STL剖析笔记
Posted 刘二毛
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了STL剖析笔记相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
序列式容器
元素可序,但未必有序。
vector
vector的数据结构与array相似,不同在于array是静态空间,一旦配置了内存空间就不能改变,如果要更换内存大小,需要配置一个新空间,然后将元素从旧地址一一搬到新地址,再把原来的旧空间释放。而vector是动态空间,新加入元素时,会自动扩充空间以容纳新元素。
vector源码
// 默认allocator为alloc, 其具体使用版本请参照<stl_alloc.h>
template <class T, class Alloc = alloc>
class vector
public:
// 标记为'STL标准强制要求'的typedefs用于提供iterator_traits<I>支持
typedef T value_type; // STL标准强制要求
typedef value_type* pointer; // STL标准强制要求
typedef const value_type* const_pointer;
// 由于vector的特性, 一般我们实作的时候都分配给其连续的内存空间,
// 所以其迭代器只需要定义成原生指针即可满足需要
typedef value_type* iterator; // STL标准强制要求
typedef const value_type* const_iterator;
typedef value_type& reference; // STL标准强制要求
typedef const value_type& const_reference;
typedef size_t size_type;
typedef ptrdiff_t difference_type; // STL标准强制要求
#ifdef __STL_CLASS_PARTIAL_SPECIALIZATION
typedef reverse_iterator<const_iterator> const_reverse_iterator;
typedef reverse_iterator<iterator> reverse_iterator;
#else /* __STL_CLASS_PARTIAL_SPECIALIZATION */
typedef reverse_iterator<const_iterator, value_type, const_reference,
difference_type> const_reverse_iterator;
typedef reverse_iterator<iterator, value_type, reference, difference_type>
reverse_iterator;
#endif /* __STL_CLASS_PARTIAL_SPECIALIZATION */
protected:
// 这个提供STL标准的allocator接口
typedef simple_alloc<value_type, Alloc> data_allocator;
iterator start; // 内存空间起始点
iterator finish; // 当前使用的内存空间结束点
iterator end_of_storage; // 实际分配内存空间的结束点
void insert_aux(iterator position, const T& x);
// 释放分配的内存空间
void deallocate()
// 由于使用的是data_allocator进行内存空间的分配,
// 所以需要同样嗲用data_allocator::deallocate()进行释放
// 如果直接释放, 对于data_allocator内部使用内存池的版本
// 就会发生错误
if (start) data_allocator::deallocate(start, end_of_storage - start);
void fill_initialize(size_type n, const T& value)
start = allocate_and_fill(n, value);
finish = start + n; // 设置当前使用内存空间的结束点
// 构造阶段, 此实作不多分配内存,
// 所以要设置内存空间结束点和, 已经使用的内存空间结束点相同
end_of_storage = finish;
public:
// 获取几种迭代器
iterator begin() return start;
const_iterator begin() const return start;
iterator end() return finish;
const_iterator end() const return finish;
reverse_iterator rbegin() return reverse_iterator(end());
const_reverse_iterator rbegin() const
return const_reverse_iterator(end());
reverse_iterator rend() return reverse_iterator(begin());
const_reverse_iterator rend() const
return const_reverse_iterator(begin());
// 返回当前对象个数
size_type size() const return size_type(end() - begin());
size_type max_size() const return size_type(-1) / sizeof(T);
// 返回重新分配内存前最多能存储的对象个数
size_type capacity() const return size_type(end_of_storage - begin());
bool empty() const return begin() == end();
reference operator[](size_type n) return *(begin() + n);
const_reference operator[](size_type n) const return *(begin() + n);
// 本实作中默认构造出的vector不分配内存空间
vector() : start(0), finish(0), end_of_storage(0)
// 本实作中给定个数和对象, 则只分配所需内存, 不会多分配
// vector(size_type n, const T& value)
// ↓
// fill_initialize(n, value)
// ↓
// allocate_and_fill(n, value)
// ↓
// data_allocator::allocate(n) <stl_alloc.h>
// uninitialized_fill_n(result, n, x) <stl_uninitialized.h>
vector(size_type n, const T& value) fill_initialize(n, value);
vector(int n, const T& value) fill_initialize(n, value);
vector(long n, const T& value) fill_initialize(n, value);
// 需要对象提供默认构造函数
explicit vector(size_type n) fill_initialize(n, T());
// 复制构造, 同样不会多分配内存
// vector(const vector<T, Alloc>& x)
// ↓
// allocate_and_copy(x.end() - x.begin(), x.begin(), x.end());
// ↓
// data_allocator::allocate(n) <stl_alloc.h>
// uninitialized_copy(first, last, result); <stl_uninitialized.h>
vector(const vector<T, Alloc>& x)
start = allocate_and_copy(x.end() - x.begin(), x.begin(), x.end());
finish = start + (x.end() - x.begin());
end_of_storage = finish;
// 复制指定区间的元素, 同样不多分配内存
#ifdef __STL_MEMBER_TEMPLATES
// 复制一个区间进行构造, 可能会导致多分配内存
// vector(InputIterator first, InputIterator last)
// ↓
// range_initialize(first, last, iterator_category(first));
// ↓
// for ( ; first != last; ++first)
// push_back(*first);
// 由于使用push_back()操作, 可能导致多次重复分配内存,个人感觉应该先
// data_allocator::allocate((last - first) * sizeof(T));
// 然后uninitialized_copy(first, last, result);
// 这样不会多分配内存, 也不会导致多次重新分配内存问题
template <class InputIterator>
vector(InputIterator first, InputIterator last) :
start(0), finish(0), end_of_storage(0)
range_initialize(first, last, iterator_category(first));
#else /* __STL_MEMBER_TEMPLATES */
// 复制一个区间进行构造, 可能会导致多分配内存
// vector(const_iterator first, const_iterator last)
// ↓
// distance(first, last, n);
// ↓
// allocate_and_copy(n, first, last);
// ↓
// data_allocator::allocate(n) <stl_alloc.h>
// uninitialized_copy(first, last, result); <stl_uninitialized.h>
vector(const_iterator first, const_iterator last)
size_type n = 0;
distance(first, last, n);
start = allocate_and_copy(n, first, last);
finish = start + n;
end_of_storage = finish;
#endif /* __STL_MEMBER_TEMPLATES */
~vector()
// 析构对象
destroy(start, finish);
// 释放内存
deallocate();
vector<T, Alloc>& operator=(const vector<T, Alloc>& x);
void reserve(size_type n)
if (capacity() < n)
const size_type old_size = size();
iterator tmp = allocate_and_copy(n, start, finish);
destroy(start, finish);
deallocate();
start = tmp;
finish = tmp + old_size;
end_of_storage = start + n;
// 提供访问函数
reference front() return *begin();
const_reference front() const return *begin();
reference back() return *(end() - 1);
const_reference back() const return *(end() - 1);
// 向容器尾追加一个元素, 可能导致内存重新分配
// push_back(const T& x)
// |
// |---------------- 容量已满?
// |
// ----------------------------
// No | | Yes
// | |
// ↓ ↓
// construct(finish, x); insert_aux(end(), x);
// ++finish; |
// |------ 内存不足, 重新分配
// | 大小为原来的2倍
// new_finish = data_allocator::allocate(len); <stl_alloc.h>
// uninitialized_copy(start, position, new_start); <stl_uninitialized.h>
// construct(new_finish, x); <stl_construct.h>
// ++new_finish;
// uninitialized_copy(position, finish, new_finish); <stl_uninitialized.h>
void push_back(const T& x)
// 内存满足条件则直接追加元素, 否则需要重新分配内存空间
if (finish != end_of_storage)
construct(finish, x);
++finish;
else
insert_aux(end(), x);
// 交换两个vector, 实际上是交换内部的状态指针
void swap(vector<T, Alloc>& x)
__STD::swap(start, x.start);
__STD::swap(finish, x.finish);
__STD::swap(end_of_storage, x.end_of_storage);
iterator insert(iterator position, const T& x)
size_type n = position - begin();
if (finish != end_of_storage && position == end())
construct(finish, x);
++finish;
else
insert_aux(position, x);
return begin() + n;
iterator insert(iterator position) return insert(position, T());
#ifdef __STL_MEMBER_TEMPLATES
// 在指定位置插入一个区间
// insert(iterator position, InputIterator first, InputIterator last)
// ↓
// range_insert(position, first, last, iterator_category(first));
// ↓
// for ( ; first != last; ++first)
// pos = insert(pos, *first);
// ++pos;
//
template <class InputIterator>
void insert(iterator position, InputIterator first, InputIterator last)
range_insert(position, first, last, iterator_category(first));
#else /* __STL_MEMBER_TEMPLATES */
void insert(iterator position,
const_iterator first, const_iterator last);
#endif /* __STL_MEMBER_TEMPLATES */
void insert (iterator pos, size_type n, const T& x);
void insert (iterator pos, int n, const T& x)
insert(pos, (size_type) n, x);
void insert (iterator pos, long n, const T& x)
insert(pos, (size_type) n, x);
void pop_back()
--finish;
destroy(finish);
iterator erase(iterator position)
if (position + 1 != end())
copy(position + 1, finish, position);
--finish;
destroy(finish);
return position;
iterator erase(iterator first, iterator last)
iterator i = copy(last, finish, first);
// 析构掉需要析构的元素
destroy(i, finish);
finish = finish - (last - first);
return first;
// 调整size, 但是并不会重新分配内存空间
void resize(size_type new_size, const T& x)
if (new_size < size())
erase(begin() + new_size, end());
else
insert(end(), new_size - size(), x);
void resize(size_type new_size) resize(new_size, T());
void clear() erase(begin(), end());
protected:
// 分配空间, 并且复制对象到分配的空间处
iterator allocate_and_fill(size_type n, const T& x)
iterator result = data_allocator::allocate(n);
__STL_TRY
uninitialized_fill_n(result, n, x);
return result;
__STL_UNWIND(data_allocator::deallocate(result, n));
// 分配空间并且拷贝一个区间的元素到新分配空间处
#ifdef __STL_MEMBER_TEMPLATES
template <class ForwardIterator>
iterator allocate_and_copy(size_type n,
ForwardIterator first, ForwardIterator last)
iterator result = data_allocator::allocate(n);
__STL_TRY
uninitialized_copy(first, last, result);
return result;
__STL_UNWIND(data_allocator::deallocate(result, n));
#else /* __STL_MEMBER_TEMPLATES */
iterator allocate_and_copy(size_type n,
const_iterator first, const_iterator last)
iterator result = data_allocator::allocate(n);
__STL_TRY
uninitialized_copy(first, last, result);
return result;
__STL_UNWIND(data_allocator::deallocate(result, n));
#endif /* __STL_MEMBER_TEMPLATES */
#ifdef __STL_MEMBER_TEMPLATES
// 初始化一个区间, 使用push_back()操作, 可能引发内存多次重新分配
// 解决方案见
// template <class InputIterator>
// vector(InputIterator first, InputIterator last)
// 我评注部分
template <class InputIterator>
void range_initialize(InputIterator first, InputIterator last,
input_iterator_tag)
for ( ; first != last; ++first)
push_back(*first);
// This function is only called by the constructor. We have to worry
// about resource leaks, but not about maintaining invariants.
template <class ForwardIterator>
void range_initialize(ForwardIterator first, ForwardIterator last,
forward_iterator_tag)
size_type n = 0;
distance(first, last, n);
start = allocate_and_copy(n, first, last);
finish = start + n;
end_of_storage = finish;
template <class InputIterator>
void range_insert(iterator pos,
InputIterator first, InputIterator last,
input_iterator_tag);
template <class ForwardIterator>
void range_insert(iterator pos,
ForwardIterator first, ForwardIterator last,
forward_iterator_tag);
#endif /* __STL_MEMBER_TEMPLATES */
;
// vector实现部分
template <class T, class Alloc>
inline bool operator==(const vector<T, Alloc>& x, const vector<T, Alloc>& y)
return x.size() == y.size() && equal(x.begin(), x.end(), y.begin());
// 字典序比较
template <class T, class Alloc>
inline bool operator<(const vector<T, Alloc>& x, const vector<T, Alloc>& y)
return lexicographical_compare(x.begin(), x.end(), y.begin(), y.end());
#ifdef __STL_FUNCTION_TMPL_PARTIAL_ORDER
template <class T, class Alloc>
inline void swap(vector<T, Alloc>& x, vector<T, Alloc>& y)
x.swap(y);
#endif /* __STL_FUNCTION_TMPL_PARTIAL_ORDER */
// 重载赋值运算符
// operator=(const vector<T, Alloc>& x)
// |
// |---------------- 是否是自赋值?
// ↓
// -----------------------------------------
// No | | Yes
// | |
// ↓ |------- 容量判断
// return *this; |
// ↓
// -----------------------------------------------------------------
// |x.size() > capacity() | size() >= x.size() | other
// | | |
// ↓ ↓ |
// 容量不足, 需要重新分配 容量足够, 只需要析构掉多余的对象 |
// allocate_and_copy( copy(x.begin(), x.end(), begin()); |
// x.end() - x.begin(), destroy(i, finish); |
// x.begin(), x.end()); |
// destroy(start, finish); |
// deallocate(); ↓
// copy(x.begin(), x.begin() + size(), start);
// uninitialized_copy(x.begin() + size(), x.end(), finish);
template <class T, class Alloc>
vector<T, Alloc>& vector<T, Alloc>::operator=(const vector<T, Alloc>& x)
if (&x != this)
// 如果x.size() > capacity()那么就需要重新分配内存
// 首先分配内存, 并将容器内原来的元素拷贝到新分配内存中
// 然后析构原容器中元素, 调整内存状态变量
if (x.size() > capacity())
iterator tmp = allocate_and_copy(x.end() - x.begin(),
x.begin(), x.end());
destroy(start, finish);
deallocate();
start = tmp;
end_of_storage = start + (x.end() - x.begin());
else if (size() >= x.size())
iterator i = copy(x.begin(), x.end(), begin());
destroy(i, finish);
else
copy(x.begin(), x.begin() + size(), start);
uninitialized_copy(x.begin() + size(), x.end(), finish);
finish = start + x.size();
return *this;
// 提供插入操作
// insert_aux(iterator position, const T& x)
// |
// |---------------- 容量是否足够?
// ↓
// -----------------------------------------
// Yes | | No
// | |
// ↓ |
// 从opsition开始, 整体向后移动一个位置 |
// construct(finish, *(finish - 1)); |
// ++finish; |
// T x_copy = x; |
// copy_backward(position, finish - 2, finish - 1); |
// *position = x_copy; |
// ↓
// data_allocator::allocate(len);
// uninitialized_copy(start, position, new_start);
// construct(new_finish, x);
// ++new_finish;
// uninitialized_copy(position, finish, new_finish);
// destroy(begin(), end());
// deallocate();
template <class T, class Alloc>
void vector<T, Alloc>::insert_aux(iterator position, const T& x)
if (finish != end_of_storage) // 还有剩余内存
construct(finish, *(finish - 1));
++finish;
T x_copy = x;
copy_backward(position, finish - 2, finish - 1);
*position = x_copy;
else // 内存不足, 需要重新分配
// 本实作中是按原内存2倍进行重新分配
const size_type old_size = size();
const size_type len = old_size != 0 ? 2 * old_size : 1;
iterator new_start = data_allocator::allocate(len);
iterator new_finish = new_start;
// 将内存重新配置
__STL_TRY
new_finish = uninitialized_copy(start, position, new_start);
construct(new_finish, x);
++new_finish;
new_finish = uninitialized_copy(position, finish, new_finish);
// 分配失败则抛出异常
# ifdef __STL_USE_EXCEPTIONS
catch(...)
destroy(new_start, new_finish);
data_allocator::deallocate(new_start, len);
throw;
# endif /* __STL_USE_EXCEPTIONS */
// 析构原容器中的对象
destroy(begin(), end());
// 释放原容器分配的内存
deallocate();
// 调整内存指针状态
start = new_start;
finish = new_finish;
end_of_storage = new_start + len;
template <class T, class Alloc>
void vector<T, Alloc>::insert(iterator position, size_type n, const T& x)
// 如果n为0则不进行任何操作
if (n != 0)
if (size_type(end_of_storage - finish) >= n) // 剩下的内存够分配
T x_copy = x;
const size_type elems_after = finish - position;
iterator old_finish = finish;
if (elems_after > n)
uninitialized_copy(finish - n, finish, finish);
finish += n;
copy_backward(position, old_finish - n, old_finish);
fill(position, position + n, x_copy);
else
uninitialized_fill_n(finish, n - elems_after, x_copy);
finish += n - elems_after;
uninitialized_copy(position, old_finish, finish);
finish += elems_after;
fill(position, old_finish, x_copy);
else // 剩下的内存不够分配, 需要重新分配
const size_type old_size = size();
const size_type len = old_size + max(old_size, n);
iterator new_start = data_allocator::allocate(len);
iterator new_finish = new_start;
__STL_TRY
new_finish = uninitialized_copy(start, position, new_start);
new_finish = uninitialized_fill_n(new_finish, n, x);
new_finish = uninitialized_copy(position, finish, new_finish);
# ifdef __STL_USE_EXCEPTIONS
catch(...)
destroy(new_start, new_finish);
data_allocator::deallocate(new_start, len);
throw;
# endif /* __STL_USE_EXCEPTIONS */
destroy(start, finish);
deallocate();
start = new_start;
finish = new_finish;
end_of_storage = new_start + len;
#ifdef __STL_MEMBER_TEMPLATES
// 在指定位置插入指定区间的对象
template <class T, class Alloc> template <class InputIterator>
void vector<T, Alloc>::range_insert(iterator pos,
InputIterator first, InputIterator last,
input_iterator_tag)
for ( ; first != last; ++first)
pos = insert(pos, *first);
++pos;
template <class T, class Alloc> template <class ForwardIterator>
void vector<T, Alloc>::range_insert(iterator position,
ForwardIterator first,
ForwardIterator last,
forward_iterator_tag)
if (first != last)
size_type n = 0;
distance(first, last, n);
if (size_type(end_of_storage - finish) >= n)
const size_type elems_after = finish - position;
iterator old_finish = finish;
if (elems_after > n)
uninitialized_copy(finish - n, finish, finish);
finish += n;
copy_backward(position, old_finish - n, old_finish);
copy(first, last, position);
else
ForwardIterator mid = first;
advance(mid, elems_after);
uninitialized_copy(mid, last, finish);
finish += n - elems_after;
uninitialized_copy(position, old_finish, finish);
finish += elems_after;
copy(first, mid, position);
else
const size_type old_size = size();
const size_type len = old_size + max(old_size, n);
iterator new_start = data_allocator::allocate(len);
iterator new_finish = new_start;
__STL_TRY
new_finish = uninitialized_copy(start, position, new_start);
new_finish = uninitialized_copy(first, last, new_finish);
new_finish = uninitialized_copy(position, finish, new_finish);
# ifdef __STL_USE_EXCEPTIONS
catch(...)
destroy(new_start, new_finish);
data_allocator::deallocate(new_start, len);
throw;
# endif /* __STL_USE_EXCEPTIONS */
destroy(start, finish);
deallocate();
start = new_start;
finish = new_finish;
end_of_storage = new_start + len;
#else /* __STL_MEMBER_TEMPLATES */
template <class T, class Alloc>
void vector<T, Alloc>::insert(iterator position,
const_iterator first,
const_iterator last)
if (first != last)
size_type n = 0;
distance(first, last, n);
if (size_type(end_of_storage - finish) >= n)
const size_type elems_after = finish - position;
iterator old_finish = finish;
if (elems_after > n)
uninitialized_copy(finish - n, finish, finish);
finish += n;
copy_backward(position, old_finish - n, old_finish);
copy(first, last, position);
else
uninitialized_copy(first + elems_after, last, finish);
finish += n - elems_after;
uninitialized_copy(position, old_finish, finish);
finish += elems_after;
copy(first, first + elems_after, position);
else
const size_type old_size = size();
const size_type len = old_size + max(old_size, n);
iterator new_start = data_allocator::allocate(len);
iterator new_finish = new_start;
__STL_TRY
new_finish = uninitialized_copy(start, position, new_start);
new_finish = uninitialized_copy(first, last, new_finish);
new_finish = uninitialized_copy(position, finish, new_finish);
# ifdef __STL_USE_EXCEPTIONS
catch(...)
destroy(new_start, new_finish);
data_allocator::deallocate(new_start, len);
throw;
# endif /* __STL_USE_EXCEPTIONS */
destroy(start, finish);
deallocate();
start = new_start;
finish = new_finish;
end_of_storage = new_start + len;
#endif /* __STL_MEMBER_TEMPLATES */
#if defined(__sgi) && !defined(__GNUC__) && (_MIPS_SIM != _MIPS_SIM_ABI32)
#pragma reset woff 1174
#endif
__STL_END_NAMESPACE
#endif /* __SGI_STL_INTERNAL_VECTOR_H */
// Local Variables:
// mode:C++
// End: vector迭代器
vector维护的是一个连续的线性空间,不论其元素类型为何,普通指针都可以作为vector的迭代器。vector支持随机存取,而普通指针也有这样的能力。所以,vector提供的是random access 迭代器。
vector数据结构
vector是线性连续空间,一个迭代器start指向头,一个迭代器finish指向使用的结束,代表目前被使用的空间范围,并以end_of_storage指向空间的尾端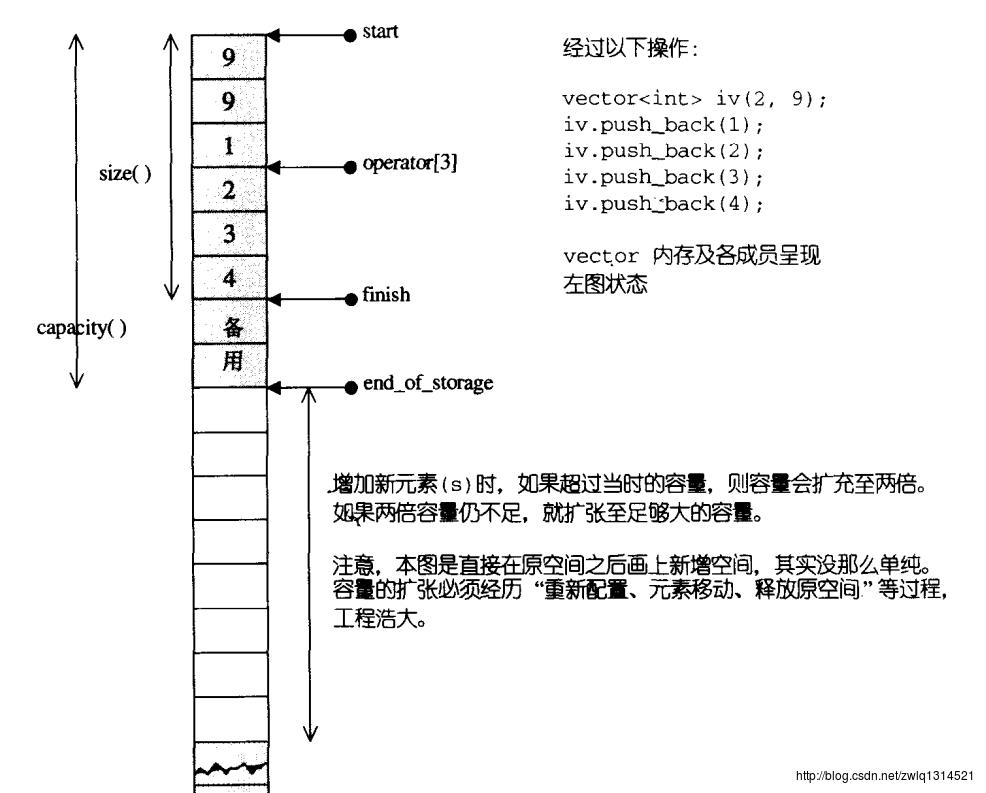 。
。
当我们使用push_back()将新元素插入vector尾端时,这个函数首先会检查是否有备用空间,如果有,就直接在备用空间上构造元素,然后调整迭代器finish,是vector 的size变大。如果没有空间了,就重新配置-移动数据-释放元空间,可以参见push_back的实现。
所以,这里vector的动态空间分配并不是在原空间之后接续新空间,而是以原空间的两倍另外配置一块较大空间,并释放原空间。
以上是关于STL剖析笔记的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章