKey selectionKey = iterator.next();
int interestOps = selectionKey.interestOps();
switch (interestOps)
case SelectionKey.OP_ACCEPT:
//获取这个链接
SocketChannel client = server.accept();
//设置为非阻塞
client.configureBlocking(false);
//还是在复用器上注册 , 关心的时间是read
client.register(selector , SelectionKey.OP_READ);
System.out.println("链接来了===="+client.getRemoteAddress());
break;
case SelectionKey.OP_READ:
SocketChannel clientRead = (SocketChannel) selectionKey.channel();
ByteBuffer buf = ByteBuffer.allocate(1024);
int len = 0 ;
while ((len = clientRead.read(buf))>0)
buf.flip();
System.out.println(new String(buf.array(),0 , len) );
buf.clear();
break;
default:
continue;
iterator.remove();
select / poll
epoll

以上是关于netty之io模型的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章