计算模型的GFLOPs和参数量 & 举例VGG16和DETR
Posted Flying Bulldog
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了计算模型的GFLOPs和参数量 & 举例VGG16和DETR相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
近期忙于写论文,分享一下论文中表格数据的计算方法。
目录
一、FLOPS、FLOPs和GFLOPs的概念
- FLOPS:注意S是大写,是 “每秒所执行的浮点运算次数”(floating-point operations per second)的缩写。它常被用来估算电脑的执行效能,尤其是在使用到大量浮点运算的科学计算领域中。正因为FLOPS字尾的那个S,代表秒,而不是复数,所以不能省略掉。
- FLOPs:注意s小写,是floating point operations的缩写(s表复数),意指浮点运算数,理解为计算量。可以用来衡量算法/模型的复杂度。
- GFLOPs:一个GFLOPs等于每秒十亿(=10^9)次的浮点运算。
二、计算VGG16的GFLOPs和参数量
from thop import profile
import torch
import torchvision.models as models
model = models.vgg16()
device = torch.device("cuda:0" if torch.cuda.is_available() else "cpu")
model.to(device)
input = torch.zeros((1, 3, 224, 224)).to(device)
flops, params = profile(model.to(device), inputs=(input,))
print("参数量:", params)
print("FLOPS:", flops)>>>output
参数量: 138357544.0
FLOPS: 15470314496.0
三、计算DETR的GFLOPs和参数量
- 首先,访问网址:GitHub - facebookresearch/detr: End-to-End Object Detection with Transformers
- 然后,下载DETR源码压缩包,调通源码。
- 最后,把下面的代码封装到py文件中,放到DETR源码的根目录即可。
import os
import time
from PIL import Image
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import torch
import torchvision.transforms as T
torch.set_grad_enabled(False)
from models import build_model
import argparse
from torch.nn.functional import dropout,linear,softmax
def get_args_parser():
parser = argparse.ArgumentParser('Set transformer detector', add_help=False)
parser.add_argument('--lr', default=1e-4, type=float)
parser.add_argument('--lr_backbone', default=1e-5, type=float)
parser.add_argument('--batch_size', default=1, type=int)
parser.add_argument('--weight_decay', default=1e-4, type=float)
# parser.add_argument('--epochs', default=300, type=int)
parser.add_argument('--epochs', default=100, type=int)
parser.add_argument('--lr_drop', default=200, type=int)
parser.add_argument('--clip_max_norm', default=0.1, type=float,
help='gradient clipping max norm')
# Model parameters
parser.add_argument('--frozen_weights', type=str, default=None,
help="Path to the pretrained model. If set, only the mask head will be trained")
# * Backbone
parser.add_argument('--backbone', default='resnet50', type=str,
help="Name of the convolutional backbone to use")
parser.add_argument('--dilation', action='store_true',
help="If true, we replace stride with dilation in the last convolutional block (DC5)")
parser.add_argument('--position_embedding', default='sine', type=str, choices=('sine', 'learned'),
help="Type of positional embedding to use on top of the image features")
# * Transformer
parser.add_argument('--enc_layers', default=6, type=int,
help="Number of encoding layers in the transformer")
parser.add_argument('--dec_layers', default=6, type=int,
help="Number of decoding layers in the transformer")
parser.add_argument('--dim_feedforward', default=2048, type=int,
help="Intermediate size of the feedforward layers in the transformer blocks")
parser.add_argument('--hidden_dim', default=256, type=int,
help="Size of the embeddings (dimension of the transformer)")
parser.add_argument('--dropout', default=0.1, type=float,
help="Dropout applied in the transformer")
parser.add_argument('--nheads', default=8, type=int,
help="Number of attention heads inside the transformer's attentions")
parser.add_argument('--num_queries', default=40, type=int,
help="Number of query slots") # 论文中对象查询为100
parser.add_argument('--pre_norm', action='store_true')
# * Segmentation
parser.add_argument('--masks', action='store_true',
help="Train segmentation head if the flag is provided")
# Loss
parser.add_argument('--no_aux_loss', dest='aux_loss', action='store_false',
help="Disables auxiliary decoding losses (loss at each layer)")
# * Matcher
parser.add_argument('--set_cost_class', default=1, type=float,
help="Class coefficient in the matching cost")
parser.add_argument('--set_cost_bbox', default=5, type=float,
help="L1 box coefficient in the matching cost")
parser.add_argument('--set_cost_giou', default=2, type=float,
help="giou box coefficient in the matching cost")
# * Loss coefficients
parser.add_argument('--mask_loss_coef', default=1, type=float)
parser.add_argument('--dice_loss_coef', default=1, type=float)
parser.add_argument('--bbox_loss_coef', default=5, type=float)
parser.add_argument('--giou_loss_coef', default=2, type=float)
parser.add_argument('--eos_coef', default=0.1, type=float,
help="Relative classification weight of the no-object class")
# dataset parameters
parser.add_argument('--dataset_file', default='coco')
parser.add_argument('--coco_path', default='', type=str)
parser.add_argument('--coco_panoptic_path', type=str)
parser.add_argument('--remove_difficult', action='store_true')
parser.add_argument('--output_dir', default='E:\\project_yd\\paper_sci_one_yd\\Transformer\\DETR\\detr\\\\runs\\\\train',
help='path where to save, empty for no saving')
parser.add_argument('--device', default='cuda',
help='device to use for training / testing')
parser.add_argument('--seed', default=42, type=int)
# ============================================================================= #
parser.add_argument('--resume', default='', help='resume from checkpoint')
# ============================================================================= #
parser.add_argument('--start_epoch', default=0, type=int, metavar='N',
help='start epoch')
parser.add_argument('--eval', action='store_true')
parser.add_argument('--num_workers', default=2, type=int)
# distributed training parameters
parser.add_argument('--world_size', default=1, type=int,
help='number of distributed processes')
parser.add_argument('--dist_url', default='env://', help='url used to set up distributed training')
return parser
if __name__ == '__main__':
parser = argparse.ArgumentParser('DETR training and evaluation script', parents=[get_args_parser()])
args = parser.parse_args()
# 建立模型
model, criterion, postprocessors = build_model(args)
model.to('cuda:0')
url = r'detr-r50-dc5-f0fb7ef5.pth'
state_dict = torch.load(url)
# print(state_dict)
# 加载模型参数,以字典的形式表示
model.load_state_dict(state_dict['model'])
model.eval() # 把字符串类型转换成字典类型
# ==================================================== #
from thop import profile
import torchsummary
device = torch.device("cuda:0" if torch.cuda.is_available() else "cpu")
model.to(device)
input = torch.zeros((1, 3, 800, 1422)).to(device)
flops, params = profile(model.to(device), inputs=(input,))
print("参数量:", params)
print("FLOPS:", flops)
# ==================================================== #>>> output
参数量: 36739785.0
FLOPS: 100937364480.0
四、整理数据表格
| Model | GFLOPs | Params |
|---|---|---|
| VGG16 | 15.47 | 13.84 M |
| DETR | 100.94 | 36.74 M |
>>> 如有疑问,欢迎评论区一起探讨!
神经网络模型复杂度分析
前言
现阶段的轻量级模型 MobileNet/ShuffleNet 系列、CSPNet、RepVGG、VoVNet 等都必须依赖于于具体的计算平台(如 CPU/GPU/ASIC 等)才能更完美的发挥网络架构。
1,计算平台主要有两个指标:算力 $\\pi$和 带宽 $\\beta$。
- 算力指的是计算平台每秒完成的最大浮点运算次数,单位是
FLOPS - 带宽指的是计算平台一次每秒最多能搬运多少数据(每秒能完成的内存交换量),单位是
Byte/s。
计算强度上限 $I_max$,上面两个指标相除得到计算平台的计算强度上限。它描述了单位内存交换最多用来进行多少次计算,单位是 FLOPs/Byte。
$$I_max = \\frac \\pi \\beta$$
2,和计算平台的两个指标相呼应,模型也有两个主要的反馈速度的间接指标:计算量 FLOPs 和访存量 MAC。
- 计算量(FLOPs):指的是输入单个样本(一张图像),模型完成一次前向传播所发生的浮点运算次数,即模型的时间复杂度,单位是
FLOPs。 - 访存量(MAC):指的是输入单个样本(一张图像),模型完成一次前向传播所发生的内存交换总量,即模型的空间复杂度,单位是
Byte,因为数据类型通常为float32,所以需要乘以4。CNN网络中每个网络层MAC的计算分为读输入feature map大小、权重大小(DDR读)和写输出feature map大小(DDR写)三部分。 - 模型的计算强度 $I$ :$I = \\fracFLOPsMAC$,即计算量除以访存量后的值,表示此模型在计算过程中,每
Byte内存交换到底用于进行多少次浮点运算。单位是FLOPs/Byte。可以看到,模计算强度越大,其内存使用效率越高。 - 模型的理论性能 $P$ :我们最关心的指标,即模型在计算平台上所能达到的每秒浮点运算次数(理论值)。单位是
FLOPS or FLOP/s。Roof-line Model给出的就是计算这个指标的方法。
3,Roofline 模型讲的是程序在计算平台的算力和带宽这两个指标限制下,所能达到的理论性能上界,而不是实际达到的性能,因为实际计算过程中还有除算力和带宽之外的其他重要因素,它们也会影响模型的实际性能,这是 Roofline Model 未考虑到的。例如矩阵乘法,会因为 cache 大小的限制、GEMM 实现的优劣等其他限制,导致你几乎无法达到 Roofline 模型所定义的边界(屋顶)。
所谓 “Roof-line”,指的就是由计算平台的算力和带宽上限这两个参数所决定的“屋顶”形态,如下图所示。
- 算力决定“屋顶”的高度(绿色线段)
- 带宽决定“房檐”的斜率(红色线段)

Roof-line 划分出的两个瓶颈区域定义如下:

个人感觉如果在给定计算平台上做模型部署工作,因为芯片的算力已定,工程师能做的主要工作应该是提升带宽。
一,模型计算量分析
为了分析模型计算复杂度,一个广泛采用的度量方式是模型推断时浮点运算的次数 (FLOPs),即模型理论计算量,但是,它是一个间接的度量,是对我们真正关心的直接度量比如速度或者时延的一种近似估计。
本文的卷积核尺寸假设为为一般情况,即正方形,长宽相等都为 K。
FLOPs:floating point operations 指的是浮点运算次数,理解为计算量,可以用来衡量算法/模型时间的复杂度。FLOPS:(全部大写),Floating-point Operations Per Second,每秒所执行的浮点运算次数,理解为计算速度,是一个衡量硬件性能/模型速度的指标。MACCs:multiply-accumulate operations,乘-加操作次数,MACCs大约是 FLOPs 的一半。将 $w[0]*x[0] + ...$ 视为一个乘法累加或1个MACC。
注意相同 FLOPs 的两个模型其运行速度是会相差很多的,因为影响模型运行速度的两个重要因素只通过 FLOPs 是考虑不到的,比如 MAC(Memory Access Cost)和网络并行度;二是具有相同 FLOPs 的模型在不同的平台上可能运行速度不一样。
卷积层 FLOPs 计算
- $FLOPs=(2\\times C_i\\times K^2-1)\\times H\\times W\\times C_o$(不考虑bias)
- $FLOPs=(2\\times C_i\\times K^2)\\times H\\times W\\times C_o$(考虑bias)
- $MACCs=(C_i\\times K^2)\\times H\\times W\\times C_o$(考虑bias)
$C_i$ 为输入特征图通道数,$K$ 为过卷积核尺寸,$H,W,C_o$ 为输出特征图的高,宽和通道数。二维卷积过程如下图所示:
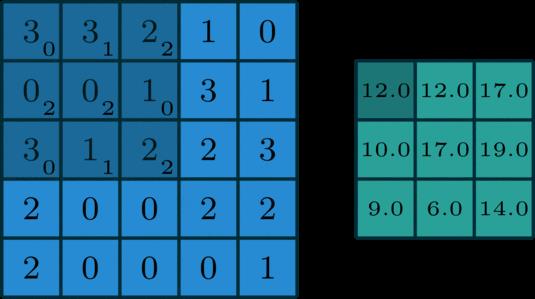
公式解释,参考这里,如下:
理解 FLOPs 的计算公式分两步。括号内是第一步,计算出output feature map 的一个 pixel,然后再乘以 $H\\times W\\times C_o$,从而拓展到整个 output feature map。括号内的部分又可以分为两步:$(2\\times C_i\\times K^2-1)=(C_i\\times K^2) + (C_i\\times K^2-1)$。第一项是乘法运算次数,第二项是加法运算次数,因为 $n$ 个数相加,要加 $n-1$次,所以不考虑 bias 的情况下,会有一个 -1,如果考虑 bias,刚好中和掉,括号内变为$(2\\times C_i\\times K^2)$。
所以卷积层的 $FLOPs=(2\\times C_i\\times K^2-1)\\times H\\times W\\times C_o$ ($C_i$ 为输入特征图通道数,$K$ 为过滤器尺寸,$H, W, C_o$为输出特征图的高,宽和通道数)。
全连接层的 FLOPs 计算
全连接层的 $FLOPs = (2I − 1)O$,$I$ 是输入层的维度,$O$ 是输出层的维度。
二,模型参数量分析
模型参数量的分析是为了了解内存占用情况,内存带宽其实比 FLOPs 更重要。目前的计算机结构下,单次内存访问比单次运算慢得多的多。对每一层网络,端侧设备需要:
- 从主内存中读取输入向量 /
feature map; - 从主内存中读取权重并计算点积;
- 将输出向量或
feature map写回主内存。
MAes:memory accesse,内存访问次数。
卷积层参数量
卷积层权重参数量 = $C_i\\times K^2\\times C_o + C_o$。
$C_i$ 为输入特征图通道数,$K$ 为过滤器(卷积核)尺寸,$C_o$ 为输出的特征图的 channel 数(也是 filter 的数量),算式第二项是偏置项的参数量 。(一般不写偏置项,偏置项对总参数量的数量级的影响可以忽略不记,这里为了准确起见,把偏置项的参数量也考虑进来。)
假设输入层矩阵维度是 96×96×3,第一层卷积层使用尺寸为 5×5、深度为 16 的过滤器(卷积核尺寸为 5×5、卷积核数量为 16),那么这层卷积层的参数个数为 5×5×3×16+16=1216个。
BN 层参数量
BN 层参数量 = $2\\times C_i$。
其中 $C_i$ 为输入的 channel 数(BN层有两个需要学习的参数,平移因子和缩放因子)
全连接层参数量
全连接层参数量 = $T_i\\times T_o + T_O$。
$T_i$ 为输入向量的长度, $T_o$ 为输出向量的长度,公式的第二项为偏置项参数量。(目前全连接层已经逐渐被 Global Average Pooling 层取代了。) 注意,全连接层的权重参数量(内存占用)远远大于卷积层。
三,模型内存访问代价计算
MAC(memory access cost) 内存访问代价也叫内存使用量,指的是输入单个样本(一张图像),模型/卷积层完成一次前向传播所发生的内存交换总量,即模型的空间复杂度,单位是 Byte。
CNN 网络中每个网络层 MAC 的计算分为读输入 feature map 大小(DDR 读)、权重大小(DDR 读)和写输出 feature map 大小(DDR 写)三部分。
卷积层 MAC 计算
以卷积层为例计算 MAC,可假设某个卷积层输入 feature map 大小是 (Cin, Hin, Win),输出 feature map 大小是 (Hout, Wout, Cout),卷积核是 (Cout, Cin, K, K),理论 MAC(理论 MAC 一般小于 实际 MAC)计算公式如下:
# 端侧推理IN8量化后模型,单位一般为 1 byte
input = Hin x Win x Cin # 输入 feature map 大小
output = Hout x Wout x Cout # 输出 feature map 大小
weights = K x K x Cin x Cout + bias # bias 是卷积层偏置
ddr_read = input + weights
ddr_write = output
MAC = ddr_read + ddr_write
四,一些概念
双精度、单精度和半精度
CPU/GPU 的浮点计算能力得区分不同精度的浮点数,分为双精度 FP64、单精度 FP32 和半精度 FP16。因为采用不同位数的浮点数的表达精度不一样,所以造成的计算误差也不一样,对于需要处理的数字范围大而且需要精确计算的科学计算来说,就要求采用双精度浮点数,而对于常见的多媒体和图形处理计算,32 位的单精度浮点计算已经足够了,对于要求精度更低的机器学习等一些应用来说,半精度 16 位浮点数就可以甚至 8 位浮点数就已经够用了。
对于浮点计算来说, CPU 可以同时支持不同精度的浮点运算,但在 GPU 里针对单精度和双精度就需要各自独立的计算单元。
浮点计算能力
FLOPS:每秒浮点运算次数,每秒所执行的浮点运算次数,浮点运算包括了所有涉及小数的运算,比整数运算更费时间。下面几个是表示浮点运算能力的单位。我们一般常用 TFLOPS(Tops) 作为衡量 NPU/GPU 性能/算力的指标,比如海思 3519AV100 芯片的算力为 1.7Tops 神经网络运算性能。
MFLOPS(megaFLOPS):等于每秒一佰万(=10^6)次的浮点运算。GFLOPS(gigaFLOPS):等于每秒拾亿(=10^9)次的浮点运算。TFLOPS(teraFLOPS):等于每秒万亿(=10^12)次的浮点运算。PFLOPS(petaFLOPS):等于每秒千万亿(=10^15)次的浮点运算。EFLOPS(exaFLOPS):等于每秒百亿亿(=10^18)次的浮点运算。
硬件利用率(Utilization)
在这种情况下,利用率(Utilization)是可以有效地用于实际工作负载的芯片的原始计算能力的百分比。深度学习和神经网络使用相对数量较少的计算原语(computational primitives),而这些数量很少的计算原语却占用了大部分计算时间。矩阵乘法(MM)和转置是基本操作。MM 由乘法累加(MAC)操作组成。OPs/s(每秒完成操作的数量)指标通过每秒可以完成多少个 MAC(每次乘法和累加各被认为是 1 个 operation,因此 MAC 实际上是 2 个 OP)得到。所以我们可以将利用率定义为实际使用的运算能力和原始运算能力的比值,计算公式如下。
$$ mac\\ utilization = \\frac used\\ Ops/sraw\\ OPs/s = \\frac FLOPs/time(s)Raw_FLOPs(Raw_FLOPs = 1.7T\\ at\\ 3519)$$
五,参考资料
- PRUNING CONVOLUTIONAL NEURAL NETWORKS FOR RESOURCE EFFICIENT INFERENCE
- 神经网络参数量的计算:以UNet为例
- How fast is my model?
- MobileNetV1 & MobileNetV2 简介
- 双精度,单精度和半精度
- AI硬件的Computational Capacity详解
- Roofline Model与深度学习模型的性能分析
以上是关于计算模型的GFLOPs和参数量 & 举例VGG16和DETR的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章