Spring中的资源文件框架——Resource
Posted
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了Spring中的资源文件框架——Resource相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
参考技术A Spring对于资源加载有着一套自己的框架——Resource,Resource继承自InputStream。
下面的是Resource的源码:
下面的是Resource的继承图:(这里只是一部分)
那就是Resource的选择,这么多的Resource如何知道选择使用哪一个?Spring提供了一个强大的资源加载机制,,他可以通过前缀标识加载资源,如:classpath, file等,同时还支持使用Ant风格的通配符。
关于classpath:和classpath :前缀。如果有多个JAR包或文件系统路径都拥有同一个相同的包。classpath:只会找到第一个加载的,而classpath :会扫描所有的这些JAR包及类路径下出现的。
Ant风格的资源地址支持三种通配符:
ResourceLoader接口仅有一个getResource(String location)方法,可根据资源地址加载资源。不过,资源地址仅支持带资源类型前缀的表达式,不支持Ant风格的资源路径表达式。ResourcePatternResolver扩展ResourceLoader接口,定义了一个新的接口方法getResources(String locationPatern),该方法支持带资源前缀及Ant风格的资源路径表达式。
Spring Resource框架体系介绍
Resource介绍
在使用spring作为容器进行项目开发中会有很多的配置文件,这些配置文件都是通过Spring的Resource接口来实现加载,但是,Resource对于所有低级资源的访问都不够充分。例如,没有标准化的URL实现可用于访问需要从类路径或相对于ServletContext获取的资源。(更多关于ServletContext的理解,请访问https://www.cnblogs.com/cxuanBlog/p/10927813.html)虽然可以为专用的URL前缀注册新的处理程序(类似于http :)这样的前缀的现有处理程序,但这通常非常复杂,并且URL接口仍然缺少一些理想的功能,例如检查存在的方法被指向的资源。
JavaDoc解释
从实际类型的底层资源(例如文件或类路径资源)中抽象出来的资源描述符的接口。
Resource接口方法
Spring的Resource接口旨在成为一个更有能力的接口,用于抽象对低级资源的访问。以下清单显示了Resource接口定义
public interface Resource extends InputStreamSource
boolean exists();
default boolean isReadable()
return true;
default boolean isOpen()
return false;
default boolean isFile()
return false;
URL getURL() throws IOException;
URI getURI() throws IOException;
File getFile() throws IOException;
default ReadableByteChannel readableChannel() throws IOException
return Channels.newChannel(getInputStream());
long contentLength() throws IOException;
long lastModified() throws IOException;
Resource createRelative(String relativePath) throws IOException;
String getFilename();
String getDescription();
Resource接口继承了InputStreamSource接口,提供了很多InputStreamSource所没有的方法
下面来看一下InputStreamSource接口,只有一个方法
public interface InputStreamSource
InputStream getInputStream() throws IOException;
其中一些大部分重要的接口是:
getInputStream(): 找到并打开资源,返回一个InputStream以从资源中读取。预计每次调用都会返回一个新的InputStream(),调用者有责任关闭每个流exists(): 返回一个布尔值,表明某个资源是否以物理形式存在isOpen: 返回一个布尔值,指示此资源是否具有开放流的句柄。如果为true,InputStream就不能够多次读取,只能够读取一次并且及时关闭以避免内存泄漏。对于所有常规资源实现,返回false,但是InputStreamResource除外。getDescription(): 返回资源的描述,用来输出错误的日志。这通常是完全限定的文件名或资源的实际URL。
其他方法:
isReadable(): 表明资源的目录读取是否通过getInputStream()进行读取。isFile(): 表明这个资源是否代表了一个文件系统的文件。getURL(): 返回一个URL句柄,如果资源不能够被解析为URL,将抛出IOExceptiongetURI(): 返回一个资源的URI句柄getFile(): 返回某个文件,如果资源不能够被解析称为绝对路径,将会抛出FileNotFoundExceptionlastModified(): 资源最后一次修改的时间戳createRelative(): 创建此资源的相关资源getFilename(): 资源的文件名是什么 例如:最后一部分的文件名 myfile.txt
Resource的实现类
Resource 接口是 Spring 资源访问策略的抽象,它本身并不提供任何资源访问实现,具体的资源访问由该接口的实现类完成——每个实现类代表一种资源访问策略。
基础类介绍
Resource一般包括这些实现类:UrlResource、ClassPathResource、FileSystemResource、ServletContextResource、InputStreamResource、ByteArrayResource
使用UrlResource访问网络资源
访问网络资源的实现类。Resource的一个实现类用来定位URL中的资源。它支持URL的绝对路径,用来作为file: 端口的一个资源,创建一个maven项目,配置Spring依赖(不再赘述)和dom4j 的依赖,并在根目录下创建一个books.xml。
代码表示:
public class UrlResourceTest
public static void loadAndReadUrlResource(String path) throws Exception
// 创建一个 Resource 对象,指定从文件系统里读取资源,相对路径
UrlResource resource = new UrlResource(path);
// 绝对路径
// UrlResource resource = new UrlResource("file:///Users/mr.l/test/CXuan-Spring/CXuan-Spring-Resource/books.xml");
// 获取文件名
System.out.println("resource.getFileName = " + resource.getFilename());
// 获取文件描述
System.out.println("resource.getDescription = "+ resource.getDescription());
SAXReader reader = new SAXReader();
System.out.println(resource.getFile());
Document document = reader.read("file:///Users/mr.l/test/CXuan-Spring/CXuan-Spring-Resource/books.xml");
Element parent = document.getRootElement();
List<Element> elements = parent.elements();
for(Element element : elements)
// 获取name,description,price
System.out.println(element.getName() + " = " +element.getText());
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception
loadAndReadUrlResource("file:books.xml");
上面程序使用UrlResource来访问网络资源,也可以通过file 前缀访问本地资源,上述代码就是这样做的。如果要访问网络资源,可以有两种形式
- http:-该前缀用于访问基于 HTTP 协议的网络资源。
- ftp:-该前缀用于访问基于 FTP 协议的网络资源。
使用ClassPathResource 访问类加载路径下的资源
ClassPathResource 用来访问类加载路径下的资源,相对于其他的 Resource 实现类,其主要优势是方便访问类加载路径里的资源,尤其对于 Web 应用,ClassPathResource 可自动搜索位于 WEB-INF/classes 下的资源文件,无须使用绝对路径访问。
public class ClassPathResourceTest
public static void loadAndReadUrlResource(String path) throws Exception
// 创建一个 Resource 对象,指定从文件系统里读取资源,相对路径
ClassPathResource resource = new ClassPathResource(path);
// 绝对路径
// UrlResource resource = new UrlResource("file:///Users/mr.l/test/CXuan-Spring/CXuan-Spring-Resource/books.xml");
// 获取文件名
System.out.println("resource.getFileName = " + resource.getFilename());
// 获取文件描述
System.out.println("resource.getDescription = "+ resource.getDescription());
SAXReader reader = new SAXReader();
System.out.println(resource.getPath());
Document document = reader.read("file:///Users/mr.l/test/CXuan-Spring/CXuan-Spring-Resource/books.xml");
Element parent = document.getRootElement();
List<Element> elements = parent.elements();
for(Element element : elements)
// 获取name,description,price
System.out.println(element.getName() + " = " +element.getText());
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception
loadAndReadUrlResource("books.xml");
除了以上新建方式的不同,其他代码和上述代码一致,这就是 Spring 资源访问的优势:Spring 的资源访问消除了底层资源访问的差异,允许程序以一致的方式来访问不同的底层资源。
使用FileSystemResource 访问文件资源系统
Spring 提供的 FileSystemResource 类用于访问文件系统资源,使用 FileSystemResource 来访问文件系统资源并没有太大的优势,因为 Java 提供的 File 类也可用于访问文件系统资源。
当然使用 FileSystemResource 也可消除底层资源访问的差异,程序通过统一的 Resource API 来进行资源访问。下面程序是使用 FileSystemResource 来访问文件系统资源的示例程序。
public class FileSystemResourceTest
public static void loadAndReadUrlResource(String path) throws Exception
// 创建一个 Resource 对象,指定从文件系统里读取资源,相对路径
FileSystemResource resource = new FileSystemResource(path);
// 绝对路径
// UrlResource resource = new UrlResource("file:///Users/mr.l/test/CXuan-Spring/CXuan-Spring-Resource/books.xml");
// 获取文件名
System.out.println("resource.getFileName = " + resource.getFilename());
// 获取文件描述
System.out.println("resource.getDescription = "+ resource.getDescription());
SAXReader reader = new SAXReader();
System.out.println(resource.getFile());
Document document = reader.read("file:///Users/mr.l/test/CXuan-Spring/CXuan-Spring-Resource/books.xml");
Element parent = document.getRootElement();
List<Element> elements = parent.elements();
for(Element element : elements)
// 获取name,description,price
System.out.println(element.getName() + " = " +element.getText());
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception
loadAndReadUrlResource("books.xml");
FileSystemResource 实例可使用 FileSystemResource 构造器显式地创建。但更多的时候它都是隐式创建的,执行 Spring 的某个方法时,该方法接受一个代表资源路径的字符串参数,当 Spring 识别该字符串参数中包含 file: 前缀后,系统将会自动创建 FileSystemResource 对象。
ServletContextResource
这是ServletContext资源的Resource实现,它解释相关Web应用程序根目录中的相对路径。
它始终支持流(stream)访问和URL访问,但只有在扩展Web应用程序存档且资源实际位于文件系统上时才允许java.io.File访问。无论它是在文件系统上扩展还是直接从JAR或其他地方(如数据库)访问,实际上都依赖于Servlet容器。
InputStreamResource
InputStreamResource 是给定的输入流(InputStream)的Resource实现。它的使用场景在没有特定的资源实现的时候使用(感觉和@Component 的适用场景很相似)。
与其他Resource实现相比,这是已打开资源的描述符。 因此,它的isOpen()方法返回true。如果需要将资源描述符保留在某处或者需要多次读取流,请不要使用它。
ByteArrayResource
字节数组的Resource实现类。通过给定的数组创建了一个ByteArrayInputStream。
它对于从任何给定的字节数组加载内容非常有用,而无需求助于单次使用的InputStreamResource。
Resource类图与策略模式
上述Resource实现类与Resource顶级接口之间的关系可以用下面的UML关系模型来表示
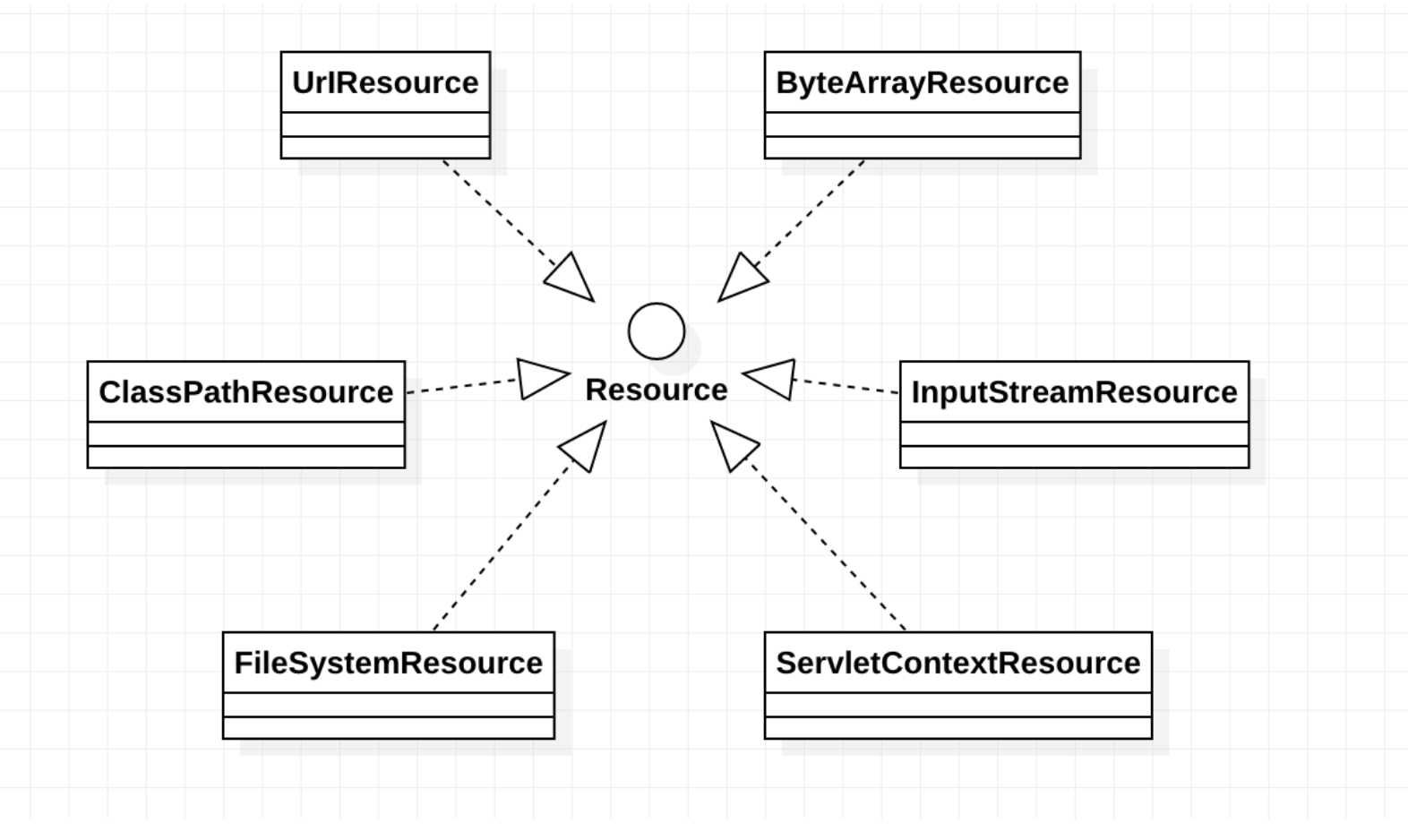
策略模式
上述流程图是不是对同一行为的不同实现方式,这种实现方式像极了策略模式?具体关于策略模式的文章,请参考
https://www.runoob.com/design-pattern/strategy-pattern.html
ResourceLoader 接口
ResourceLoader接口旨在由可以返回(即加载)Resource实例的对象实现,该接口实现类的实例将获得一个 ResourceLoader 的引用。下面是ResourceLoader的定义
public interface ResourceLoader
//该接口仅包含这个方法,该方法用于返回一个 Resource 实例。ApplicationContext 的实现类都实现 ResourceLoader 接口,因此 ApplicationContext 可用于直接获取 Resource 实例
Resource getResource(String location);
所有的应用程序上下文都实现了ResourceLoader接口。因此,所有的应用程序上下文都可能会获取Resource实例。
在特定应用程序上下文上调用getResource()并且指定的位置路径没有特定前缀时,将返回适合该特定应用程序上下文的Resource类型。 例如,假设针对ClassPathXmlApplicationContext实例执行了以下代码:
Resource template = ctx.getResource("some/resource/path/myTemplate.txt");你暂时不知道具体的上下文资源类型是什么,假设指定的是ClassPathXmlApplicationContext,上述代码就会返回ClassPathResource,如果执行上面相同的方法的是FileSystemXmlApplicationContext,上述代码就会返回的是FileSystemResource,对于web系统来说,如果上下文容器时候WebApplicationContext,那么返回的将是ServletContextResource,它同样会为每个上下文返回适当的对象。因此,您可以以适合特定应用程序上下文的方式加载资源。
另一方面,你可能强制使用ClassPathResource,忽略应用程序的上下文类型,通过添加特定的前缀classpath:,以下示例说明了这一点。
Resource template = ctx.getResource("classpath:some/resource/path/myTemplate.txt");同样的,你能够强制使用UrlResource通过使用特定的前缀:java.net.URL。下述两个例子分别表示使用http和file前缀。
Resource template = ctx.getResource("file:///some/resource/path/myTemplate.txt");
Resource template = ctx.getResource("https://myhost.com/resource/path/myTemplate.txt");下列表格对资源类型和前缀进行更好的汇总:
| Prefix | Example | Explanation |
|---|---|---|
| classpath: | classpath:com/myapp/config.xml | 从类路径加载 |
| file: | file:///data/config.xml | 从文件系统加载作为URL,查阅FileSystemResource |
| http: | https://myserver/logo.png | 加载作为URL |
| (none) | /data/config.xml | 依赖于ApplicationContext |
ResourceLoaderAware 接口
这个ResourceLoaderAware接口是一个特殊的回调接口,用于标识希望随ResourceLoader引用提供的组件,下面是ResourceLoaderAware 接口的定义
public interface ResourceLoaderAware extends Aware
void setResourceLoader(ResourceLoader resourceLoader);
ResourceLoaderAware 接口用于指定该接口的实现类必须持有一个 ResourceLoader 实例。
类似于BeanNameAware,BeanFactoryAware接口,ResourceLoaderAware接口也提供了一个setResourceLoader()方法,该方法由Spring容器负责,Spring 容器会将一个 ResourceLoader 对象作为该方法的参数传入。
当然了,一个 bean 若想加载指定路径下的资源,除了刚才提到的实现 ResourcesLoaderAware 接口之外(将 ApplicationContext 作为一个 ResourceLoader 对象注入),bean 也可以实现 ApplicationContextAware 接口,这样可以直接使用应用上下文来加载资源。但总的来说,在需求满足都满足的情况下,最好是使用的专用 ResourceLoader 接口,因为这样代码只会与接口耦合,而不会与整个 spring ApplicationContext 耦合。与 ResourceLoader 接口耦合,抛开 spring 来看,就是提供了一个加载资源的工具类接口。由于ApplicationContext也是一个ResourceLoader,因此bean还可以实现ApplicationContextAware接口并直接使用提供的应用程序上下文来加载资源。但是,通常情况下,如果有需要的话最好还是使用特定的ResourceLoader接口。
在应用程序的组件中,除了实现 ResourceLoaderAware 接口,也可采取另外一种替代方案——依赖于 ResourceLoader 的自动装配。传统的构造函数注入和byType自动装配模式(如自动装配协作者中所述)能够分别为构造函数参数或setter方法参数提供ResourceLoader。若为了获得更大的灵活性(包括属性注入的能力和多参方法),可以考虑使用基于注解的新注入方式。使用注解 @Autowiring 标记 ResourceLoader 变量,便可将其注入到成员属性、构造参数或方法参数中。
使用Resource作为属性
前面介绍了 Spring 提供的资源访问策略,但这些依赖访问策略要么需要使用 Resource 实现类,要么需要使用 ApplicationContext 来获取资源。实际上,当应用程序中的 Bean 实例需要访问资源时,Spring 有更好的解决方法:直接利用依赖注入。
从这个意义上来看,Spring 框架不仅充分利用了策略模式来简化资源访问,而且还将策略模式和 IoC 进行充分地结合,最大程度地简化了 Spring 资源访问。
归纳起来,如果 Bean 实例需要访问资源,有如下两种解决方案:
- 代码中获取 Resource 实例。
- 使用依赖注入。
对于第一种方式的资源访问,当程序获取 Resource 实例时,总需要提供 Resource 所在的位置,不管通过 FileSystemResource 创建实例,还是通过 ClassPathResource 创建实例,或者通过 ApplicationContext 的 getResource() 方法获取实例,都需要提供资源位置。这意味着:资源所在的物理位置将被耦合到代码中,如果资源位置发生改变,则必须改写程序。因此,通常建议采用第二种方法,让 Spring 为 Bean 实例依赖注入资源。
以下示例说明了这一点(可以使用set方法注入):
public class TestBean
private Resource resource;
public Resource getResource()
return resource;
public void setResource(Resource resource)
this.resource = resource;
public void parse() throws Exception
// 获取文件名
System.out.println("resource.getFileName = " + resource.getFilename());
// 获取文件描述
System.out.println("resource.getDescription = "+ resource.getDescription());
SAXReader reader = new SAXReader();
Document document = reader.read("file:///Users/mr.l/test/CXuan-Spring/CXuan-Spring-Resource/books.xml");
Element parent = document.getRootElement();
List<Element> elements = parent.elements();
for(Element element : elements)
// 获取name,description,price
System.out.println(element.getName() + " = " +element.getText());
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception
TestBean testBean = new TestBean();
testBean.setResource(new ClassPathResource("beans.xml"));
testBean.parse();
上面配置文件配置了资源的位置,并使用了 classpath: 前缀,这指明让 Spring 从类加载路径里加载 book.xml 文件。与前面类似的是,此处的前缀也可采用 http:、ftp: 等,这些前缀将强制 Spring 采用怎样的资源访问策略(也就是指定具体使用哪个 Resource 实现类);如果不采用任何前缀,则 Spring 将采用与该 ApplicationContext 相同的资源访问策略来访问资源。
<property name="template" value="classpath:some/resource/path/myTemplate.txt">
<property name="template" value="file:///some/resource/path/myTemplate.txt"/>应用程序上下文和资源路径
本节介绍如何使用资源创建应用程序上下文,包括使用XML的快捷方式,如何使用通配符以及其他详细信息。
构造应用程序上下文
应用程序上下文构造函数(对于特定的应用程序上下文类型)通常将字符串或字符串数组作为资源的位置路径,例如构成上下文定义的XML文件。
当这样的位置路径没有前缀时,从该路径构建并用于加载bean定义的特定资源类型取决于并且适合于特定的应用程序上下文。 例如,请考虑以下示例,该示例创建ClassPathXmlApplicationContext:
ApplicationContext ctx = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("conf/appContext.xml");bean 定义从类路径中加载,因为ClassPathResource被使用了,然而,考虑以下例子,创建了一个FileSystemXmlApplicationContext:
ApplicationContext ctx = new FileSystemXmlApplicationContext("conf/appContext.xml");现在bean的定义信息会从文件系统中加载,请注意,在位置路径上使用特殊类路径前缀或标准URL前缀会覆盖为加载定义而创建的默认资源类型。 请考虑以下示例:
ApplicationContext ctx = new FileSystemXmlApplicationContext("classpath:conf/appContext.xml");创建 Spring 容器时,系统将从类加载路径来搜索 appContext.xml;但使用 ApplicationContext 来访问资源时,依然采用的是 FileSystemResource 实现类,这与 FileSystemXmlApplicationContext 的访问策略是一致的。这表明:通过 classpath: 前缀指定资源访问策略仅仅对当次访问有效,程序后面进行资源访问时,还是会根据 AppliactionContext 的实现类来选择对应的资源访问策略。
应用程序上下文路径中的通配符
上下文构造资源的路径可能是一些简单路径,但是对于每一个映射来说,不可能只有简单路径,也会有特殊复杂的路径出现,这就需要使用到路径通配符(ant-style)。
ant-style示例
/WEB-INF/*-context.xml com/mycompany/**/applicationContext.xml file:C:/some/path/*-context.xml classpath:com/mycompany/**/applicationContext.xml
classpath* 和 classpath的区别:
classpath: 当使用 classpath :时前缀来指定 XML 配置文件时,系统将搜索类加载路径,找出所有与文件名的文件,分别装载文件中的配置定义,最后合并成一个 ApplicationContext。
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception
// 使用 classpath* 装载多份配置文件输出 ApplicationContext 实例。
ApplicationContext ctx = new FileSystemXmlApplicationContext("classpath*:bean.xml");
System.out.println(ctx);
如果不是采用 classpath*: 前缀,而是改为使用 classpath: 前缀,Spring 只加载第一份符合条件的 XML 文件,例如如下代码
ApplicationContext ctx = new FileSystemXmlApplicationContext("classpath:bean.xml");当使用 classpath: 前缀时,系统通过类加载路径搜索 bean.xml 文件,如果找到文件名匹配的文件,系统立即停止搜索,装载该文件,即使有多份文件名匹配的文件,系统只装载第一份文件。
路径匹配
另外,还有一种可以一次性装载多份配置文件的方式:指定配置文件时指定使用通配符,例如如下代码:
ApplicationContext ctx = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("bean*.xml");除此之外,Spring 甚至允许将 classpath*: 前缀和通配符结合使用,如下语句也是合法的:
ApplicationContext ctx = new FileSystemXmlApplicationContext("classpath*:bean*.xml");file 前缀的用法
相对路径的写法:
ApplicationContext ctx = new FileSystemXmlApplicationContext("bean.xml");绝对路径的写法:
ApplicationContext ctx = new FileSystemXmlApplicationContext("/bean.xml");如果程序中需要访问绝对路径,则不要直接使用 FileSystemResource 或 FileSystemXmlApplicationContext 来指定绝对路径。建议强制使用 file: 前缀来区分相对路径和绝对路径,例如如下两行代码
ApplicationContext ctx = new FileSystemXmlApplicationContext("file:bean.xml");
ApplicationContext ctx = new FileSystemXmlApplicationContext("file:/bean.xml");文章参考:
Spring官方文档: https://docs.spring.io/spring/docs/5.1.7.RELEASE/spring-framework-reference/core.html#resources
IBM使用手册:https://www.ibm.com/developerworks/cn/java/j-lo-spring-resource/index.html
以上是关于Spring中的资源文件框架——Resource的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章
《Spring揭秘》 ---- ApplicationContext之统一资源加载策略
Springboot框架中如何读取位于resource资源中的properties配置文件,并将配置文件中的键对应的值赋值到目标bean中?