Python3 网络编程
Posted SPIRT00
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了Python3 网络编程相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
文章目录
一、Python3 网络编程
-
Python 提供了两个级别访问的网络服务。:
低级别的网络服务支持基本的 Socket,它提供了标准的 BSD Sockets API,可以访问底层操作系统Socket接口的全部方法。
高级别的网络服务模块 SocketServer, 它提供了服务器中心类,可以简化网络服务器的开发。 -
什么是 Socket?
Socket又称"套接字",应用程序通常通过"套接字"向网络发出请求或者应答网络请求,使主机间或者一台计算机上的进程间可以通讯。 -
socket()函数
Python 中,我们用 socket() 函数来创建套接字,语法格式如下:
socket.socket([family[, type[, proto]]])
参数
family: 套接字家族可以是 AF_UNIX 或者 AF_INET
type: 套接字类型可以根据是面向连接的还是非连接分为SOCK_STREAM或SOCK_DGRAM
proto: 一般不填默认为0.
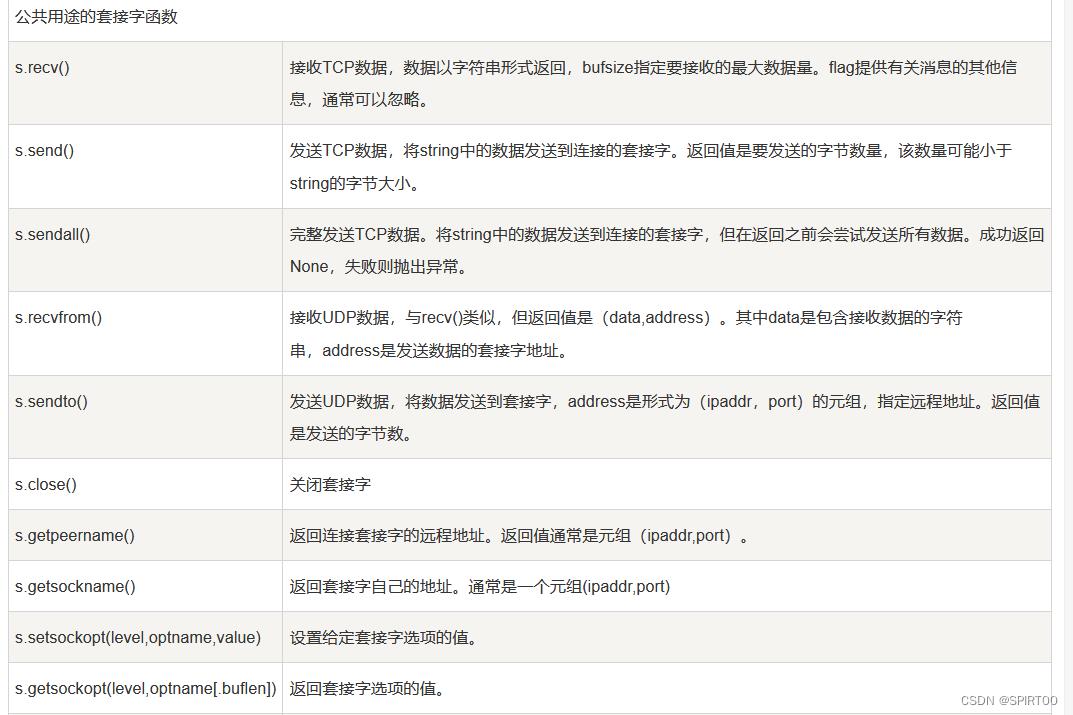
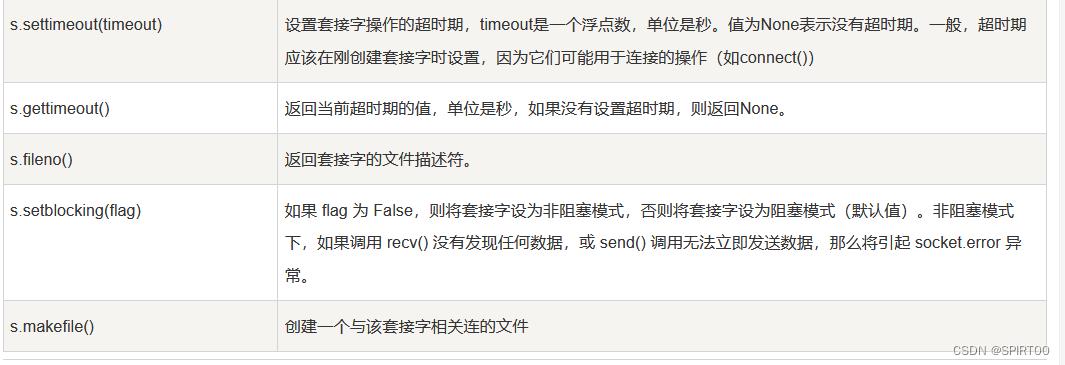
- Socket 对象(内建)方法
| 函数 | 描述 |
|---|---|
| 服务器端套接字 | |
| s.bind() | 绑定地址(host,port)到套接字, 在AF_INET下,以元组(host,port)的形式表示地址。 |
| s.listen() | 开始TCP监听。backlog指定在拒绝连接之前,操作系统可以挂起的最大连接数量。该值至少为1,大部分应用程序设为5就可以了。 |
| s.accept() | 被动接受TCP客户端连接,(阻塞式)等待连接的到来 |
| 客户端套接字 | |
| s.connect() | 主动初始化TCP服务器连接,。一般address的格式为元组(hostname,port),如果连接出错,返回socket.error错误。 |
| s.connect_ex() | connect()函数的扩展版本,出错时返回出错码,而不是抛出异常 |
- 简单实例
服务端
我们使用 socket 模块的 socket 函数来创建一个 socket 对象。socket 对象可以通过调用其他函数来设置一个 socket 服务。
现在我们可以通过调用 bind(hostname, port) 函数来指定服务的 port(端口)。
接着,我们调用 socket 对象的 accept 方法。该方法等待客户端的连接,并返回 connection 对象,表示已连接到客户端。
完整代码如下:

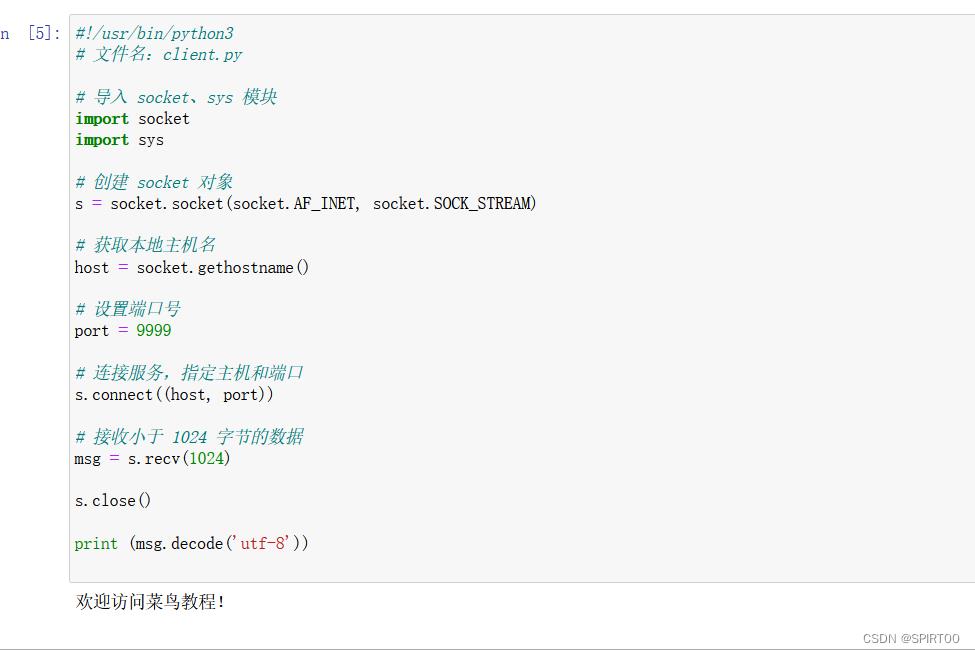
- 客户端
接下来我们写一个简单的客户端实例连接到以上创建的服务。端口号为 9999。
socket.connect(hostname, port ) 方法打开一个 TCP 连接到主机为 hostname 端口为 port 的服务商。连接后我们就可以从服务端获取数据,记住,操作完成后需要关闭连接。
完整代码如下:
- Python Internet 模块
以下列出了 Python 网络编程的一些重要模块:
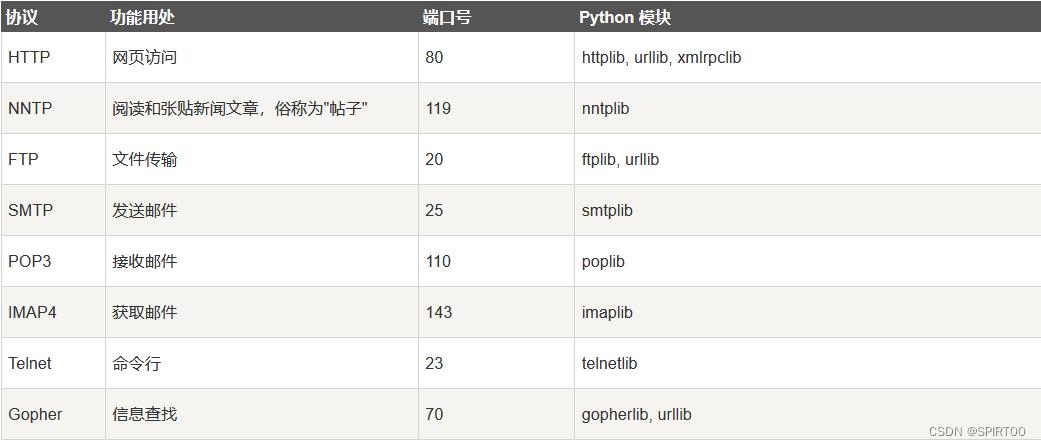
来自“https://www.runoob.com/python3/python3-smtp.html”
总结
至人无己,神人无功,圣人无名。
Python 十python网络编程
一、MySQLdb模块
python访问mariadb|mysql依赖于第三方模块MySQLdb,在pypi上下载下来
路径:https://pypi.python.org/pypi/MySQL-python/
MySQL-python依赖于easy_install那先安装setuptools,这里省略
[[email protected] ~]# unzip MySQL-python-1.2.5.zip [[email protected] ~]# cd MySQL-python-1.2.5 [[email protected] MySQL-python-1.2.5]# ls doc MANIFEST.in _mysql_exceptions.py README.md setup.py GPL-2.0 metadata.cfg MySQL_python.egg-info setup.cfg setup_windows.py HISTORY _mysql.c PKG-INFO setup_common.py site.cfg INSTALL MySQLdb pymemcompat.h setup_posix.py tests [[email protected] MySQL-python-1.2.5]# python2.7 setup.py install sh: mysql_config: command not found #没找到这个命令 Traceback (most recent call last): File "setup.py", line 17, in <module> metadata, options = get_config() File "/root/MySQL-python-1.2.5/setup_posix.py", line 43, in get_config libs = mysql_config("libs_r") File "/root/MySQL-python-1.2.5/setup_posix.py", line 25, in mysql_config raise EnvironmentError("%s not found" % (mysql_config.path,)) EnvironmentError: mysql_config not found [[email protected] MySQL-python-1.2.5]# yum install mysql [[email protected] MySQL-python-1.2.5]# rpm -ql mysql /usr/bin/msql2mysql /usr/bin/my_print_defaults /usr/bin/mysql /usr/bin/mysql_config #在这里 /usr/bin/mysql_find_rows /usr/bin/mysql_waitpid /usr/bin/mysqlaccess /usr/bin/mysqladmin /usr/bin/mysqlbinlog /usr/bin/mysqlcheck /usr/bin/mysqldump /usr/bin/mysqlimport /usr/bin/mysqlshow /usr/bin/mysqlslap /usr/lib64/mysql/mysql_config /usr/lib64/mysql/mysqlbug /usr/share/doc/mysql-5.1.73 [[email protected] MySQL-python-1.2.5]# python2.7 setup.py install _mysql.c: In function ‘_mysql_ConnectionObject_getattr’: _mysql.c:2666: error: ‘_mysql_ConnectionObject’ has no member named ‘open’ error: command ‘gcc‘ failed with exit status 1 #又遇到报错,google后是需要mysql-devel [[email protected] MySQL-python-1.2.5]# yum install mysql-devel [[email protected] MySQL-python-1.2.5]# python2.7 setup.py install Adding MySQL-python 1.2.5 to easy-install.pth file Installed /usr/local/python27/lib/python2.7/site-packages/MySQL_python-1.2.5-py2.7-linux-x86_64.egg Processing dependencies for MySQL-python==1.2.5 Finished processing dependencies for MySQL-python==1.2.5 #安装成功
导入MySQLdb模块:
In [4]: import MySQLdb In [5]: import MySQLdb. #有众多方法和属性 MySQLdb.BINARY MySQLdb.NULL MySQLdb.connect MySQLdb.Binary MySQLdb.NUMBER MySQLdb.connections MySQLdb.Connect MySQLdb.NotSupportedError MySQLdb.constants MySQLdb.Connection MySQLdb.OperationalError MySQLdb.converters MySQLdb.DATE MySQLdb.ProgrammingError MySQLdb.cursors MySQLdb.DBAPISet MySQLdb.ROWID MySQLdb.debug MySQLdb.DataError MySQLdb.STRING MySQLdb.escape MySQLdb.DatabaseError MySQLdb.TIME MySQLdb.escape_dict MySQLdb.Date MySQLdb.TIMESTAMP MySQLdb.escape_sequence MySQLdb.DateFromTicks MySQLdb.Time MySQLdb.escape_string MySQLdb.Error MySQLdb.TimeFromTicks MySQLdb.get_client_info MySQLdb.FIELD_TYPE MySQLdb.Timestamp MySQLdb.paramstyle MySQLdb.IntegrityError MySQLdb.TimestampFromTicks MySQLdb.release MySQLdb.InterfaceError MySQLdb.Warning MySQLdb.string_literal MySQLdb.InternalError MySQLdb._mysql MySQLdb.threadsafety MySQLdb.MySQLError MySQLdb._mysql_exceptions MySQLdb.times MySQLdb.MySQLdb MySQLdb.apilevel MySQLdb.version_info In [11]: help(MySQLdb) Help on package MySQLdb: NAME MySQLdb - MySQLdb - A DB API v2.0 compatible interface to MySQL. FILE /usr/local/python27/lib/python2.7/site-packages/MySQL_python-1.2.5-py2.7-linux-x86_64.egg/MySQLdb/__init__.py DESCRIPTION This package is a wrapper around _mysql, which mostly implements the MySQL C API. connect() -- connects to server See the C API specification and the MySQL documentation for more info on other items. For information on how MySQLdb handles type conversion, see the MySQLdb.converters module. PACKAGE CONTENTS #包内容|子模块 connections #连接mysql constants (package) # converters #将Python中的字符串转化成mysql可以处理的数据类型 cursors #游标 release times In [24]: help(MySQLdb.connection) Help on class connection in module _mysql: class connection(__builtin__.object) | Returns a MYSQL connection object. Exclusive use of | keyword parameters strongly recommended. Consult the | MySQL C API documentation for more details. | | host | string, host to connect | | user | string, user to connect as | | passwd | string, password to use | | db | string, database to use | | port | integer, TCP/IP port to connect to | | unix_socket | string, location of unix_socket (UNIX-ish only) | | conv | mapping, maps MySQL FIELD_TYPE.* to Python functions which | convert a string to the appropriate Python type | | connect_timeout | number of seconds to wait before the connection | attempt fails. | | compress | if set, gzip compression is enabled
示例:
In [2]: import MySQLdb In [7]: conn=MySQLdb.connect(host=‘127.0.0.1‘,user=‘root‘) #创建连接使用conncet In [10]: conn. conn.DataError conn.close conn.get_host_info conn.set_character_set conn.DatabaseError conn.commit conn.get_proto_info conn.set_server_option conn.Error conn.converter conn.get_server_info conn.set_sql_mode conn.IntegrityError conn.cursor conn.info conn.show_warnings conn.InterfaceError conn.cursorclass conn.insert_id conn.shutdown conn.InternalError conn.default_cursor conn.kill conn.sqlstate conn.NotSupportedError conn.dump_debug_info conn.literal conn.stat conn.OperationalError conn.encoders conn.messages conn.store_result conn.ProgrammingError conn.errno conn.next_result conn.string_decoder conn.Warning conn.error conn.open conn.string_literal conn.affected_rows conn.errorhandler conn.ping conn.thread_id conn.autocommit conn.escape conn.port conn.unicode_literal conn.begin conn.escape_string conn.query conn.use_result conn.change_user conn.field_count conn.rollback conn.warning_count conn.character_set_name conn.get_autocommit conn.select_db conn.client_flag conn.get_character_set_info conn.server_capabilities In [14]: conn.stat Out[14]: <function stat> In [15]: conn.stat() Out[15]: ‘Uptime: 719 Threads: 1 Questions: 6 Slow queries: 0 Opens: 15 Flush tables: 1 Open tables: 8 Queries per second avg: 0.8‘ In [4]: s1=conn.cursor() #创建游标 In [5]: s1. s1.DataError s1.arraysize s1.fetchone s1.DatabaseError s1.callproc s1.lastrowid s1.Error s1.close s1.messages s1.IntegrityError s1.connection s1.nextset s1.InterfaceError s1.description s1.rowcount s1.InternalError s1.description_flags s1.rownumber s1.MySQLError s1.errorhandler s1.scroll s1.NotSupportedError s1.execute s1.setinputsizes s1.OperationalError s1.executemany s1.setoutputsizes s1.ProgrammingError s1.fetchall s1.Warning s1.fetchmany In [5]: s1.execute(‘SHOW DATABASES;‘) #执行SQL语句 Out[5]: 3L #返回的结果 In [6]: s1.fe s1.fetchall s1.fetchmany s1.fetchone In [6]: s1.fetchall() #详细查看返回的结果,此时游标已经指到了尾部 Out[6]: ((‘information_schema‘,), (‘mysql‘,), (‘test‘,)) In [7]: s1.fetchone() #这里没数据了,需要调整游标的位置 In [8]: s1.fetchmany Out[8]: <bound method Cursor.fetchmany of <MySQLdb.cursors.Cursor object at 0x2db8e90>> In [9]: s1.fetchmany() Out[9]: () In [11]: s1.scroll(0,mode=‘absolute‘) #移到首部 In [13]: s1.fetchone() #读取一行 Out[13]: (‘information_schema‘,) In [14]: s1.fetchone() Out[14]: (‘mysql‘,) In [15]: s1.fetchone() Out[15]: (‘test‘,) In [16]: s1.fetchone() In [17]: s1.scroll(1,mode=‘absolute‘) In [18]: s1.fetchone() Out[18]: (‘mysql‘,) In [19]: s1.fetchone() Out[19]: (‘test‘,) In [20]: s1.fetchone() In [21]: s1.scroll(0,mode=‘absolute‘) In [22]: s1.fetchmany() Out[22]: ((‘information_schema‘,),) In [23]: s1.fetchmany() Out[23]: ((‘mysql‘,),) In [24]: s1.fetchmany() Out[24]: ((‘test‘,),) In [25]: s1.fetchmany() Out[25]: () In [26]: s1.scroll(0,mode=‘absolute‘) In [32]: s1.fetchmany(3) #可以指定一次读取几行 Out[32]: ((‘information_schema‘,), (‘mysql‘,), (‘test‘,)) In [33]: s1.fetchmany(2) Out[33]: () In [34]: s1.scroll(0,mode=‘absolute‘) In [35]: s1.fetchmany(2) Out[35]: ((‘information_schema‘,), (‘mysql‘,)) In [36]: s1.close() #关闭游标 In [37]: conn.close() #关闭连接
二、socket模块
1、编写服务器端程序
1)创建socket
socket.socket(family,type)
family
AF_INET:
AF_UNIX:
type
SOCK_STREAM:tcp
SOCK_DGRAM:udp
示例:
tcpconn=scoket.socket(socket.AF_INET,sockot.SOCK_STREAM)
In [44]: import socket In [45]: tcpconn=socket.socket(socket.AF_INET,socket.SOCK_STREAM) In [46]: tcpconn. tcpconn.accept tcpconn.getsockname tcpconn.recvfrom_into tcpconn.bind tcpconn.getsockopt tcpconn.send tcpconn.close tcpconn.gettimeout tcpconn.sendall tcpconn.connect tcpconn.listen tcpconn.sendto tcpconn.connect_ex tcpconn.makefile tcpconn.setblocking tcpconn.dup tcpconn.proto tcpconn.setsockopt tcpconn.family tcpconn.recv tcpconn.settimeout tcpconn.fileno tcpconn.recv_into tcpconn.shutdown tcpconn.getpeername tcpconn.recvfrom tcpconn.type
2)绑定地址
使用套接字对象bind方法绑定于某地址和端口
tcpconn.bind((‘ip‘,port))
In [47]: help(tcpconn.bind)
Help on method bind:
bind(...) method of socket._socketobject instance
bind(address)
Bind the socket to a local address. For IP sockets, the address is a
pair (host, port); the host must refer to the local host. For raw packet
sockets the address is a tuple (ifname, proto [,pkttype [,hatype]])
(END)
In [48]: tcpconn.bind("192.168.10.3",8023)
---------------------------------------------------------------------------
TypeError Traceback (most recent call last)
<ipython-input-48-a9abfbcc4351> in <module>()
----> 1 tcpconn.bind("192.168.10.3",8023)
/usr/local/python27/lib/python2.7/socket.pyc in meth(name, self, *args)
222
223 def meth(name,self,*args):
--> 224 return getattr(self._sock,name)(*args)
225
226 for _m in _socketmethods:
TypeError: bind() takes exactly one argument (2 given)
In [49]: tcpconn.bind(("192.168.10.3",8023)3)使用listen方法进行监听状态
tcpconn.listen(backlog) #backlog 等待队列的长度
tcpconn.listen(100)
In [50]: tcpconn.listen(30) [[email protected] ~]# ss -nlt State Recv-Q Send-Q Local Address:Port Peer Address:Port LISTEN 0 128 *:7500 *:* LISTEN 0 128 *:7501 *:* LISTEN 0 100 *:9422 *:* LISTEN 0 128 :::22 :::* LISTEN 0 128 *:22 *:* LISTEN 0 30 192.168.10.3:8023 *:* LISTEN 0 100 ::1:25 :::* LISTEN 0 100 127.0.0.1:25 *:* LISTEN 0 128 127.0.0.1:6010 *:* LISTEN 0 128 ::1:6010 :::* LISTEN 0 128 127.0.0.1:6011 *:* LISTEN 0 128 ::1:6011 :::* LISTEN 0 50 *:3306 *:*
4)循环监听状态
使用套接字对象的accept方法接收用户请求
In [51]: help(tcpconn.accept) #返回(客户端Ip地址,端口) Help on method accept in module socket: accept(self) method of socket._socketobject instance accept() -> (socket object, address info) Wait for an incoming connection. Return a new socket representing the connection, and the address of the client. For IP sockets, the address info is a pair (hostaddr, port). In [52]: ci,cp=tcpconn.accept() #此时服务端阻塞
2、编写客户端程序
1)创建一个socket对象,以连接服务器端
clientsock=socket.socket(socket.AF_INET,sock.SOCK_STREAM)
In [6]: import socket In [7]: clientsock=socket.socket(socket.AF_INET,socket.SOCK_STREAM)
2)连接至服务器
clientscok.connect((‘server_ip‘,server_port))
In [8]: clientsock.connect((‘192.168.10.3‘,8023))
此时再观察服务器端:
In [55]: ci,cp=tcpconn.accept() #服务器端收到数据,结束阻塞 In [56]: ci Out[56]: <socket._socketobject at 0x2f16590> In [57]: ci() --------------------------------------------------------------------------- TypeError Traceback (most recent call last) <ipython-input-57-3d2081a2327e> in <module>() ----> 1 ci() TypeError: ‘_socketobject‘ object is not callable In [58]: ci,cp #返回2各对象,ci是一个socket对象,cp是一个元祖对象 Out[58]: (<socket._socketobject at 0x2f16590>, (‘192.168.10.3‘, 34873))
3)发送请求
clientscok.send()
In [9]: clientsock.send(‘hello server‘) Out[9]: 11
但这么操作当客户端连接进服务器端后,连接就断开了,我们应该写脚本来实现服务器处于循环监听状态
脚本文件:
[[email protected] ~]# cat server.py #服务器端 #!/usr/local/bin/python2.7 # import socket s=socket.socket(socket.AF_INET,socket.SOCK_STREAM) sa=("192.168.10.3",8030) s.bind(sa) s.listen(20) while True: cinfo,caddr=s.accept() print "Got a connection from %s" %caddr[0] data=cinfo.recv(1024) print "Receive data:%s" %data cinfo.send("echo: " + data) cinfo.close() [[email protected] ~]# cat client.py #客户端 #!/usr/local/bin/python2.7 # import socket c=socket.socket(socket.AF_INET,socket.SOCK_STREAM) saddr=("192.168.10.3",8030) c.connect(saddr) c.send("Hello Server") data=c.recv(1024) print "Reply from server %s" %data
执行脚本:
[[email protected] ~]# python2.7 server.py #执行服务器端脚本 #阻塞状态
[[email protected] ~]# python2.7 client.py #执行客户端脚本 Reply from server echo: Hello Server
再看服务器端:
[[email protected] ~]# python2.7 server.py Got a connection from 192.168.10.3 Receive data:Hello Server #仍阻塞状态
修改下客户端脚本再执行一次:
[[email protected] ~]# vi client.py [[email protected] ~]# python2.7 client.py Reply from server echo: Hello SB
服务器端:
[[email protected] ~]# python2.7 server.py Got a connection from 192.168.10.3 Receive data:Hello Server Got a connection from 192.168.10.3 Receive data:Hello SB
以上是关于Python3 网络编程的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章