“蔚来杯“2022牛客暑期多校训练营2,签到题GJK
Posted 小哈里
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了“蔚来杯“2022牛客暑期多校训练营2,签到题GJK相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
题号 标题 已通过代码 通过率 团队的状态
A Falfa with Polygon 点击查看 56/445
B light 点击查看 50/326
C Link with Nim Game 点击查看 192/1035
D Link with Game Glitch 点击查看 831/6211
E Falfa with Substring 点击查看 264/3287
F NIO with String Game 点击查看 52/412
G Link with Monotonic Subsequence 点击查看 1667/7564
H Take the Elevator 点击查看 290/769
I let fat tension 点击查看 204/454
J Link with Arithmetic Progression 点击查看 1407/7990
K Link with Bracket Sequence I 点击查看 996/3057
L Link with Level Editor I 点击查看 564/2616
文章目录
G.Link with Monotonic Subsequence
题意:
- 官方
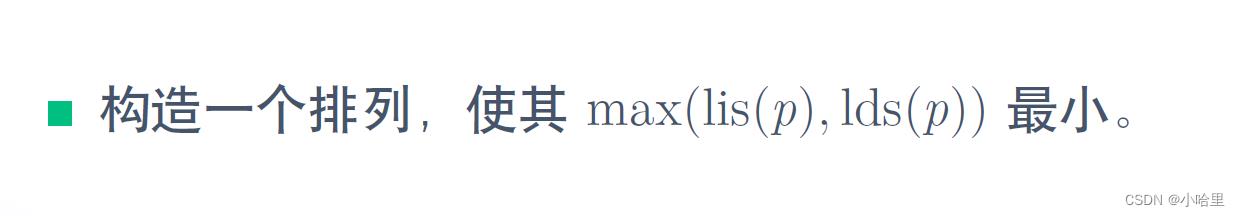
思路:
- 开始想的是构造(1, 2, 3, 4)(9, 8, 7, ,6 , 5)这样的排列,这样前面一个组最多与后面的组中的一个形成LIS,答案就是n/2+1,然后再想可以多弄几个组,就可以变得更小。
- 构造形如(3, 2, 1),( 6, 5, 4),( 9, 8, 7) 的排列,这样每个组与后一个组都只能选一个,然后如果组数变多,长度也会变大,在此基础上要让每组元素相对更多,所以就是继续求平均的根号n,即每组根号n个元素即可。
- 注意要向上取整,因为比如7的时候,介于2~3之间,我们肯定是选3来让组数变得更少。
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
int main()
int T; cin>>T;
while(T--)
int n; cin>>n;
int sq = ceil(sqrt(n));
for(int i = n; i > 0; i -= sq)//(7 8 9 )(4 5 6) (1 2 3)
for(int j = max(1,i-sq+1); j <= i; j++)
cout<<j<<" ";
cout<<"\\n";
return 0;
J.Link with Arithmetic Progression
题意:
- 官方:

思路:
-
官方:

-
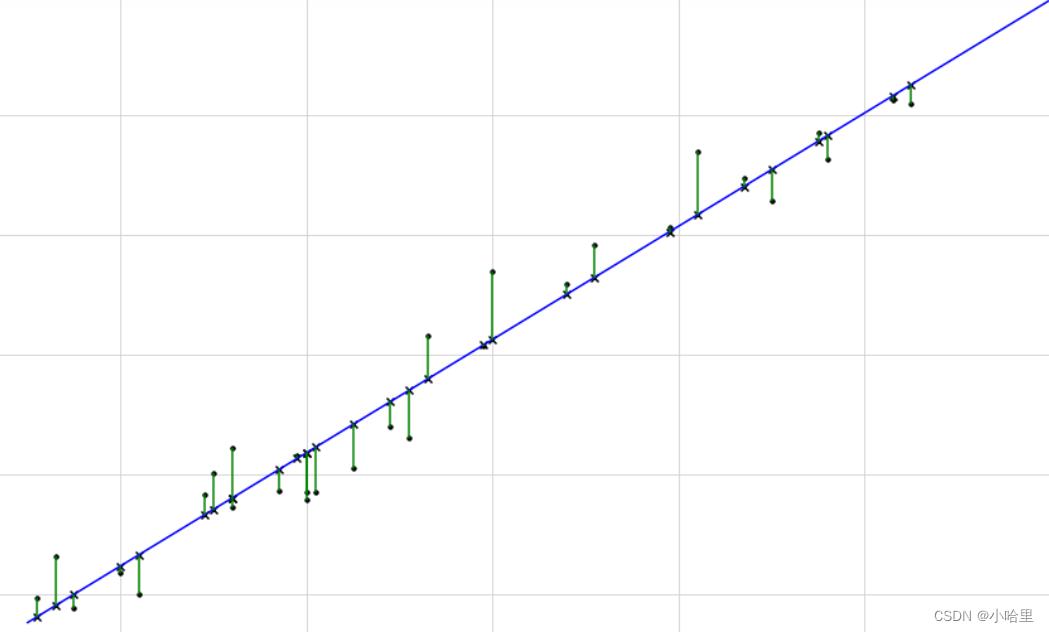
讲一下线性回归
最小二乘法,即最小化残差的平方和,就是本题要求的值,等差数列和当前数列的差值平方。
证明过程可以参考:https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/73494604,
公式可以参考:https://blog.csdn.net/snowdroptulip/article/details/79020590
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
typedef long long LL;
typedef long double LD;
const int maxn = 1e6+10;
int a[maxn];
int main()
int T; cin>>T;
while(T--)
LD n; cin>>n;
LD x = 0, y = 0; //坐标(i,a[i])
for(int i = 1; i <= n; i++)
cin>>a[i];
x += i; y += a[i];
x /= n; y /= n; //期望E(x),E(y),即x,y均值
LD s1 = 0, s2 = 0;
for(int i = 1; i <= n; i++)
s1 += (i-x)*(a[i]-y); //协方差:Cov(X,Y) = E[(X-E[X])(Y-E[Y])]?
s2 += (i-x)*(i-x); //方差:D(x) = E[(X-E[X])(X-E[X])]
LD k = s1/s2, b = y-k*x; //公式
LD ans = 0;
for(int i = 1; i <= n; i++)
ans += (a[i]-k*i-b)*(a[i]-k*i-b);
printf("%.15Lf\\n",ans);
return 0;
- 三分做法
已知f(x)在l,r上单峰且连续,求极值。每次迭代将当前区间的长度缩小1/3直到找到极值。
前面我们知道等差数列是一条直线,这条直线与所有给出的点(i,a[i])求方差最小时就是要找的点。
所以设直线y = kx+b ,即b^2=(y-kx)^2,令y=a[i], x=i,此时我们只需要最小化b的方差即可。
b关于k单峰且连续,b=f(k)。
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
#define ios ios::sync_with_stdio(0), cin.tie(0),cout.tie(0)
typedef long long LL;
typedef long double LD;
const LL maxn = 1e6+10;
const LD eps = 1e-10;
LD a[maxn], b[maxn], n;
LD check(LD k)//b=y-kx的方差
LD sum = 0, res = 0;
for(int i = 1; i <= n; i++)
b[i] = a[i]-k*i;
sum += b[i];
sum /= n;
for(int i = 1; i <= n; i++)
res += (b[i]-sum)*(b[i]-sum);
return res;
int main()
IOS;
int T; cin>>T;
while(T--)
cin>>n;
LD sum = 0;
for(int i = 1; i <= n; i++)
cin>>a[i]; sum += a[i];
LD l = -1e15, r = 1e15, ans = 1e100;
while(r-l > eps)
LD mt = (r-l)/3;
LD m1 = l+mt, m2 = r-mt;
LD v1 = check(m1), v2 = check(m2);
if(v1 >= v2)
ans = min(ans, v2);
l = m1;
else
ans = min(ans, v1);
r = m2;
printf("%.15Lf\\n",ans);
return 0;
K.Link with Bracket Sequence I
题意:
- 官方:

思路:
- 官方

#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
#define IOS ios::sync_with_stdio(0), cin.tie(0),cout.tie(0)
typedef long long LL;
const int maxn = 210;
const int mod = 1e9+7;
LL f[maxn][maxn][maxn];//b前i位,'('比')'多j个,a前k位的方案数
int main()
IOS;
int T; cin>>T;
while(T--)
int n, m; cin>>n>>m;
string a; cin>>a;
a = "0"+a;
// memset(f,0,sizeof(f)); //TLE 70%
for (int i = 0; i <= m; ++ i)
for (int j = 0; j <= m; ++ j)
for (int k = 0; k <= m; ++ k)
f[i][j][k] = 0;
f[0][0][0] = 1;
for(int i = 0; i < m; i++)
for(int j = 0; j <= i; j++)
for(int k = 0; k <= i; k++)
//对于b[i+1], a[k+1]选或不选
if(a[k+1]==')')
if(j>0)(f[i+1][j-1][k+1] += f[i][j][k]) %= mod;
(f[i+1][j+1][k] += f[i][j][k]) %= mod;
else if(a[k+1]=='(')
(f[i+1][j+1][k+1] += f[i][j][k]) %= mod;
if(j>0)(f[i+1][j-1][k] += f[i][j][k]) %= mod;
else
(f[i+1][j+1][k] += f[i][j][k]) %= mod;
if(j>0)(f[i+1][j-1][k] += f[i][j][k]) %= mod;
cout<<f[m][0][n]<<"\\n";
return 0;
以上是关于“蔚来杯“2022牛客暑期多校训练营2,签到题GJK的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章