Mybatis之Mapper代理开发
Posted Super algorithm
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了Mybatis之Mapper代理开发相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
目录
一、Mapper概述
通用Mapper都可以极大的方便开发人员。可以随意的按照自己的需要选择通用方法,还可以很方便的开发自己的通用方法。
参考gitee:MyBatis 通用 Mapper4
1.Mapper代理开发
之前我们写的Mybatis代码是基本使用方式,【参考Mybatis快速入门】,它存在硬编码的问题,例如执行sql:sqlSession.selectList("test.selectAll");,传递的字符串参数是映射配置文件中的 namespace.id值,这样写不便于后期的维护。如果使用 Mapper 代理方式则不存在硬编码问题。
2.Mapper开发流程
准备
新建一个Maven项目:
一个module已建立好:
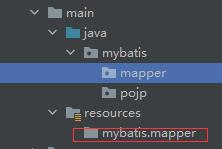
在main的java里面创建好你的包mybatis,在这个包下面可以再建立2个包,一个存放你的mapper接口,一个创建一个类来存储我们后面用于接收数据。同时在resource里面建立一个和mapper同样结构的文件目录,里面存放SQL映射文件,这个文件名称要和mapper接口一致。
然后在mapper里面新建一个接口,查询所有数据的例子:
package mybatis.mapper;
import mybatis.pojp.Brand;
import java.util.List;
public interface BrandMapper
List<Brand> selectAll();
继续编写我们的mapper xml文件,也就是SQL映射文件。namespace是对应接口相对于source的目录+名称, resultType是对应类的目录名称,当在mybatis的配置文件中设置好给类起别名映射,就也可以直接不区分大小写写类名了。
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8" ?>
<!DOCTYPE mapper PUBLIC "-//mybatis.org//DTD Mapper 3.0//EN" "http://mybatis.org/dtd/mybatis-3-mapper.dtd">
<mapper namespace="mybatis.mapper.BrandMapper">
<select id="selectAll" resultType="brand">
select *
from tb_brand;
</select>
</mapper>
<!-- mybatis的配置文件中设置好给类起别名映射-->
<typeAliases>
<package name="mybatis.pojp"/>
</typeAliases>
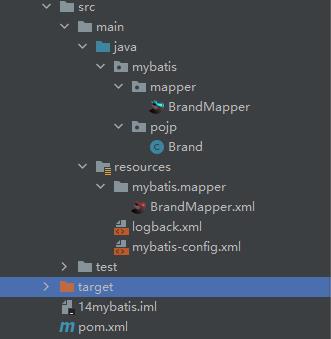
至此mapper的前置文件部分准备好了。
如果Mapper接口名称和SQL映射文件名称相同,并在同一目录下,则可以使用包扫描的方式简化SQL映射文件的加载。也就是将核心配置文件的加载映射配置文件的配置修改为:
<mappers>
<!--加载sql映射文件-->
<!-- <mapper resource="com/itheima/mapper/UserMapper.xml"/>-->
<!--Mapper代理方式-->
<package name="com.itheima.mapper"/>
</mappers>
实现查询
我们可以在test里面建立我们测试项目:mybatis/test/MyBatisTest.java。使用了代理mapper之后我们执行SQL的代码就从字符串参数"test.selectAll"变为UserMapper.class了。
sqlSession.selectList("test.selectAll");—>sqlSession.getMapper(UserMapper.class);
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException
//1. 加载mybatis的核心配置文件,获取 SqlSessionFactory
String resource = "mybatis-config.xml";
InputStream inputStream = Resources.getResourceAsStream(resource);
SqlSessionFactory sqlSessionFactory = new SqlSessionFactoryBuilder().build(inputStream);
//2. 获取SqlSession对象,用它来执行sql
SqlSession sqlSession = sqlSessionFactory.openSession();
//3. 执行sql
//3.1 获取UserMapper接口的代理对象
UserMapper userMapper = sqlSession.getMapper(UserMapper.class);
List<User> users = userMapper.selectAll();
System.out.println(users);
//4. 释放资源
sqlSession.close();
二、Mybatis-CRUD
这一节我们使用映射配置文件实现CRUD操作,也就是增删改查操作。
create table tb_brand
(
id int primary key auto_increment,
brand_name varchar(20),
company_name varchar(20),
ordered int,
description varchar(100),
-- 状态:0:禁用 1:启用
status int
);
继续上一节的内容,我们操作一个这样的数据表。
0.编辑类Brand
上一节我们在pojp包下创建了 Brand 实体类。我们根据数据表编辑对应的参数:
public class Brand
private Integer id;
private String brandName;
private String companyName;
private Integer ordered;
private String description;
private Integer status;
1.查询所有数据
- 编写接口方法:
List<Brand> selectAll();
- 编写SQL
<select id="selectAll" resultType="brand">
select *
from tb_brand;
</select>
- 测试代码
在测试项目mybatis/test/MyBatisTest.java中开始我们的测试代码。我们可以使用@Test注解。
@Test
public void testSelectAll() throws IOException
//1. 获取SqlSessionFactory
String resource = "mybatis-config.xml";
InputStream inputStream = Resources.getResourceAsStream(resource);
SqlSessionFactory sqlSessionFactory = new SqlSessionFactoryBuilder().build(inputStream);
//2. 获取SqlSession对象
SqlSession sqlSession = sqlSessionFactory.openSession();
//3. 获取Mapper接口的代理对象
BrandMapper brandMapper = sqlSession.getMapper(BrandMapper.class);
//4. 执行方法
List<Brand> brands = brandMapper.selectAll();
System.out.println(brands);
//5. 释放资源
sqlSession.close();
成功运行测试:
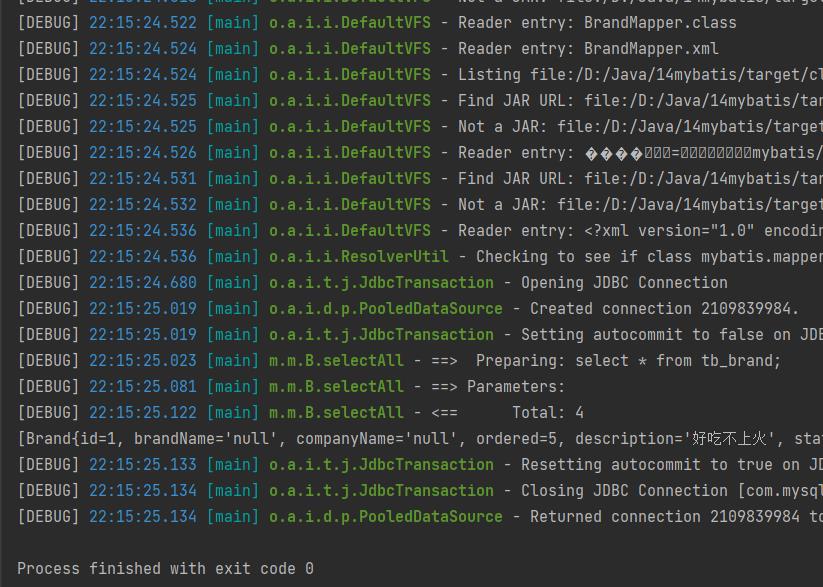
写到这里,我们会发现使用mapper代理后面只需要操作三个文件内容,

其实在测试方法里面我们需要修改的也只是执行方法,在后面会有具体体现。
但是在这里我们发现一个问题,就是打印出来的内容有一些是null,但是数据库里面的表是存在数据的。还有注意是不是写了tostring。从打印结果可以看到 brandName 和 companyName 这两个属性的数据没有封装成功,查询 实体类 和 表中的字段 发现,是因为他们的名称不一致,这个问题可以通过两种方式进行解决:
1.给字段起别名;
2.使用resultMap定义字段和属性的映射关系。
- 起别名
写sql语句时给这两个字段起别名,将别名定义成和属性名一致:
<select id="selectAll" resultType="brand">
select
id, brand_name as brandName, company_name as companyName, ordered, description, status
from tb_brand;
</select>
SQL语句中一大串的内容很麻烦也不美观,Mybatis提供了sql 片段可以提高sql的复用性。id属性值是唯一标识,后面通过该值进行引用。
<sql id="brand_column">
id, brand_name as brandName, company_name as companyName, ordered, description, status
</sql>
原sql语句引用 id="selectAll":
<select id="selectAll" resultType="brand">
select
<include refid="brand_column" />
from tb_brand;
</select>
- 映射
使用resultMap定义字段和属性(不一致)的映射关系。
<resultMap id="brandResultMap" type="brand">
<result column="brand_name" property="brandName"/>
<result column="company_name" property="companyName"/>
</resultMap>
sql语句的resultType改为resultMap并引用其id。
<select id="selectAll" resultMap="brandResultMap">
select *
from tb_brand;
</select>
2.根据id查询
- 编写接口方法
Brand selectById(int id); - 编写SQL语句
这里是根据id来查询,所以就有了参数的传入。就需要用到参数占位符,参数占位符在sql中就是?
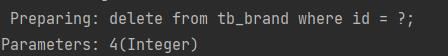
mybatis提供了两种参数占位符:
1. # :执行SQL时,会将 # 占位符替换为?,将来自动设置参数值。
2. $ :拼接SQL。底层使用的是Statement,会存在SQL注入问题。
编写如下的SQL语句:
<select id="selectById" resultMap="brandResultMap">
select *
from tb_brand where id = #id;
</select>
- 测试代码
@Test
public void testSelectById() throws IOException
//接收参数id
int id = 1;
//1. 获取SqlSessionFactory
String resource = "mybatis-config.xml";
InputStream inputStream = Resources.getResourceAsStream(resource);
SqlSessionFactory sqlSessionFactory = new SqlSessionFactoryBuilder().build(inputStream);
//2. 获取SqlSession对象
SqlSession sqlSession = sqlSessionFactory.openSession();
//3. 获取Mapper接口的代理对象
BrandMapper brandMapper = sqlSession.getMapper(BrandMapper.class);
//4. 执行方法
Brand brand = brandMapper.selectById(id);
System.out.println(brand);
//5. 释放资源
sqlSession.close();
是不是测试代码就是修改了对应执行方法。
- 特殊字段处理
映射配置文件是xml类型的问题,而><等字符在xml中有特殊含义,所以这些符号需要转义,有两种方式进行转义:转义字符、CDATA区<![CDATA[内容]]>。
3.多条件查询
使用条件查询返回多个结果,所以我们需要使用list来存储。还需要考虑如何实现条件。
- 编写接口方法
我们需要传多个参数,所以这里也有多个写法:
1、使用 @Param("参数名称") 标记每一个参数,在编写SQL时使用 #参数名称 进行占位
List<Brand> selectByCondition(@Param("status") int status,
@Param("companyName") String companyName,
@Param("brandName") String brandName
);
2、将多个参数封装成一个 实体对象 ,将该实体对象作为接口的方法参数。在SQL中使用 #内容 ,内容和实体类属性名一致。
List<Brand> selectByCondition(Brand brand);
3、将多个参数封装到map集合中,将map集合作为接口的方法参数。在SQL中使用 #内容 ,内容和map集合中键的名称一致。
List<Brand> selectByCondition(Map map);
- SQL语句
<select id="selectByCondition" resultMap="brandResultMap">
select *
from tb_brand
where status = #status
and company_name like #companyName
and brand_name like #brandName
</select>
- 测试代码
存在一个模糊匹配,所以需要进行参数处理:%
@Test
public void testSelectByCondition() throws IOException
//接收参数
int status = 1;
String companyName = "华为";
String brandName = "华为";
// 处理参数
companyName = "%" + companyName + "%";
brandName = "%" + brandName + "%";
//1. 获取SqlSessionFactory
String resource = "mybatis-config.xml";
InputStream inputStream = Resources.getResourceAsStream(resource);
SqlSessionFactory sqlSessionFactory = new SqlSessionFactoryBuilder().build(inputStream);
//2. 获取SqlSession对象
SqlSession sqlSession = sqlSessionFactory.openSession();
//3. 获取Mapper接口的代理对象
BrandMapper brandMapper = sqlSession.getMapper(BrandMapper.class);
//4. 执行方法 3kind
//方式一 :接口方法参数使用 @Param 方式调用的方法
// List<Brand> brands = brandMapper.selectByCondition(status,companyName,brandName);
//方式二 :接口方法参数是 实体类对象 方式调用的方法
/* Brand brand = new Brand();
brand.setStatus(status);
brand.setCompanyName(companyName);
brand.setBrandName(brandName);
List<Brand> brands = brandMapper.selectByCondition(brand);*/
//方式三 :接口方法参数是 map集合对象 方式调用的方法
Map map = new HashMap();
// map.put("status" , status);
map.put("companyName", companyName);
map.put("brandName" , brandName);
List<Brand> brands = brandMapper.selectByCondition(map);
System.out.println(brands);
//5. 释放资源
sqlSession.close();
- 动态SQL
使用动态SQL可以解决输入条件时,不需要填写全部条件,自动根据输入内容进行匹配。
我们可以利用mybatis提供的if 标签和 where 标签:
【if标签】
可以判断是不是存在对于参数,进行sql的拼接。
<select id="selectByCondition" resultMap="brandResultMap">
select *
from tb_brand
where
<if test="status != null">
status = #status
</if>
<if test="companyName != null and companyName != '' ">
and company_name like #companyName
</if>
<if test="brandName != null and brandName != '' ">
and brand_name like #brandName
</if>
</select>
这样的情况又会出现问题:如果第一个参数没有,那么首位出现and,SQL语句肯定报错。
【where标签】
where标签就是解决这一问题的,会自动去掉非法的and,如果没有参数则不加where关键字。第一个条件也写了and。
<where>
<if test="status != null">
and status = #status
</if>
<if test="companyName != null and companyName != '' ">
and company_name like #companyName
</if>
<if test="brandName != null and brandName != '' ">
and brand_name like #brandName
</if>
</where>
4.动态单个条件查询
- 编写接口方法
List<Brand> selectByConditionSingle(Brand brand); - SQL语句
为了实现动态查询我们使用 choose(when,otherwise)标签 , choose 标签相当于Java 的switch。
<select id="selectByConditionSingle" resultMap="brandResultMap">
select *
from tb_brand
<where>
<choose><!--相当于switch-->
<when test="status != null"><!--相当于case-->
status = #status
</when>
<when test="companyName != null and companyName != '' "><!--相当于case-->
company_name like #companyName
</when>
<when test="brandName != null and brandName != ''"><!--相当于case-->
brand_name like #brandName
</when>
</choose>
</where>
</select>
- 测试代码
@Test
public void testSelectByConditionSingle() throws IOException
//接收参数
int status = 1;
String companyName = "华为";
String brandName = "华为";
// 处理参数
companyName = "%" + companyName + "%";
brandName = "%" + brandName + "%";
//封装对象
Brand brand = new Brand();
//brand.setStatus(status);
brand.setCompanyName(companyName);
//brand.setBrandName(brandName);
//1. 获取SqlSessionFactory
String resource = "mybatis-config.xml";
InputStream inputStream = Resources.getResourceAsStream(resource);
SqlSessionFactory sqlSessionFactory = new SqlSessionFactoryBuilder().build(inputStream);
//2. 获取SqlSession对象
SqlSession sqlSession = sqlSessionFactory.openSession();
//3. 获取Mapper接口的代理对象
BrandMapper brandMapper = sqlSession.getMapper(BrandMapper.class);
//4. 执行方法
List<Brand> brands = brandMapper.selectByConditionSingle(brand);
System.out.println(brands);
//5. 释放资源
sqlSession.close();
5.添加数据
-
编写接口方法
void add(Brand brand); -
SQL语句
<insert id="add">
insert into tb_brand (brand_name, company_name, ordered, description, status)
values (#brandName, #companyName, #ordered, #description, #status);
</insert>
- 测试代码
@Test
public void testAdd() throws IOException
//接收参数
int status = 1;
String companyName = "AA科技";
String brandName = "AA";
String description = "AA创新生活!";
int ordered = 100;
//封装对象
Brand brand = new Brand();
brand.setStatus(status);
brand.setCompanyName(companyName);
brand.setBrandName(brandName);Mybatis-Dao层开发之Mapper接口
Mapper接口开发方法只需要程序员编写Mapper接口(相当于Dao接口),由Mybatis框架根据接口定义创建接口的动态代理对象,代理对象的方法体同上边Dao接口实现类方法。
Mapper接口开发需要遵循以下规范:
1、 Mapper.xml文件中的namespace与mapper接口的类路径相同。
2、 Mapper接口方法名和Mapper.xml中定义的每个statement的id相同
3、 Mapper接口方法的输入参数类型和mapper.xml中定义的每个sql 的parameterType的类型相同
4、 Mapper接口方法的输出参数类型和mapper.xml中定义的每个sql的resultType的类型相同
1、Mapper映射文件
定义mapper映射文件UserMapper.xml(内容同Users.xml),需要修改namespace的值为UserMapper接口路径。将UserMapper.xml放在classpath 下mapper目录下。
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8" ?>
<!DOCTYPE mapper
PUBLIC "-//mybatis.org//DTD Mapper 3.0//EN"
"http://mybatis.org/dtd/mybatis-3-mapper.dtd">
<!-- 命名空间,对sql进行分类化管理(sql隔离) -->
<mapper namespace="com.sw.mapper.UserMapper">
<!-- 在映射文件中配置sql语句 -->
<!-- 通过select执行查询,id用于标识映射文件中的sql(Statement-id)
将sql语句封装到mappedstatement中
#{}表示占位符
parameterType-指定输入参数的类型
#{id}-id表示输入的参数,参数名称就是id,如果输入参数是简单类型,#{}中的参数可以任意
resultType-指定sql输出结果所映射的java对象类型
-->
<!-- 通过id查询用户表的记录 -->
<select id="findUserById" parameterType="int" resultType="com.sw.po.User">
select *from user where id=#{id}
</select>
<!-- 根据用户名称模糊查询用户信息 -->
<!-- resultType-指定单条记录所映射的对象类型
${}拼接sql串,接收参数的内容,不加任何修饰,拼接在sql中(存在sql漏洞)
${}接收输入参数的内容,如果传入的类型是简单类型,${}中只能使用value
-->
<select id="findUserByName" parameterType="java.lang.String" resultType="com.sw.po.User">
SELECT *FROM USER WHERE username LIKE ‘%${value}%‘
</select>
<!-- 添加用户 -->
<!-- 指定输入参数类型是pojo(包括用户信息)
#{}中指定pojo(User)属性名,接收到pojo的属性值
Mybatis通过OGNL获取对象的属性值
-->
<insert id="insertUser" parameterType="com.sw.po.User">
<!-- 获取刚增加的记录主键
返回id到poio对象(User)
SELECT LAST_INSERT_ID():得到刚插入金进去记录的主键值,只适用于自增逐主键
keyProperty:将查询到的主键值设置到parameterType指定的对象User里面的用来做id的属性,这里是:id,
然后在执行插入的时候,从parameterType(也就是这里的User)的Id里面取出来,进行插入
order:指SELECT LAST_INSERT_ID()的执行顺序,相对于insert来说(before/after)
resultType:指定SELECT LAST_INSERT_ID()的结果类型
-->
<selectKey keyProperty="id" order="AFTER" resultType="java.lang.Integer">
SELECT LAST_INSERT_ID()
</selectKey>
INSERT INTO USER (id,username,birthday,sex,address) VALUES(#{id},#{username},#{birthday},#{sex},#{address})
<!-- 使用mysql的uuid生成主键返回
执行过程:
首先通过uuid得到主键,然后将主键设置到id属性中
其次在Inster执行的时候从User对象中取出id的属性值
-->
<!--
<selectKey keyProperty="id" order="BEFORE" resultType="java.lang.String">
SELECT UUID()
</selectKey>
INSERT INTO USER (id,username,birthday,sex,address) VALUES(#{id},#{username},#{birthday},#{sex},#{address})
-->
</insert>
<!-- 根据id删除用户 -->
<delete id="deleteUser" parameterType="java.lang.Integer">
DELETE FROM USER WHERE id=#{id}
</delete>
<!-- 根据id更新用户
传入用户id以及相关更新信息
#{id}:从输入的user对象中获取user的属性值
-->
<update id="updateUser" parameterType="com.sw.po.User">
UPDATE USER SET username=#{username},birthday=#{birthday},sex=#{sex},address=#{address} WHERE id=#{id}
</update>
</mapper>
2、Mapper.java-接口文件
Mapper接口定义有如下特点:
1、Mapper接口方法名与Mapper.xml(UserMapper.xml)中定义的statement的id相同
2、Mapper接口方法的输入参数类型和mapper.xml(User.xml)中定义的statement的parameterType的类型相同
3、 Mapper接口方法的输出参数类型和mapper.xml中定义的statement的resultType的类型相同
代码如下:
package com.sw.mapper;
import java.util.List;
import com.sw.po.User;
/*
*@Author swxctx
*@time 2016年12月1日
*@Explain:使用mapper接口(用户管理),相当于dao接口
*/
public interface UserMapper {
//根据id查询用户的信息
public User findUserById(int id)throws Exception;
//根据用户名查看用户列表
public List<User> findUserByName(String username)throws Exception;
//添加用户
public void insertUser(User user)throws Exception;
//删除用户
public void deleteUser(int id)throws Exception;
}
3、测试类
package com.sw.mapper.test;
import java.io.InputStream;
import java.util.Date;
import java.util.List;
import org.apache.ibatis.io.Resources;
import org.apache.ibatis.session.SqlSession;
import org.apache.ibatis.session.SqlSessionFactory;
import org.apache.ibatis.session.SqlSessionFactoryBuilder;
import org.junit.Before;
import org.junit.Test;
import com.sw.mapper.UserMapper;
import com.sw.po.User;
/*
*@Author swxctx
*@time 2016年12月1日
*@Explain:
*/
public class UserMapperTest {
private SqlSessionFactory sqlSessionFactory;
@Before
public void setUpBefore() throws Exception {
//执行其他方法前需要创建SqlSessionFactory
// mybatis配置文件
String resource = "SqlMapConfig.xml";
// 得到配置文件流
InputStream inputStream = Resources.getResourceAsStream(resource);
// 创建会话工厂,传入mybatis的配置文件信息
sqlSessionFactory = new SqlSessionFactoryBuilder()
.build(inputStream);
}
@Test
public void testFindUserById() throws Exception{
SqlSession sqlSession = sqlSessionFactory.openSession();
//创建UserMapper对象,mybatis自动生成mapper代理对象
UserMapper userMapper = sqlSession.getMapper(UserMapper.class);
//调用UserMapper方法
User user = userMapper.findUserById(27);
sqlSession.close();
System.out.println(user);
}
@Test
public void testFindUserByName() throws Exception{
SqlSession sqlSession = sqlSessionFactory.openSession();
//创建UserMapper对象,mybatis自动生成mapper代理对象
UserMapper userMapper = sqlSession.getMapper(UserMapper.class);
//调用UserMapper方法
List<User> user = userMapper.findUserByName("王");
sqlSession.close();
System.out.println(user);
}
@Test
public void testInsertUser()throws Exception{
SqlSession sqlSession = sqlSessionFactory.openSession();
//创建UserMapper
UserMapper userMapper = sqlSession.getMapper(UserMapper.class);
User user = new User();
user.setUsername("李小二");
user.setSex("1");
user.setBirthday(new Date());
user.setAddress("广州");
//调用方法
userMapper.insertUser(user);
//提交事务
sqlSession.commit();
//释放资源
sqlSession.close();
}
@Test
public void testDeleteUser() throws Exception{
SqlSession sqlSession = sqlSessionFactory.openSession();
//创建UserMapper对象,mybatis自动生成mapper代理对象
UserMapper userMapper = sqlSession.getMapper(UserMapper.class);
//调用UserMapper方法
userMapper.deleteUser(44);
sqlSession.commit();
sqlSession.close();
}
}
注:
selectOne和selectList
动态代理对象调用sqlSession.selectOne()和sqlSession.selectList()是根据mapper接口方法的返回值决定,如果返回list则调用selectList方法,如果返回单个对象则调用selectOne方法。
namespace
mybatis官方推荐使用mapper代理方法开发mapper接口,程序员不用编写mapper接口实现类,使用mapper代理方法时,输入参数可以使用pojo包装对象或map对象,保证dao的通用性。
以上是关于Mybatis之Mapper代理开发的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章