如何用C语言实现一元多项式简单计算器的设计
Posted
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了如何用C语言实现一元多项式简单计算器的设计相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
〔问题描述〕输入并建立两个多项式并输出多项式设计一个程序:对两个多项式进行加、减法及乘法运算,建立一个新多项式并输出. 或设计一个程序对其中一个多项式求导。 〔实现提示〕 选择带头结点的单链表或循环链表存储多项式,头结点中存放多项式的参数.此单链表的数据结构为:typedef struct pdode{ float coef ; /* 系数域*/ int expn ; /* 指数域*/ struct pnode *next ; /* 链域*/ } pnode ,*polylink
一元多项式简单的计算器的功能:
1)输入并建立多项式;
2)输出多项式;
3)两个多项式相加,输出和多项式;
4)两个多项式相减,输出差多项式。
例程
#include <math.h> /*数学函数的定义*/
#include <conio.h> /*屏幕操作函数*/
#include <stdio.h> /*I/O函数*/
#include <stdlib.h> /*库函数*/
#include <stdarg.h> /*变量长度参数表*/
#include <graphics.h> /*图形函数*/
#include <string.h> /*字符串函数*/
#include <ctype.h> /*字符操作函数*/
#define UP 0x48 /*光标上移键*/
#define DOWN 0x50 /*光标下移键*/
#define LEFT 0x4b /*光标左移键*/
#define RIGHT 0x4d /*光标右移键*/
#define ENTER 0x0d /*回车键*/
void *rar; /*全局变量,保存光标图象*/
struct palettetype palette; /*使用调色板信息*/
int GraphDriver; /* 图形设备驱动*/
int GraphMode; /* 图形模式值*/
int ErrorCode; /* 错误代码*/
int MaxColors; /* 可用颜色的最大数值*/
int MaxX, MaxY; /* 屏幕的最大分辨率*/
double AspectRatio; /* 屏幕的像素比*/
void drawboder(void); /*画边框函数*/
void initialize(void); /*初始化函数*/
void computer(void); /*计算器计算函数*/
void changetextstyle(int font, int direction, int charsize); /*改变文本样式函数*/
void mwindow(char *header); /*窗口函数*/
int specialkey(void) ; /*获取特殊键函数*/
int arrow(); /*设置箭头光标函数*/
/*主函数*/
int main()
initialize();/* 设置系统进入图形模式 */
computer(); /*运行计算器 */
closegraph();/*系统关闭图形模式返回文本模式*/
return(0); /*结束程序*/
/* 设置系统进入图形模式 */
void initialize(void)
int xasp, yasp; /* 用于读x和y方向纵横比*/
GraphDriver = DETECT; /* 自动检测显示器*/
initgraph( &GraphDriver, &GraphMode, "" );
/*初始化图形系统*/
ErrorCode = graphresult(); /*读初始化结果*/
if( ErrorCode != grOk ) /*如果初始化时出现错误*/
printf("Graphics System Error: %s\\n",
grapherrormsg( ErrorCode ) ); /*显示错误代码*/
exit( 1 ); /*退出*/
getpalette( &palette ); /* 读面板信息*/
MaxColors = getmaxcolor() + 1; /* 读取颜色的最大值*/
MaxX = getmaxx(); /* 读屏幕尺寸 */
MaxY = getmaxy(); /* 读屏幕尺寸 */
getaspectratio( &xasp, &yasp ); /* 拷贝纵横比到变量中*/
AspectRatio = (double)xasp/(double)yasp;/* 计算纵横比值*/
/*计算器函数*/
void computer(void)
struct viewporttype vp; /*定义视口类型变量*/
int color, height, width;
int x, y,x0,y0, i, j,v,m,n,act,flag=1;
float num1=0,num2=0,result; /*操作数和计算结果变量*/
char cnum[5],str2[20]="",c,temp[20]="";
char str1[]="1230.456+-789*/Qc=^%";/* 定义字符串在按钮图形上显示的符号 */
mwindow( "Calculator" ); /* 显示主窗口 */
color = 7; /*设置灰颜色值*/
getviewsettings( &vp ); /* 读取当前窗口的大小*/
width=(vp.right+1)/10; /* 设置按钮宽度 */
height=(vp.bottom-10)/10 ; /*设置按钮高度 */
x = width /2; /*设置x的坐标值*/
y = height/2; /*设置y的坐标值*/
setfillstyle(SOLID_FILL, color+3);
bar( x+width*2, y, x+7*width, y+height );
/*画一个二维矩形条显示运算数和结果*/
setcolor( color+3 ); /*设置淡绿颜色边框线*/
rectangle( x+width*2, y, x+7*width, y+height );
/*画一个矩形边框线*/
setcolor(RED); /*设置颜色为红色*/
outtextxy(x+3*width,y+height/2,"0."); /*输出字符串"0."*/
x =2*width-width/2; /*设置x的坐标值*/
y =2*height+height/2; /*设置y的坐标值*/
for( j=0 ; j<4 ; ++j ) /*画按钮*/
for( i=0 ; i<5 ; ++i )
setfillstyle(SOLID_FILL, color);
setcolor(RED);
bar( x, y, x+width, y+height ); /*画一个矩形条*/
rectangle( x, y, x+width, y+height );
sprintf(str2,"%c",str1[j*5+i]);
/*将字符保存到str2中*/
outtextxy( x+(width/2), y+height/2, str2);
x =x+width+ (width / 2) ; /*移动列坐标*/
y +=(height/2)*3; /* 移动行坐标*/
x =2*width-width/2; /*复位列坐标*/
x0=2*width;
y0=3*height;
x=x0;
y=y0;
gotoxy(x,y); /*移动光标到x,y位置*/
arrow(); /*显示光标*/
putimage(x,y,rar,XOR_PUT);
m=0;
n=0;
strcpy(str2,""); /*设置str2为空串*/
while((v=specialkey())!=45) /*当压下Alt+x键结束程序,否则执行下面的循环*/
while((v=specialkey())!=ENTER) /*当压下键不是回车时*/
putimage(x,y,rar,XOR_PUT); /*显示光标图象*/
if(v==RIGHT) /*右移箭头时新位置计算*/
if(x>=x0+6*width)
/*如果右移,移到尾,则移动到最左边字符位置*/
x=x0;
m=0;
else
x=x+width+width/2;
m++;
/*否则,右移到下一个字符位置*/
if(v==LEFT) /*左移箭头时新位置计算*/
if(x<=x0)
x=x0+6*width;
m=4;
/*如果移到头,再左移,则移动到最右边字符位置*/
else
x=x-width-width/2;
m--;
/*否则,左移到前一个字符位置*/
if(v==UP) /*上移箭头时新位置计算*/
if(y<=y0)
y=y0+4*height+height/2;
n=3;
/*如果移到头,再上移,则移动到最下边字符位置*/
else
y=y-height-height/2;
n--;
/*否则,移到上边一个字符位置*/
if(v==DOWN) /*下移箭头时新位置计算*/
if(y>=7*height)
y=y0;
n=0;
/*如果移到尾,再下移,则移动到最上边字符位置*/
else
y=y+height+height/2;
n++;
/*否则,移到下边一个字符位置*/
putimage(x,y,rar,XOR_PUT); /*在新的位置显示光标箭头*/
c=str1[n*5+m]; /*将字符保存到变量c中*/
if(isdigit(c)||c=='.') /*判断是否是数字或小数点*/
if(flag==-1) /*如果标志为-1,表明为负数*/
strcpy(str2,"-"); /*将负号连接到字符串中*/
flag=1;
/*将标志值恢复为1*/
sprintf(temp,"%c",c); /*将字符保存到字符串变量temp中*/
strcat(str2,temp); /*将temp中的字符串连接到str2中*/
setfillstyle(SOLID_FILL,color+3);
bar(2*width+width/2,height/2,15*width/2,3*height/2);
outtextxy(5*width,height,str2); /*显示字符串*/
if(c=='+')
num1=atof(str2); /*将第一个操作数转换为浮点数*/
strcpy(str2,""); /*将str2清空*/
act=1; /*做计算加法标志值*/
setfillstyle(SOLID_FILL,color+3);
bar(2*width+width/2,height/2,15*width/2,3*height/2);
outtextxy(5*width,height,"0."); /*显示字符串*/
if(c=='-')
if(strcmp(str2,"")==0) /*如果str2为空,说明是负号,而不是减号*/
flag=-1; /*设置负数标志*/
else
num1=atof(str2); /*将第二个操作数转换为浮点数*/
strcpy(str2,""); /*将str2清空*/
act=2; /*做计算减法标志值*/
setfillstyle(SOLID_FILL,color+3);
bar(2*width+width/2,height/2,15*width/2,3*height/2); /*画矩形*/
outtextxy(5*width,height,"0."); /*显示字符串*/
if(c=='*')
num1=atof(str2); /*将第二个操作数转换为浮点数*/
strcpy(str2,""); /*将str2清空*/
act=3; /*做计算乘法标志值*/
setfillstyle(SOLID_FILL,color+3); bar(2*width+width/2,height/2,15*width/2,3*height/2);
outtextxy(5*width,height,"0."); /*显示字符串*/
if(c=='/')
num1=atof(str2); /*将第二个操作数转换为浮点数*/
strcpy(str2,""); /*将str2清空*/
act=4; /*做计算除法标志值*/
setfillstyle(SOLID_FILL,color+3);
bar(2*width+width/2,height/2,15*width/2,3*height/2);
outtextxy(5*width,height,"0."); /*显示字符串*/
if(c=='^')
num1=atof(str2); /*将第二个操作数转换为浮点数*/
strcpy(str2,""); /*将str2清空*/
act=5; /*做计算乘方标志值*/
setfillstyle(SOLID_FILL,color+3); /*设置用淡绿色实体填充*/
bar(2*width+width/2,height/2,15*width/2,3*height/2); /*画矩形*/
outtextxy(5*width,height,"0."); /*显示字符串*/
if(c=='%')
num1=atof(str2); /*将第二个操作数转换为浮点数*/
strcpy(str2,""); /*将str2清空*/
act=6; /*做计算模运算乘方标志值*/
setfillstyle(SOLID_FILL,color+3); /*设置用淡绿色实体填充*/
bar(2*width+width/2,height/2,15*width/2,3*height/2); /*画矩形*/
outtextxy(5*width,height,"0."); /*显示字符串*/
if(c=='=')
num2=atof(str2); /*将第二个操作数转换为浮点数*/
switch(act) /*根据运算符号计算*/
case 1:result=num1+num2;break; /*做加法*/
case 2:result=num1-num2;break; /*做减法*/
case 3:result=num1*num2;break; /*做乘法*/
case 4:result=num1/num2;break; /*做除法*/
case 5:result=pow(num1,num2);break; /*做x的y次方*/
case 6:result=fmod(num1,num2);break; /*做模运算*/
setfillstyle(SOLID_FILL,color+3); /*设置用淡绿色实体填充*/
bar(2*width+width/2,height/2,15*width/2,3*height/2); /*覆盖结果区*/
sprintf(temp,"%f",result); /*将结果保存到temp中*/
outtextxy(5*width,height,temp); /*显示结果*/
if(c=='c')
num1=0; /*将两个操作数复位0,符号标志为1*/
num2=0;
flag=1;
strcpy(str2,""); /*将str2清空*/
setfillstyle(SOLID_FILL,color+3); /*设置用淡绿色实体填充*/
bar(2*width+width/2,height/2,15*width/2,3*height/2); /*覆盖结果区*/
outtextxy(5*width,height,"0."); /*显示字符串*/
if(c=='Q')exit(0); /*如果选择了q回车,结束计算程序*/
putimage(x,y,rar,XOR_PUT); /*在退出之前消去光标箭头*/
return; /*返回*/
/*窗口函数*/
void mwindow( char *header )
int height;
cleardevice(); /* 清除图形屏幕 */
setcolor( MaxColors - 1 ); /* 设置当前颜色为白色*/
setviewport( 20, 20, MaxX/2, MaxY/2, 1 ); /* 设置视口大小 */
height = textheight( "H" ); /* 读取基本文本大小 */
settextstyle( DEFAULT_FONT, HORIZ_DIR, 1 );/*设置文本样式*/
settextjustify( CENTER_TEXT, TOP_TEXT );/*设置字符排列方式*/
outtextxy( MaxX/4, 2, header ); /*输出标题*/
setviewport( 20,20+height+4, MaxX/2+4, MaxY/2+20, 1 ); /*设置视口大小*/
drawboder(); /*画边框*/
void drawboder(void) /*画边框*/
struct viewporttype vp; /*定义视口类型变量*/
setcolor( MaxColors - 1 ); /*设置当前颜色为白色 */
setlinestyle( SOLID_LINE, 0, NORM_WIDTH );/*设置画线方式*/
getviewsettings( &vp );/*将当前视口信息装入vp所指的结构中*/
rectangle( 0, 0, vp.right-vp.left, vp.bottom-vp.top ); /*画矩形边框*/
/*设计鼠标图形函数*/
int arrow()
int size;
int raw[]=4,4,4,8,6,8,14,16,16,16,8,6,8,4,4,4; /*定义多边形坐标*/
setfillstyle(SOLID_FILL,2); /*设置填充模式*/
fillpoly(8,raw); /*画出一光标箭头*/
size=imagesize(4,4,16,16); /*测试图象大小*/
rar=malloc(size); /*分配内存区域*/
getimage(4,4,16,16,rar); /*存放光标箭头图象*/
putimage(4,4,rar,XOR_PUT); /*消去光标箭头图象*/
return 0;
/*按键函数*/
int specialkey(void)
int key;
while(bioskey(1)==0); /*等待键盘输入*/
key=bioskey(0); /*键盘输入*/
key=key&0xff? key&0xff:key>>8; /*只取特殊键的扫描值,其余为0*/
return(key); /*返回键值*/
#include <stdio.h>
#include <malloc.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
struct polylink
char ch; /*变量名*/
float coef; /* 系数域*/
int expn; /* 指数域*/
struct polylink *next; /* 链域*/
;
/*初始化链表*/
polylink *initpoly()
polylink *p;
p = (polylink *)malloc(sizeof(polylink));
if(p == NULL)
printf("memory error!");
exit(0);
p->next = NULL;
return p;
/*销毁链表*/
void destroy_link(polylink *p)
polylink *q;
while(p != NULL)
q = p;
p = p->next;
free(q);
/*将多项式存入链表*/
polylink * creat_ploy(polylink *p)
char c[1];
int i = 0, n=0;
polylink *p1;
p = initpoly();
printf("input variable's name 输入变量名:\n");
scanf("%s", c);
printf("input the polynomial's number 输入多项式项数:\n");
scanf("%d", &n);
for(i = 0; i < n; i++)
p1 = (polylink *)malloc(sizeof(polylink));
if(p1 == NULL)/*分配不成功时*/
printf("memory error!");
exit(0);
printf("input the %dst's coefficient 输入第%d项的系数:\n", i+1, i+1);
scanf("%f", &p1->coef);
printf("input the variable's index 输入变量的指数:\n");
scanf("%d", &p1->expn);
p1->ch = c[0];
p1->next = p->next;
p->next = p1;
return p;
/*删除节点函数*/
polylink *delnode(polylink * h , polylink * maxp) /*删除一个节点,返回剩下的链表首地址*/
polylink *t;
t = h;
while(t->next != maxp )
t=t->next; /*找到maxp 的前节点t */
t->next = maxp->next ; /*删除maxp,maxp后面的接到t后面*/
maxp->next = NULL;
return h; /*链首依然是h ,返回 */
/*求表长函数*/
void link_lenth(polylink *p, int &a)/* &是引用*/
while(p->next != NULL)
p = p->next;
a++;
/*排序*/
polylink *sort(polylink *h)
int min; /*保存指数最小的值*/
polylink *t=NULL, *minp=NULL, *head=NULL;
if(h ->next == NULL)
printf("don't exist number");
exit(0);
while(h->next !=NULL) /*只要当前链中不为空就循环 */
t= h->next; // t :临时指针
min=t->expn; minp=t; /*把当前t中的值作为最小*/
while (t->next !=NULL) /*只要t后面还有节点就循环*/
t=t->next ; /*t往后移动一个*/
if (t->expn < min) /*如果t中的值大于maxn,则记下其值和位置*/
min = t->expn;
minp=t;
/*找出当前头开始在链中最大节点 maxp*/
h = delnode(h, minp); /*删除minp节点,返回剩下的链表*/
minp->next=head; /*将每次的最小节点接在头结点之前*/
head = minp; /*head 重新回到该链的开头*/
h->next = head; /*将head 接在头节点之后*/
return h;
/*对一元多项式求导*/
polylink *poly_derivation(polylink *p)
polylink *n, *q;
q= p;
if(p->next == NULL)
printf("polynomial don't exist!\n");
while(p->next != NULL)
p = p->next;
if(p->expn == 0 || p->coef == 0) /*指数为零或者系数为零就删除*/
q = delnode(q, p);
n = q; /*保存删除无用节点的链表之后的头结点, 用于返回*/
if(q->next == NULL)
printf("polynomial don't exist!\n");
while(q->next != NULL)
q = q->next;
q->coef = q->coef * q->expn; /*系数乘指数*/
q->expn = q->expn - 1; /*指数减一*/
return n;
/*显示多项式*/
void display_poly(polylink *p)
int a;
p = sort(p); /*排序*/
while(p->next != NULL )
p = p->next;
a = 1;
if(p->coef < 0) a = 0;
a ? printf(" +"): printf(" ");
printf("%.1f%c^%d", p->coef, p->ch, p->expn);
printf("\n");
/*查找函数*/
polylink *locate_link(polylink *p, int index)
p = p->next;
while(p != NULL && p->expn != index)
p = p->next;
if(p == NULL)
return NULL;
else
return p;
/*为了代码重用*/
void creat(polylink *&p1, polylink *&p2)
p1 = creat_ploy(p1); /*创建多项式*/
printf("another polynomial building:\n");
p2 = creat_ploy(p2); /*创建多项式*/
printf("first :\n");
display_poly(p1); /*显示创建的多项式*/
printf("the second:\n");
display_poly(p2); /*显示创建的多项式*/
/*多项式相加*/
polylink * poly_add(polylink *head1, polylink *head2, char a)
char ch[1];
polylink *p1, *p2, *p, *r;
p1 = head1;
p2 = head2;
if(a == '+') /*其他函数调用时不执行*/
system("cls");
creat(p1, p2); /*创建p1 p2*/
r = p1;
while(r->next != NULL)
p1 = r->next;
r = delnode(r, p1); /*删除p1*/
p = locate_link(p2, p1->expn); /*查找p2中是否有 系数等于p1->expn的节点,有就返回该点,否则返回NULL*/
if(p != NULL)
p->coef = p->coef + p1->coef;
else /*把节点p1插入到链表p2*/
p1->next = p2->next;
p2->next = p1;
if(a == '+') /*被减或者乘运算时不调用*/
printf("add result:\n");
display_poly(p2); /*显示*/
printf("whether to derivat:y/n\n");
scanf("%s", ch);
if( ch[0] == 'Y' || ch[0] == 'y')
p2 = poly_derivation(p2);
display_poly(p2);
destroy_link(p2); /*销毁链表*/
else
destroy_link(p2);/*销毁链表*/
getchar();/*让屏幕显示停在运算结果*/
return NULL;
return p2;
/*多项式相减*/
void poly_sub(polylink *p1, polylink *p2)
char ch[1];
polylink *n, *p;
system("cls"); /*清屏*/
creat(p1, p2);
p = p2;
while(p->next != NULL)
p = p->next;
p->coef = -1 * p->coef;
printf("\nsub 1st - 2st\n");
n = poly_add(p1, p2, '-'); /*调用加运算函数*/
display_poly(n);
printf("whether to derivat:y/n\n");
scanf("%s", ch);
if( ch[0] == 'Y' || ch[0] == 'y')
n = poly_derivation(n); /*求导*/
display_poly(n);
destroy_link(n);
else destroy_link(n);
getchar();
/*多项式相乘*/
polylink *multiply(polylink *p, float coef, int index)
/*传入系数和指数,分别与p的每个节点运算 最后返回该链*/
polylink *q, *n;
n = (polylink *)malloc(sizeof(polylink));
n->next = NULL; /*n作为头节点*/
while(p->next != NULL)
p = p->next;
q = (polylink *)malloc(sizeof(polylink));
q->ch = p->ch;
q->coef = coef * p->coef;
q->expn = index + p->expn;
q->next = n->next;
n->next = q;
return n;
/*多项式相乘所用,另外为了提高代码重用性*/
void run_mul(polylink *p1, polylink *p2, int num)
int i = 0;
char ch[1];
polylink **p, *q; /*二维指针存每次multiply()函数返回的链表*/
p = (polylink **)malloc( num *sizeof(polylink));
while(p1->next != NULL)
p1 = p1->next;
p[i++] = multiply(p2, p1->coef, p1->expn);
q = poly_add(p[0], p[1], '*');
for(i = 2; i < num; i++)
q = poly_add(q, p[i], '*');
printf("mul result:\n");
display_poly(q);
printf("whether to derivat:y/n\n");
scanf("%s", ch);
if( ch[0] == 'Y' || ch[0] == 'y')
q = poly_derivation(q);
display_poly(q);
destroy_link(q);
else destroy_link(q);
getchar();
void poly_mul(polylink *p1, polylink *p2)
int num1 =0 , num2 = 0; /*用于存放p1 ,p2的表长*/
system("cls");
creat(p1, p2);
link_lenth(p1, num1);
link_lenth(p2, num2);
if(num2 >= num1) /*根据链表*/
run_mul(p1, p2, num1);
else
run_mul(p2, p1, num2);
/*选择函数*/
int menu_select()
int n;
printf("press enter key to enter the menu......"); /*按任一键进入主菜单*/
getchar(); /*从键盘读取一个字符,但不显示于屏幕*/
system("cls"); /*清屏*/
printf("\n\n\n\n\n\n");
printf("\t\t\tIt just for a variables\n\n");
printf("\t*************************************MENU***********************\n\n");
printf("\t\t\t1. 多项式相加 add operation\n\n");
printf("\t\t\t2. 多项式相减 sub operation\n\n"); /*显示*/
printf("\t\t\t3. 多项式相乘 mul operation\n\n"); /*寻找*/
printf("\t\t\t4. 退出 Quit\n\n"); /*删除*/
printf("\t****************************************************************\n\n");
do
printf("\n\t输入你的选择Enter your choice(1~4):");
scanf("%d",&n);
while(n < 1 || n > 4); /*如果选择项不在1~4之间则重输*/
return n; /*返回选择项,主函数根据该数调用相应的函数*/
void main()
polylink *head1=NULL, *head2=NULL, *head3=NULL; /*head3的作用不是很大*/
for(;;) /*循环无限次*/
switch( menu_select() )
case 1: head3 = poly_add(head1, head2, '+'); break;
case 2: poly_sub(head1, head2); break;
case 3: poly_mul(head1, head2); break;
case 4: exit(0); /*如菜单返回值为4则程序结束*/
本回答被提问者采纳
[PAT] 一元多项式的乘法与加法运算 C语言实现
好的,宝宝又来写东西啦~这次的题目是一道多项式计算题:输入两个多项式,输出他们的乘积与和,格式大概是这样:[PAT] 02-线性结构1 一元多项式的乘法与加法运算
设计函数分别求两个一元多项式的乘积与和。
输入格式:
输入分2行,每行分别先给出多项式非零项的个数,再以指数递降方式输入一个多项式非零项系数和指数(绝对值均为不超过1000的整数)。数字间以空格分隔。
输出格式:
输出分2行,分别以指数递降方式输出乘积多项式以及和多项式非零项的系数和指数。数字间以空格分隔,但结尾不能有多余空格。零多项式应输出
0 0。输入样例:
4 3 4 -5 2 6 1 -2 0 3 5 20 -7 4 3 1输出样例:
15 24 -25 22 30 21 -10 20 -21 8 35 6 -33 5 14 4 -15 3 18 2 -6 1 5 20 -4 4 -5 2 9 1 -2 0
- 时间限制:200ms
- 内存限制:64MB
- 代码长度限制:16kB
- 判题程序:系统默认
- 作者:DS课程组
- 单位:浙江大学
[
15 24] [-25 22] [30 21] [-10 20]...
每个中括号前面的是系数,后面的是指数,排序是指数从高到低.
这题难度本身不大,做出来很容易.但是要追求速度和更少内存消耗的话还是需要考虑用什么方式去储存和处理这些数据,下面给出我个人的一个方法:求乘积用双向链表,求和用动态数组.另外,我的代码比较长,因为我采用的是"空间换时间"的总体方向,所以消耗较多储存空间,好处是不用递归函数,那个是计算机最不擅长的事情.
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
typedef struct
{
int cofe;
int expo;
} NODE;
typedef struct _List
{
int cofe;
int expo;
struct _List * _next;
struct _List * _back;
} List;
构造一个NODE型的struct.存放原始每一项的系数(cofe)和指数(expo),再构造一个List型的struct,这是一个可以增长的链表,在原始数据里面不断抽取数据按指数大小进行比较排序,若指数比当前指的小就向后(左)移动一位,比当前大就向后(右)移动一位如果已经指到头则新建一个节点再写入,这其中的判断逻辑还包括系数相乘后写入系数区,排序结束后的双向链表就可以直接输出了.
1 int main(void) //全局初始化,包括建立各种变量以及读入原始数据
2 {
3 int PolyOneCount,PolyTwoCount,i,k,cofe_temp,expo_temp,flag=1,Once=1,NotZeroCount=0;
4 NODE* PolyOne=NULL;
5 NODE* PolyTwo=NULL;
6 List* PL=NULL;
7 NODE* PolySum=NULL;
8 List* PTemp;
9 NODE* P1=NULL;
10 NODE* P2=NULL;
11 scanf("%d",&PolyOneCount);
12 P1=PolyOne=(NODE*)malloc(PolyOneCount*sizeof(NODE));
13 for ( i=0; i<PolyOneCount; i++ )
14 {
15 scanf("%d",&((PolyOne+i)->cofe));
16 scanf("%d",&((PolyOne+i)->expo));
17 }
18 scanf("%d",&PolyTwoCount);
19 P2=PolyTwo=(NODE*)malloc(PolyTwoCount*sizeof(NODE));
20 for ( i=0; i<PolyTwoCount; i++ )
21 {
22 scanf("%d",&((PolyTwo+i)->cofe));
23 scanf("%d",&((PolyTwo+i)->expo));
24 }
25 List* PC=(List*)calloc(1,sizeof(List)); //PC是游走的指针,相当于一个爪子,把元素送到它需要去的地方
全局初始化,包括建立各种变量以及读入原始数据.
1 for (i=0; i<PolyOneCount; i++) 2 for (k=0; k<PolyTwoCount; k++) 3 { 4 cofe_temp=((PolyOne+i)->cofe)*((PolyTwo+k)->cofe); 5 expo_temp=((PolyOne+i)->expo)+((PolyTwo+k)->expo); 6 while (1) 7 { 8 if (Once) 9 { 10 PC->cofe = cofe_temp; 11 PC->expo = expo_temp; 12 PL=PC; 13 Once=0; 14 break; 15 } 16 17 18 if (expo_temp > PC->expo) //元素需要后移 19 { 20 if (PC->_next) //链表存在下一节点 21 { 22 flag=1; 23 if (expo_temp > (PC->_next)->expo) //尚未到位 24 PC=PC->_next; 25 else if (expo_temp < (PC->_next)->expo) //已到位 26 { 27 PTemp = (List*)calloc(1,sizeof(List)); 28 PTemp->_next = (PC->_next); 29 (PC->_next)->_back = PTemp; 30 PC->_next = PTemp; 31 PTemp->_back = PC; 32 PC=PC->_next; 33 PC->cofe = cofe_temp; 34 PC->expo = expo_temp; 35 break; 36 } 37 else if (expo_temp == (PC->_next)->expo) //元素与下一个相等 38 { 39 PC=PC->_next; 40 (PC->cofe)+=cofe_temp; 41 flag=0; 42 break; 43 } 44 } 45 46 else //双向链表无下一节点. 47 { 48 PTemp = (List*)calloc(1,sizeof(List)); 49 PTemp->_back = PC; 50 PL=PTemp; 51 PC->_next = PTemp; 52 PC=PC->_next; 53 PC->cofe = cofe_temp; 54 PC->expo = expo_temp; 55 56 break; 57 } 58 } 59 60 else if (expo_temp < PC->expo) //元素需要前移 61 { 62 if (PC->_back) //存在前驱节点 63 { 64 flag=1; 65 if (expo_temp < (PC->_back)->expo) //未到位 66 PC=PC->_back; 67 else if (expo_temp > (PC->_back)->expo) //已到位 68 { 69 PTemp = (List*)calloc(1,sizeof(List)); 70 PTemp->_back = (PC->_back); 71 (PC->_back)->_next = PTemp; 72 PC->_back = PTemp; 73 PTemp->_next = PC; 74 PC=PC->_back; 75 PC->cofe = cofe_temp; 76 PC->expo = expo_temp; 77 break; 78 } 79 else if (expo_temp == (PC->_back)->expo) 80 { 81 PC=PC->_back; 82 (PC->cofe)+=cofe_temp; 83 flag=0; 84 } 85 } 86 else //不存在前驱节点 87 { 88 PTemp = (List*)calloc(1,sizeof(List)); 89 PTemp->_next = PC; 90 // PH=PTemp; 91 PC->_back = PTemp; 92 PC=PC->_back; 93 PC->cofe = cofe_temp; 94 PC->expo = expo_temp; 95 break; 96 97 } 98 } 99 100 else 101 { 102 if (flag) (PC->cofe)+=cofe_temp; 103 break; 104 } 105 } 106 }
107 PC=PL;
以上是乘积计算代码,Once是一个标志,用来创建第一个节点.两个for循环用来遍历所有的乘积组合,当然也是这个程序中时间复杂度最高的一段代码,达到了O(N2).
1 for (;PC;PC=PC->_back)
2 {
3 if (PC->_back != NULL)
4 {
5 if (PC->cofe)
6 {
7 printf("%d %d ",PC->cofe,PC->expo);
8 NotZeroCount++;
9 }
10 else continue;
11 }
12 else
13 {
14 printf("%d %d\n",PC->cofe,PC->expo);
15 NotZeroCount++;
16 }
17 }
18 if (!NotZeroCount) printf("0 0\n");
19 NotZeroCount=0;
输出语句,中间有个if是因为题目要求最后一个不带空格;最后一个判断是看看是否是零多项式,如果是就输出"0 0"(题目要求)
1 int max = 0,Lowest = 0;
2 if ( PolyOne->expo >= PolyTwo->expo ) max = PolyOne->expo;
3 else max = PolyTwo->expo;
4 PolySum=(NODE*)calloc(max+1,sizeof(NODE));
5 i=k=0;
6 for (i=0;i<PolyOneCount;i++)
7 {
8 (PolySum+((PolyOne+i)->expo))->cofe += (PolyOne+i)->cofe;
9 (PolySum+((PolyOne+i)->expo))->expo = (PolyOne+i)->expo;
10 }
11 for (i=0;i<PolyTwoCount;i++)
12 {
13 (PolySum+((PolyTwo+i)->expo))->cofe += (PolyTwo+i)->cofe;
14 (PolySum+((PolyTwo+i)->expo))->expo = (PolyTwo+i)->expo;
15
16 }
17 NotZeroCount=0;
18 for (i=0;i<=max;i++)
19 {
20 if( (PolySum+i)->cofe )
21 {
22 NotZeroCount=1;
23 Lowest=i;
24 break;
25 }
26 }
27 if (!NotZeroCount) printf("0 0");
28 else
29 for (k=max;k>=0;k--)
30 if ((PolySum+k)->cofe != 0)
31 {
32
33 if (k==Lowest) printf("%d %d",(PolySum+k)->cofe,(PolySum+k)->expo);
34 else printf("%d %d ",(PolySum+k)->cofe,(PolySum+k)->expo);
35
36 }
37 return 0;
38 }//这里没有写free,因为做题时追求速度就省略了这一步,但是大家应当养成"一个malloc一个free"的好习惯
这里是加法的处理,直接给一个NODE型数组,其大小取两个多项式中最大指数加一为数组大小.毕竟相加的指数最大值不超过单个指数的最大值,于是数组的下标就是对应指数的存放地址啦.这里不需要考虑太多,直接连续把两个多项式加到新建的数组上,加完以后用一个for检查系数是不是全是0,如果不是,再用一个for从高指数往低指数输出所有系数非0的一组数据,就此完成~
P.S 下方附PTA运行结果
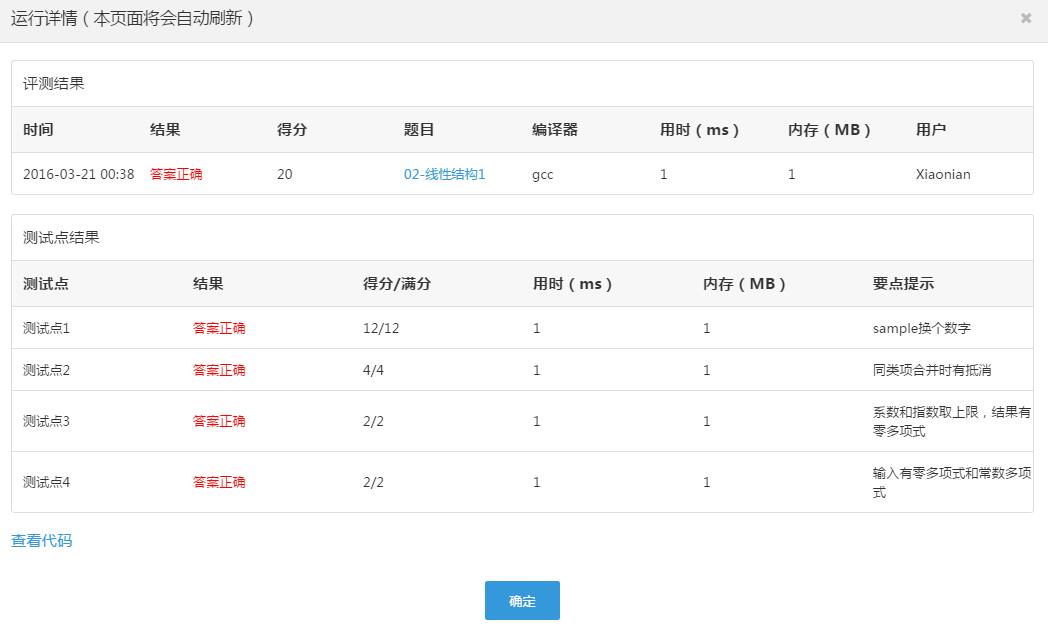

以上是关于如何用C语言实现一元多项式简单计算器的设计的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章