SpringMVC执行流程
Posted 一个风轻云淡
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了SpringMVC执行流程相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
SpringMVC常用组件
DispatcherServlet:前端控制器,不需要工程师开发,由框架提供
作用:统一处理请求和响应,整个流程控制的中心,由它调用其它组件处理用户的请求
HandlerMapping:处理器映射器,不需要工程师开发,由框架提供
作用:根据请求的url、method等信息查找Handler,即控制器方法
Handler:处理器,需要工程师开发
作用:在DispatcherServlet的控制下Handler对具体的用户请求进行处理
HandlerAdapter:处理器适配器,不需要工程师开发,由框架提供
作用:通过HandlerAdapter对处理器(控制器方法)进行执行
ViewResolver:视图解析器,不需要工程师开发,由框架提供
作用:进行视图解析,得到相应的视图,例如:ThymeleafView、InternalResourceView、
RedirectView
View:视图
作用:将模型数据通过页面展示给用户
DispatcherServlet初始化过程
DispatcherServlet 本质上是一个 Servlet,所以天然的遵循 Servlet 的生命周期。所以宏观上是 Servlet生命周期来进行调度。
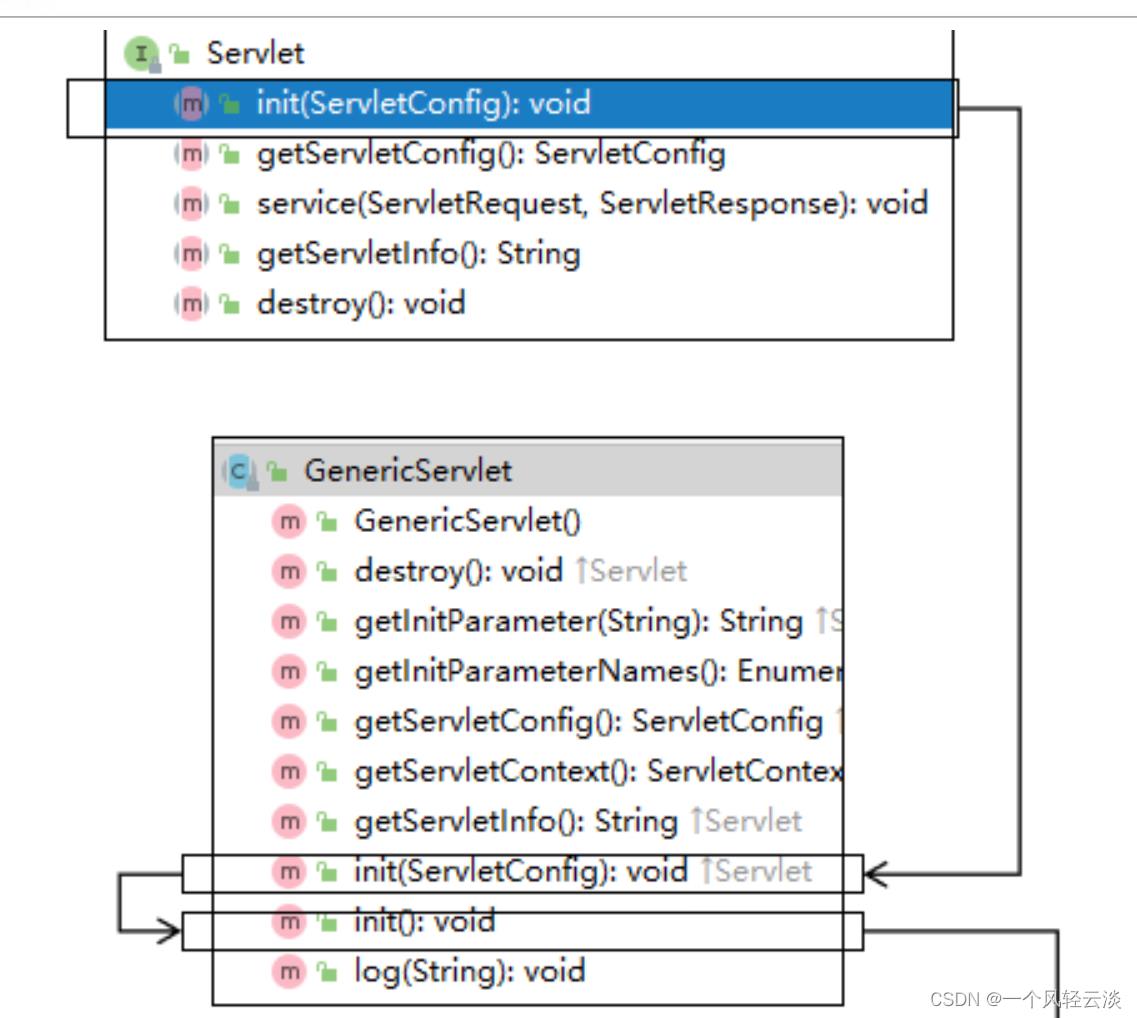
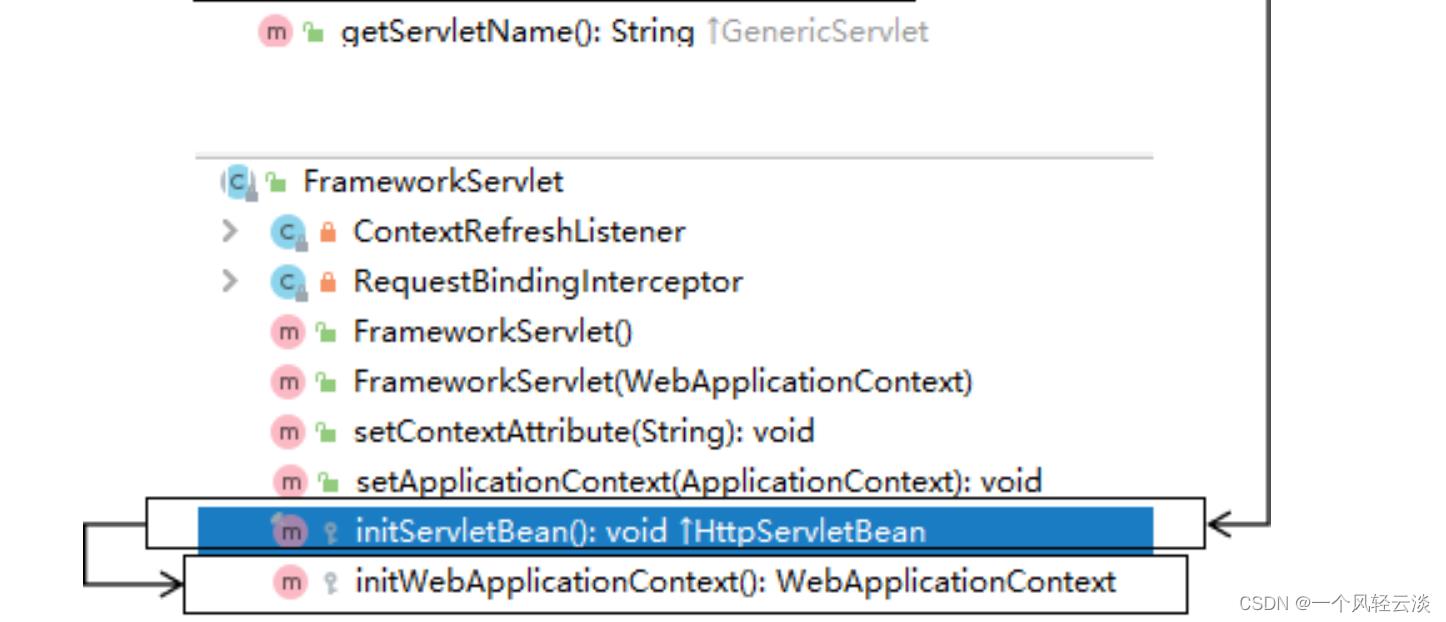
初始化WebApplicationContext
所在类:org.springframework.web.servlet.FrameworkServle
protected WebApplicationContext initWebApplicationContext()
WebApplicationContext rootContext =
WebApplicationContextUtils.getWebApplicationContext(getServletContext());
WebApplicationContext wac = null;
if (this.webApplicationContext != null)
// A context instance was injected at construction time -> use it
wac = this.webApplicationContext;
if (wac instanceof ConfigurableWebApplicationContext)
ConfigurableWebApplicationContext cwac =
(ConfigurableWebApplicationContext) wac;
if (!cwac.isActive())
// The context has not yet been refreshed -> provide services
such as
// setting the parent context, setting the application context
id, etc
if (cwac.getParent() == null)
// The context instance was injected without an explicit
parent -> set
// the root application context (if any; may be null) as the
parent
cwac.setParent(rootContext);
configureAndRefreshWebApplicationContext(cwac);
if (wac == null)
// No context instance was injected at construction time -> see if one
// has been registered in the servlet context. If one exists, it is
assumed
// that the parent context (if any) has already been set and that the
// user has performed any initialization such as setting the context id
wac = findWebApplicationContext();
if (wac == null)
// No context instance is defined for this servlet -> create a local one
// 创建WebApplicationContext
wac = createWebApplicationContext(rootContext);
if (!this.refreshEventReceived)
// Either the context is not a ConfigurableApplicationContext with
refresh
// support or the context injected at construction time had already been
// refreshed -> trigger initial onRefresh manually here.
synchronized (this.onRefreshMonitor)
// 刷新WebApplicationContext
onRefresh(wac);
if (this.publishContext)
// Publish the context as a servlet context attribute.
// 将IOC容器在应用域共享
String attrName = getServletContextAttributeName();
getServletContext().setAttribute(attrName, wac);
return wac;
②创建WebApplicationContext
所在类:org.springframework.web.servlet.FrameworkServlet
protected WebApplicationContext createWebApplicationContext(@Nullable
ApplicationContext parent)
Class<?> contextClass = getContextClass();
if (!ConfigurableWebApplicationContext.class.isAssignableFrom(contextClass))
throw new ApplicationContextException(
"Fatal initialization error in servlet with name '" +
getServletName() +
"': custom WebApplicationContext class [" + contextClass.getName() +
"] is not of type ConfigurableWebApplicationContext");
// 通过反射创建 IOC 容器对象
ConfigurableWebApplicationContext wac =
(ConfigurableWebApplicationContext)
BeanUtils.instantiateClass(contextClass);
wac.setEnvironment(getEnvironment());
// 设置父容器
wac.setParent(parent);
String configLocation = getContextConfigLocation();
if (configLocation != null)
wac.setConfigLocation(configLocation);
configureAndRefreshWebApplicationContext(wac);
return wac;
③DispatcherServlet初始化策略
FrameworkServlet创建WebApplicationContext后,刷新容器,调用onRefresh(wac),此方法在DispatcherServlet中进行了重写,调用了initStrategies(context)方法,初始化策略,即初始化
DispatcherServlet的各个组件
所在类:org.springframework.web.servlet.DispatcherServlet
protected void initStrategies(ApplicationContext context)
initMultipartResolver(context);
initLocaleResolver(context);
initThemeResolver(context);
initHandlerMappings(context);
initHandlerAdapters(context);
initHandlerExceptionResolvers(context);
initRequestToViewNameTranslator(context);
initViewResolvers(context);
initFlashMapManager(context);
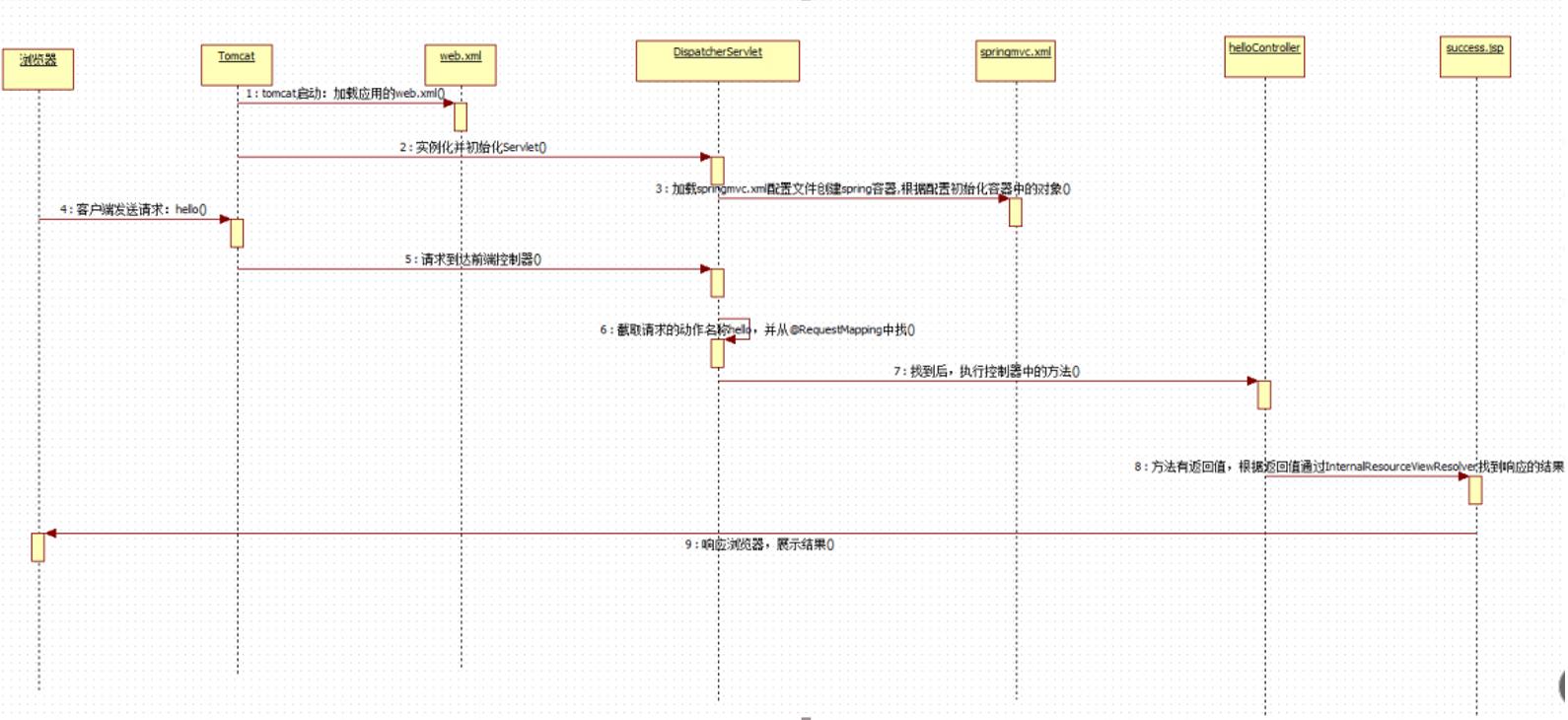
SpringMVC的执行流程
用户向服务器发送请求,请求被SpringMVC 前端控制器 DispatcherServlet捕获。
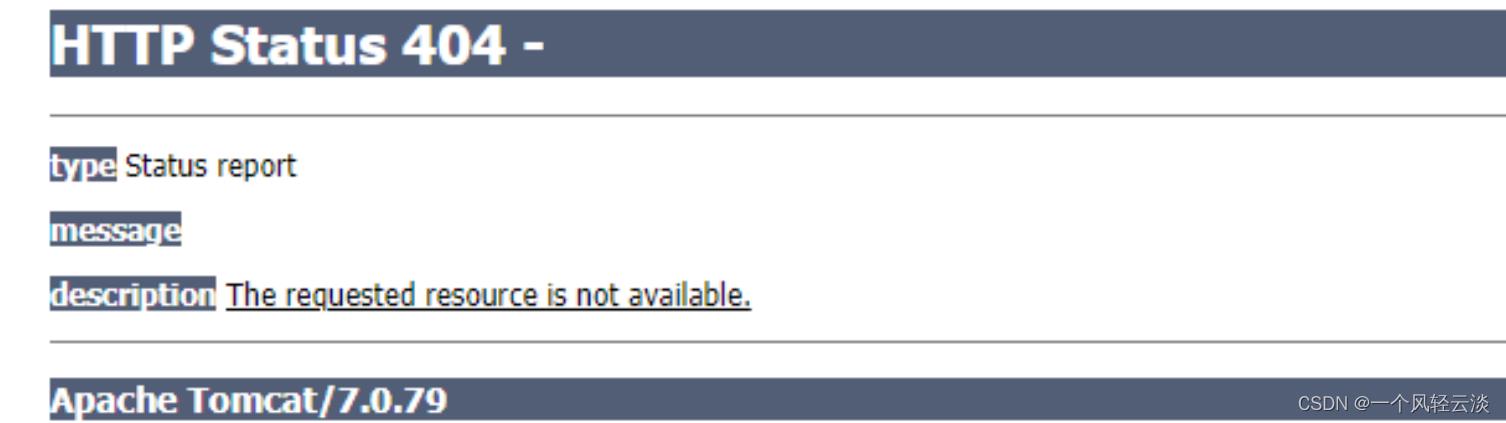
2) DispatcherServlet对请求URL进行解析,得到请求资源标识符(URI),判断请求URI对应的映射:
a) 不存在
i. 再判断是否配置了mvc:default-servlet-handler
ii. 如果没配置,则控制台报映射查找不到,客户端展示404错误
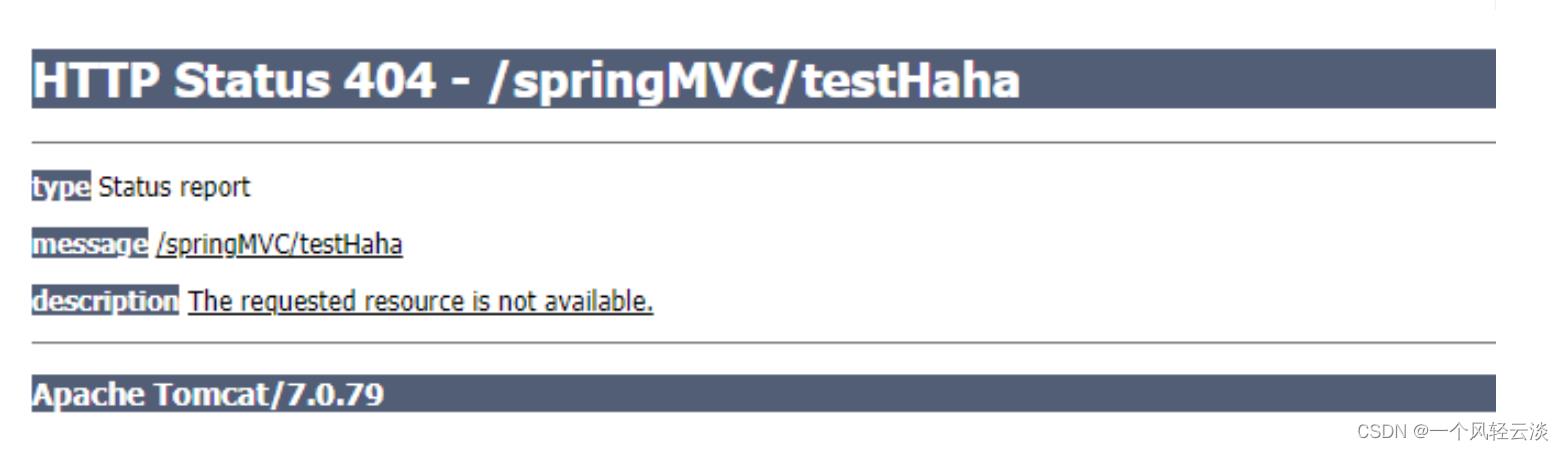
iii. 如果有配置,则访问目标资源(一般为静态资源,如:JS,CSS,html),找不到客户端也会展示404错误
b) 存在则执行下面的流程
3) 根据该URI,调用HandlerMapping获得该Handler配置的所有相关的对象(包括Handler对象以及Handler对象对应的拦截器),最后以HandlerExecutionChain执行链对象的形式返回。
4) DispatcherServlet 根据获得的Handler,选择一个合适的HandlerAdapter。
5) 如果成功获得HandlerAdapter,此时将开始执行拦截器的preHandler(...)方法【正向】
6) 提取Request中的模型数据,填充Handler入参,开始执行Handler(Controller)方法,处理请求。在填充Handler的入参过程中,根据你的配置,Spring将帮你做一些额外的工作:
a) HttpMessageConveter: 将请求消息(如Json、xml等数据)转换成一个对象,将对象转换为指定的响应信息
b) 数据转换:对请求消息进行数据转换。如String转换成Integer、Double等
c) 数据格式化:对请求消息进行数据格式化。 如将字符串转换成格式化数字或格式化日期等
d) 数据验证: 验证数据的有效性(长度、格式等),验证结果存储到BindingResult或Error中
7) Handler执行完成后,向DispatcherServlet 返回一个ModelAndView对象。
8) 此时将开始执行拦截器的postHandle(...)方法【逆向】。
9) 根据返回的ModelAndView(此时会判断是否存在异常:如果存在异常,则执行
HandlerExceptionResolver进行异常处理)选择一个适合的ViewResolver进行视图解析,根据Model
和View,来渲染视图。
10) 渲染视图完毕执行拦截器的afterCompletion(...)方法【逆向】。
11) 将渲染结果返回给客户端。
SpringMVC:SpringMVC执行流程

文章目录
三、Handler:处理器 (自己定义的Controller处理单元)
SpringMVC执行流程
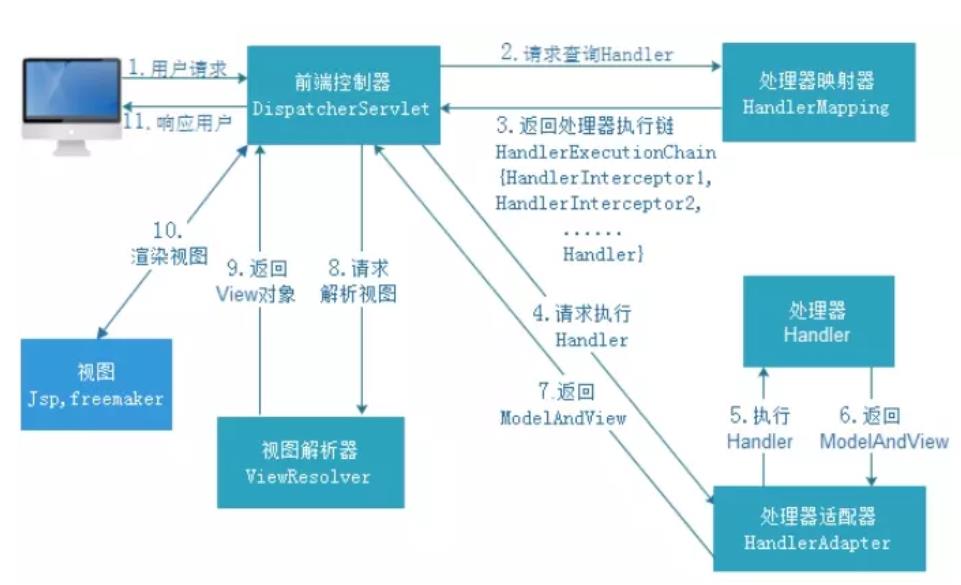
一、DispatcherServlet:前端控制器
用户请求到达前端控制器,它就相当于 mvc 模式中的 c,dispatcherServlet 是整个流程控制的中心,由 它调用其它组件处理用户的请求,dispatcherServlet 的存在降低了组件之间的耦合性。
二、HandlerMapping:处理器映射器
HandlerMapping 负责根据用户请求找到 Handler 即处理器,SpringMVC 提供了不同的映射器实现不同的 映射方式,例如:配置文件方式,实现接口方式,注解方式等。
三、Handler:处理器 (自己定义的Controller处理单元)
它就是我们开发中要编写的具体业务控制器。由 DispatcherServlet 把用户请求转发到 Handler。由 Handler 对具体的用户请求进行处理。
四、HandlAdapter:处理器适配器
通过 HandlerAdapter 对处理器进行执行,这是适配器模式的应用,通过扩展适配器可以对更多类型的处理器进行执行

五、View Resolver:视图解析器
View Resolver 负责将处理结果生成 View 视图,View Resolver 首先根据逻辑视图名解析成物理视图名 即具体的页面地址,再生成 View 视图对象,最后对 View 进行渲染将处理结果通过页面展示给用户。
六、View:视图
SpringMVC 框架提供了很多的 View 视图类型的支持,包括:jstlView、freemarkerView、pdfView等。我们最常用的视图就是 jsp。 一般情况下需要通过页面标签或页面模版技术将模型数据通过页面展示给用户,需要由程序员根据业务需求开 发具体的页面。
七、<mvc:annotation-driven>说明
在 SpringMVC 的各个组件中,处理器映射器、处理器适配器、视图解析器称为 SpringMVC 的三大组件。
使 用 <mvc:annotation-driven> 自动加载 RequestMappingHandlerMapping (处理映射器) 和 RequestMappingHandlerAdapter ( 处 理 适 配 器 ) , 可 用 在 SpringMVC.xml 配 置 文 件 中 使 用 <mvc:annotation-driven>替代注解处理器和适配器的配置。
protected void doDispatch(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws Exception
HttpServletRequest processedRequest = request;
HandlerExecutionChain mappedHandler = null;
boolean multipartRequestParsed = false;
WebAsyncManager asyncManager = WebAsyncUtils.getAsyncManager(request);
try
try
ModelAndView mv = null;
Object dispatchException = null;
try
processedRequest = this.checkMultipart(request);
multipartRequestParsed = processedRequest != request;
mappedHandler = this.getHandler(processedRequest);
if (mappedHandler == null)
this.noHandlerFound(processedRequest, response);
return;
HandlerAdapter ha = this.getHandlerAdapter(mappedHandler.getHandler());
String method = request.getMethod();
boolean isGet = "GET".equals(method);
if (isGet || "HEAD".equals(method))
long lastModified = ha.getLastModified(request, mappedHandler.getHandler());
if ((new ServletWebRequest(request, response)).checkNotModified(lastModified) && isGet)
return;
if (!mappedHandler.applyPreHandle(processedRequest, response))
return;
mv = ha.handle(processedRequest, response, mappedHandler.getHandler());
if (asyncManager.isConcurrentHandlingStarted())
return;
this.applyDefaultViewName(processedRequest, mv);
mappedHandler.applyPostHandle(processedRequest, response, mv);
catch (Exception var20)
dispatchException = var20;
catch (Throwable var21)
dispatchException = new NestedServletException("Handler dispatch failed", var21);
this.processDispatchResult(processedRequest, response, mappedHandler, mv, (Exception)dispatchException);
catch (Exception var22)
this.triggerAfterCompletion(processedRequest, response, mappedHandler, var22);
catch (Throwable var23)
this.triggerAfterCompletion(processedRequest, response, mappedHandler, new NestedServletException("Handler processing failed", var23));
finally
if (asyncManager.isConcurrentHandlingStarted())
if (mappedHandler != null)
mappedHandler.applyAfterConcurrentHandlingStarted(processedRequest, response);
else if (multipartRequestParsed)
this.cleanupMultipart(processedRequest);
private void applyDefaultViewName(HttpServletRequest request, @Nullable ModelAndView mv) throws Exception
if (mv != null && !mv.hasView())
String defaultViewName = this.getDefaultViewName(request);
if (defaultViewName != null)
mv.setViewName(defaultViewName);
HandlerMapping的实现类的作用
实现类RequestMappingHandlerMapping,它会处理@RequestMapping 注解,并将其注册到请求映射表中。
HandlerAdapter的实现类的作用
实现类RequestMappingHandlerAdapter,则是处理请求的适配器,确定调用哪个类的哪个方法,并且构造方法参数,返回值。
当配置了mvc:annotation-driven/后,Spring就知道了我们启用注解驱动。然后Spring通过context:component-scan/标签的配置,会自动为我们将扫描到的@Component,@Controller,@Service,@Repository等注解标记的组件注册到工厂中,来处理我们的请求,这个时候接收返回json数据、参数验证、统一异常等功能。
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns:p="http://www.springframework.org/schema/p"
xmlns:c="http://www.springframework.org/schema/c"
xmlns:util="http://www.springframework.org/schema/util"
xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context"
xmlns:aop="http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop"
xmlns:tx="http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx"
xmlns:mvc="http://www.springframework.org/schema/mvc"
xsi:schemaLocation="
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/util
http://www.springframework.org/schema/util/spring-util.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop
http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop/spring-aop.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx
http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx/spring-tx.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/mvc
http://www.springframework.org/schema/mvc/spring-mvc.xsd
">
<!--配置spring包扫描-->
<context:component-scan base-package="com.lanson"></context:component-scan>
<!--配置处理器映射器-->
<!-- <bean class="org.springframework.web.servlet.mvc.method.annotation.RequestMappingHandlerMapping"></bean>-->
<!--配置处理器适配器-->
<!-- <bean class="org.springframework.web.servlet.mvc.method.annotation.RequestMappingHandlerAdapter"></bean>-->
<!--一个注解替换上面的两个配置-->
<!--<mvc:annotation-driven>会自动注册RequestMappingHandlerMapping与RequestMappingHandlerAdapter两个Bean-->
<mvc:annotation-driven/>
<!--配置视图解析器-->
<bean class="org.springframework.web.servlet.view.InternalResourceViewResolver">
<property name="prefix" value="/WEB-INF/view/" ></property>
<property name="suffix" value=".jsp" ></property>
</bean>
<!--静态资源放行-->
<!--<mvc:resources mapping="/js/**" location="/js/"></mvc:resources>
<mvc:resources mapping="/img/**" location="/img/"></mvc:resources>
<mvc:resources mapping="/css/**" location="/css/"></mvc:resources>-->
<mvc:resources mapping="/static/**" location="/static/"></mvc:resources>
</beans>
- 📢博客主页:https://lansonli.blog.csdn.net
- 📢欢迎点赞 👍 收藏 ⭐留言 📝 如有错误敬请指正!
- 📢本文由 Lansonli 原创,首发于 CSDN博客🙉
- 📢停下休息的时候不要忘了别人还在奔跑,希望大家抓紧时间学习,全力奔赴更美好的生活✨
以上是关于SpringMVC执行流程的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章