mybatis注解
Posted brevity_souls
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了mybatis注解相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
mybatis常用注解有:@Select、@SelectKey、@Insert、@Update、@Delete。以及结果集三大注解:@Result、@Results、@ResultMap;除此之外还有:@One、@Many等,接下来一一介绍这些注解。
@Select注解:
@Select("select id,username,phone from db_user where id = #key")User selectUserByPrimaryKey(Long key);
查询相关的SQL写在@Select注解中,花括号里面的内容可以是字符串也可以是字符串数组。
@SelectKey:
@SelectKey(statement = "select last_insert_id()" ,keyProperty = "id",keyColumn = "id",resultType = int.class,before = false)public int insert(User user);
@Insert:
@Insert("insert into db_user(username, password, nickname, phone, email) values (#username, #password, #nickname, #phone, #email)")@Options(useGeneratedKeys = true, keyProperty = "id")int insertUser(User user);
添加相关的SQL写在@Insert注解中,花括号里面的内容可以是字符串也可以是字符串数组。当添加操作需要返回自增主键时可以使用@Options注释。添加属性useGeneratedKeys = true和keyProperty = "id"即可在数据添加后获取添加数据的ID值。
@Update:
@Update("update db_user set name = #name where id = #id")int updateUserByPrimaryKey(User user);
修改相关的SQL写在@Update注解中,花括号里面的内容可以是字符串也可以是字符串数组。
@Delete:
@Delete("delete from db_user where id = #key")int deleteUserByPrimaryKey(Long key);
删除相关的SQL写在@Delete注解中,花括号里面的内容可以是字符串也可以是字符串数组。
结果集注解:
@Select("select id, name, class_id from student")@Results(id="studentMap", value=@Result(column="id", property="id", jdbcType=JdbcType.INTEGER, id=true),@Result(column="name", property="name", jdbcType=JdbcType.VARCHAR),@Result(column="class_id ", property="classId", jdbcType=JdbcType.INTEGER))List<Student> selectAll();引用结果集:@Select("select id, name, class_id from student where id = #id")@ResultMap(value="studentMap")Student selectById(integer id);
@Results和@Result注解是结合起来用的,@Result注解包含在@Results注解的value属性中。
@Results 注解
@Results 注解有两个属性,分别是id和value。其中id属性对应的是XML配置中resultMap标签的id属性,这样只要在接口中写一次就可以公用一个resultMap了。而value属性对应的是XML配置中resultMap标签下的<id>和<result>标签,<id>标签用id=true属性来确定。
@Result 注解
@Result 注解常用属性id、column和property。id属性是用来确定是否是id的,布尔类型。column属性是对应数据库字段的,字符串类型。property属性是对应JavaBean对象属性的,字符串类型。
@ResultMap 注解就一个作用,使用已经定义好的@Results或XML配置里已经写好的resultMap。里面的value属性即是@Results的id属性值或XML里resultMap的id属性值。
@One,用于一对一的关系映射:
@Select("select * from student")@Results(@Result(id=true,property="id",column="id"),@Result(property="name",column="name"),@Result(property="age",column="age"),@Result(property="address",column="address_id",one=@One(select="com.breivty.mappers.AddressMapper.getAddress")))public List<Student> getAllStudents();
@Many,用于一对多的关系映射:
@Select("select * from t_class where id=#id")@Results(@Result(id=true,column="id",property="id"),@Result(column="class_name",property="className"),@Result(property="students", column="id", many=@Many(select="com.brevity.mappers.StudentMapper.getStudentsByClassId")))public Class getClass(int id);
上面这些注解分别对应着xml文件的的标签,具体更复杂的写法就可以结合xml文件中的写法了,不过,当SQL有变化时都需要重新编译代码,一般情况下不建议使用注解方式,复杂的SQL还是建议在xml文件中编写,可读性比较强,也便于维护,唯一不足的就是需要切换文件比较麻烦哈。
MyBatis| MyBatis的注解式开发
目录
一:MyBatis的注解式开发
MyBatis中也提供了注解式开发⽅式,采⽤注解可以减少Sql映射⽂件的配置。 当然,使⽤注解式开发的话,sql语句是写在java程序中的,这种⽅式也会给sql语句的维护带来成本。
官⽅是这么说的:

使⽤注解编写复杂的SQL是这样的:
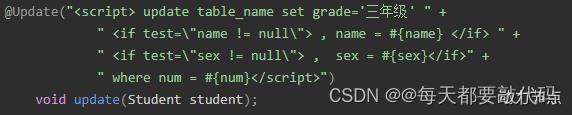
原则:简单sql可以注解,复杂sql使⽤xml!使用注解式开发以后三兄弟之一的SqlMapper.xml文件就不需要了!
1. @Insert注解
二兄弟之一CarMapper接口,用来编写方法
使用@Insert的注解方式,在注解上就可以写上SQL语句,对于SQL语句当中的变量就是pojo类Car对应的变量名
package com.bjpowernode.mybatis.mapper;
import com.bjpowernode.mybatis.pojo.Car;
import org.apache.ibatis.annotations.Insert;
public interface CarMapper
// 使用注解式开发,插入数据
@Insert("insert into t_car values(null,#carNum,#brand,#guidePrice,#produceTime,#carType)")
int insert(Car car);
二兄弟之二CarMapperTest,用来测试
package com.bjpowernode.mybatis.test;
import com.bjpowernode.mybatis.mapper.CarMapper;
import com.bjpowernode.mybatis.pojo.Car;
import com.bjpowernode.mybatis.utils.SqlSessionUtil;
import org.apache.ibatis.session.SqlSession;
import org.junit.Test;
public class CarMapperTest
@Test
public void testInsert()
SqlSession sqlSession = SqlSessionUtil.openSession();
CarMapper mapper = sqlSession.getMapper(CarMapper.class);
// 创建Car对象
Car car = new Car(null, "666", "丰田霸道", 32.0, "2023-1-9", "燃油车");
int count = mapper.insert(car);
System.out.println(count);
sqlSession.commit();
sqlSession.close();
执行结果:

2. @Delete注解
二兄弟之一CarMapper接口,用来编写方法
package com.bjpowernode.mybatis.mapper;
import com.bjpowernode.mybatis.pojo.Car;
import org.apache.ibatis.annotations.Insert;
public interface CarMapper
// 使用注解式开发,删除数据
@Delete("delete from t_car where id = #id")
int deleteById(Long id);
二兄弟之二CarMapperTest,用来测试
package com.bjpowernode.mybatis.test;
import com.bjpowernode.mybatis.mapper.CarMapper;
import com.bjpowernode.mybatis.pojo.Car;
import com.bjpowernode.mybatis.utils.SqlSessionUtil;
import org.apache.ibatis.session.SqlSession;
import org.junit.Test;
public class CarMapperTest
@Test
public void testDeleteById()
SqlSession sqlSession = SqlSessionUtil.openSession();
CarMapper mapper = sqlSession.getMapper(CarMapper.class);
int count = mapper.deleteById(40L);
System.out.println(count);
sqlSession.commit();
sqlSession.close();
执行结果:
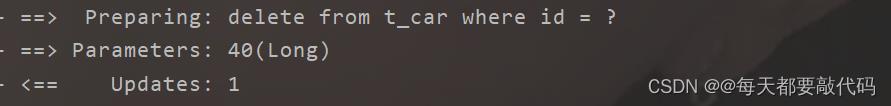
3. @Update注解
二兄弟之一CarMapper接口,用来编写方法
package com.bjpowernode.mybatis.mapper;
import com.bjpowernode.mybatis.pojo.Car;
import org.apache.ibatis.annotations.Insert;
public interface CarMapper
// 使用注解式开发,更新数据
@Update("update t_car set car_num=#carNum,brand=#brand,guide_price=#guidePrice,produce_time=#produceTime,car_type=#carType where id = #id")
int update(Car car);
二兄弟之二CarMapperTest,用来测试
package com.bjpowernode.mybatis.test;
import com.bjpowernode.mybatis.mapper.CarMapper;
import com.bjpowernode.mybatis.pojo.Car;
import com.bjpowernode.mybatis.utils.SqlSessionUtil;
import org.apache.ibatis.session.SqlSession;
import org.junit.Test;
public class CarMapperTest
@Test
public void testUpdate()
SqlSession sqlSession = SqlSessionUtil.openSession();
CarMapper mapper = sqlSession.getMapper(CarMapper.class);
// 创建Car对象,根据id进行更新
Car car = new Car(34L, "666", "丰田霸道", 32.0, "2023-1-9", "燃油车");
int count = mapper.update(car);
System.out.println(count);
sqlSession.commit();
sqlSession.close();
执行结果:

4. @Select注解
二兄弟之一CarMapper接口,用来编写方法
package com.bjpowernode.mybatis.mapper;
import com.bjpowernode.mybatis.pojo.Car;
import org.apache.ibatis.annotations.Insert;
public interface CarMapper
// 使用注解式开发,查询数据
@Select("select * from t_car where id = #id")
Car selectById(Long id);
二兄弟之二CarMapperTest,用来测试
package com.bjpowernode.mybatis.test;
import com.bjpowernode.mybatis.mapper.CarMapper;
import com.bjpowernode.mybatis.pojo.Car;
import com.bjpowernode.mybatis.utils.SqlSessionUtil;
import org.apache.ibatis.session.SqlSession;
import org.junit.Test;
public class CarMapperTest
@Test
public void testSelectById()
SqlSession sqlSession = SqlSessionUtil.openSession();
CarMapper mapper = sqlSession.getMapper(CarMapper.class);
Car car = mapper.selectById(41L);
System.out.println(car);
sqlSession.close();
执行结果:

5. @Results注解
我们知道数据库表中的字段和pojo类的属性名有的是不一样的,我们之所以能够完整的查出数据,是因为在核心配置文件mybatis-config.xml当中配置了:启用驼峰命名⾃动映射
<!--启⽤驼峰命名⾃动映射-->
<settings>
<setting name="mapUnderscoreToCamelCase" value="true"/>
</settings>如果我们不启用,不对应的字段就是null,查询的数据如下:

那还有什么办法呢?还可以使用@Results注解!
注:从这里也能看出,使用注解的方式开发,对于简单点的SQL还行,对于稍微复杂的查询语句就太麻烦了!
package com.bjpowernode.mybatis.mapper;
import com.bjpowernode.mybatis.pojo.Car;
import org.apache.ibatis.annotations.*;
public interface CarMapper
// 使用注解式开发,查询数据
@Select("select * from t_car where id = #id")
@Results(
@Result(property = "id",column = "id"),
@Result(property = "carNum",column = "car_num"),
@Result(property = "brand",column = "brand"),
@Result(property = "guidePrice",column = "guide_price"),
@Result(property = "produceTime",column = "produce_time"),
@Result(property = "carType",column = "car_type"),
)
Car selectById(Long id);
这样计算我们不启用驼峰命名⾃动映射,也能正常查询数据

结语:直到今天MyBatis的学习就完美撒花了,接下来就开始Spring的学习,敬请期待!
以上是关于mybatis注解的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章