手撕死锁代码
Posted Panda_Java
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了手撕死锁代码相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
手撕死锁代码
0. 死锁基础知识
- 多个线程同时被阻塞,它们中的⼀个或者全部都在等待某个资源被释放。由于线程被⽆限期地阻塞,因此程序不可能正常终⽌。
- 如何避免线程死锁?

1. 产生死锁代码1
public class DeadLock
public static void main(String[] args)
dataSource da = new dataSource();
//开启线程A,先获取A锁,在获取B锁
new Thread(() ->
try
da.getLockA();
catch (InterruptedException e)
e.printStackTrace();
, "线程A").start();
//开启线程B,先获取B锁,在获取A锁
new Thread(() ->
try
da.getLockB();
catch (InterruptedException e)
e.printStackTrace();
, "线程B").start();
//资源类
class dataSource
private String lockA = "A锁";
private String lockB = "B锁";
//getLockA()方法先获取A锁,在获取B锁
public void getLockA() throws InterruptedException
synchronized (lockA)
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "已经获取" +lockA);
Thread.sleep(1000); //获取A锁后,睡眠1秒钟,让getLockB()方法获取B锁
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "尝试获取" +lockB);
synchronized (lockB)
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "已经获取" +lockB);
//getLockB()方法先获取B锁,在获取A锁
public void getLockB() throws InterruptedException
synchronized (lockB)
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "已经获取" +lockB);
Thread.sleep(1000);//获取B锁后,睡眠1秒钟,让getLockA()方法获取A锁
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "尝试获取" +lockA);
synchronized (lockA)
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "已经获取" +lockA);
2. 运行结果2
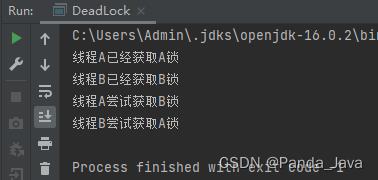
3.产生死锁代码2
public class DeadLockDemo
private static Object resource1 = new Object();//资源 1
private static Object resource2 = new Object();//资源 2
public static void main(String[] args)
new Thread(() ->
synchronized (resource1)
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread() + "get resource1");
try
Thread.sleep(1000);
catch (InterruptedException e)
e.printStackTrace();
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread() + "waiting get
resource2");
synchronized (resource2)
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread() + "get
resource2");
, "线程 1").start();
new Thread(() ->
synchronized (resource2)
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread() + "get resource2");
try
Thread.sleep(1000);
catch (InterruptedException e)
e.printStackTrace();
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread() + "waiting get
resource1");
synchronized (resource1)
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread() + "get
resource1");
, "线程 2").start();
4. 运行结果2
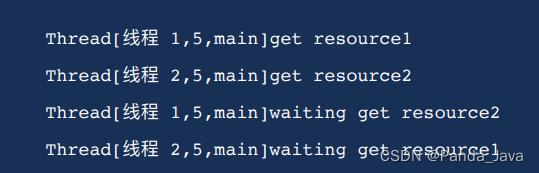
5. 避免死锁 修改线程2(靠按序申请资源来预防)
new Thread(() ->
synchronized (resource1)
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread() + "get resource1");
try
Thread.sleep(1000);
catch (InterruptedException e)
e.printStackTrace();
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread() + "waiting get
resource2");
synchronized (resource2)
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread() + "get
resource2");
, "线程 2").start();
6. 运行结果3

以上是关于手撕死锁代码的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章