JAVA——通过自定义注解实现每次程序启动时,自动扫描被注解的方法,获取其路径及访问该路径所需的权限并写入数据库
Posted 叶不修233
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了JAVA——通过自定义注解实现每次程序启动时,自动扫描被注解的方法,获取其路径及访问该路径所需的权限并写入数据库相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
JAVA——通过自定义注解实现每次程序启动时,自动扫描被注解的方法,获取其路径及访问该路径所需的权限并写入数据库
一、需求背景
在spring cloud微服务项目中,要想实现鉴权,有以下两个方案:
-
方案一:和网关关系不是特别大。auth-service 进行登录认证;各个微服务自己去做鉴权。
网关最多也就只是做一些 jwt-token 的合法性校验(判断它是否是伪造的)。 -
方案二:和网关关系很大。auth-service 进行登录认证;gate网关进行鉴权;各个微服务就不用再做鉴权(不需要去"引" spring-security)。
这里选择方案二:
方案二的优势在于:
- 整个认证鉴权的工作的"参与方"变少了,更利于 bug 的定位和编码;
- 各个微服务之间的调用变简单了,不用再相互之间传递 jwt-token 了。
但是方案二的"代价":
以前某个路径需要什么权限才能访问,是在 spring-security 的配置类中配置,或者是使用注解标明。现在需要将 路径-访问权 的关系存到数据库中
那么就要求我们每写一个controller方法,都需要在 路径-访问权 表中插入一条数据,来表示访问该方法的路径所需要的权限
因此决定采用自定义注解的方法,在需要进行权限控制的controller方法上面加上注解:
用注解的value来表示访问该路径所需要的权限。
在每次微服务启动的时候自动获取这些注解,并将这些信息写入 路径-访问权 表中。
二、实现步骤
1.自定义注解
在需要扫描的微服务项目中新建一个自定义注解,因为这里定义的注解用于鉴权,因此给该注解取名叫做MyAccessControlAnnotation
import java.lang.annotation.ElementType;
import java.lang.annotation.Retention;
import java.lang.annotation.RetentionPolicy;
import java.lang.annotation.Target;
//@Retention--用于指定注解保留范围:SOURCE源码 --> CLASS字节码 --> RUNTIME运行
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
//@Target--用于标记这个注解应该是哪种 Java 成员,METHOD用于放方法头上
@Target(ElementType.METHOD)
public @interface MyAccessControlAnnotation
//自定义成员变量:role,默认值是""
String role() default "";
//自定义成员变量:permission,默认值是""
String permission() default "";
2.使用注解
在需要进行权限控制的方法头上添加上面定义好的注解。
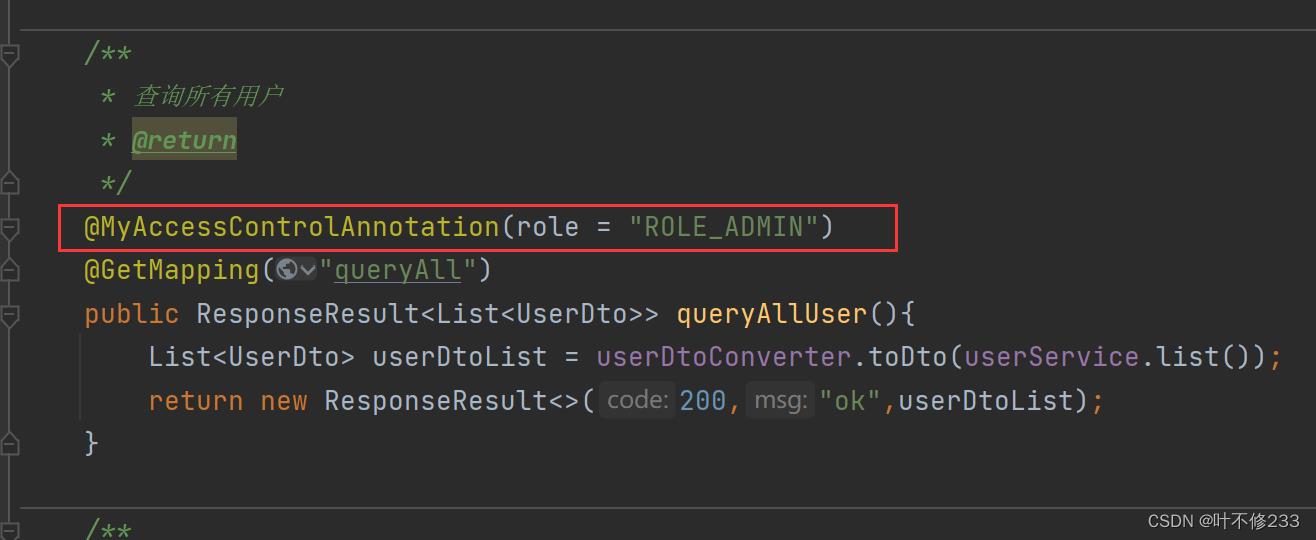
如图所示,这里在user-service中的查询所有用户方法上加上了权限控制
role = “ROLE_ADMIN”
即,访问这个方法需要角色ROLE_ADMIN
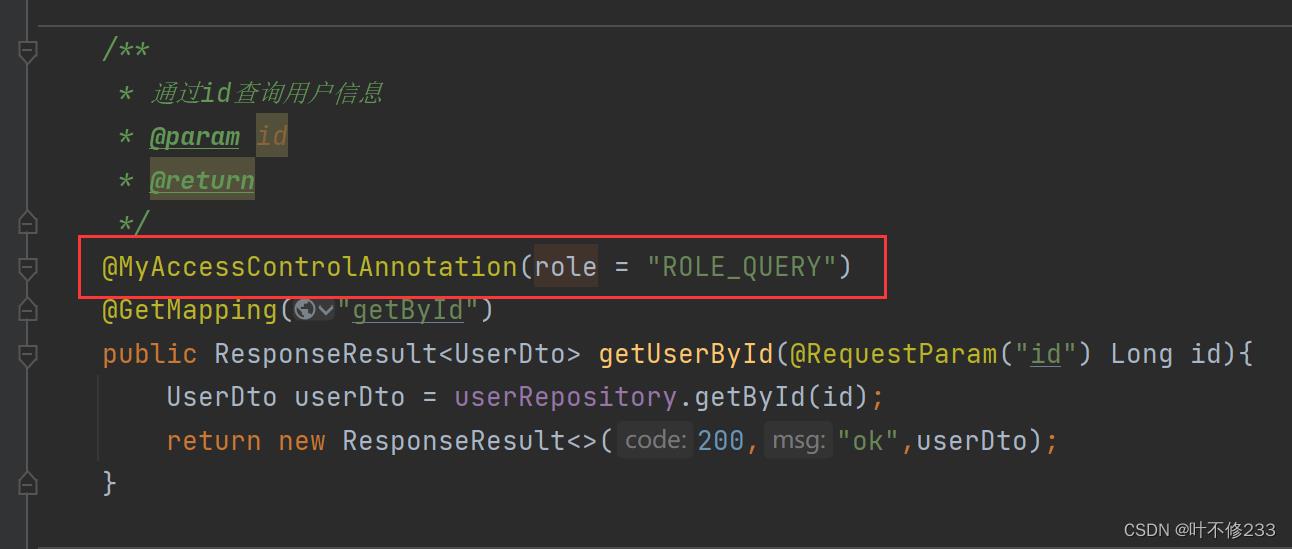
在根据id查询用户信息这个方法上加上了权限控制
role = “ROLE_QUERY”
即,访问这个方法需要角色ROLE_QUERY
全部代码如下:
package com.example.controller;
import com.example.anno.MyAccessControlAnnotation;
import com.example.converter.UserDtoConverter;
import com.example.dao.po.UserPo;
import com.example.http.dto.UserDto;
import com.example.repository.UserRepository;
import com.example.service.impl.UserServiceImpl;
import com.example.util.ResponseResult;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.*;
import javax.annotation.Resource;
import java.util.List;
/**
* <p>
* 用户表 前端控制器
* </p>
*
* @author z
* @since 2022-09-15
*/
@RestController
@RequestMapping("/user")
public class UserController
@Resource
private UserServiceImpl userService;
@Resource
private UserDtoConverter userDtoConverter;
@Resource
private UserRepository userRepository;
/**
* 查询所有用户
* @return
*/
@MyAccessControlAnnotation(role = "ROLE_ADMIN")
@GetMapping("queryAll")
public ResponseResult<List<UserDto>> queryAllUser()
List<UserDto> userDtoList = userDtoConverter.toDto(userService.list());
return new ResponseResult<>(200,"ok",userDtoList);
/**
* 注册用户
* @param user
* @return
*/
@PostMapping("register")
public ResponseResult<Boolean> register(UserPo user)
Boolean result = userService.register(user);
return new ResponseResult<Boolean>(200,"ok",result);
/**
* 通过id查询用户信息
* @param id
* @return
*/
@MyAccessControlAnnotation(role = "ROLE_QUERY")
@GetMapping("getById")
public ResponseResult<UserDto> getUserById(@RequestParam("id") Long id)
UserDto userDto = userRepository.getById(id);
return new ResponseResult<>(200,"ok",userDto);
/**
* 通过角色id查询用户列表
* @param roleId
* @return
*/
@GetMapping("getListByRoleId")
public ResponseResult<List<UserDto>> getUserListByRoleId(@RequestParam("roleId") Long roleId)
List<UserDto> userDtoList = userRepository.getListByRoleId(roleId);
return new ResponseResult<>(200,"ok",userDtoList);
/**
* 通过用户名查询用户信息
* @param account
* @return
*/
@GetMapping("getByAccount")
public ResponseResult<UserDto> getUserByAccount(@RequestParam("account") String account)
UserDto userDto = userRepository.getByAccount(account);
return new ResponseResult<>(200,"ok",userDto);
/**
* 通过id更新用户状态
* @param id
* @param statusId
* @return
*/
@PostMapping("updateStatus")
public ResponseResult<Boolean> updateUserStatus(@RequestParam("id") Long id,
@RequestParam("statusId") Long statusId)
Boolean result = userService.updateStatus(id,statusId);
return new ResponseResult<Boolean>(200,"ok",result);
/**
* 通过id更新用户角色
* @param id
* @param roleId
* @return
*/
@PostMapping("updateRole")
public ResponseResult<Boolean> updateUserRole(@RequestParam("id") Long id,
@RequestParam("roleId") Long roleId)
Boolean result = userService.updateRole(id,roleId);
return new ResponseResult<Boolean>(200,"ok",result);
3.利用反射获取和处理注解相关信息
定义一个方法handle()。
扫描被自定义注解修饰的方法。
将访问方法的路径和注解里设置的权限写入数据库。
MyAccessControlAnnotationHandle.java
package com.example.config.handle;
import com.example.anno.MyAccessControlAnnotation;
import com.example.http.api.AuthServiceClient;
import com.example.http.dto.ServiceUriAuthorityDto;
import com.example.util.ResponseResult;
import org.reflections.Reflections;
import org.springframework.expression.spel.support.ReflectivePropertyAccessor;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.GetMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.PostMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController;
import javax.annotation.Resource;
import java.lang.annotation.Annotation;
import java.lang.reflect.Method;
import java.util.Set;
@Component
public class MyAccessControlAnnotationHandle
@Resource
private AuthServiceClient authServiceClient;
public void handle()
//扫描这个包下所有被@RestController注解修饰的类
Reflections reflections = new Reflections("com.example.controller");
Set<Class<?>> restController = reflections.getTypesAnnotatedWith(RestController.class);
//遍历这些类
restController.forEach(aClass ->
//获取类中所有的方法
Method[] methods = aClass.getDeclaredMethods();
for (int i = 0; i < methods.length; i++)
//遍历类里的方法,获取被我们自定义注解修饰的方法
if(methods[i].isAnnotationPresent(MyAccessControlAnnotation.class))
// System.out.println(aClass.getSimpleName()+"类中被我自定义注解修饰的方法");
// System.out.println(methods[i].getName());
//获取类和方法中的一些信息
String path1 = "";
String path2 = "";
String methodType = "";
if(aClass.isAnnotationPresent(RequestMapping.class))
path1=aClass.getAnnotation(RequestMapping.class).value()[0];
;
if(methods[i].isAnnotationPresent(RequestMapping.class))
path2 = methods[i].getAnnotation(RequestMapping.class).value()[0];
;
if(methods[i].isAnnotationPresent(GetMapping.class))
path2 = methods[i].getAnnotation(GetMapping.class).value()[0];
methodType = "GET";
;
if(methods[i].isAnnotationPresent(PostMapping.class))
path2 = methods[i].getAnnotation(PostMapping.class).value()[0];
methodType = "POST";
;
//获取到自定义注解对象
MyAccessControlAnnotation annotation = methods[i].getAnnotation(MyAccessControlAnnotation.class);
//获取自定义注解中的成员属性值
String role = annotation.role();
String permission = annotation.permission();
//拼接以上得到的信息,用于写入数据库
if(!"".equals(path1))
path1 = path1 +"/";
//拼接得到的访问该方法的路径
String uri = "/user-service"+path1+path2;
//从注解的成员属性值中获取到访问该方法所需的角色或权限
String authority = role+","+permission;
if(authority.endsWith(","))
authority = authority.substring(0, authority.length()-1);
//把以上信息写入数据库
ServiceUriAuthorityDto serviceUriAuthorityDto = new ServiceUriAuthorityDto(methodType,uri,authority);
// System.out.println(serviceUriAuthorityDto);
//如果路径已存在,删除数据库里这些路径对应的数据
authServiceClient.deleteUriByUri(uri);
//写入路径对应的数据到数据库
ResponseResult<Boolean> booleanResponseResult = authServiceClient.addUri(serviceUriAuthorityDto);
if (booleanResponseResult.getData())
System.out.println(methods[i]+"方法的访问权限已初始化。");
else
System.out.println(methods[i]+"方法访问权限初始化失败!");
) ;
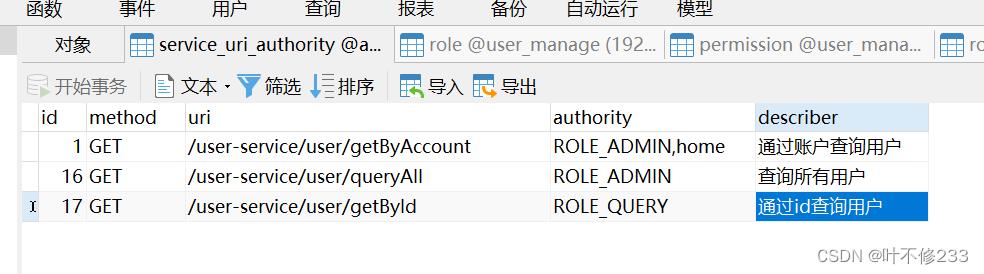
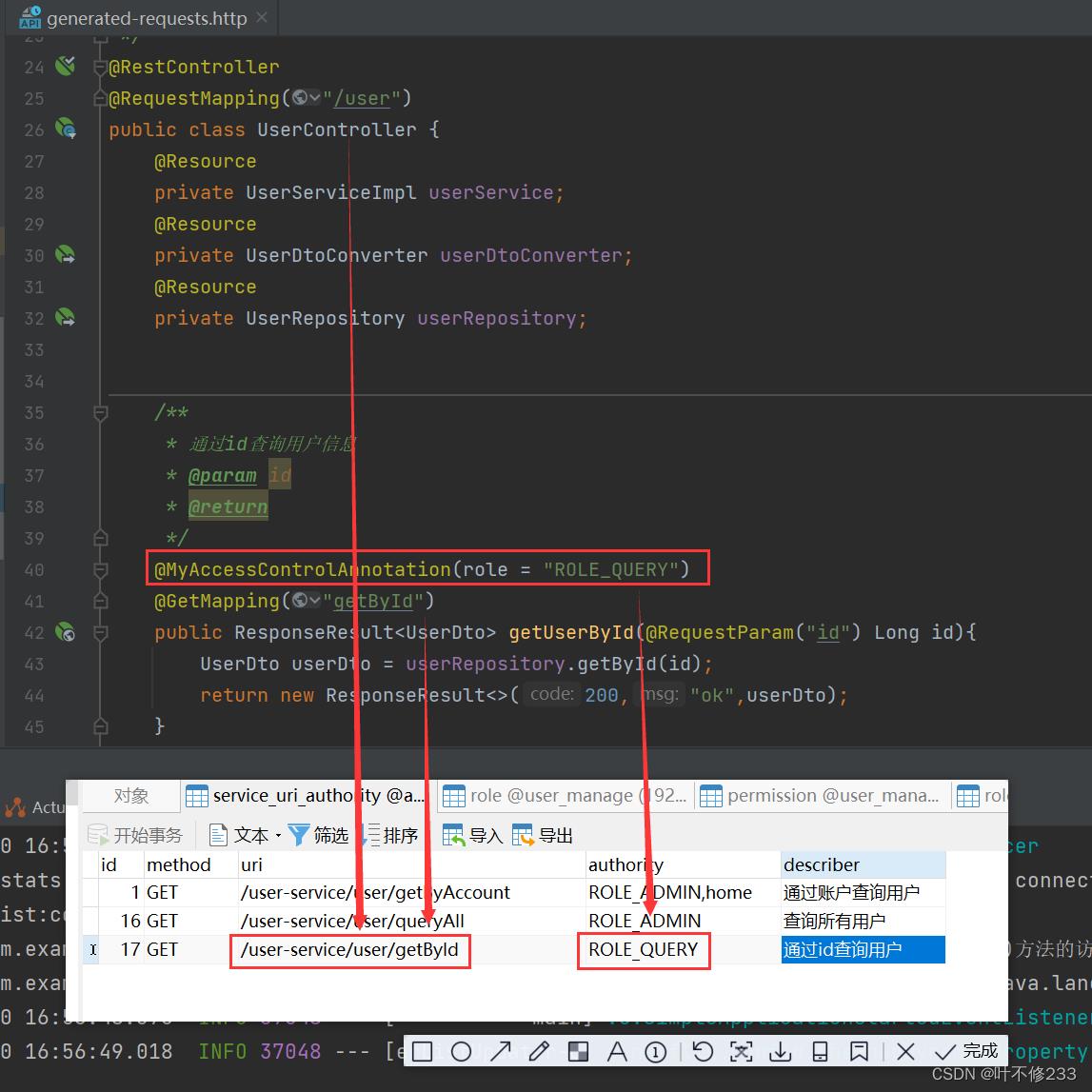
为了概念上更加便于理解,写入数据库的数据长这样子,它来自于这里:
4.设置每次微服务启动时运行方法
配置一个监听事件,用于在每次微服务启动时,自动运行上面定义好的方法。
这样,每次微服务启动,系统都会自动扫描所有的controller类下面被我们自定义的注解@MyAccessControlAnnotation修饰的方法,并将访问该方法的路径和所需权限写入数据库。
package com.example.config;
import com.example.anno.MyAccessControlAnnotation;
import com.example.config.handle.MyAccessControlAnnotationHandle;
import lombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j;
import org.springframework.boot.context.event.ApplicationStartedEvent;
import org.springframework.context.ApplicationListener;
import org.springframework.data.redis.core.StringRedisTemplate;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
import javax.annotation.Resource;
@Slf4j
@Component
public class SimpleApplicationStartedEventListener implements ApplicationListener<ApplicationStartedEvent>
@Resource
private StringRedisTemplate stringRedisTemplate;
@Resource
private MyAccessControlAnnotationHandle myAccessControlAnnotationHandle;
@Override
public void onApplicationEvent(ApplicationStartedEvent event)
//在每次微服务启动的时候调用这个方法
myAccessControlAnnotationHandle.handle();
log.info("已写入访问路径和权限到数据库");
以上是关于JAVA——通过自定义注解实现每次程序启动时,自动扫描被注解的方法,获取其路径及访问该路径所需的权限并写入数据库的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章