shiro框架04会话管理+缓存管理+Ehcache使用
Posted 天蝎座的程序媛
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了shiro框架04会话管理+缓存管理+Ehcache使用相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
目录
1)导入相关依赖(注意:这里使用shiro的1.4.1版本)
2)实现spring与ehcache缓存(创建spring-ehcache.xml)
3)在SecurityManager安全管理器中设置缓存管理器
一、会话管理
Shiro提供了完整的企业级会话管理功能,不依赖于底层容器(如Tomcat、WebLogic),不管是J2SE还是J2EE环境都可以使用,提供了会话管理,会话事件监听,会话存储/持久化,容器无关的集群,失效/过期支持,对Web的透明支持,SSO单点登录的支持等特性。
所谓会话,即用户访问应用时保持的连接关系,在多次交互中应用能够识别出当前访问的用户是谁,且可以在多次交互中保存一些数据。如访问一些网站时登录成功后,网站可以记住用户,且在退出之前都可以识别当前用户是谁。
1.基础组件
1.1 SessionManager
会话管理器管理着应用中所有 Subject 的会话的创建、维护、删除、失效、验证等工作。是Shiro 的核心组件,顶层组件SecurityManager直接继承了SessionManager,且提供了SessionsSecurityManager实现直接把会话管理委托给相应的SessionManager
1)DefaultSessionManager:使用的默认实现,用于JavaSE环境
2)ServletContainerSessionManager:使用的默认实现,用于Web环境,其直接使用Servlet容器的会话
3)DefaultWebSessionManager:用于Web环境的实现,可以替代ServletContainerSessionManager,自己维护着会话,直接废弃了Servlet容器的会话管理
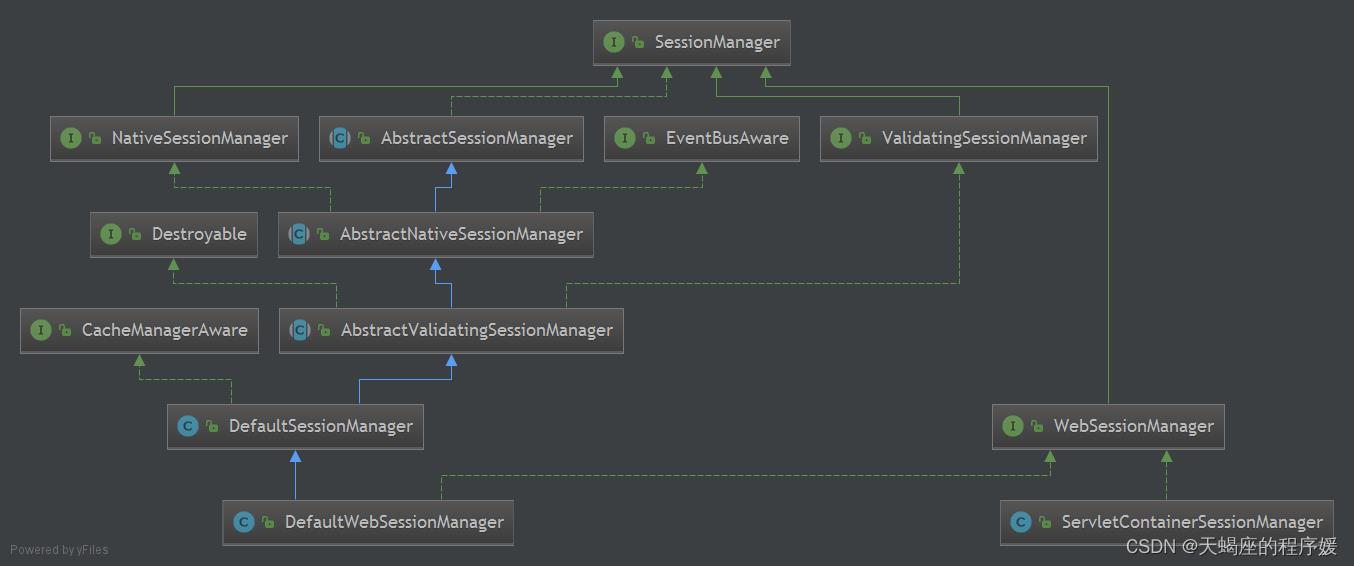
1.2 SessionListener
SessionListener会话监听器用于监听会话创建、过期及停止事件。
实现方式:
1)实现SessionListener,必须实现所有方法
2)继承SessionListenerAdapter,重写指定方法
相关API:
1)onStart(Session session):监听会话创建事件
2)onStop(Session session):监听会话销毁事件
3)onExpiration(Session session):监听会话过期事件
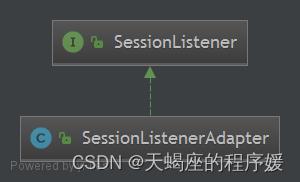
1.3 SessionDao
Shiro提供SessionDAO用于会话的CRUD,即DAO(Data Access Object)模式实现。
1)AbstractSessionDAO:提供了SessionDAO的基础实现,如生成会话ID等
2)CachingSessionDAO:提供了对开发者透明的会话缓存的功能,需要设置相应的CacheManager
3)MemorySessionDAO:直接在内存中进行会话维护(默认方式)
4)EnterpriseCacheSessionDAO:提供了缓存功能的会话维护,默认情况下使用MapCache实现,内部使用ConcurrentHashMap保存缓存的会话。
//如DefaultSessionManager在创建完session后会调用该方法;
//如保存到关系数据库/文件系统/NoSQL数据库;redis
//即可以实现会话的持久化;返回会话ID;主要此处返回的ID.equals(session.getId());
Serializable create(Session session);
//根据会话ID获取会话
Session readSession(Serializable sessionId) throws UnknownSessionException;
//更新会话;如更新会话最后访问时间/停止会话/设置超时时间/设置移除属性等会调用
void update(Session session) throws UnknownSessionException;
//删除会话;当会话过期/会话停止(如用户退出时)会调用
void delete(Session session);
//获取当前所有活跃用户,如果用户量多此方法影响性能
Collection<Session> getActiveSessions();1.4 会话验证
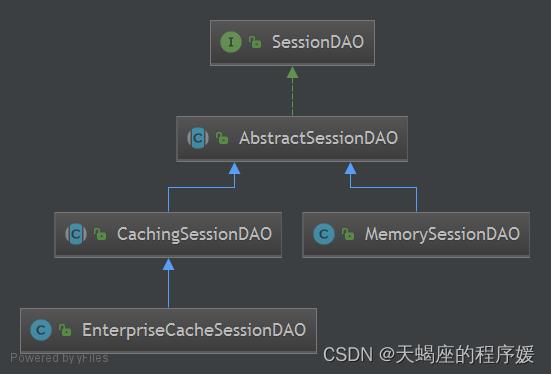
1)Shiro提供了会话验证调度器,用于定期的验证会话是否已过期,如果过期将停止会话。
2)出于性能考虑,一般情况下都是获取会话的同时来验证会话是否过期并停止会话的;但是如果在Web环境中,如果用户不主动退出是不知道会话是否过期的,因此需要定义的检测会话是否过期,Shiro提供了会话验证调度器来定期检查会话是否过期,SessionValidationScheduler 。
3)Shrio也提供了使用Quartz会话验证调度器 QuartzSessionValidationScheduler 。
1.5 案例
<!-- 创建Session ID生成器 -->
<!-- Session ID 生成器 -->
<bean id="sessionIdGenerator" class="org.apache.shiro.session.mgt.eis.JavaUuidSessionIdGenerator">
</bean><!--自定义会话管理-->
<!--sessionDao自定义会话管理,针对Session会话进行CRUD操作-->
<bean id="customSessionDao" class="org.apache.shiro.session.mgt.eis.MemorySessionDAO">
<property name="sessionIdGenerator" ref="sessionIdGenerator"/>
</bean>
<!--会话监听器-->
<bean id="shiroSessionListener" class="com.zking.ssm.book.shiro.ShiroSessionListener"/>
<!--会话cookie模板-->
<bean id="sessionIdCookie" class="org.apache.shiro.web.servlet.SimpleCookie">
<!--设置cookie的name-->
<constructor-arg value="shiro.session"/>
<!--设置cookie有效时间-->
<property name="maxAge" value="-1"/>
<!--设置httpOnly-->
<property name="httpOnly" value="true"/>
</bean><bean id="sessionManager" class="org.apache.shiro.web.session.mgt.DefaultWebSessionManager">
<!--设置session会话过期时间 毫秒 3分钟=180000-->
<property name="globalSessionTimeout" value="180000"/>
<!--设置sessionDao-->
<property name="sessionDAO" ref="customSessionDao"/>
<!--设置间隔多久检查一次session的有效性 默认60分钟-->
<property name="sessionValidationInterval" value="1800000"/>
<!--配置会话验证调度器-->
<!--<property name="sessionValidationScheduler" ref="sessionValidationScheduler"/>-->
<!--是否开启检测,默认开启-->
<!--<property name="sessionValidationSchedulerEnabled" value="true"/>-->
<!--是否删除无效的session,默认开启-->
<property name="deleteInvalidSessions" value="true"/>
<!--配置session监听器-->
<property name="sessionListeners">
<list>
<ref bean="shiroSessionListener"/>
</list>
</property>
<!--会话Cookie模板-->
<property name="sessionIdCookie" ref="sessionIdCookie"/>
<!--取消URL后面的JSESSIONID-->
<property name="sessionIdUrlRewritingEnabled" value="false"/>
</bean>
二、缓存管理
1、为什么要使用缓存
在没有使用缓存的情况下,我们每次发送请求都会调用一次doGetAuthorizationInfo方法来进行用户的授权操作,但是我们知道,一个用户具有的权限一般不会频繁的修改,也就是每次授权的内容都是一样的,所以我们希望在用户登录成功的第一次授权成功后将用户的权限保存在缓存中,下一次请求授权的话就直接从缓存中获取,这样效率会更高一些。
2、什么是ehcache
Ehcache是现在最流行的纯Java开源缓存框架,配置简单、结构清晰、功能强大。是Hibernate中默认CacheProvider。Ehcache是一种广泛使用的开源Java分布式缓存。主要面向通用缓存,Java EE和轻量级容器。它具有内存和磁盘存储,缓存加载器,缓存扩展,缓存异常处理程序,一个gzip缓存servlet过滤器,支持REST和SOAP api等特点。
注1:本章介绍的是2.X版本,3.x的版本和2.x的版本API差异比较大
3、ehcache特点
1) 够快
Ehcache的发行有一段时长了,经过几年的努力和不计其数的性能测试,Ehcache终被设计于large, high concurrency systems.
2) 够简单
开发者提供的接口非常简单明了,从Ehcache的搭建到运用运行仅仅需要的是你宝贵的几分钟。其实很多开发者都不知道自己用在用Ehcache,Ehcache被广泛的运用于其他的开源项目
3) 够袖珍
关于这点的特性,官方给了一个很可爱的名字small foot print ,一般Ehcache的发布版本不会到2M,V 2.2.3 才 668KB。
4) 够轻量
核心程序仅仅依赖slf4j这一个包,没有之一!
5) 好扩展
Ehcache提供了对大数据的内存和硬盘的存储,最近版本允许多实例、保存对象高灵活性、提供LRU、LFU、FIFO淘汰算法,基础属性支持热配置、支持的插件多
6) 监听器
缓存管理器监听器 (CacheManagerListener)和 缓存监听器(CacheEvenListener),做一些统计或数据一致性广播挺好用的
7) 分布式缓存
从Ehcache 1.2开始,支持高性能的分布式缓存,兼具灵活性和扩展性
4、ehcache入门
1)导入相关依赖
<dependency>
<groupId>net.sf.ehcache</groupId>
<artifactId>ehcache</artifactId>
<version>2.10.0</version>
</dependency>2)核心接口
CacheManager:缓存管理器
Cache:缓存对象,缓存管理器内可以放置若干cache,存放数据的实质,所有cache都实现了Ehcache接口
Element:单条缓存数据的组成单位
CacheManager -> Cache(可定义各种缓存策略) -> Element
3)核心配置文件
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<ehcache xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:noNamespaceSchemaLocation="http://ehcache.org/ehcache.xsd"
updateCheck="false">
<!--磁盘存储:将缓存中暂时不使用的对象,转移到硬盘,类似于Windows系统的虚拟内存-->
<!--path:指定在硬盘上存储对象的路径-->
<!--java.io.tmpdir 是默认的临时文件路径。 可以通过如下方式打印出具体的文件路径 System.out.println(System.getProperty("java.io.tmpdir"));-->
<diskStore path="java.io.tmpdir"/>
<!--defaultCache:默认的管理策略-->
<!--eternal:设定缓存的elements是否永远不过期。如果为true,则缓存的数据始终有效,如果为false那么还要根据timeToIdleSeconds,timeToLiveSeconds判断-->
<!--maxElementsInMemory:在内存中缓存的element的最大数目-->
<!--overflowToDisk:如果内存中数据超过内存限制,是否要缓存到磁盘上-->
<!--diskPersistent:是否在磁盘上持久化。指重启jvm后,数据是否有效。默认为false-->
<!--timeToIdleSeconds:对象空闲时间(单位:秒),指对象在多长时间没有被访问就会失效。只对eternal为false的有效。默认值0,表示一直可以访问-->
<!--timeToLiveSeconds:对象存活时间(单位:秒),指对象从创建到失效所需要的时间。只对eternal为false的有效。默认值0,表示一直可以访问-->
<!--memoryStoreEvictionPolicy:缓存的3 种清空策略-->
<!--FIFO:first in first out (先进先出)-->
<!--LFU:Less Frequently Used (最少使用).意思是一直以来最少被使用的。缓存的元素有一个hit 属性,hit 值最小的将会被清出缓存-->
<!--LRU:Least Recently Used(最近最少使用). (ehcache 默认值).缓存的元素有一个时间戳,当缓存容量满了,而又需要腾出地方来缓存新的元素的时候,那么现有缓存元素中时间戳离当前时间最远的元素将被清出缓存-->
<defaultCache eternal="false" maxElementsInMemory="1000" overflowToDisk="false" diskPersistent="false"
timeToIdleSeconds="0" timeToLiveSeconds="600" memoryStoreEvictionPolicy="LRU"/>
<!--name: Cache的名称,必须是唯一的(ehcache会把这个cache放到HashMap里)-->
<cache name="stuCache" eternal="false" maxElementsInMemory="100"
overflowToDisk="false" diskPersistent="false" timeToIdleSeconds="0"
timeToLiveSeconds="300" memoryStoreEvictionPolicy="LRU"/>
</ehcache>5、shiro与ehcache整合
1)导入相关依赖(注意:这里使用shiro的1.4.1版本)
注:之前是使用的1.3.1版本,在安全退出的时候引发了UnknownSessionException: There is no session with id错误,通过升级shiro版本后问题解决!!!o(╥﹏╥)o 一下午时间啊!!!
<dependency>
<groupId>org.apache.shiro</groupId>
<artifactId>shiro-ehcache</artifactId>
<version>1.4.1</version>
</dependency><!-- spring对ehcache的相关支持-->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-context-support</artifactId>
<version>$spring.version</version>
</dependency>2)实现spring与ehcache缓存(创建spring-ehcache.xml)
<!--使用ehcache缓存-->
<bean id="cacheManagerFactory" class="org.springframework.cache.ehcache.EhCacheManagerFactoryBean">
<property name="configLocation" value="classpath:ehcache.xml"/>
<property name="shared" value="true"/>
</bean>
<!-- 默认是cacheManager -->
<bean id="cacheManager" class="org.apache.shiro.cache.ehcache.EhCacheManager">
<property name="cacheManager" ref="cacheManagerFactory"/>
</bean>3)在SecurityManager安全管理器中设置缓存管理器
<!--设置缓存管理器-->
<property name="cacheManager" ref="cacheManager"/>
4)开启Shiro的授权或者认证数据缓存
在自定义Realm配置中开启并设置授权或者认证数据缓存
<!--开启缓存-->
<property name="cachingEnabled" value="true"/>
<!--开启授权缓存-->
<property name="authorizationCachingEnabled" value="true"/>
<!--设置ehcache的中的缓存对象名-->
<property name="authorizationCacheName" value="shiroAuthzCache"/>
注:这里只开启了授权缓存,避免每次请求都要重新查询授权数据!!!
以上就是有关会话管理的分享,关于Shiro到这也就完结了,我会发出项目包,也就是我学习Shiro所写的那个项目。感谢大家观赏!
SpringBoot项目+Shiro(权限框架)+Redis(缓存)集成
项目是SpringCloud框架,分布式项目,包括Eureka、Zuul、Config、User-Svr(用户管理的服务,既是服务端也是客户端);
SpringCloud框架的SpringBoot 的项目搭建就不再赘述,这里重点介绍如何引入集成 Shiro 框架:
Apache Shiro是一个强大且易用的Java安全框架,执行身份验证、授权、密码学和会话管理。使用Shiro的易于理解的API,您可以快速、轻松地获得任何应用程序,从最小的移动应用程序到最大的网络和企业应用程序。
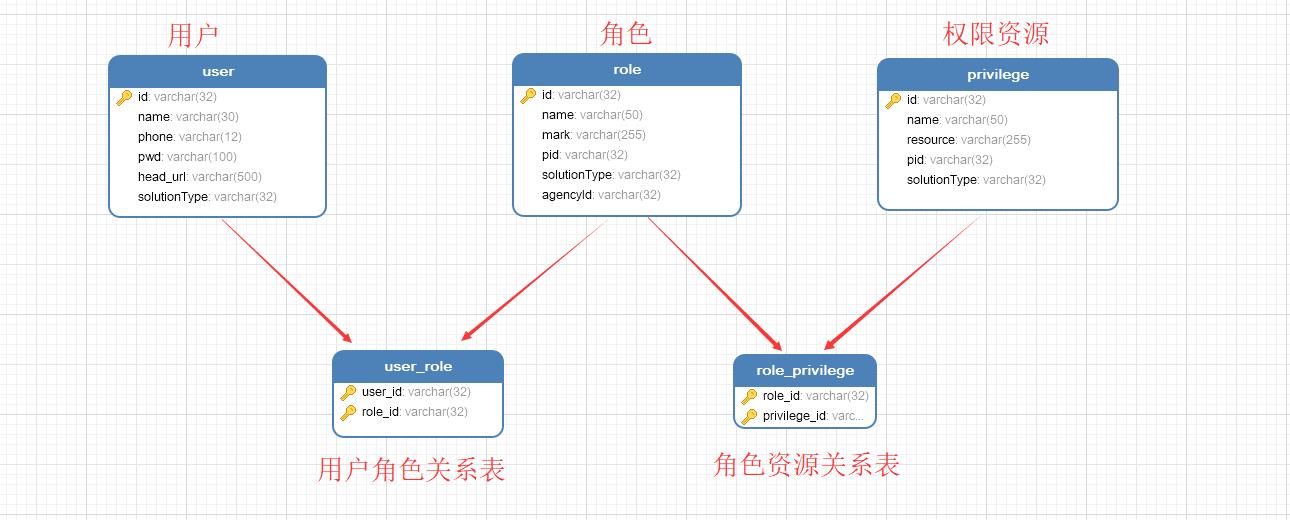
一、数据库设计
这里数据库表为5个分别是: 用户表、角色表、权限表、用户角色关系表、角色权限资源关系表
遵循三步走:导包,配置,写代码
二、导包(引入依赖)
<!-- shiro -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.apache.shiro</groupId>
<artifactId>shiro-ehcache</artifactId>
<version>1.4.2</version>
</dependency>
<!-- https://mvnrepository.com/artifact/com.sun.xml.fastinfoset/FastInfoset -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.apache.shiro</groupId>
<artifactId>shiro-spring</artifactId>
<scope>compile</scope>
<version>1.4.2</version>
</dependency>
<!-- shiro+redis缓存插件 -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.crazycake</groupId>
<artifactId>shiro-redis</artifactId>
<version>2.4.2.1-RELEASE</version>
<scope>compile</scope>
</dependency>
三、创建ShiroConfig配置ShiroServerConfig、ShiroAnnotionConfig
package com.iot.microservice.shiroconfig; import org.apache.shiro.mgt.SecurityManager; import org.apache.shiro.spring.security.interceptor.AuthorizationAttributeSourceAdvisor; import org.apache.shiro.spring.web.ShiroFilterFactoryBean; import org.apache.shiro.web.mgt.DefaultWebSecurityManager; import org.apache.shiro.web.session.mgt.DefaultWebSessionManager; import org.crazycake.shiro.RedisCacheManager; import org.crazycake.shiro.RedisManager; import org.crazycake.shiro.RedisSessionDAO; import org.springframework.aop.framework.autoproxy.DefaultAdvisorAutoProxyCreator; import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean; import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration; import java.util.LinkedHashMap; import java.util.Map; /** * Created by IntelliJ IDEA * 这是一个神奇的Class * * @author zhz * @date 2019/12/13 16:31 */ @Configuration public class ShiroServerConfig { @Bean public ShiroFilterFactoryBean shirFilter(SecurityManager securityManager) { ShiroFilterFactoryBean shiroFilterFactoryBean = new ShiroFilterFactoryBean(); // 必须设置 SecurityManager shiroFilterFactoryBean.setSecurityManager(securityManager); // 如果不设置默认会自动寻找Web工程根目录下的"/login.jsp"页面 //访问的是后端url的地址,这里要写base 服务的公用登录接口。 shiroFilterFactoryBean.setLoginUrl("http://localhost:18900/base/loginpage"); // 登录成功后要跳转的链接;现在应该没用 //shiroFilterFactoryBean.setSuccessUrl("/index"); // 未授权界面;可以写个公用的403页面 shiroFilterFactoryBean.setUnauthorizedUrl("/403"); // private Map<String, Filter> filters; shiro有一些默认的拦截器 比如auth,它就是FormAuthenticationFilter表单拦截器 <取名,拦截器地址>,可以自定义拦截器放在这 //private Map<String, String> filterChainDefinitionMap; <url,拦截器名>哪些路径会被此拦截器拦截到 //Map<String, Filter> filters = shiroFilterFactoryBean.getFilters(); //AdminFilter ad=new AdminFilter(); //filters.put("ad", ad); // 拦截器. Map<String, String> filterChainDefinitionMap = new LinkedHashMap<String, String>(); // 配置不会被拦截的链接 顺序判断 filterChainDefinitionMap.put("/static/**", "anon"); filterChainDefinitionMap.put("/login", "anon"); filterChainDefinitionMap.put("/loginpage", "anon"); filterChainDefinitionMap.put("/swagger-ui.html#", "anon"); filterChainDefinitionMap.put("/base/test", "authc"); // 配置退出过滤器,其中的具体的退出代码Shiro已经替我们实现了,加上这个会导致302,请求重置,暂不明白原因 //filterChainDefinitionMap.put("/logout", "logout"); //配置某个url需要某个权限码 //filterChainDefinitionMap.put("/hello", "perms[how_are_you]"); // 过滤链定义,从上向下顺序执行,一般将 /**放在最为下边 // <!-- authc:所有url都必须认证通过才可以访问; anon:所有url都都可以匿名访问;user:remember me的可以访问--> // filterChainDefinitionMap.put("/fine", "user"); //filterChainDefinitionMap.put("/focus/**", "ad"); shiroFilterFactoryBean.setFilterChainDefinitionMap(filterChainDefinitionMap); System.out.println("Shiro拦截器工厂类注入成功"); return shiroFilterFactoryBean; } @Bean public SecurityManager securityManager() { DefaultWebSecurityManager securityManager = new DefaultWebSecurityManager(); // 设置realm. securityManager.setRealm(myShiroRealm()); // 自定义缓存实现 使用redis securityManager.setCacheManager(cacheManager()); // 自定义session管理 使用redis securityManager.setSessionManager(sessionManager()); return securityManager; } /** * 身份认证realm; (这个需要自己写,账号密码校验;权限等) * * @return */ @Bean public ShiroServerRealm myShiroRealm() { ShiroServerRealm myShiroRealm = new ShiroServerRealm(); return myShiroRealm; } /** * cacheManager 缓存 redis实现 * 使用的是shiro-redis开源插件 * * @return */ public RedisCacheManager cacheManager() { RedisCacheManager redisCacheManager = new RedisCacheManager(); redisCacheManager.setRedisManager(redisManager()); return redisCacheManager; } /** * 配置shiro redisManager * 使用的是shiro-redis开源插件 * * @return */ @Bean public RedisManager redisManager() { RedisManager redisManager = new MyRedisManager(); // RedisManager redisManager = new RedisManager(); // redisManager.setHost(host); // redisManager.setPort(port); // // 配置缓存过期时间 // redisManager.setExpire(expireTime); // redisManager.setTimeout(timeOut); // redisManager.setPassword(password); return redisManager; } // /** // * 配置shiro redisManager // * 网上的一个 shiro-redis 插件,实现了shiro的cache接口、CacheManager接口就 // * @return // */ // @Bean // public RedisManager redisManager() { // RedisManager redisManager = new RedisManager(); // redisManager.setHost("localhost"); // redisManager.setPort(6379); // redisManager.setExpire(18000);// 配置过期时间 // // redisManager.setTimeout(timeout); // // redisManager.setPassword(password); // return redisManager; // } /** * Session Manager * 使用的是shiro-redis开源插件 */ @Bean public DefaultWebSessionManager sessionManager() { DefaultWebSessionManager sessionManager = new DefaultWebSessionManager(); sessionManager.setSessionDAO(redisSessionDAO()); return sessionManager; } /** * RedisSessionDAO shiro sessionDao层的实现 通过redis * 使用的是shiro-redis开源插件 */ @Bean public RedisSessionDAO redisSessionDAO() { RedisSessionDAO redisSessionDAO = new RedisSessionDAO(); redisSessionDAO.setRedisManager(redisManager()); return redisSessionDAO; } // /** // * 限制同一账号登录同时登录人数控制 // * // * @return // */ // @Bean // public KickoutSessionControlFilter kickoutSessionControlFilter() { // KickoutSessionControlFilter kickoutSessionControlFilter = new KickoutSessionControlFilter(); // kickoutSessionControlFilter.setCacheManager(cacheManager()); // kickoutSessionControlFilter.setSessionManager(sessionManager()); // kickoutSessionControlFilter.setKickoutAfter(false); // kickoutSessionControlFilter.setMaxSession(1); // kickoutSessionControlFilter.setKickoutUrl("/auth/kickout"); // return kickoutSessionControlFilter; // } /*** * 授权所用配置 * * @return */ @Bean public DefaultAdvisorAutoProxyCreator getDefaultAdvisorAutoProxyCreator() { DefaultAdvisorAutoProxyCreator defaultAdvisorAutoProxyCreator = new DefaultAdvisorAutoProxyCreator(); defaultAdvisorAutoProxyCreator.setProxyTargetClass(true); return defaultAdvisorAutoProxyCreator; } /*** * 使授权注解起作用不如不想配置可以在pom文件中加入 * <dependency> *<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId> *<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-aop</artifactId> *</dependency> * @param securityManager * @return */ @Bean public AuthorizationAttributeSourceAdvisor authorizationAttributeSourceAdvisor(SecurityManager securityManager){ AuthorizationAttributeSourceAdvisor authorizationAttributeSourceAdvisor = new AuthorizationAttributeSourceAdvisor(); authorizationAttributeSourceAdvisor.setSecurityManager(securityManager); return authorizationAttributeSourceAdvisor; } }
package com.iot.microservice.shiroconfig; import org.apache.shiro.spring.LifecycleBeanPostProcessor; import org.springframework.aop.framework.autoproxy.DefaultAdvisorAutoProxyCreator; import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean; import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration; import org.springframework.context.annotation.DependsOn; @Configuration public class ShiroAnnotionConfig { /** * Shiro生命周期处理器 * @return */ @Bean public LifecycleBeanPostProcessor lifecycleBeanPostProcessor(){ return new LifecycleBeanPostProcessor(); } /** * 开启Shiro的注解(如@RequiresRoles,@RequiresPermissions),需借助SpringAOP扫描使用Shiro注解的类,并在必要时进行安全逻辑验证 * 配置以下两个bean(DefaultAdvisorAutoProxyCreator(可选)和AuthorizationAttributeSourceAdvisor)即可实现此功能 * @return */ @Bean @DependsOn({"lifecycleBeanPostProcessor"}) public DefaultAdvisorAutoProxyCreator advisorAutoProxyCreator(){ DefaultAdvisorAutoProxyCreator advisorAutoProxyCreator = new DefaultAdvisorAutoProxyCreator(); advisorAutoProxyCreator.setProxyTargetClass(true); return advisorAutoProxyCreator; } }
四、自定义Realm ShiroServerRealm
package com.iot.microservice.shiroconfig; import com.keenyoda.iot.microservice.userservice.PrivilegeService; import com.keenyoda.iot.microservice.userservice.UserService; import com.keenyoda.iot.pojos.rbac.ResourceVo; import com.keenyoda.iot.pojos.user.UserEntity; import org.apache.shiro.authc.*; import org.apache.shiro.authz.AuthorizationInfo; import org.apache.shiro.authz.SimpleAuthorizationInfo; import org.apache.shiro.realm.AuthorizingRealm; import org.apache.shiro.subject.PrincipalCollection; import org.apache.shiro.util.ByteSource; import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired; import java.util.List; /** * Created by IntelliJ IDEA * 这是一个神奇的Class * * @author zhz * @date 2019/12/13 16:31 */ public class ShiroServerRealm extends AuthorizingRealm { Boolean cachingEnabled=true; @Autowired private PrivilegeService privilegeService; @Autowired private UserService userService; /** * 1.授权方法,在请求需要操作码的接口时会执行此方法。不需要操作码的接口不会执行 * 2.实际上是 先执行 AuthorizingRealm,自定义realm的父类中的 getAuthorizationInfo方法, * 逻辑是先判断缓存中是否有用户的授权信息(用户拥有的操作码),如果有 就直返回不调用自定义 realm的授权方法了, * 如果没缓存,再调用自定义realm,去数据库查询。 * 用库查询一次过后,如果 在安全管理器中注入了 缓存,授权信息就会自动保存在缓存中,下一次调用需要操作码的接口时, * 就肯定不会再调用自定义realm授权方法了。 网上有分析AuthorizingRealm,shiro使用缓存的过程 * 3.AuthorizingRealm 有多个实现类realm,推测可能是把 自定义realm注入了安全管理器,所以才调用自定义的 */ @Override protected AuthorizationInfo doGetAuthorizationInfo(PrincipalCollection principals) { SimpleAuthorizationInfo simpleAuthorInfo = new SimpleAuthorizationInfo(); UserEntity userEntity=(UserEntity) principals.getPrimaryPrincipal(); List<ResourceVo> resourceVos = privilegeService.selectResourceVoListByUserId(userEntity.getId()); if(resourceVos!=null){ for (ResourceVo resourceVo:resourceVos) { simpleAuthorInfo.addStringPermission(resourceVo.getResource()); } } return simpleAuthorInfo; } /** * 1.和授权方法一样,AuthenticatingRealm的getAuthenticationInfo,先判断缓存是否有认证信息,没有就调用 * 但试验,登录之后,再次登录,发现还是调用了认证方法,说明第一次认证登录时,没有将认证信息存到缓存中。不像授权信息, * 将缓存注入安全管理器,就自动保存了授权信息。 难道无法 防止故意多次登录 ,按理说不应该啊? * 2 可以在登录controller简单用session是否有key 判断是否登录? */ @Override protected AuthenticationInfo doGetAuthenticationInfo( AuthenticationToken authcToken) throws AuthenticationException { //获取基于用户名和密码的令牌 //实际上这个authcToken是从LoginController里面currentUser.login(token)传过来的 UsernamePasswordToken token = (UsernamePasswordToken) authcToken; String account = token.getUsername(); UserEntity user = userService.findUserUserId(account); if(user==null){throw new AuthenticationException("用户不存在");} //进行认证,将正确数据给shiro处理 //密码不用自己比对,AuthenticationInfo认证信息对象,一个接口,new他的实现类对象SimpleAuthenticationInfo /* 第一个参数随便放,可以放user对象,程序可在任意位置获取 放入的对象 * 第二个参数必须放密码, * 第三个参数放 当前realm的名字,因为可能有多个realm*/ UserEntity baseUserVM = EntityUtils.entity2VM(user, UserEntity.class, ""); SimpleAuthenticationInfo authcInfo=new SimpleAuthenticationInfo(baseUserVM, user.getPwd(), this.getName()); //密码凭证器加盐 authcInfo.setCredentialsSalt(ByteSource.Util.bytes(user.getId())); //清缓存中的授权信息,保证每次登陆 都可以重新授权。因为AuthorizingRealm会先检查缓存有没有 授权信息,再调用授权方法 super.clearCachedAuthorizationInfo(authcInfo.getPrincipals()); return authcInfo; //返回给安全管理器,securityManager,由securityManager比对数据库查询出的密码和页面提交的密码 //如果有问题,向上抛异常,一直抛到控制器 } }
工具类
package com.iot.microservice.shiroconfig; import com.github.pagehelper.Page; import org.springframework.beans.BeanUtils; import org.springframework.util.CollectionUtils; import java.lang.reflect.InvocationTargetException; import java.lang.reflect.Method; import java.util.ArrayList; import java.util.Iterator; import java.util.List; import java.util.Map; import java.util.concurrent.ConcurrentHashMap; public class EntityUtils { /** * 实体列表转Vm * * @param source 原列表 * @param vmClass vm类 * @param ignoreProperties 忽略的字段 * @param <T> 泛型 * @return vm列表 */ public static <T> List<T> entity2VMList(List<?> source, Class<T> vmClass, String... ignoreProperties) { List<T> target = (source instanceof Page ? new Page<T>() : new ArrayList<T>()); if (source instanceof Page) { BeanUtils.copyProperties(source, target); } if (CollectionUtils.isEmpty(source)) { return target; } source.forEach(e -> { target.add(entity2VM(e, vmClass, ignoreProperties)); }); return target; } /** * 实体转VM * * @param source 原对象 * @param vmClass 要转换的对象 * @param ignoreProperties 忽略的属性 * @param <T> 泛型 * @return 转换后对象 * @author Say */ public static <T> T entity2VM(Object source, Class<T> vmClass, String... ignoreProperties) { if (null == source) { return null; } try { T target = vmClass.newInstance(); BeanUtils.copyProperties(source, target, ignoreProperties); return target; } catch (InstantiationException | IllegalAccessException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } return null; } /** * VM转实体 * 底层用的vm2Entity,只是方法名做区分 * * @param source vm * @param entClass 实体 * @param ignoreProperties 忽略的属性 * @param <T> 泛型 * @return 转换后的对象 * @author Say */ public static <T> T vm2Entity(Object source, Class<T> entClass, String... ignoreProperties) { return entity2VM(source, entClass, ignoreProperties); } /** * VM转实体集合 * 底层用的entity2VMList,只是方法名做区分 * * @param source 原对象 * @param entClass 实体 * @param ignoreProperties 忽略的属性 * @param <T> 泛型 * @return 转换后的对象 * @author Say */ public static <T> List<T> vm2EntityList(List<?> source, Class<T> entClass, String... ignoreProperties) { return entity2VMList(source, entClass, ignoreProperties); } /** * Entity VM 互转 * * @param object 数据源 * @param laterObject 转换对象 * @param <T> 泛型 */ public static <T> void copyProperties(final T object, T laterObject) { if (null == object || null == laterObject) { return; } ConcurrentHashMap<String, Method> getMethods = findGetMethods(object.getClass().getMethods()); ConcurrentHashMap<String, Method> setMethods = findSetMethods(laterObject.getClass().getDeclaredMethods()); Iterator<Map.Entry<String, Method>> iterator = getMethods.entrySet().iterator(); while (iterator.hasNext()) { Map.Entry<String, Method> entry = iterator.next(); String methodName = entry.getKey(); Method getMethod = entry.getValue(); Method setMethod = setMethods.get(methodName); if (null == setMethod) { continue; } try { Object value = getMethod.invoke(object, new Object[]{}); setMethod.invoke(laterObject, value); } catch (IllegalAccessException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } catch (IllegalArgumentException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } catch (InvocationTargetException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } } /** * 获取所有的get方法 * * @param methods 所有的方法 * @return 所有的get方法 */ private static ConcurrentHashMap<String, Method> findGetMethods(Method[] methods) { ConcurrentHashMap<String, Method> getMethodsMap = new ConcurrentHashMap<>(); for (Method method : methods) { if (isGetMethod(method.getName())) { getMethodsMap.put(getMethodName(method.getName()), method); } } return getMethodsMap; } /** * 获取所有的set方法 * * @param methods 所有的方法 * @return 所有的set方法 */ private static ConcurrentHashMap<String, Method> findSetMethods(Method[] methods) { ConcurrentHashMap<String, Method> setMethodsMap = new ConcurrentHashMap<>(); for (Method method : methods) { if (isSetMethod(method.getName())) { setMethodsMap.put(getMethodName(method.getName()), method); } } return setMethodsMap; } /** * 取方法名 * * @param getMethodName 方法名称 * @return 去掉get set的方法名 */ private static String getMethodName(String getMethodName) { String fieldName = getMethodName.substring(3, getMethodName.length()); return fieldName; } /** * 判断是否是get方法 * * @param methodName * @return */ private static boolean isGetMethod(String methodName) { int index = methodName.indexOf("get"); if (index == 0) { return true; } return false; } /** * 判断是否是set方法 * * @param methodName 方法名 * @return 是否为set 方法 */ private static boolean isSetMethod(String methodName) { int index = methodName.indexOf("set"); if (index == 0) { return true; } return false; } }
五、异常处理类,拦截未授权页面(未授权页面有三种实现方式,我这里使用异常处理)
package com.iot.microservice.shiroconfig; import com.iot.commons.Message; import com.iot.commons.enumpackage.ErrorCodeEnum; import org.apache.shiro.authz.AuthorizationException; import org.apache.shiro.authz.UnauthorizedException; import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.ControllerAdvice; import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.ExceptionHandler; import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.ResponseBody; import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest; /** * Created by IntelliJ IDEA * 这是一个神奇的Class * 全局捕捉无权限异常 * * @author zhz * @date 2019/12/13 15:40 */ @ControllerAdvice public class GlobalDefaultExceptionHandler { @ExceptionHandler(UnauthorizedException.class) @ResponseBody public Message defaultExceptionHandler(HttpServletRequest req,Exception e){ return new Message(ErrorCodeEnum.UNAUTHORIZED.getValue(),"对不起,你没有访问权限!"); } @ExceptionHandler(AuthorizationException.class) @ResponseBody public Message throwAuthenticationException(HttpServletRequest req,Exception e){ return new Message(ErrorCodeEnum.AUTHENTICATION_EXCEPTION.getValue(),"账号验证异常,请重新登录!"); } }
六、因为不想我这里把redis单独做成了一个服务,为了不用多次配置,重写RedisManager 中的两个方法
package com.iot.microservice.shiroconfig; import com.iot.microservice.redisservice.RedisService; import org.crazycake.shiro.RedisManager; import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired; import org.springframework.stereotype.Component; import java.util.Base64; /** * Created by IntelliJ IDEA * 这是一个神奇的Class * * @author zhz * @date 2019/12/13 16:31 */ @Component public class MyRedisManager extends RedisManager { @Autowired RedisService redisService; @Override public byte[] set(byte[] key, byte[] value, int expire) { String val = Base64.getEncoder().encodeToString(value); expire=12000; redisService.set(new String(key),val,expire); return value; } @Override public byte[] get(byte[] key){ String s = redisService.get(new String(key)); if (s == null){ return null; } return Base64.getDecoder().decode(s); } public static void main(String[] args) { String a = null; System.out.println(Base64.getDecoder().decode(a)); } }
七、登录部分代码
/** * 用户登录 * zhz * * @param loginUser */ @RequestMapping("login") @ResponseBody public Message<String> login(LoginUserVM loginUser) throws IncorrectCredentialsException { Asserts.notEmpty(loginUser,"登录用户不能为空"); String account=loginUser.getLoginName(); String password=loginUser.getPassword(); UsernamePasswordToken token = new UsernamePasswordToken(account,password,false); token.setRememberMe(true); Subject currentUser = SecurityUtils.getSubject(); try { currentUser.login(token); } catch(IncorrectCredentialsException e){ return Message.ok("密码错误",500); } catch (AuthenticationException e) { // return Message.ok("登录失败"); return Message.ok(e.getMessage(),500); } return Message.ok(FocusMicroBaseConstants.SUCCESS); }
private Message getUserToken(UserEntity userEntity, UserInfo userInfo) { UsernamePasswordToken userToken = new UsernamePasswordToken(userEntity.getId(), userEntity.getPwd(), false); userToken.setRememberMe(true); Subject currentUser = SecurityUtils.getSubject(); try { currentUser.login(userToken); } catch (IncorrectCredentialsException e) { return <以上是关于shiro框架04会话管理+缓存管理+Ehcache使用的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章