JavaString类
Posted 沉着的码农
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了JavaString类相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
String类
字符串构造
String类提供了很多的构造方式 常用的就三种
public static void main(String[] args)
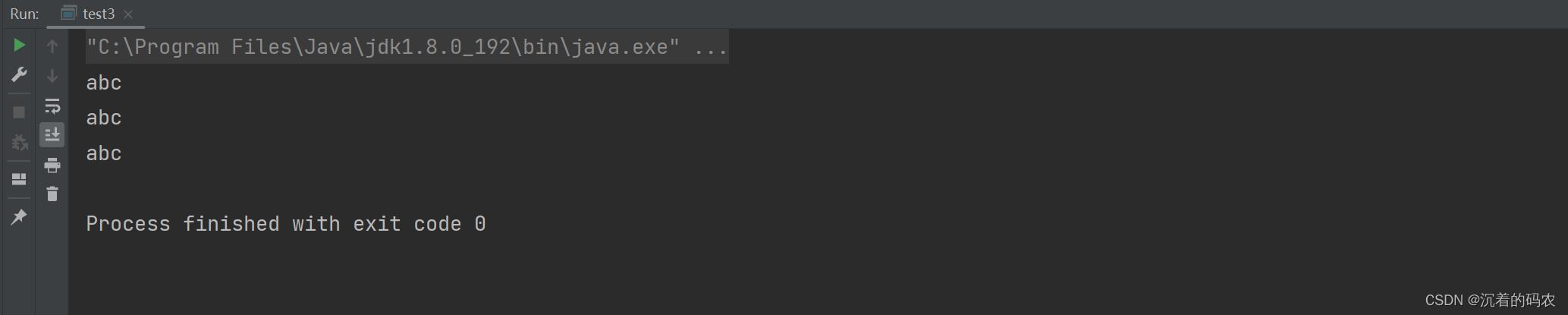
String string1 = "abc";
//常量字符串构造
String string2 = new String("abc");
//new对象构造
char[] arr = new char[]'a','b','c';
String string3 = new String(arr);
//利用字符数组构造
System.out.println(string1);
System.out.println(string2);
System.out.println(string3);
字符串对象的比较
==比较是否引用同一个对象
注意:对于内置类型,比较的是变量中的值;对于引用类型比较的是引用中的地址。
public static void main(String[] args)
int a = 10;
int b = 20;
int c = 10;
// 对于基本类型变量,==比较两个变量中存储的值是否相同
System.out.println(a == b); // false
System.out.println(a == c); // true
// 对于引用类型变量,==比较两个引用变量引用的是否为同一个对象
String s1 = new String("hello");
String s2 = new String("hello");
String s3 = new String("world");
String s4 = s1;
System.out.println(s1 == s2); // false
System.out.println(s2 == s3); // false
System.out.println(s1 == s4); // true
boolean equals(Object anObject) 方法:按照字典序比较
字典序:字符大小的顺序
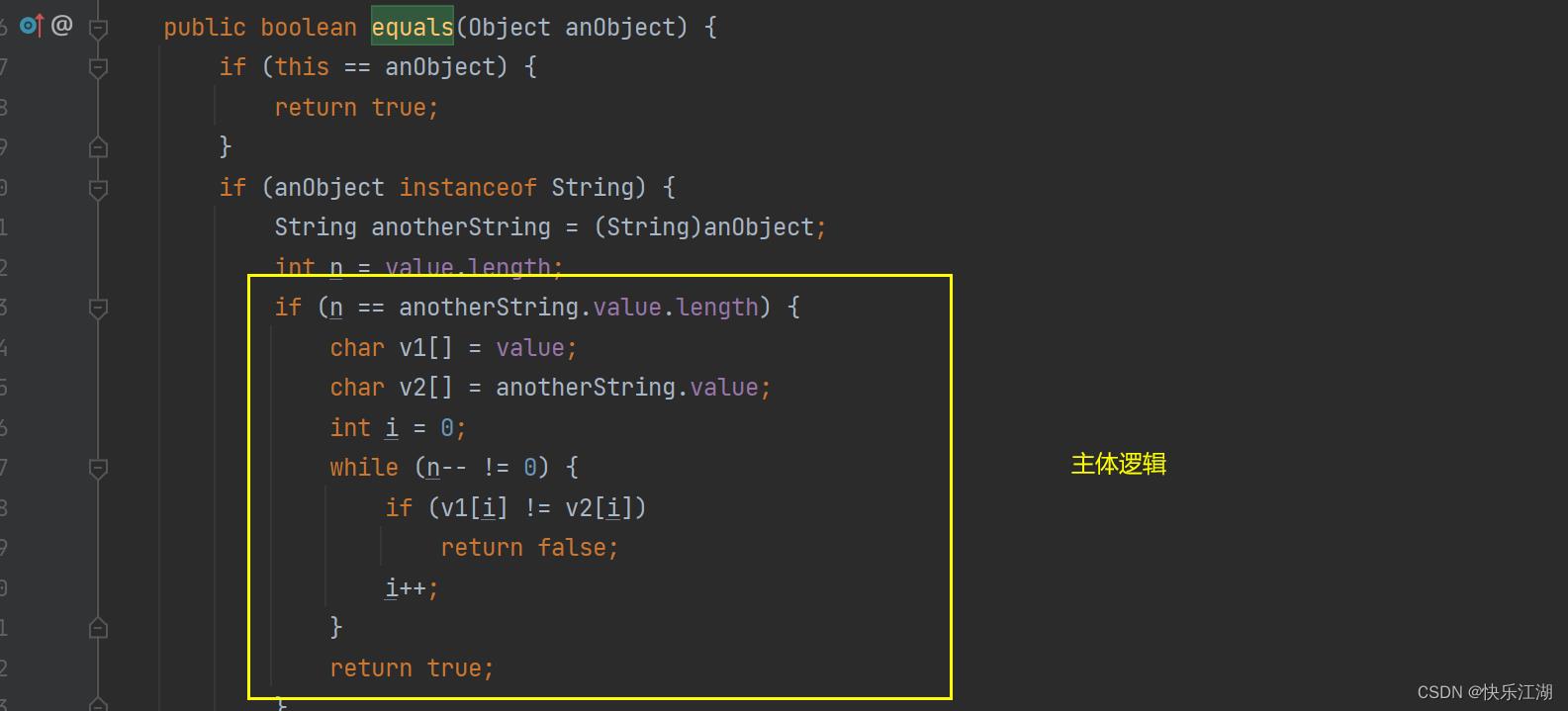
String类重写了父类Object中equals方法,Object中equals默认按照==比较,String重写equals方法后,按照如下规则进行比较,
比如: s1.equals(s2)
public boolean equals(Object anObject)
// 1. 先检测this 和 anObject 是否为同一个对象比较,如果是返回true
if (this == anObject)
return true;
// 2. 检测anObject是否为String类型的对象,如果是继续比较,否则返回false
if (anObject instanceof String)
// 将anObject向下转型为String类型对象
String anotherString = (String)anObject;
int n = value.length;
// 3. this和anObject两个字符串的长度是否相同,是继续比较,否则返回false
if (n == anotherString.value.length)
char v1[] = value;
char v2[] = anotherString.value;
int i = 0;
// 4. 按照字典序,从前往后逐个字符进行比较
while (n-- != 0)
if (v1[i] != v2[i])
return false;
i++;
return true;
return false;
public static void main(String[] args)
String s1 = new String("hello");
String s2 = new String("hello");
String s3 = new String("Hello");
// s1、s2、s3引用的是三个不同对象,因此==比较结果全部为false
System.out.println(s1 == s2); // false
System.out.println(s1 == s3); // false
/*equals比较:String对象中的逐个字符
虽然s1与s2引用的不是同一个对象,但是两个对象中放置的内容相同,因此输出true
s1与s3引用的不是同一个对象,而且两个对象中内容也不同,因此输出false
*/
System.out.println(s1.equals(s2)); // true
System.out.println(s1.equals(s3)); // false
int compareTo(String s) 方法: 按照字典序进行比较
与equals不同的是,equals返回的是boolean类型,而compareTo返回的是int类型。具体比较方式:
- 先按照字典次序大小比较,如果出现不等的字符,直接返回这两个字符的大小差值
- 如果前k个字符相等(k为两个字符长度最小值),返回值两个字符串长度差值
public static void main(String[] args)
String s1 = new String("abc");
String s2 = new String("ac");
String s3 = new String("abc");
String s4 = new String("abcdef");
System.out.println(s1.compareTo(s2)); // 不同输出字符差值-1
System.out.println(s1.compareTo(s3)); // 相同输出 0
System.out.println(s1.compareTo(s4)); // 前k个字符完全相同,输出长度差值 -3
int compareToIgnoreCase(String str) 方法:与compareTo方式相同,但是忽略大小写比较
public static void main(String[] args)
String s1 = new String("abc");
String s2 = new String("ac");
String s3 = new String("ABc");
String s4 = new String("abcdef");
System.out.println(s1.compareToIgnoreCase(s2)); // 不同输出字符差值-1
System.out.println(s1.compareToIgnoreCase(s3)); // 相同输出 0
System.out.println(s1.compareToIgnoreCase(s4)); // 前k个字符完全相同,输出长度差值 -3
字符串查找
字符串查找也是字符串中非常常见的操作,String类提供的常用查找的方法:
char charAt(int index)
返回index位置上字符,如果index为负数或者越界,抛出
IndexOutOfBoundsException异常
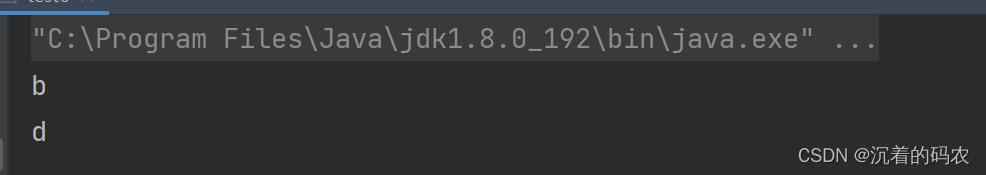
public static void main(String[] args)
String str = new String("abcdefg");
char ch1 = str.charAt(1);
char ch2 = str.charAt(3);
System.out.println(ch1);
System.out.println(ch2);
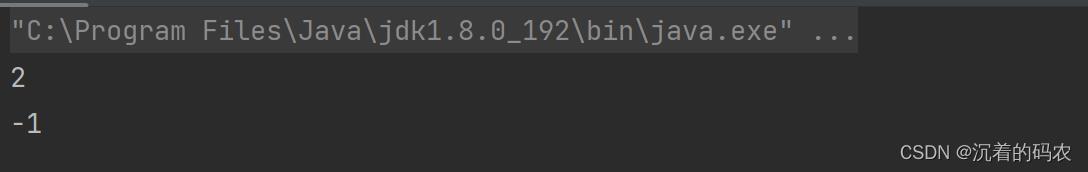
int indexOf(int ch)
返回ch第一次出现的位置,没有返回-1
public static void main(String[] args)
String str = new String("abcdefg");
int index1 = str.indexOf('c');
int index2 = str.indexOf('z');
System.out.println(index1);
System.out.println(index2);
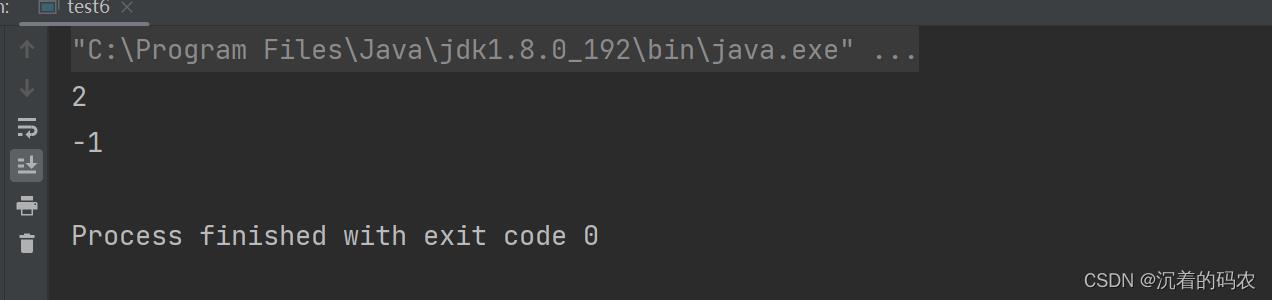
int indexOf(int ch, int fromIndex)
从fromIndex位置开始找ch第一次出现的位置,没有返回-1
public static void main(String[] args)
String str = new String("abcdefg");
int index1 = str.indexOf('c',1);
int index2 = str.indexOf('z',1);
System.out.println(index1);
System.out.println(index2);
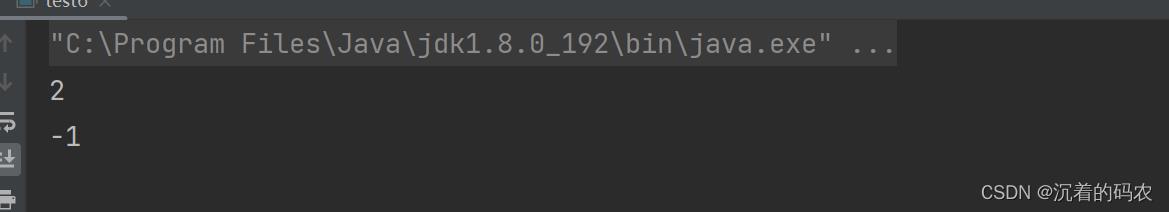
int indexOf(String str)
返回str第一次出现的位置,没有返回-1
public static void main(String[] args)
String str = new String("abcdefghijklmn");
int index1 = str.indexOf("cde");
int index2 = str.indexOf("zxc");
System.out.println(index1);
System.out.println(index2);
int indexOf(String str, int fromIndex)
和int indexOf(int ch) 一致
int lastIndexOf(int ch)
从后往前找,返回ch第一次出现的位置,没有返回-1
lastIndexOf其他用法和indexOf相同 都是重载的方法
转化
数值和字符串转化
数字转字符串
class Student
String name;
int age;
public Student(String name, int age)
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
@Override
public String toString()
return "Student" +
"name='" + name + '\\'' +
", age=" + age +
'';
public class test1
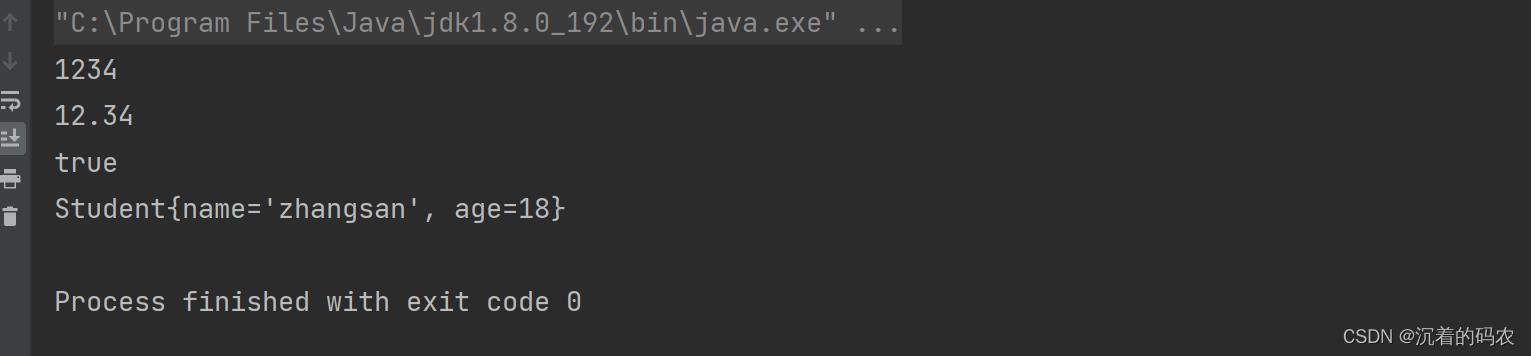
public static void main(String[] args)
String s1 = String.valueOf(1234);
String s2 = String.valueOf(12.34);
String s3 = String.valueOf(true);
String s4 = String.valueOf(new Student("zhangsan", 18));
System.out.println(s1);
System.out.println(s2);
System.out.println(s3);
System.out.println(s4);
//可以将很多类型转化为字符串
//甚至是一个自定义的类 只要重写了toString方法就可以做到
字符串转数字
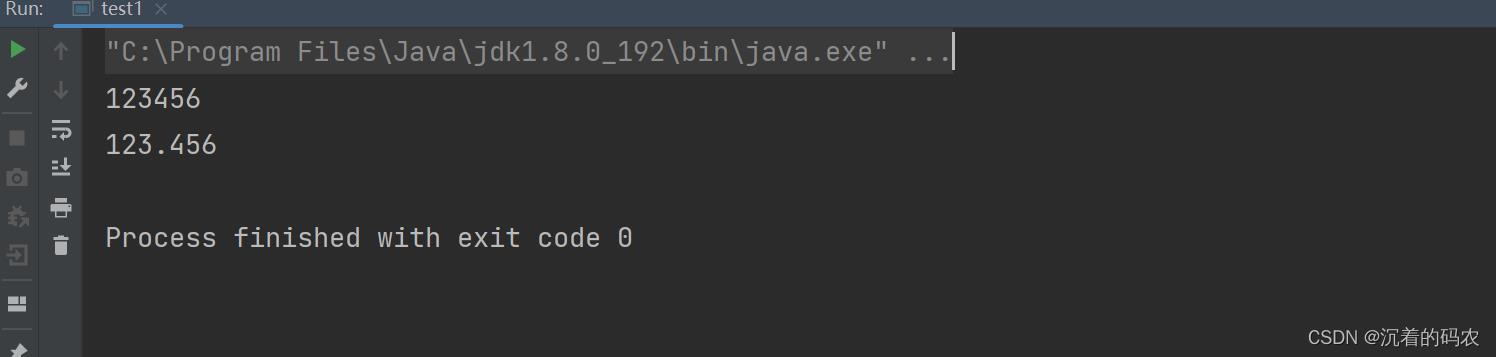
public static void main(String[] args)
String s1 = "123456";
String s2 = "123.456";
int num1 = Integer.valueOf(s1);
double num2 = Double.valueOf(s2);
// 注意:Integer、Double等是Java中的包装类型
System.out.println(num1);
System.out.println(num2);
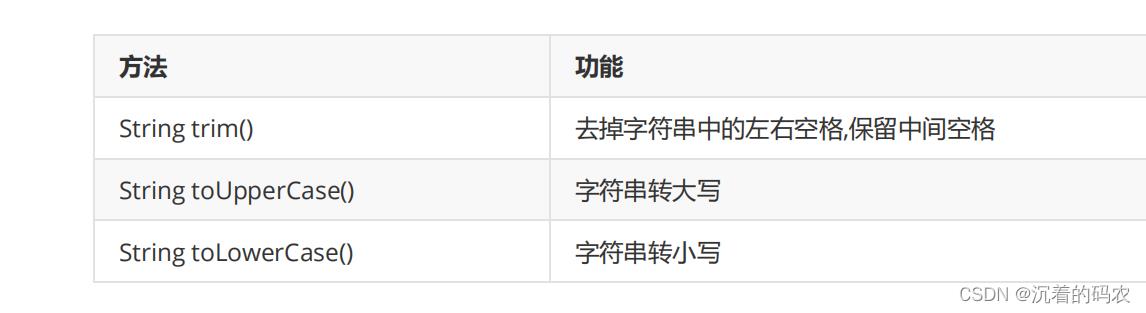
大小写转化
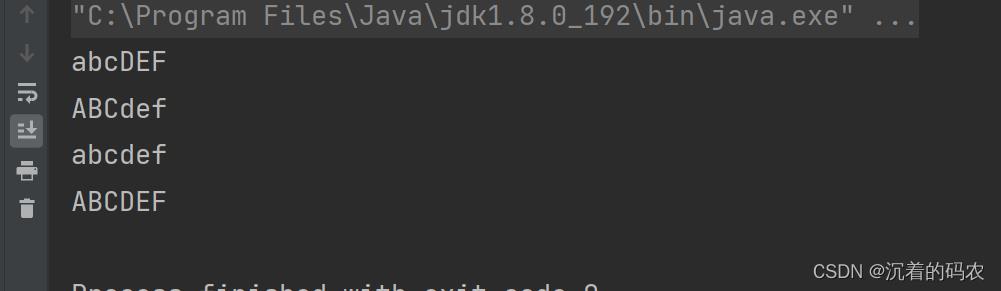
public static void main(String[] args)
String s1 = "abcDEF";
String s2 = "ABCdef";
String s3 = s1.toLowerCase();
String s4 = s2.toUpperCase();
System.out.println(s1);
System.out.println(s2);
System.out.println(s3);
System.out.println(s4);
//不是修改原字符串
字符串转数组
public static void main(String[] args)
String s1 = "abcdefg";
char[] array = s1.toCharArray();
for (int i = 0; i < array.length ; i++)
System.out.print(array[i] + " ");
格式化
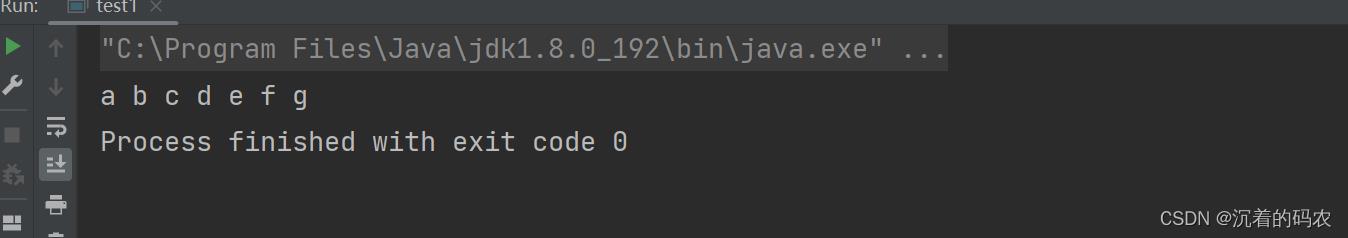
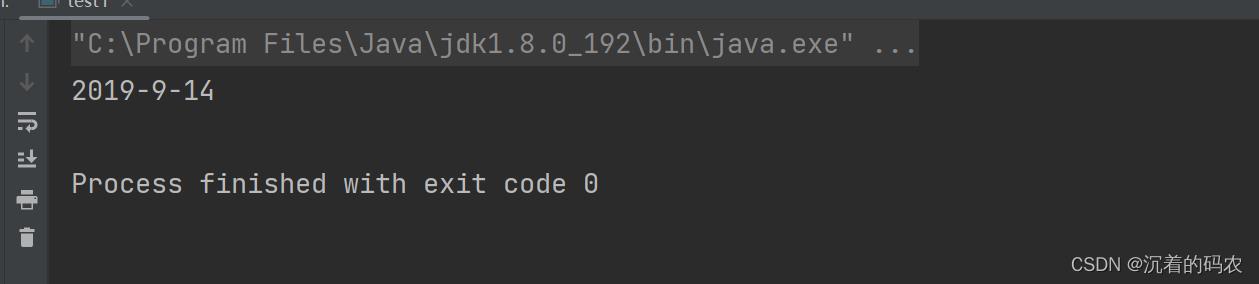
public static void main(String[] args)
String s = String.format("%d-%d-%d", 2019, 9,14);
//有种c语言的感觉
System.out.println(s);
字符串替换
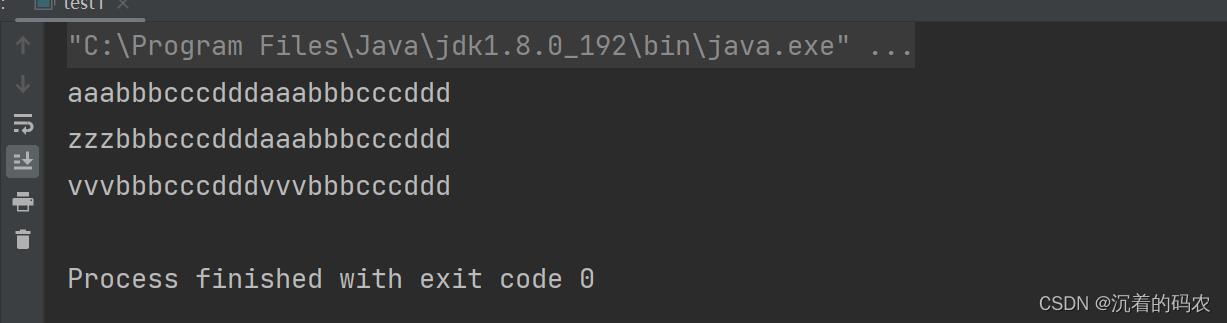
public static void main(String[] args)
String s1 = "aaabbbcccdddaaabbbcccddd";
String s2 = s1.replaceFirst("aaa","zzz");
String s3 = s1.replaceAll("aaa","vvv");
System.out.println(s1);
//原字符串没有改变
System.out.println(s2);
//replaceFirst只修改第一个
System.out.println(s3);
//replaceAll修改所有出现的
字符串拆分
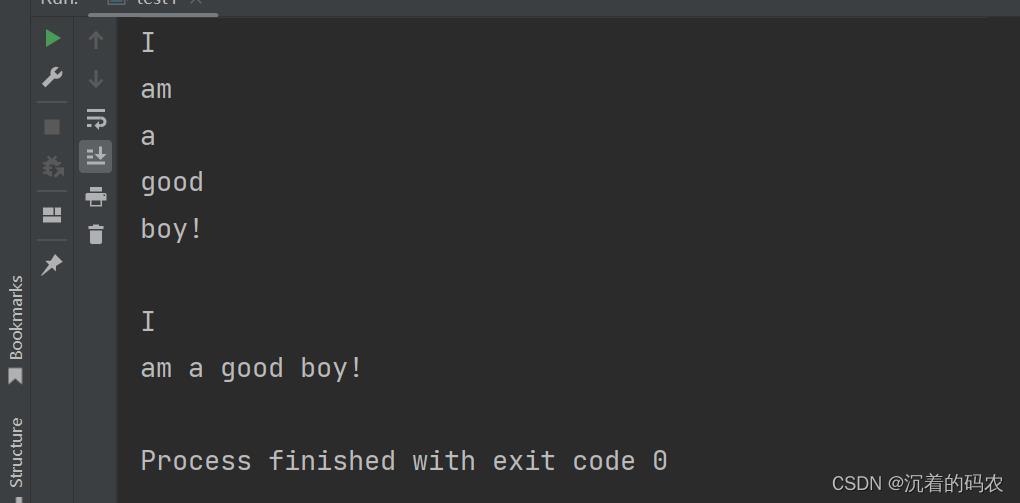
public static void main(String[] args)
String s1 = "I am a good boy!";
String[] arr1 = s1.split(" ");
String[] arr2 = s1.split(" ",2);
for (int i = 0; i < arr1.length; i++)
System.out.println(arr1[i]);
System.out.println();
for (int i = 0; i < arr2.length; i++)
System.out.println(arr2[i]);
可以将一个完整的字符串按照指定的分隔符划分为若干个子字符串。

字符串截取
public static void main(String[] args)
String s1 = "hello world!!!";
System.out.println(s1.substring(5));
System.out.println(s1.substring(3,9));
其他操作方法
StringBuilder和StringBuffer
字符串的不可变性
String是一种不可变对象. 字符串中的内容是不可改变。字符串不可被修改,是因为:
- String类在设计时就是不可改变的,String类实现描述中已经说明了

String类中的字符实际保存在内部维护的value字符数组中,该图还可以看出:
- String类被final修饰,表明该类不能被继承
- value被修饰被final修饰,表明value自身的值不能改变,即不能引用其它字符数组,但是其引用空间中的内容可以修改。
所有涉及到可能修改字符串内容的操作都是创建一个新对象,改变的是新对象
final修饰类表明该类不想被继承,final修饰引用类型表明该引用变量不能引用其他对象,但是其引用对象中的内容是可以修改的。
字符串修改
注意:尽量避免直接对String类型对象进行修改,因为String类是不能修改的,所有的修改都会创建新对象,效率非常低下。
public static void main(String[] args)
String s = "hello";
s += " world";
System.out.println(s); // 输出:hello world
但是这种方式不推荐使用,因为其效率非常低,中间创建了好多临时对象。
StringBuilder的介绍
由于String的不可更改特性,为了方便字符串的修改,Java中又提供StringBuilder和StringBuffer类。这两个类大部分功能是相同的,这里介绍 StringBuilder第一节:JavaString类介绍和常用方法
文章目录
一:什么是String类
String类:字符串string的使用是极其频繁的,但是在C语言中要表示字符串只能依靠字符数组或字符指针,十分麻烦。所以在Java中设计了String类来方便我们对字符串的使用
- 注意: String类是Java面试中的高频考点
二:String类常用方法
(1)字符串构造
A:常用构造方法
字符串构造:构造一个字符串方法有很多,常用的有以下三种
- 使用常量字符串构造
- 直接
newString对象 - 使用字符数组构造
public class TestDemo
public static void main(String[] args)
//使用常量字符串构造
String str1 = "Hello World1";
//直接newString对象
String str2 = new String("Hello World2");
//使用字符数组进行构造
char[] arr = 'H','e','l','l','o','W','o','r','l','d','3';
String str3 = new String(arr);
System.out.println(str1);
System.out.println(str2);
System.out.println(str3);
B:注意
String是引用类型,但是其内部并不存储字符串本身,实际回报存在一个char类型的数组中
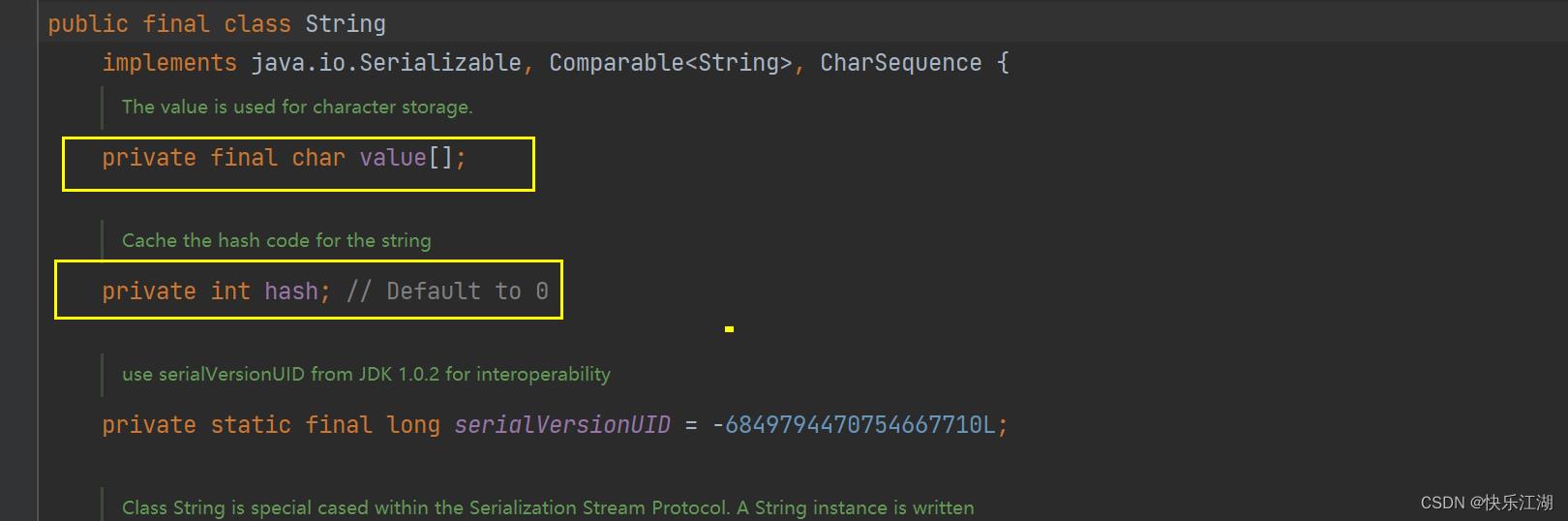
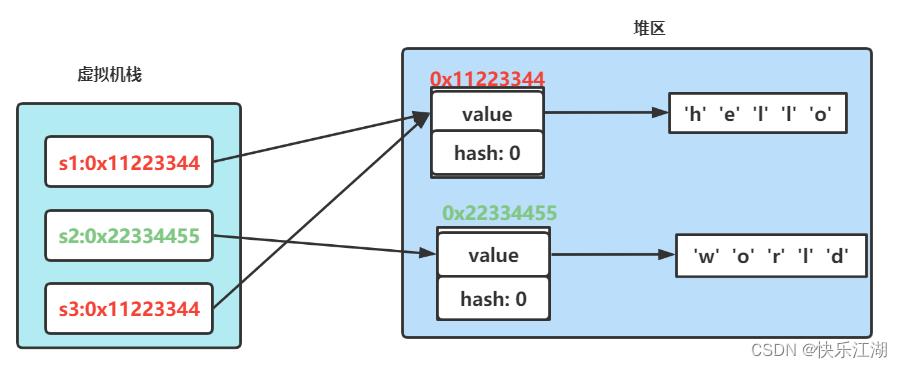
完整的关系应该是下面这样
public static void main(String[] args)
//s1和s2引用的不是同一个对象
//s1和s3引用的是同一个对象
String s1 = new String("hello");
String s2 = new String("world");
String s3 = s1;
(2)字符串比较
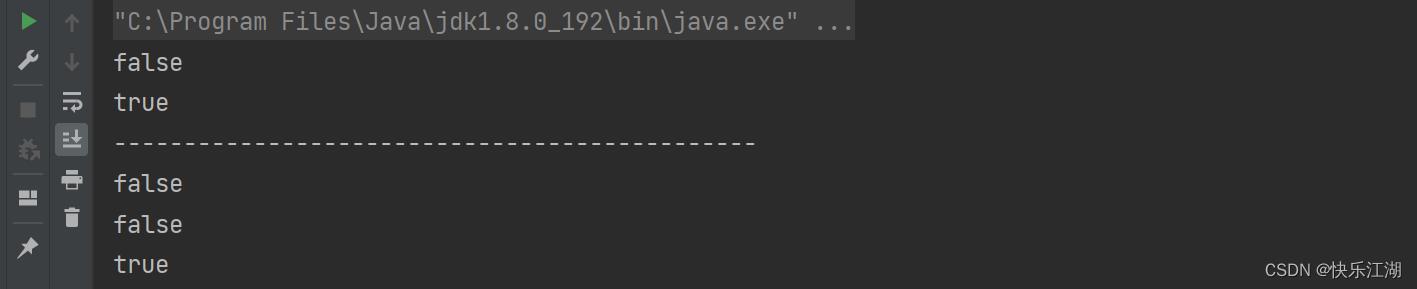
①:==用于比较是否引用的是同一个对象
- 内置类型:比较的是变量的值
- 引用类型:比较的是地址
public class TestDemo
public static void main(String[] args)
int a = 10;
int b = 20;
int c = 10;
//对于基本类型,比较的是值
System.out.println(a == b);
System.out.println(a == c);
System.out.println("----------------------------------------------");
//对于引用类型,比较是否引用的是同一个对象
String s1 = new String("hello");
String s2 = new String("hello");
String s3 = new String("world");
String s4 = s1;
System.out.println(s1 == s2);
System.out.println(s2 == s3);
System.out.println(s1 == s4);
②:boolean equals(Object anObject)方法会按照字典序进行比较。如下,String类中重写了父类Object中的equals方法
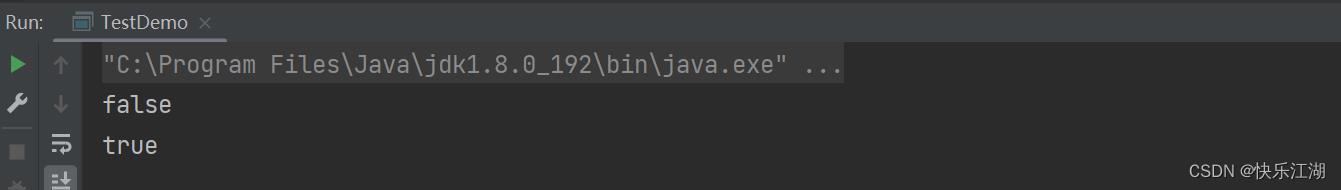
public class TestDemo
public static void main(String[] args)
String s1 = new String("hello");
String s2 = new String("hello");
String s3 = new String("hello");
System.out.println(s1 == s2);
System.out.println(s1.equals(s2));
③:int compareTo(String s)方法也会按照字典序进行比较,但与equals有所不同的是,它返回的是int。具体比较规则如下
- 先按照字典序进行比较,如果出现不等的字符,直接返回这两个字符的大小差值
- 如果前k个字符相等(k为两个字符长度最小值),则返回两个字符串长度差值
public class TestDemo
public static void main(String[] args)
String s1 = new String("abc");
String s2 = new String("ac");
String s3 = new String("abc");
String s4 = new String("abcdef");
System.out.println(s1.compareTo(s2));//不同输出字符差值 -1
System.out.println(s1.compareTo(s3)); //相同为零
System.out.println(s1.compareTo(s4)); //前k个字符完全相同,输出长度差值 -3
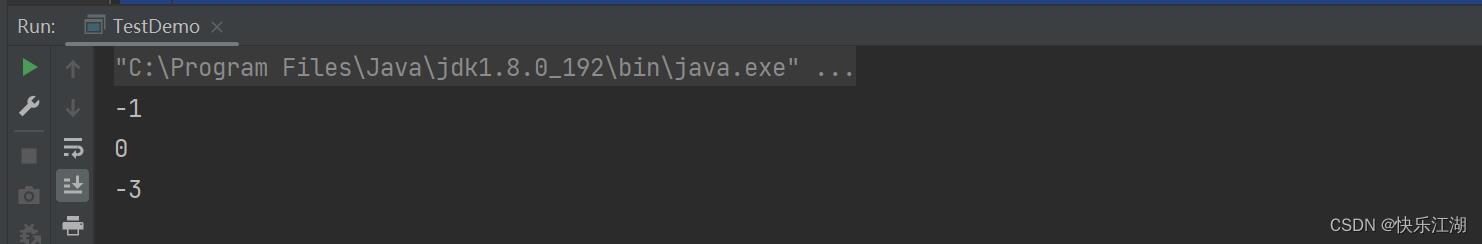
④:int compareTolgnoreCase(String str)方法:与compareTo方法相同,但是忽略大小写
public class TestDemo
public static void main(String[] args)
String s1 = new String("abc");
String s2 = new String("ac");
String s3 = new String("ABc");
String s4 = new String("abcdef");
System.out.println(s1.compareToIgnoreCase(s2));
System.out.println(s1.compareToIgnoreCase(s3));//相同
System.out.println(s1.compareToIgnoreCase(s4));
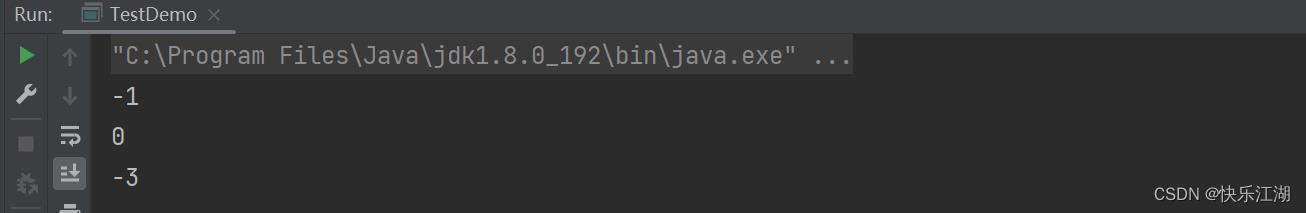
(3)字符串查找
①:char charAt(inde index):返回index位置上字符
- 如果
index为负数或者越界,抛出"indexOutofBoundsException"异常
public class TestDemo
public static void main(String[] args)
String s1 = new String("Hello");
String s2 = new String("World");
char c1 = s1.charAt(2);
System.out.println(c1);
System.out.println("-----------------------------------");
for(int i = 0; i < s2.length(); i++)
System.out.println(s2.charAt(i));
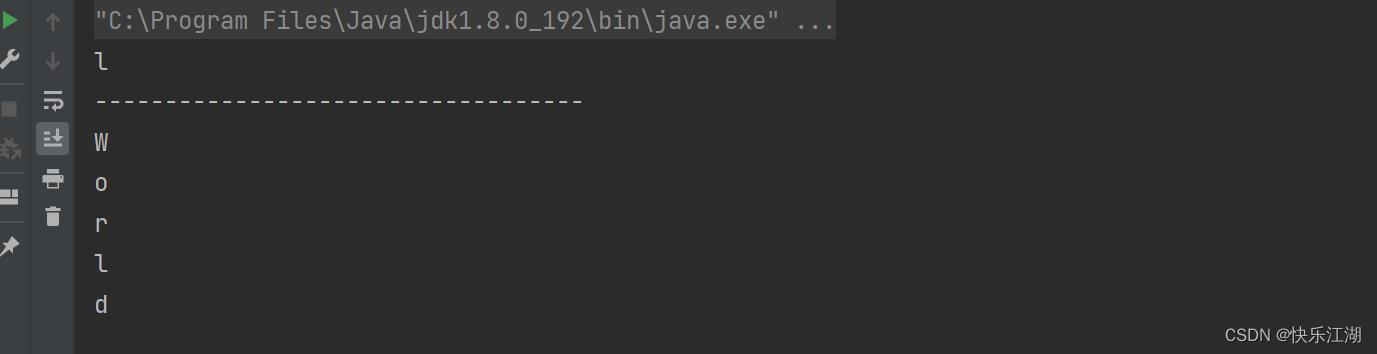
②:int indexOf(int ch):返回字符ch第一次出现的位置
- 如果没有
ch这个字符则会返回-1
public class TestDemo
public static void main(String[] args)
String s1 = new String("Hello");
String s2 = new String("World");
System.out.println(s1.indexOf('e'));
System.out.println(s2.indexOf('c'));
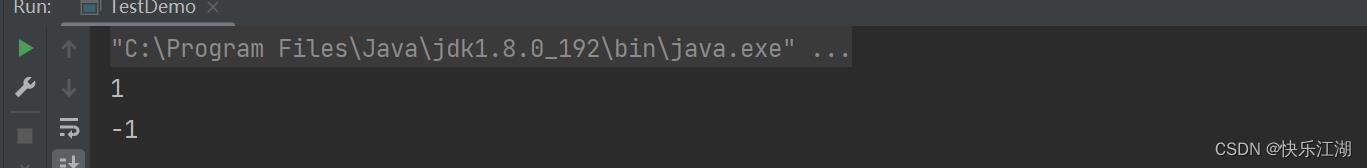
③:int indexOf(int ch, int fromIndex):从“fromIndex”位置开始寻找字符“ch”第一次出现的位置
- 如果没有
ch这个字符则会返回-1
public class TestDemo
public static void main(String[] args)
String s1 = new String("Hello World!");
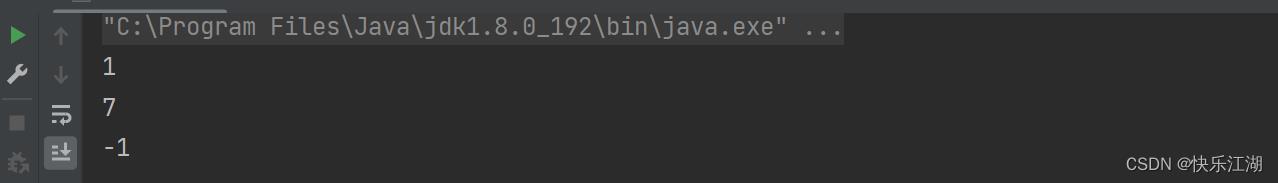
System.out.println(s1.indexOf('e', 1));
System.out.println(s1.indexOf('o', 5));
System.out.println(s1.indexOf('e', 5));
④:int indexOf(String str):返回字符串str第一次出现的位置
- 如果没有
str这个字符串则会返回-1
public class TestDemo
public static void main(String[] args)
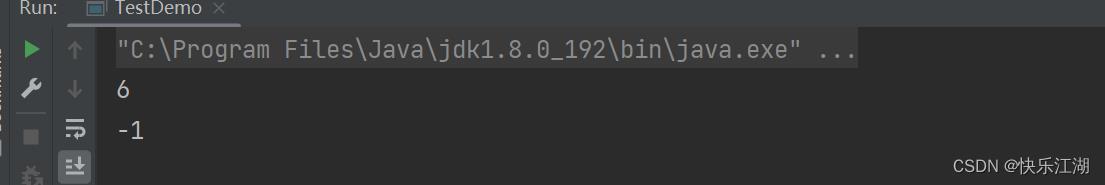
String s1 = new String("Hello World!");
System.out.println(s1.indexOf("World"));
System.out.println(s1.indexOf("Worls"));
⑤:int indexOf(String str, int fromIndex):从“fromIndex”位置开始寻找字符串“str”第一次出现的位置
- 如果没有
str这个字符串则会返回-1
public class TestDemo
public static void main(String[] args)
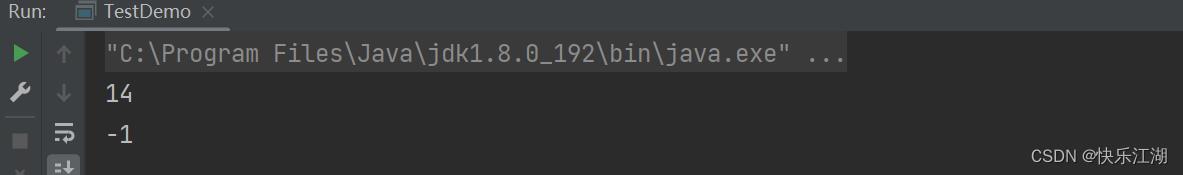
String s1 = new String("one two three one four nine");
System.out.println(s1.indexOf("one", 4));
System.out.println(s1.indexOf("one", 15));
⑥:int lastIndexOf(int ch)、int lastIndexOf(int ch, int fromIndex)、int lastIndexOf(String str)、int lastIndexOf(String str, int fromIndex):和前面类似,只不过是从后向前找
(4)字符串转化
A:数值和字符串的转换
数字转换为字符串可以使用String.valueOf()
public class TestDemo
public static void main(String[] args)
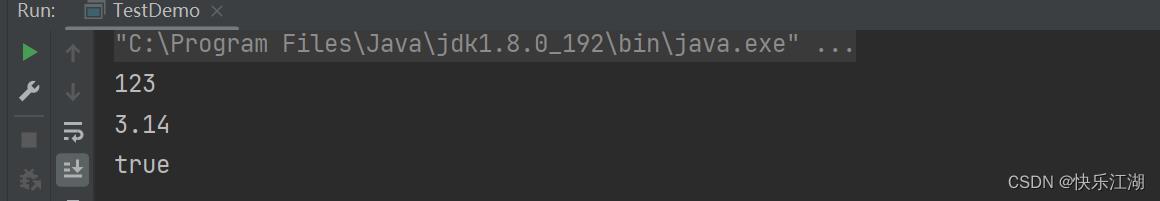
String s1 = String.valueOf(123);
String s2 = String.valueOf(3.14);
String s3 = String.valueOf(true);
System.out.println(s1);
System.out.println(s2);
System.out.println(s3);
字符串转化为数字常用方法如下
public class TestDemo
public static void main(String[] args)
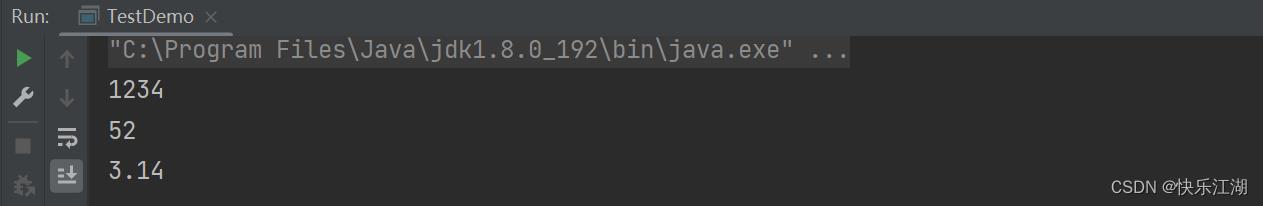
int num1 = Integer.parseInt("1234");
int num2 = Integer.parseInt("64", 8);//8表示八进制,八进制下的64对应十进制下的52
double num3 = Double.parseDouble("3.14");
System.out.println(num1);
System.out.println(num2);
System.out.println(num3);
B:大小写转换
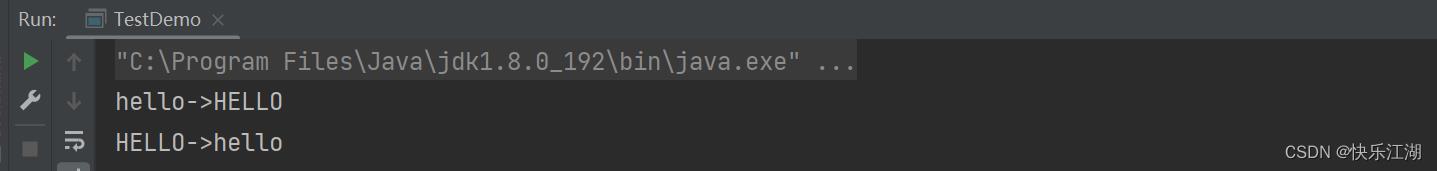
字母大小写转换可以使用toUpperCase()和toLowerCase()。需要注意是,转换完成后,原来字符串的值并不会改变
public class TestDemo
public static void main(String[] args)
String s1 = "hello";
String s2 = "HELLO";
//小写转换为大写
System.out.println(s1 + "->" + s1.toUpperCase());
//大写转换为小写
System.out.println(s2 + "->" + s2.toLowerCase());
C:字符串转数组
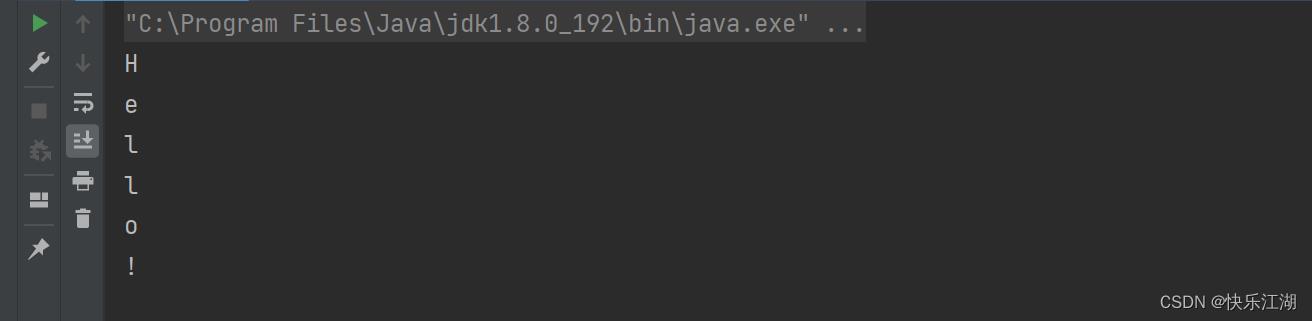
可以使用String.toCharArray()将一个字符串转为一个字符数组
public class TestDemo
public static void main(String[] args)
String str = "Hello!";
char[] ch = str.toCharArray();
for(int i = 0; i < ch.length; i++)
System.out.println(ch[i]);
D:格式化
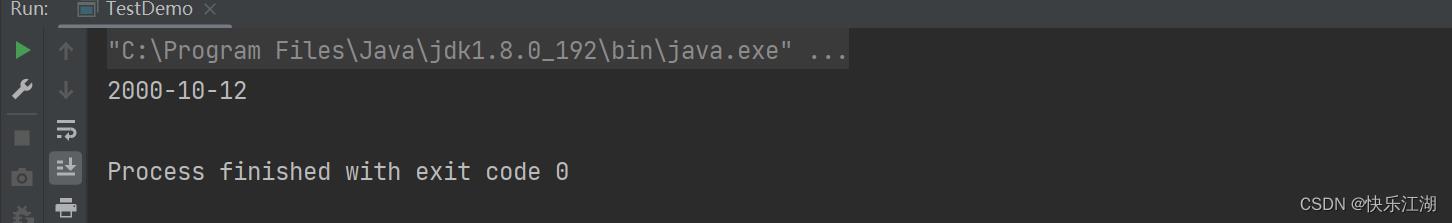
使用String.format()可以将一个字符串格式化为目标字符串
public class TestDemo
public static void main(String[] args)
String str = String.format("%d-%d-%d", 2000, 10, 12);
System.out.println(str);
(5)字符串替换
①:String replaceAll(String regex, String replacement):将原字符串中regex替换为replacement
public class TestDemo
public static void main(String[] args)
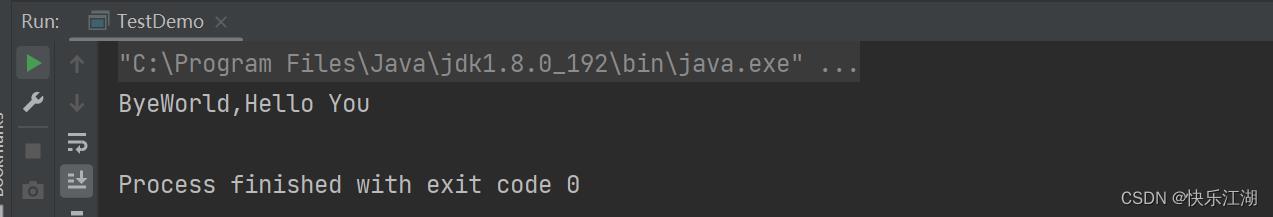
String s1 = "HelloWorld,Hello You";
String s2 = s1.replaceAll("Hello", "Bye"); //将Hello替换为Bye
String s3 = s1.replace('H', 'S'); //将H替换为S
System.out.println(s2);
System.out.println(s3);
②:String replaceFirst(String regex, String replacement):仅替换首次出现的regex
public class TestDemo
public static void main(String[] args)
String s1 = "HelloWorld,Hello You";
String s2 = s1.replaceFirst("Hello", "Bye"); //将第一个Hello替换为Bye
System.out.println(s2);
(6)字符串拆分
①:String[] split(String regex):以regex为分割标志,将原字符串拆分为多个字符串
public class TestDemo
public static void main(String[] args)
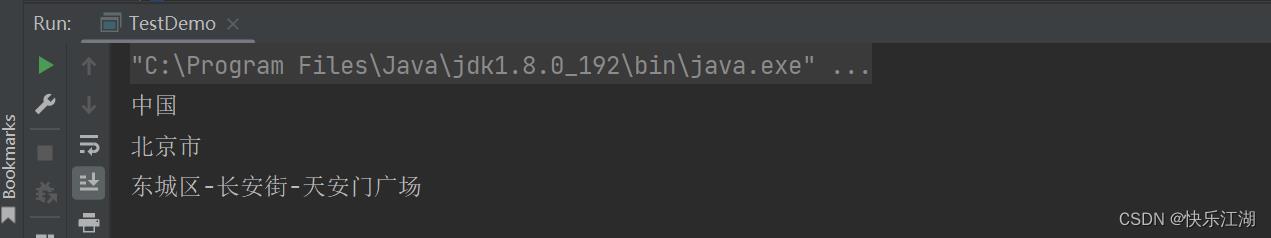
String str = "中国-北京市-东城区-长安街-天安门广场";
String[] ret = str.split("-");
for(String s : ret)
System.out.println(s);

②:String[] split(String regex, int limit):以regex为分割标志,将原字符串拆分为limit字符串
public class TestDemo
public static void main(String[] args)
String str = "中国-北京市-东城区-长安街-天安门广场";
String[] ret = str.split("-", 3);
for(String s : ret)
System.out.println(s);
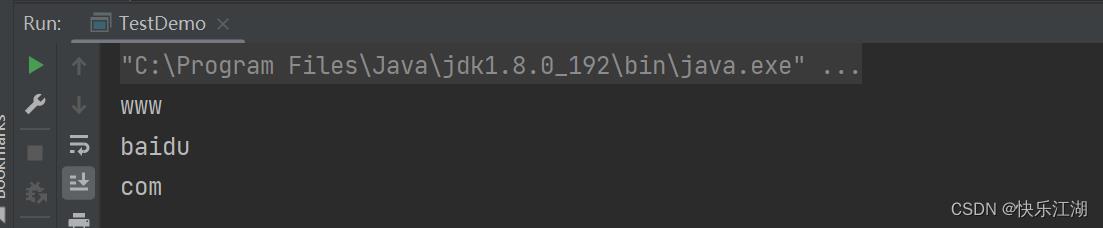
③:一旦以"|“、”*“、”+“等作为分割标志时,前面都得加上”\\\\“,而且如果是”\\“,那么就得写上”\\\\\\\\"
public class TestDemo
public static void main(String[] args)
String str = "www.baidu.com";
String[] ret = str.split("\\\\.");
for(String s : ret)
System.out.println(s);
④:如果第一次拆分出来的字符串中还需要进行拆分,那么就要使用下面这种多次拆分的写法
- 首先以
&为分割标志拆分出name=zhangsan和age=18 - 然后再以=为分割标志拆分出
name、zhangsan、age和18
public class TestDemo
public static void main(String[] args)
String str = "name=zhangsan&age=18";
String[] result = str.split("&");
for(int i = 0; i < result