Android常见异常处理
Posted lxq_xsyu
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了Android常见异常处理相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
android常见异常处理
什么是异常?
Exception是指在程序运行过程中所出现的不可预测的可处理可恢复的问题,这些错误会干扰到指令的正常执行,从而造成程序的异常退出或者意外终止。比如:FileNotFountException、NullPointException.
Error是指程序运行过程中较为严重的不可挽回的问题,大多数错误与代码编写者执行的操作无关,而表示代码运行时 JVM(Java 虚拟机)出现的问题。比如OutOfMemeryError,一旦出现错误程序就要挂。
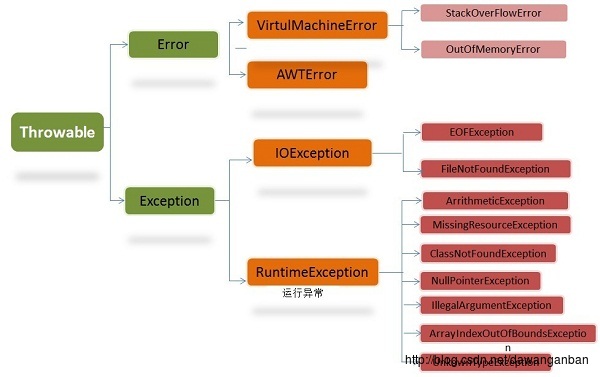
常见异常分类
编译时错误(比如:ClassNotFoundException)
从程序语法角度讲是必须进行处理的异常,如果不处理,程序就不能编译通过。如IOException、SQLException等以及用户自定义的Exception异常
运行时错误(比如:ArrayIndexOutOfBoundException)
这些异常是不检查异常,程序中可以选择捕获处理,也可以不处理。这些异常一般是由程序逻辑错误引起的,程序应该从逻辑角度尽可能避免这类异常的发生。
1、 java.lang.ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException
数组索引越界异常。当对数组的索引值为负数或大于等于数组大小时抛出。
2、java.lang.ArithmeticException
算术条件异常。譬如:整数除零等。
3、java.lang.NullPointerException
空指针异常。当应用试图在要求使用对象的地方使用了null时,抛出该异常。譬如:调用null对象的实例方法、访问null对象的属性、计算null对象的长度、使用throw语句抛出null等等
4、java.lang.ClassNotFoundException
找不到类异常。当应用试图根据字符串形式的类名构造类,而在遍历CLASSPAH之后找不到对应名称的class文件时,抛出该异常。
5、java.lang.NegativeArraySizeException 数组长度为负异常
6、java.lang.ArrayStoreException 数组中包含不兼容的值抛出的异常
7、java.lang.SecurityException 安全性异常
8、java.lang.IllegalArgumentException 非法参数异常
异常处理机制
在 Java 应用程序中,异常处理机制为:抛出异常,捕捉异常。
Java中防止空指针策略
1.使用模板方法模式规范生命周期(次序)
@Override
protected void onCreate(@Nullable Bundle savedInstanceState)
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(getContentView());
initView();
mPresenter = initPresenter();
if(mPresenter != null)
mPresenter.attachView(this);
initData();
2.明确需要创建的对象优先new出来
private List<Subscription> mSubscriptions = new ArrayList<>();
3.模块内检查非成员变量是否非空(不可靠检查)
public void setUserData(User user)
if(user == null) return;
//TODO
4.return 对象 可能为空写上必要注释
/**
* 获取用户数据
* @return User 可能返回NULL
*/
public User getUserData()
return null;
多线程异常
http://blog.csdn.net/u013256816/article/details/50417822
Thread的run方法是不抛出任何检查型异常(checked exception)的,但是它自身却可能因为一个异常而被终止,导致这个线程的终结。最麻烦的是,在线程中抛出的异常即使使用try…catch也无法截获,因此可能导致一些问题出现,比如异常的时候无法回收一些系统资源,或者没有关闭当前的连接等等。
package com.example.uncaughtException;
/**
* Created by 水寒 on 2017/11/6.
*/
public class NoCaughtThread
public static void main(String[] args)
try
Thread thread = new Thread(new Task());
thread.start();
catch(Exception e)
System.out.println("Exception:" + e.getMessage());
System.out.println("Main Thread Started....");
try
Thread.sleep(1000);
catch (InterruptedException e)
e.printStackTrace();
System.out.println("Main Thread Sleep 1000....");
class Task implements Runnable
@Override
public void run()
System.out.println(3 / 2);
System.out.println(3 / 0);
System.out.println(3 / 1);
JDK5.0之前,不能为单独的Thread设置UncaughtExceptionHandler,也不能指定一个默认的UncaughtExceptionHandler。为了可以设置一个UncaughtExceptionHandler,需要去继承ThreadGroup并覆写uncaughtException方法。
在JDK5.0中,我们通过Thread的实例方法setUncaughtExceptionHandler,可以为任何一个Thread设置一个UncaughtExceptionHandler。当然你也可以为所有Thread设置一个默认的UncaughtExceptionHandler,通过调用Thread.setDefaultUncaughtExceptionHandler(Thread.UncaughtExceptionHandler eh)方法,这是Thread的一个static方法。
public class NoCaughtThread
public static void main(String[] args)
//Thread.setDefaultUncaughtExceptionHandler(new ExceptionHandler());
Thread thread = new Thread(new Task());
thread.setUncaughtExceptionHandler(new ExceptionHandler());
thread.start();
class ExceptionHandler implements Thread.UncaughtExceptionHandler
@Override
public void uncaughtException(Thread thread, Throwable throwable)
System.out.println(thread.getName() + " Throw : " + throwable.getMessage());
Android定制错误日志系统
每当我们app测试的时候,测试人员总是对我们说这里崩溃了,那里挂掉了!我们只能默默接受,然后尝试着重现bug,更可悲的是有时候bug很难复现,为了解决这种现状所以我们要尝试这建立一个自己的bug日志系统。
Java为我们提供了一个机制,用来捕获并处理在一个线程对象中抛出的未检测异常,以避免程序终止。我们可以通过UncaughtExceptionHandler来实现这种机制。
package guohe.testkotlin.manager;
import android.app.Application;
import android.content.Context;
import java.io.PrintWriter;
import java.io.StringWriter;
import java.io.Writer;
/**
* Created by 水寒 on 2017/11/6.
* 奔溃日志管理
*/
public class CrashManager implements Thread.UncaughtExceptionHandler
private static CrashManager mInstance;
private Application mApplication;
// 系统默认的UncaughtException处理类
private Thread.UncaughtExceptionHandler mDefaultHandler;
private CrashManager(Context context)
mApplication = (Application) context.getApplicationContext();
mDefaultHandler = Thread.getDefaultUncaughtExceptionHandler();
//替换handler, 这是在主线程里执行
Thread.setDefaultUncaughtExceptionHandler(this);
public static CrashManager getInstance(Context context)
if(mInstance == null)
mInstance = new CrashManager(context);
return mInstance;
@Override
public void uncaughtException(Thread t, Throwable e)
printLog(t, e);
mDefaultHandler.uncaughtException(t, e);
private void printLog(Thread t, Throwable e)
Writer writer = new StringWriter();
PrintWriter printWriter = new PrintWriter(writer);
e.printStackTrace(printWriter);
Throwable cause = e.getCause();
while (cause != null)
cause.printStackTrace(printWriter);
cause = cause.getCause();
printWriter.close();
String result = writer.toString(); //这就是异常日志堆栈信息
System.out.println("Thread:" + t.getName() + ", exception: " + result);
Android Crash处理GitHub开源库
https://github.com/Sunzxyong/Recovery
https://github.com/drakeet/CrashWoodpecker
以上是关于Android常见异常处理的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章