一种图神经网络架构:GraphSAGE
Posted KPer_Yang
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了一种图神经网络架构:GraphSAGE相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
一种图神经网络架构:GraphSAGE
简介
提出了一个通用框架,称为 GraphSAGE(SAmple 和 aggreGatE),用于归纳节点嵌入。GraphSAGE是一种流行的图神经网络架构,具有如下的特点1
1、利用的特征:与基于矩阵分解的嵌入方法不同,利用节点特征(例如,文本属性、节点配置信息、节点度数)来学习泛化到未见节点的嵌入函数。通过在学习算法中加入节点特征,同时学习了每个节点邻域的拓扑结构以及邻域内节点特征的分布。不但专注于特征丰富的图表(例如,具有文本属性的引文数据、具有功能/分子标记的生物数据),而且还可以利用所有图表中存在的结构特征(例如,节点度数)。因此,算法也可以应用于没有节点特征的图。
2、训练的目标:不是为每个节点训练一个不同的嵌入向量,而是训练一组聚合器函数,这些函数学习从节点的本地邻域聚合特征信息)。每个聚合器函数聚合来自远离给定节点的不同跳数或搜索深度的信息。在测试或推理时,使用训练后的系统通过应用学习的聚合函数为完全看不见的节点生成嵌入。
3、监督方式:在之前生成节点嵌入的工作之后,设计了一个无监督损失函数,允许在没有特定任务监督的情况下训练 GraphSAGE。还表明 GraphSAGE 可以以完全监督的方式进行训练。
4、实验结果:在三个节点分类基准上评估的算法,这些基准测试了 GraphSAGE 在看不见的数据上生成有用嵌入的能力。使用基于引文数据和 Reddit 帖子数据(分别预测论文和帖子类别)的两个不断发展的文档图,以及基于蛋白质-蛋白质相互作用数据集(预测蛋白质功能)的多图泛化实验。使用这些基准,表明的方法能够有效地为看不见的节点生成表示,并大大优于相关基线:在跨域中,与单独使用节点特征相比,的监督方法将分类 F1 分数平均提高了 51%和 GraphSAGE 始终优于强大的转导基线 ,尽管该基线在看不见的节点上运行需要 100 倍的时间。还表明,与受图卷积网络启发的聚合器相比,提出的新聚合器架构提供了显着的收益(平均 7.4%)。最后,探讨了方法的表达能力,并通过理论分析表明 GraphSAGE 能够学习有关节点在图中的角色的结构信息,尽管它本质上是基于特征的。
网络架构1
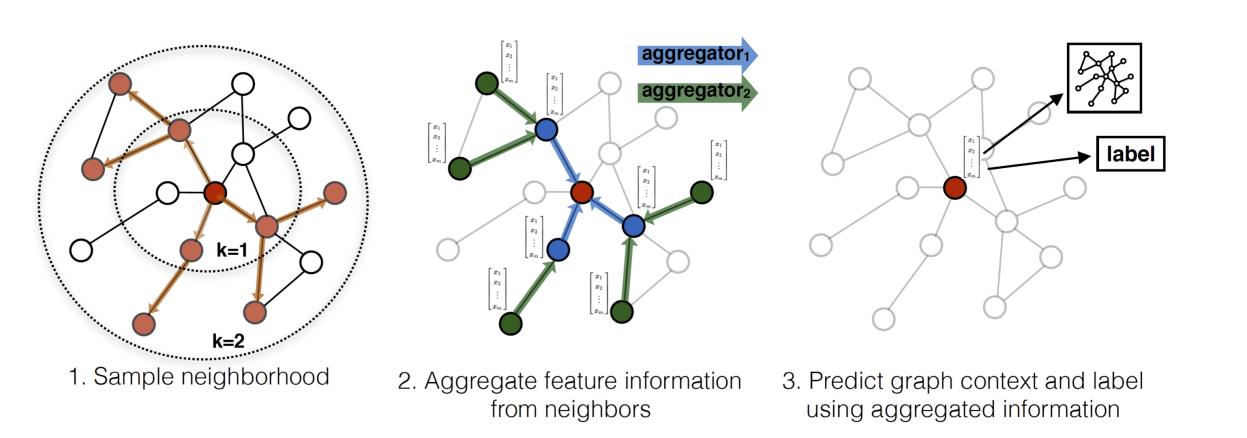
GraphSAGE分成三步:
1、对节点的邻居进行采样,采样K个邻居;
2、聚合邻居节点的信息,生成该节点的特征向量;介绍三种聚合器:
- Mean aggregator
- LSTM aggregator
- Pooling aggregator
3、使用2中聚合的节点信息进行该节点的预测(分类或者回归任务);
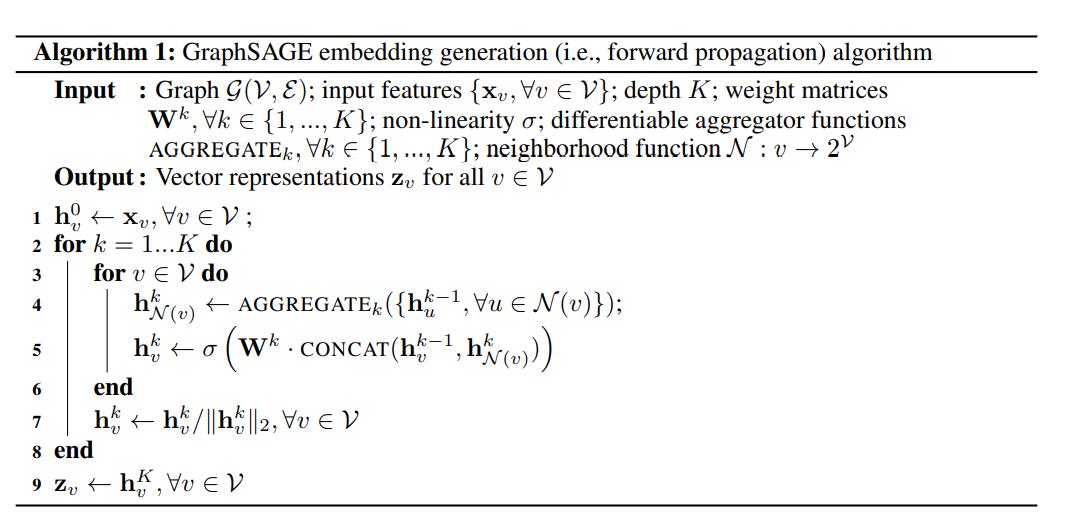
算法表示1
不用解释太多,因为开源,直接看代码一目了然:
代码实现2
引用自:https://github.com/williamleif/GraphSAGE
from collections import namedtuple
import tensorflow as tf
import math
import graphsage.layers as layers
import graphsage.metrics as metrics
from .prediction import BipartiteEdgePredLayer
from .aggregators import MeanAggregator, MaxPoolingAggregator, MeanPoolingAggregator, SeqAggregator, GCNAggregator
flags = tf.app.flags
FLAGS = flags.FLAGS
# DISCLAIMER:
# Boilerplate parts of this code file were originally forked from
# https://github.com/tkipf/gcn
# which itself was very inspired by the keras package
class Model(object):
def __init__(self, **kwargs):
allowed_kwargs = 'name', 'logging', 'model_size'
for kwarg in kwargs.keys():
assert kwarg in allowed_kwargs, 'Invalid keyword argument: ' + kwarg
name = kwargs.get('name')
if not name:
name = self.__class__.__name__.lower()
self.name = name
logging = kwargs.get('logging', False)
self.logging = logging
self.vars =
self.placeholders =
self.layers = []
self.activations = []
self.inputs = None
self.outputs = None
self.loss = 0
self.accuracy = 0
self.optimizer = None
self.opt_op = None
def _build(self):
raise NotImplementedError
def build(self):
""" Wrapper for _build() """
with tf.variable_scope(self.name):
self._build()
# Build sequential layer model
self.activations.append(self.inputs)
for layer in self.layers:
hidden = layer(self.activations[-1])
self.activations.append(hidden)
self.outputs = self.activations[-1]
# Store model variables for easy access
variables = tf.get_collection(tf.GraphKeys.GLOBAL_VARIABLES, scope=self.name)
self.vars = var.name: var for var in variables
# Build metrics
self._loss()
self._accuracy()
self.opt_op = self.optimizer.minimize(self.loss)
def predict(self):
pass
def _loss(self):
raise NotImplementedError
def _accuracy(self):
raise NotImplementedError
def save(self, sess=None):
if not sess:
raise AttributeError("TensorFlow session not provided.")
saver = tf.train.Saver(self.vars)
save_path = saver.save(sess, "tmp/%s.ckpt" % self.name)
print("Model saved in file: %s" % save_path)
def load(self, sess=None):
if not sess:
raise AttributeError("TensorFlow session not provided.")
saver = tf.train.Saver(self.vars)
save_path = "tmp/%s.ckpt" % self.name
saver.restore(sess, save_path)
print("Model restored from file: %s" % save_path)
class MLP(Model):
""" A standard multi-layer perceptron """
def __init__(self, placeholders, dims, categorical=True, **kwargs):
super(MLP, self).__init__(**kwargs)
self.dims = dims
self.input_dim = dims[0]
self.output_dim = dims[-1]
self.placeholders = placeholders
self.categorical = categorical
self.inputs = placeholders['features']
self.labels = placeholders['labels']
self.optimizer = tf.train.AdamOptimizer(learning_rate=FLAGS.learning_rate)
self.build()
def _loss(self):
# Weight decay loss
for var in self.layers[0].vars.values():
self.loss += FLAGS.weight_decay * tf.nn.l2_loss(var)
# Cross entropy error
if self.categorical:
self.loss += metrics.masked_softmax_cross_entropy(self.outputs, self.placeholders['labels'],
self.placeholders['labels_mask'])
# L2
else:
diff = self.labels - self.outputs
self.loss += tf.reduce_sum(tf.sqrt(tf.reduce_sum(diff * diff, axis=1)))
def _accuracy(self):
if self.categorical:
self.accuracy = metrics.masked_accuracy(self.outputs, self.placeholders['labels'],
self.placeholders['labels_mask'])
def _build(self):
self.layers.append(layers.Dense(input_dim=self.input_dim,
output_dim=self.dims[1],
act=tf.nn.relu,
dropout=self.placeholders['dropout'],
sparse_inputs=False,
logging=self.logging))
self.layers.append(layers.Dense(input_dim=self.dims[1],
output_dim=self.output_dim,
act=lambda x: x,
dropout=self.placeholders['dropout'],
logging=self.logging))
def predict(self):
return tf.nn.softmax(self.outputs)
class GeneralizedModel(Model):
"""
Base class for models that aren't constructed from traditional, sequential layers.
Subclasses must set self.outputs in _build method
(Removes the layers idiom from build method of the Model class)
"""
def __init__(self, **kwargs):
super(GeneralizedModel, self).__init__(**kwargs)
def build(self):
""" Wrapper for _build() """
with tf.variable_scope(self.name):
self._build()
# Store model variables for easy access
variables = tf.get_collection(tf.GraphKeys.GLOBAL_VARIABLES, scope=self.name)
self.vars = var.name: var for var in variables
# Build metrics
self._loss()
self._accuracy()
self.opt_op = self.optimizer.minimize(self.loss)
# SAGEInfo is a namedtuple that specifies the parameters
# of the recursive GraphSAGE layers
SAGEInfo = namedtuple("SAGEInfo",
['layer_name', # name of the layer (to get feature embedding etc.)
'neigh_sampler', # callable neigh_sampler constructor
'num_samples',
'output_dim' # the output (i.e., hidden) dimension
])
class SampleAndAggregate(GeneralizedModel):
"""
Base implementation of unsupervised GraphSAGE
"""
def __init__(self, placeholders, features, adj, degrees,
layer_infos, concat=True, aggregator_type="mean",
model_size="small", identity_dim=0,
**kwargs):
'''
Args:
- placeholders: Stanford TensorFlow placeholder object.
- features: Numpy array with node features.
NOTE: Pass a None object to train in featureless mode (identity features for nodes)!
- adj: Numpy array with adjacency lists (padded with random re-samples)
- degrees: Numpy array with node degrees.
- layer_infos: List of SAGEInfo namedtuples that describe the parameters of all
the recursive layers. See SAGEInfo definition above.
- concat: whether to concatenate during recursive iterations
- aggregator_type: how to aggregate neighbor information
- model_size: one of "small" and "big"
- identity_dim: Set to positive int to use identity features (slow and cannot generalize, but better accuracy)
'''
super(SampleAndAggregate, self).__init__(**kwargs)
if aggregator_type == "mean":
self.aggregator_cls = MeanAggregator
elif aggregator_type == "seq":
self.aggregator_cls = SeqAggregator
elif aggregator_type == "maxpool":
self.aggregator_cls = MaxPoolingAggregator
elif aggregator_type == "meanpool":
self.aggregator_cls = MeanPoolingAggregator
elif aggregator_type == "gcn":
self.aggregator_cls = GCNAggregator
else:
raise Exception("Unknown aggregator: ", self.aggregator_cls)
# get info from placeholders...
self.inputs1 = placeholders["batch1"]
self.inputs2 = placeholders["batch2"]
self.model_size = model_size
self.adj_info = adj
if identity_dim > 0:
self.embeds = tf.get_variable("node_embeddings", [adj.get_shape().as_list()[0], identity_dim])
else:
self.embeds = None
if features is None:
if identity_dim == 0:
raise Exception("Must have a positive value for identity feature dimension if no input features given.")
self.features = self.embeds
else:
self.features = tf.Variable(tf.constant(features, dtype=tf.float32), trainable=False)
if not self.embeds is None:
self.features = tf.concat([self.embeds, self.features], axis=1)
self.degrees = degrees
self.concat = concat
self.dims = [(0 if features is None else features.shape[1]) + identity_dim]
self.dims.extend([layer_infos[i].output_dim for i in range(len(layer_infos))])
self.batch_size = placeholders["batch_size"]
self.placeholders = placeholders
self.layer_infos = layer_infos
self.optimizer = tf.train.AdamOptimizer(learning_rate=FLAGS.learning_rate)
self.build()
def sample(self, inputs, layer_infos, batch_size=None):
""" Sample neighbors to be the supportive fields for multi-layer convolutions.
Args:
inputs: batch inputs
batch_size: the number of inputs (different for batch inputs and negative samples).
"""
if batch_size is None:
batch_size = self.batch_size
samples = [inputs]
# size of convolution support at each layer per node
support_size = 1
support_sizes = [support_size]
for k in range(len(layer_infos)):
t = len(layer_infos) - k - 1
support_size *= layer_infos[t].num_samples
sampler = layer_infos[t].neigh_sampler
node = sampler((samples[k], layer_infos[t].num_samples))
samples.append(tf.reshape(node, [support_size * batch_size,]))
support_sizes.append(support_size)
return samples, support_sizes
def aggregate(self, samples, input_features, dims, num_samples, support_sizes, batch_size=None,
aggregators=None, name=None, concat=False, model_size="small"):
""" At each layer, aggregate hidden representations of neighbors to compute the hidden representations
at next layer.
Args:
samples: a list of samples of variable hops away for convolving at each layer of the
network. Length is the number of layers + 1. Each is a vector of node indices.
input_features: the input features for each sample of various hops away.
dims: a list of dimensions of the hidden representations from the input layer to the
final layer. Length is the number of layers + 1.
num_samples: list of number of samples for each layer.
support_sizes: the number of nodes to gather information from for each layer.
batch_size: the number of inputs (different for batch inputs and negative samples).
Returns:
The hidden representation at the final layer for all nodes in batch
"""
if batch_size is None:
batch_size = self.batch_size
# length: number of layers + 1
hidden = [tf.nn.embedding_lookup(input_features, node_samples) for node_samples in samples]
new_agg = aggregators is None
if new_agg:
aggregators = []
for layer in range(len(num_samples)):
if new_agg:
dim_mult = 2 if concat and (layer != 0) else 1
# aggregator at current layer
if layer == len(num_samples) - 1:
aggregator = self.aggregator_cls(dim_mult*dims[layer], dims[layer+1], act=lambda x : x,
dropout=self.placeholders['dropout'],
name=name, concat=concat, model_size=model_size)
else:
aggregator = self.aggregator_cls(dim_mult*dims[layer], dims[layer+1],
dropout=self.placeholders['dropout'],
name=name, concat=concat, model_size=model_size)
aggregators.append(aggregator)
else:
aggregator = aggregators[layer]
# hidden representation at current layer for all support nodes that are various hops away
next_hidden = []
# as layer increases, the number of support nodes needed decreases
for hop in range(len(num_samples) - layer):
dim_mult = 2 if concat and (layer != 0) else 1
neigh_dims = [batch_size * support_sizes[hop],
num_samples[len(num_samples) - hop - 1],
dim_mult*dims[layer]]
h = aggregator((hidden[hop],
tf.reshape(hidden[hop + 1], neigh_dims)))
next_hidden.append(h)
hidden = next_hidden
return hidden[0], aggregators
def _build(self):
labels = tf.reshape(
tf.cast(self.placeholders['batch2'], dtype=tf.int64),
[self.batch_size, 1])
self.neg_samples, _, _ = (tf.nn.fixed_unigram_candidate_sampler(
true_classes=labels,
num_true=1,
num_sampled=FLAGS.neg_sample_size,
unique=False,
range_max=len(self.degrees),
distortion=0.75,
unigrams=self.degrees.tolist()))
# perform "convolution"
samples1, support_sizes1 = self.sample(self.inputs1, self.layer_infos)
samples2, support_sizes2 = self.sample(self.inputs2, self.layer_infos)
num_samples = [layer_info.num_samples for layer_info in self.layer_infos]
self.outputs1, self.aggregators = self.aggregate(samples1, [self.features], self.dims, num_samples,以上是关于一种图神经网络架构:GraphSAGE的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章