[Android5.1]Binder机制学习---Binder框架
Posted 迷途小书童Eric
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了[Android5.1]Binder机制学习---Binder框架相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
Binder框架
android系统中Binder机制的大体框架如下图所示:

- client:客户端进程
- server: 服务端进程
- ServiceManager:一个特殊的server,用来注册、管理其他的server
- /dev/binder:binder设备,进程间的通信就是通过该设备实现的
其中client、server和ServiceManager在用户空间,binder设备文件和binder驱动在内核空间。从上图还可以看到,client、server和ServiceManager三者之间没有交互,而是通过open/mmap/ioctl三个函数与binder驱动进行交互,从而间接地实现彼此之间的通信。
Binder通信架构
Binder的进程间通信架构如下所示:

可以看出,Binder采用的是Client/Server的通信模式。通信过程大致如下:
- server(比如MediaPlayService)调用ServiceManager的addService接口函数,注册服务;
- client(比如MediaPlay)调用ServiceManager的getService接口函数,查询并获取server的远程接口;
- client使用该远程接口,向server发送请求;
- server处理请求,并返回响应结果。
当然,client/server调用ServiceManager接口函数前,先要通过defaultServiceManager函数获得ServiceManager的远程接口,然后使用该远程接口,调用add/get等接口函数。
Binder框架Native层软件结构
到底client和server之间是怎样进行通信的呢?Binder框架提供了一整套的软件架构,由各种各样的类和继承关系构成。用户只要遵循该软件架构中定义的继承关系、接口实现等,就可以实现自定义的server,以及完成client和server将的通信。
注:这里只分析C++层的软件,java层只是多了对c++层的封装,原理是一样的。
软件架构的分层如下图所示:

服务端视角的类继承关系图:

客户端视角的类继承关系图:
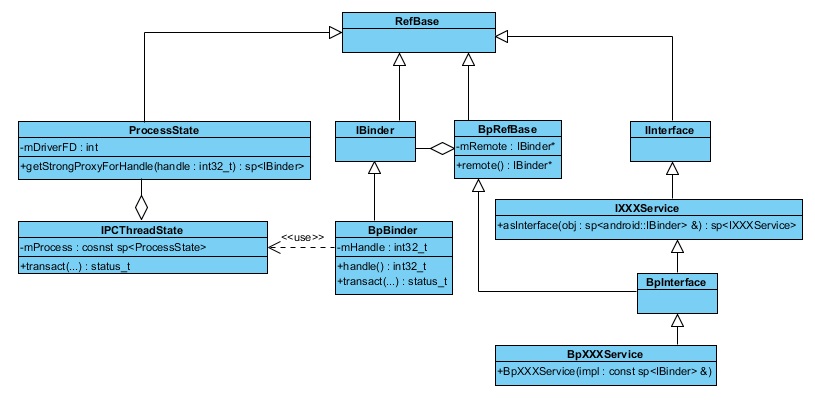
Binder驱动
binder进程间通信的核心实现代码,位于kernel层,c语言实现。
Binder适配层
封装了对/dev/binder的具体操作,实现用户空间进程和binder驱动的交互。
- ProcessState:打开/dev/binder,并将句柄存放在成员变量mDriveFD中;通过mmap来把设备文件/dev/binder映射到内存中。
- IPCThreadState:该类中有一个ProcessState类型的对象mProcess,使用mProcess就可以与binder进行通信。实际上,上层的的软件都是使用该类与binder进行通信。当client向server发送请求时,经过层层调用,最终调用IPCThreadState::transact()向binder驱动发送请求;当IPCThreadState收到client的请求后,调用IPCThreadState::executeCommand()处理请求,其中会进一步调用服务对象BBinder::transact()方法,BBinder::transact()中又继续调用BBinder派生类BnXXXService重写的onTransact()方法,从而处理client的请求。
Binder抽象层
- IBinder:接口类,里面定义的都是虚函数,由继承类BpBinder、BBinder具体实现。其中有一个很重要的虚函数IBinder::transact(),实现client和server间的通信。
- BpBinder:Binder代理对象,内部有一个成员变量mHandle,记录了远程服务对象的handle。
- BpRefBase:内部有一个成员变量mRemote,类型为IBinder*,实现类为BpBinder。BpXXXService通过该类,间接获得远程服务对象的handle,这是一个Bridge设计模式。
- BBinder:Binder本地服务对象。
Binder接口层
- IInterface:binder service接口(比如IServiceManager、 IMediaPlayService等)必须继承自IInterface。
主要是定义了asBinder()和纯虚函数onAsBinder()。其中,asBinder()直接调用onAsBinder(),onAsBinder()具体在BnInterface和BpInterface中实现。 - BpInterface:模板类,会继承两个类,IInterface和BpRefBase,然后BpXXXService继承该类。
- BnInterface:模板类,模板类,会继承两个类,IInterface和BBinder,然后BnXXXService继承该类。
Binder应用层
- IXXXXService:大部分成员函数是虚函数,由BpXXXService和BnXXXService实现,有个asInterface函数,用来new BpXXXService(obj)并返回,其中的输入参数obj就是客户端调用IServiceManager::getServie返回的BpBinder对象,这样 BpXXXService就得到了服务代理。
- BpXXXService:打包请求参数,其中包括一个功能码。然后调用remote()->transact()向服务端发送请求。由于BpXXXService通过BpInteface间接继承BpRefBase,因此这里的remote()就是BpRefBase::remote(),返回值为IBinder*类型mRemote,mRemote是IBinder接口类的实现子类BpBinder的对象引用。transact()在IBinder中定义,并在BpBinder中具体实现。于是“remote()->transact()”即BpBinder::transact(),该函数将打包的请求发送给服务端。
- BnXXXService:解包客户端发来的请求,并处理。上面介绍IPCThreadState时讲了,当IPCThreadState收到客户端的请求后,经过层层调用,最终调用BnXXXService::onTransact()。该函数根据请求参数中的功能码,完成相应的操作,并返回结果。
注意:BpXXXService和BnXXXService定义的功能码必须一致。
相关程序源码路径
以上提到的各个类的定义的程序源码整理如下:
- IServiceManager: frameworks/native/libs/binder/IServiceManager.h
- BpServiceManager: frameworks/native/libs/binder/IServiceManager.h & IServiceManager.cpp
- BpRefBase: frameworks/native/libs/binder/Binder.h & Binder.cpp
- BBinder:frameworks/native/libs/binder/Binder.h & Binder.cpp
- BpBinder: frameworks/native/libs/binder/BpBinder.h & BpBinder.cpp
- IBinder: frameworks/native/libs/binder/IBinder.h
- IPCThreadState: frameworks/native/libs/binder/IPCThreadState.h & IPCThreadState.cpp
- ProcessState: frameworks/native/libs/binder/ProcessState.h & ProcessState.cpp
- IInterface: frameworks/native/libs/binder/IInterface.h & IInterface.cpp
- BnInterface: frameworks/native/libs/binder/IInterface.h
- BpInterface: frameworks/native/libs/binder/IInterface.h
以上是关于[Android5.1]Binder机制学习---Binder框架的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章