解析PR曲线与目标检测中的mAP指标
Posted 夏小悠
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了解析PR曲线与目标检测中的mAP指标相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
文章目录
前言
本篇博客主要是介绍PR曲线与目标检测中的mAP指标。
1. PR曲线的绘制
有关PR曲线的解释,可以参考我的这篇博客:机器学习中常用评价指标(分类篇)
import numpy as np
from matplotlib import pyplot as plt
seed = 10001
np.random.seed(seed)
# 预测框个数
num_pred_boxes = 30
# 真实框个数
num_gt_boxes = 15
def draw_pr(rec, prec):
plt.plot(rec, prec, label='PR curve')
plt.xlabel('Recall')
plt.ylabel('Precision')
plt.xlim([0.0, 1.0])
plt.ylim([0.0, 1.0])
plt.title('Precision-Recall')
plt.legend()
plt.savefig('pr.png')
plt.show()
if __name__ == '__main__':
tp = np.zeros(num_pred_boxes)
fp = np.zeros(num_pred_boxes)
for i in range(num_pred_boxes):
if np.random.rand() > 0.55:
tp[i] = 1
else:
fp[i] = 1
# 按列累加
tp = np.cumsum(tp)
fp = np.cumsum(fp)
# recall
rec = tp / float(num_gt_boxes)
# precision
prec = tp / (tp + fp)
draw_pr(rec, prec)
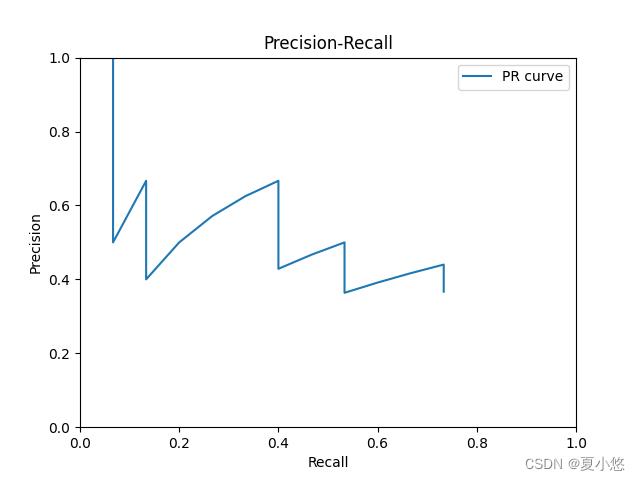
2. AP的计算
即使有了PR曲线,评价模型仍然不直观,如果直接取曲线上的点,在哪里选取都不合适,因为召回率高的时候精确率会很低,精确率高的时候往往召回率很低,这时,AP就派上用场了。AP(Average Precision)表示的是样本的平均精度,从公式中可以看出,AP代表了曲线的面积,综合考量了不同召回率下的准确率,不会对Precision与Recall有任何偏好。AP的计算公式如下:
A
P
=
∫
0
1
P
(
r
)
d
r
AP = \\int _0^1 P(r)\\ dr
AP=∫01P(r) dr
通常来讲,
AP的值越高,分类器的性能越好。
但是在实际应用中(VOC 2010以后),我们不是直接对积分进行计算,而是对其平滑操作来简化计算,对PR曲线上的每个点,precision的值取该点右侧的最大值,然后对平滑后的曲线求面积。以上图为例,平滑后的PR曲线如下:

此时的计算公式为:
A
P
=
∑
i
(
R
(
i
+
1
)
−
R
(
i
)
)
P
s
m
o
o
t
h
(
i
)
AP = \\sum _i \\big(R(i+1)-R(i)\\big) P_smooth(i)
AP=i∑(R(i+1)−R(i))Psmooth(i)
在VOC 2007中计算AP的方法是不计算所有的点,而是在[0, 1]区间上10等分,即采样得到11个点,仍然取当前点右侧的最大值作为当前点的precision的值,仍然以第一节的图为例,采样后的图如下:
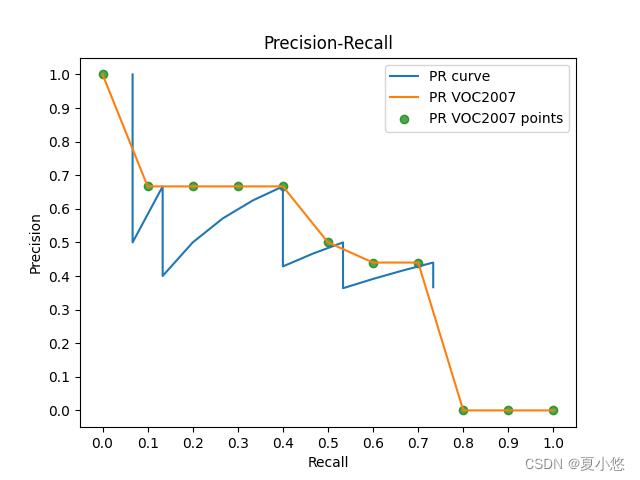
此时的计算公式为:
A
P
=
1
11
∑
i
P
s
m
o
o
t
h
(
i
)
AP = \\frac1 11 \\sum _i P_smooth(i)
AP=111i∑Psmooth(i) 其中,i的取值为[0, 0.1, 0.2, ... , 1.0]。很明显,通过11个不同位置的recall来计算AP时会有精度损失,所以现在通常采用第一种方法来计算AP。
代码实现两种AP的计算方式:
def voc_ap(rec, prec, use_07_metric=False):
""" ap = voc_ap(rec, prec, [use_07_metric])
Compute VOC AP given precision and recall.
If use_07_metric is true, uses the
VOC 07 11 point method (default:False).
"""
if use_07_metric:
# 11 point metric
ap = 0.
for t in np.arange(0., 1.1, 0.1):
if np.sum(rec >= t) == 0:
p = 0
else:
p = np.max(prec[rec >= t])
ap = ap + p / 11.
else:
# correct AP calculation
# first append sentinel values at the end
mrec = np.concatenate(([0.], rec, [1.]))
mpre = np.concatenate(([0.], prec, [0.]))
# compute the precision envelope
for i in range(mpre.size - 1, 0, -1):
mpre[i - 1] = np.maximum(mpre[i - 1], mpre[i])
# to calculate area under PR curve, look for points
# where X axis (recall) changes value
i = np.where(mrec[1:] != mrec[:-1])[0]
# and sum (\\Delta recall) * prec
# 计算PR曲线向下包围的面积
ap = np.sum((mrec[i + 1] - mrec[i]) * mpre[i + 1])
return ap
mAP(mean Average Precision) 表示的是所有类别AP值的均值,mAP越高,表示目标检测的精度越高。其计算公式如下:
m
A
P
=
1
N
∑
A
P
mAP = \\frac 1 N \\sum AP
mAP=N1∑AP 其中,N表示类别的数量。
3. 完整代码
import numpy as np
from matplotlib import pyplot as plt
seed = 10001
np.random.seed(seed)
# 预测框个数
num_pred_boxes = 30
# 真实框个数
num_gt_boxes = 15
def draw_pr(rec, prec, use_07_metric=False):
plt.plot(rec, prec, label='PR curve')
plt.xlabel('Recall')
plt.ylabel('Precision')
plt.title('Precision-Recall')
if use_07_metric:
plt.xticks(np.arange(0., 1.1, 0.1))
plt.yticks(np.arange(0., 1.1, 0.1))
rec_voc = np.arange(0., 1.1, 0.1)
prec_voc = []
for t in np.arange(0., 1.1, 0.1):
if np.sum(rec >= t) == 0:
p = 0
else:
p = np.max(prec[rec >= t])
prec_voc.append(p)
plt.plot(rec_voc, prec_voc, label='PR VOC2007')
plt.scatter(rec_voc, prec_voc, color='g', alpha=0.7, label='PR VOC2007 points')
else:
plt.xlim([0.0, 1.0])
plt.ylim([0.0, 1.0])
for i in range(len(rec)):
prec[i] = prec[i:].max()
plt.plot(rec, prec, label='PR curve smooth')
# plt.scatter(rec, prec, color='g', alpha=0.7)
plt.legend()
plt.savefig('pr.png')
plt.show()
def voc_ap(rec, prec, use_07_metric=False):
""" ap = voc_ap(rec, prec, [use_07_metric])
Compute VOC AP given precision and recall.
If use_07_metric is true, uses the
VOC 07 11 point method (default:False).
"""
if use_07_metric:
# 11 point metric
ap = 0.
for t in np.arange(0., 1.1, 0.1):
if np.sum(rec >= t) == 0:
p = 0
else:
p = np.max(prec[rec >= t])
ap = ap + p / 11.
else:
# correct AP calculation
# first append sentinel values at the end
mrec = np.concatenate(([0.], rec, [1.]))
mpre = np.concatenate(([0.], prec, [0.]))
# compute the precision envelope
for i in range(mpre.size - 1, 0, -1):
mpre[i - 1] = np.maximum(mpre[i - 1], mpre[i])
# to calculate area under PR curve, look for points
# where X axis (recall) changes value
i = np.where(mrec[1:] != mrec[:-1])[0]
# and sum (\\Delta recall) * prec
# 计算PR曲线向下包围的面积
ap = np.sum((mrec[i + 1] - mrec[i]) * mpre[i + 1])
return ap
if __name__ == '__main__':
tp = np.zeros(num_pred_boxes)
fp = np.zeros(num_pred_boxes)
for i in range(num_pred_boxes):
if np.random.rand() > 0.55:
tp[i] = 1
else:
fp[i] = 1
# 按列累加
tp = np.cumsum(tp)
fp = np.cumsum(fp)
# recall
rec = tp / float(num_gt_boxes)
# precision
prec = tp / (tp + fp)
draw_pr(rec, prec, use_07_metric=False)
ap = voc_ap(rec, prec, use_07_metric=False)
print(ap)
以上是关于解析PR曲线与目标检测中的mAP指标的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章