webpack原理篇(六十一):更复杂的 loader 的开发场
Posted 凯小默
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了webpack原理篇(六十一):更复杂的 loader 的开发场相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
说明
玩转 webpack 学习笔记
loader 的参数获取
通过 loader-utils 的 getOptions 方法获取
const loaderUtils = require("loader-utils");
module.exports = function(content)
const name = loaderUtils.getOptions(this);
;
安装依赖,这里使用 1.2.3 版本的
npm i loader-utils@1.2.3 -S
在 run-loader.js 传递参数 name:
const fs = require("fs");
const path = require("path");
const runLoaders = require("loader-runner");
runLoaders(
resource: "./src/kaimo.txt",
loaders: [
loader: path.resolve(__dirname, "./src/raw-loader.js"),
options:
name: "kaimo313"
],
context:
minimize: true
,
readResource: fs.readFile.bind(fs),
,
(err, result) =>
err ? console.error(err) : console.log(result)
);
在 raw-loader.js 接收参数
const loaderUtils = require("loader-utils");
module.exports = function(source)
const name = loaderUtils.getOptions(this);
console.log("raw-loader-getOptions-name->", name);
const json = JSON.stringify(source)
.replace('666', '313')
.replace(/\\u2028/g, '\\\\u2028' ) // 为了安全起见, ES6模板字符串的问题
.replace(/\\u2029/g, '\\\\u2029');
return `export default $json`;
;
然后运行 node run-loader.js
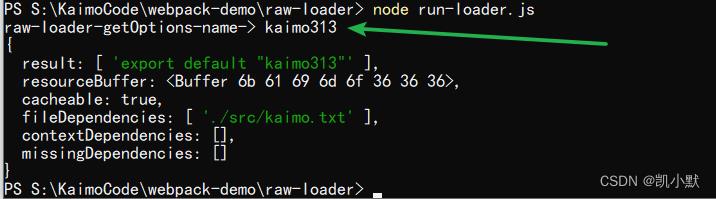
loader 异常处理
loader 内直接通过 throw 抛出
通过 this.callback 传递错误
this.callback(
err: Error | null,
content: string | Buffer,
sourceMap?: SourceMap,
meta?: any
);
const loaderUtils = require("loader-utils");
module.exports = function(source)
const name = loaderUtils.getOptions(this);
console.log("raw-loader-getOptions-name->", name);
const json = JSON.stringify(source)
.replace('666', '313')
.replace(/\\u2028/g, '\\\\u2028' ) // 为了安全起见, ES6模板字符串的问题
.replace(/\\u2029/g, '\\\\u2029');
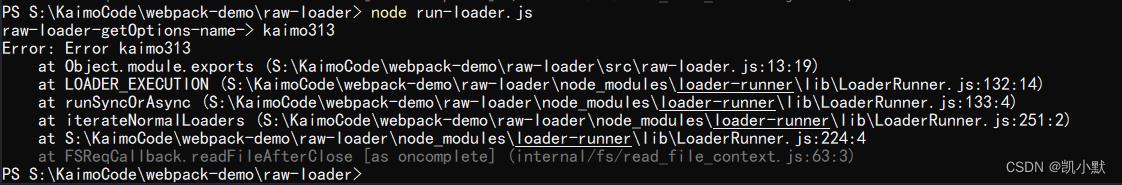
// throw new Error("Error kaimo313");
this.callback(new Error("Error kaimo313"), "");
// return `export default $json`;
// 可以回传多个值
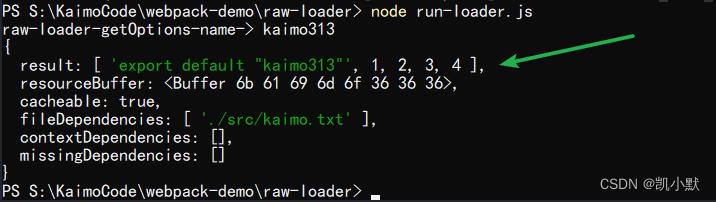
// this.callback(null, `export default $json`, 1, 2, 3, 4);
;
this.callback(null, `export default $json`, 1, 2, 3, 4);
loader 的异步处理
通过 this.async 来返回一个异步函数
- 第一个参数是 Error,第二个参数是处理的结果
示意代码:
module.exports = function (input)
const callback = this.async();
// No callback -> return synchronous results
// if (callback) ...
callback(null, input + input);
;
新建一个 async.txt 的文件,添加 async kaimo313 的内容。

添加异步读取文件
const loaderUtils = require("loader-utils");
const fs = require('fs');
const path = require('path');
const callbackify = require("util");
module.exports = function(source)
const name = loaderUtils.getOptions(this);
console.log("raw-loader-getOptions-name->", name);
const json = JSON.stringify(source)
.replace('666', '313')
.replace(/\\u2028/g, '\\\\u2028' ) // 为了安全起见, ES6模板字符串的问题
.replace(/\\u2029/g, '\\\\u2029');
// throw new Error("Error kaimo313");
// this.callback(new Error("Error kaimo313"), "");
// return `export default $json`;
// 可以回传多个值
// this.callback(null, `export default $json`, 1, 2, 3, 4);
// 上下文方法 async
const callback = this.async();
fs.readFile(path.join(__dirname, './async.txt'), 'utf-8', (err, data) =>
if(err)
callback(err, '');
callback(null, data)
);
;
然后运行 node run-loader.js
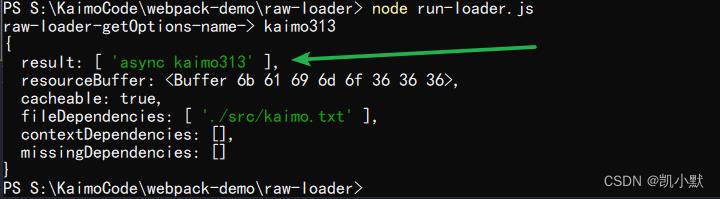
在 loader 中使用缓存
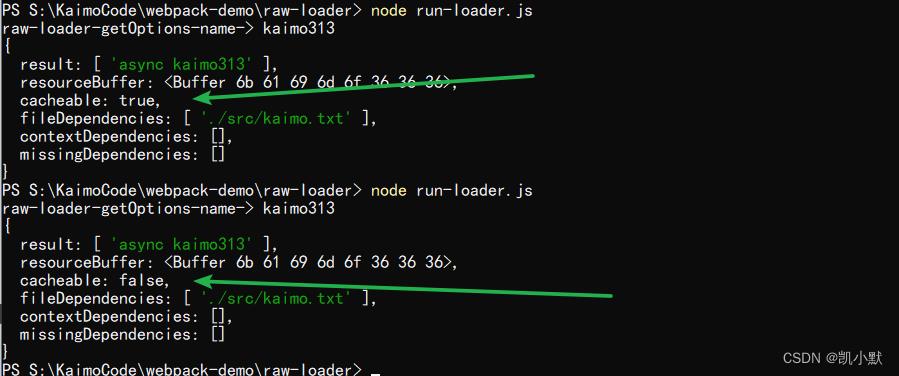
webpack 中默认开启 loader 缓存
- 可以使用 this.cacheable(false) 关掉缓存
缓存条件: loader 的结果在相同的输入下有确定的输出
- 有依赖的 loader 无法使用缓存
const loaderUtils = require("loader-utils");
const fs = require('fs');
const path = require('path');
const callbackify = require("util");
module.exports = function(source)
const name = loaderUtils.getOptions(this);
console.log("raw-loader-getOptions-name->", name);
// 不开启缓存
this.cacheable(false);
const json = JSON.stringify(source)
.replace('666', '313')
.replace(/\\u2028/g, '\\\\u2028' ) // 为了安全起见, ES6模板字符串的问题
.replace(/\\u2029/g, '\\\\u2029');
// throw new Error("Error kaimo313");
// this.callback(new Error("Error kaimo313"), "");
// return `export default $json`;
// 可以回传多个值
// this.callback(null, `export default $json`, 1, 2, 3, 4);
// 上下文方法 async
const callback = this.async();
fs.readFile(path.join(__dirname, './async.txt'), 'utf-8', (err, data) =>
if(err)
callback(err, '');
callback(null, data)
);
;
loader 如何进行文件输出?
通过 this.emitFile 进行文件写入
const loaderUtils = require("loader-utils");
module.exports = function (content)
const url = loaderUtils.interpolateName(this, "[hash].[ext]",
content,
);
this.emitFile(url, content);
const path = `__webpack_public_path__ + $JSON.stringify(url);`;
return `export default $path`;
;
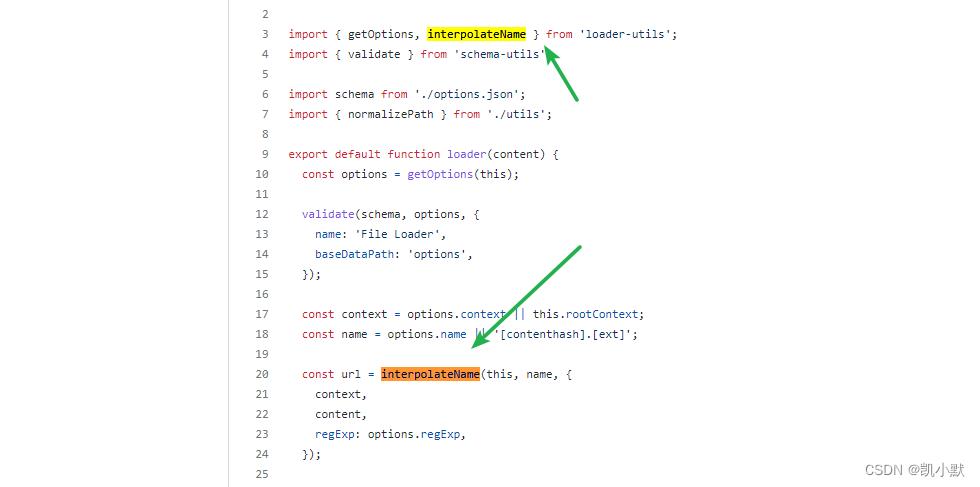
可以看一下 file-loader 的实现:https://github.com/webpack-contrib/file-loader/blob/master/src/index.js
import path from 'path';
import getOptions, interpolateName from 'loader-utils';
import validate from 'schema-utils';
import schema from './options.json';
import normalizePath from './utils';
export default function loader(content)
const options = getOptions(this);
validate(schema, options,
name: 'File Loader',
baseDataPath: 'options',
);
const context = options.context || this.rootContext;
const name = options.name || '[contenthash].[ext]';
const url = interpolateName(this, name,
context,
content,
regExp: options.regExp,
);
let outputPath = url;
if (options.outputPath)
if (typeof options.outputPath === 'function')
outputPath = options.outputPath(url, this.resourcePath, context);
else
outputPath = path.posix.join(options.outputPath, url);
let publicPath = `__webpack_public_path__ + $JSON.stringify(outputPath)`;
if (options.publicPath)
if (typeof options.publicPath === 'function')
publicPath = options.publicPath(url, this.resourcePath, context);
else
publicPath = `$
options.publicPath.endsWith('/')
? options.publicPath
: `$options.publicPath/`
$url`;
publicPath = JSON.stringify(publicPath);
if (options.postTransformPublicPath)
publicPath = options.postTransformPublicPath(publicPath);
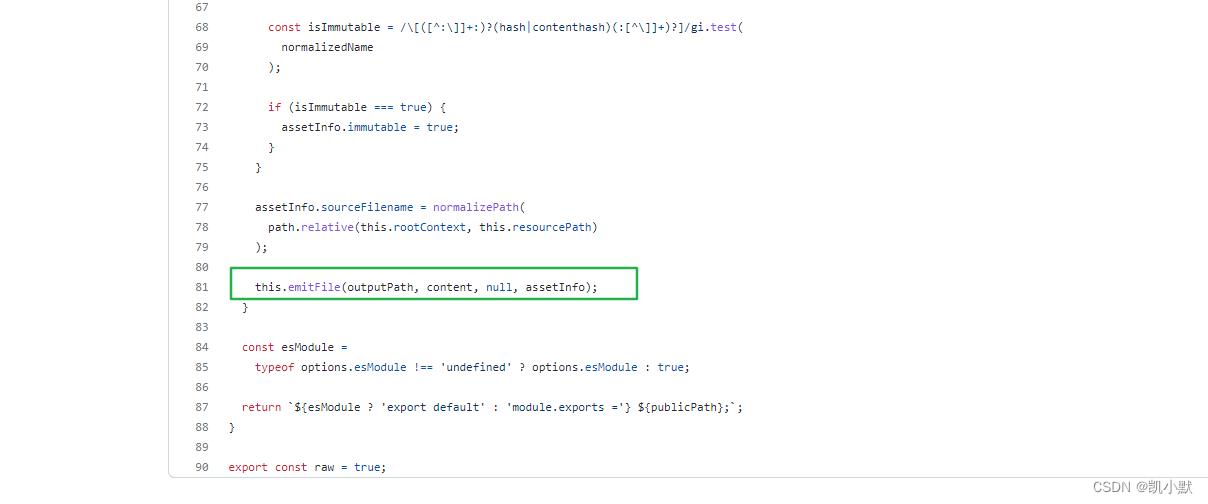
if (typeof options.emitFile === 'undefined' || options.emitFile)
const assetInfo = ;
if (typeof name === 'string')
let normalizedName = name;
const idx = normalizedName.indexOf('?');
if (idx >= 0)
normalizedName = normalizedName.substr(0, idx);
const isImmutable = /\\[([^:\\]]+:)?(hash|contenthash)(:[^\\]]+)?]/gi.test(
normalizedName
);
if (isImmutable === true)
assetInfo.immutable = true;
assetInfo.sourceFilename = normalizePath(
path.relative(this.rootContext, this.resourcePath)
);
this.emitFile(outputPath, content, null, assetInfo);
const esModule =
typeof options.esModule !== 'undefined' ? options.esModule : true;
return `$esModule ? 'export default' : 'module.exports =' $publicPath;`;
export const raw = true;
可以看到使用了 interpolateName
还有 emitFile
https://github.com/webpack/loader-utils/tree/v1.2.3
使用多个占位符和/或正则表达式插入文件名模板。 模板和正则表达式在当前加载器的上下文中设置为名为 name 和 regExp 的查询参数。
const interpolatedName = loaderUtils.interpolateName(loaderContext, name, options);
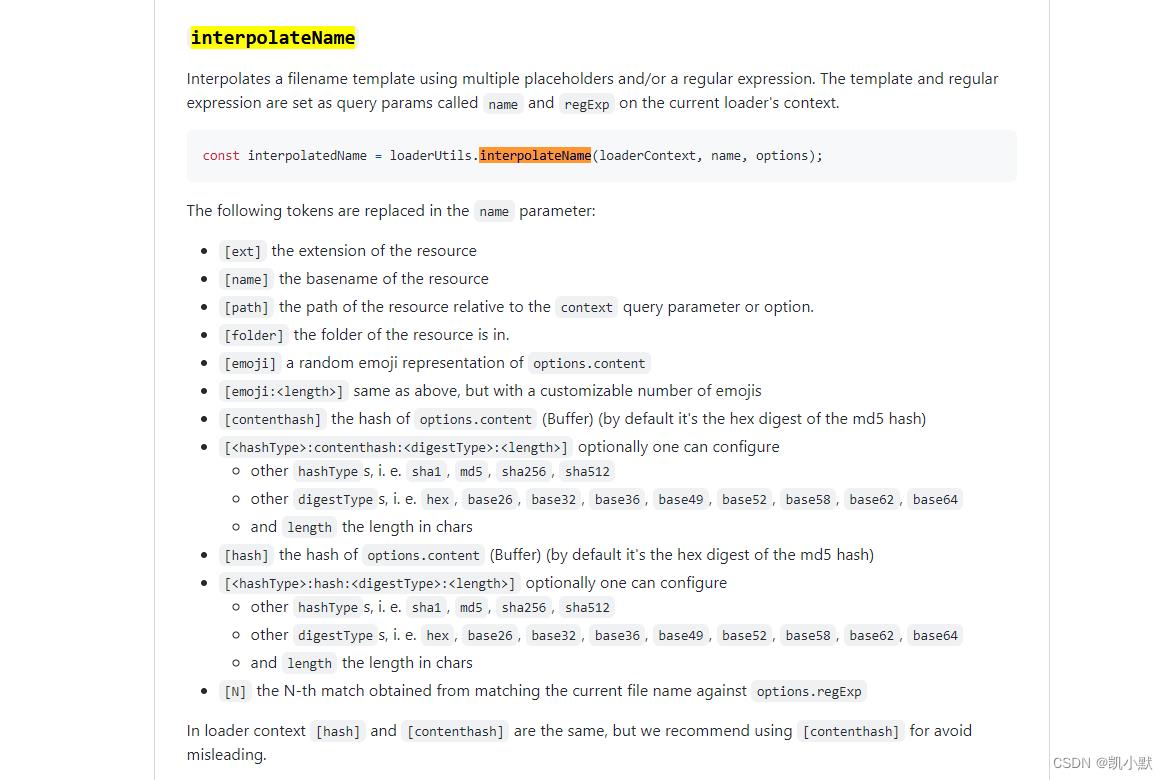
我们在 loader-order 项目里安装依赖
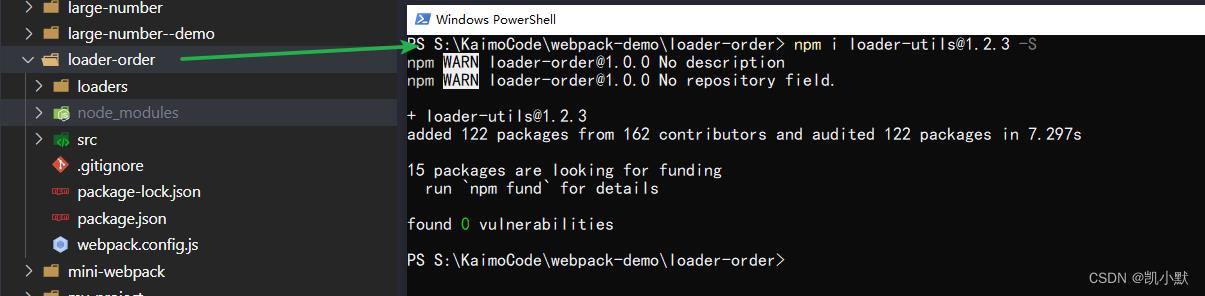
然后在 a-loader.js 添加文件输出的代码
const loaderUtils = require("loader-utils");
module.exports = function(source)
console.log ('loader a is executed');
const url = loaderUtils.interpolateName(this, '[name]_[hash].[ext]', source);
console.log("url---->", url);
this.emitFile(url, source);
return source;
;
运行 npm run build,可以看到生成出来了 index 文件
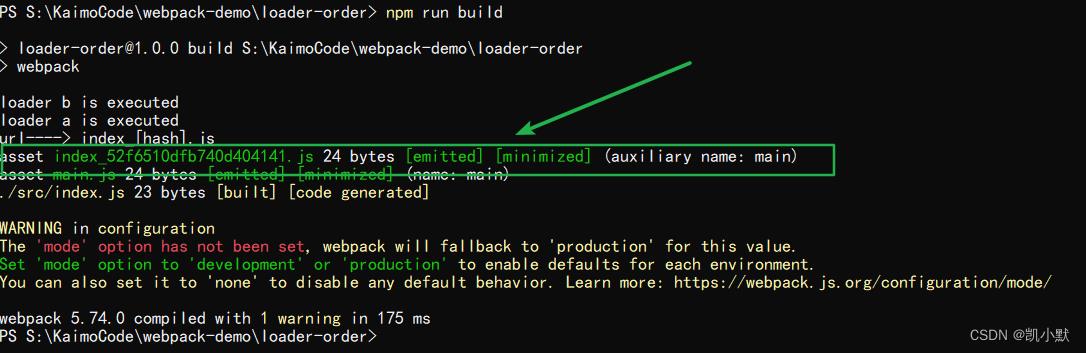
我们可以看一下 dist 文件夹
以上是关于webpack原理篇(六十一):更复杂的 loader 的开发场的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章