spring boot在Java中操作缓存:
Posted Sun Peng
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了spring boot在Java中操作缓存:相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
文章目录
一、Jedis
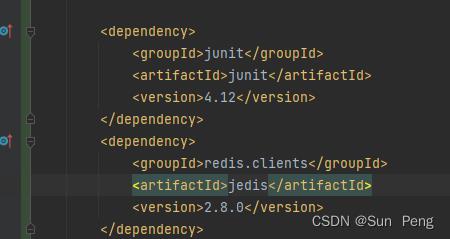
<dependency>
<groupId>junit</groupId>
<artifactId>junit</artifactId>
<version>4.12</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>redis.clients</groupId>
<artifactId>jedis</artifactId>
<version>2.8.0</version>
</dependency>
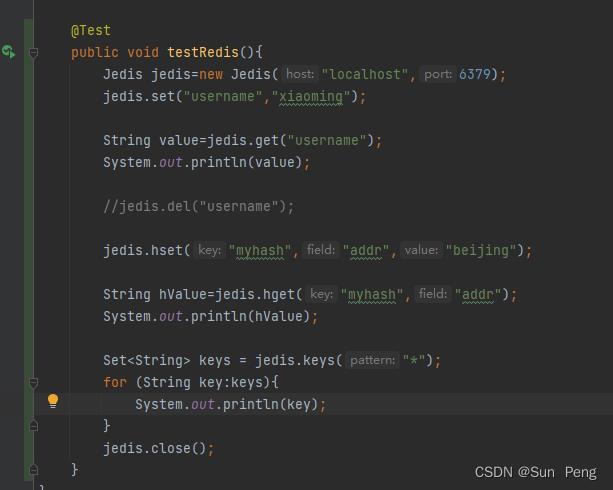
二、Spring Data Redis(常用)
【1】pom.xml
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-data-redis</artifactId>
</dependency>
【2】application.yml
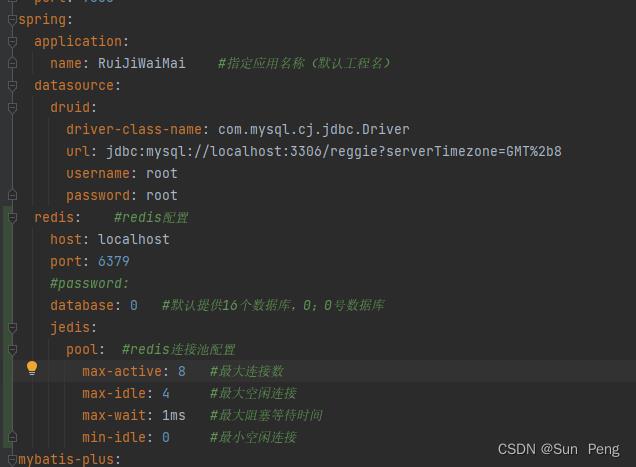
spring:
redis: #redis配置
host: localhost
port: 6379
#password:
database: 0 #默认提供16个数据库,0:0号数据库
jedis:
pool: #redis连接池配置
max-active: 8 #最大连接数
max-idle: 4 #最大空闲连接
max-wait: 1ms #最大阻塞等待时间
min-idle: 0 #最小空闲连接
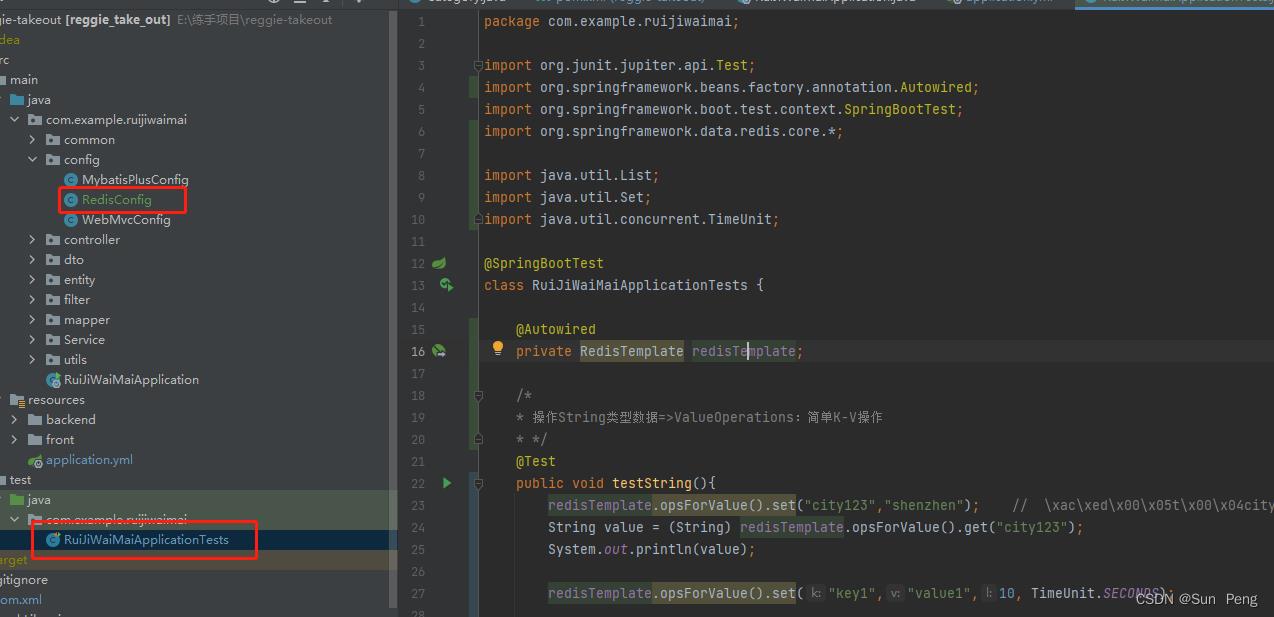
【3】RedisConfig
package com.example.ruijiwaimai.config;
import org.springframework.cache.annotation.CachingConfigurerSupport;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
import org.springframework.data.redis.connection.RedisConnectionFactory;
import org.springframework.data.redis.core.RedisTemplate;
import org.springframework.data.redis.serializer.StringRedisSerializer;
@Configuration
public class RedisConfig extends CachingConfigurerSupport
@Bean
public RedisTemplate<Object,Object> redisTemplate(RedisConnectionFactory connectionFactory)
RedisTemplate<Object,Object> redisTemplate=new RedisTemplate<>();
// 默认的key序列化器为:JdkSerializationRedisSerializer
redisTemplate.setKeySerializer(new StringRedisSerializer());
redisTemplate.setHashKeySerializer(new StringRedisSerializer());
redisTemplate.setConnectionFactory(connectionFactory);
return redisTemplate;
【4】RuiJiWaiMaiApplicationTests
package com.example.ruijiwaimai;
import org.junit.jupiter.api.Test;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.boot.test.context.SpringBootTest;
import org.springframework.data.redis.connection.DataType;
import org.springframework.data.redis.core.*;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.Set;
import java.util.concurrent.TimeUnit;
@SpringBootTest
class RuiJiWaiMaiApplicationTests
@Autowired
private RedisTemplate redisTemplate;
/*
* 操作String类型数据=>ValueOperations:简单K-V操作
* */
@Test
public void testString()
redisTemplate.opsForValue().set("city123", "shenzhen"); // \\xac\\xed\\x00\\x05t\\x00\\x04city做了序列化,无法用get city获取=》config配置RedisConfig
String value = (String) redisTemplate.opsForValue().get("city123");
System.out.println(value);
redisTemplate.opsForValue().set("key1", "value1", 10, TimeUnit.SECONDS);
Boolean aBoolean = redisTemplate.opsForValue().setIfAbsent("city1234", "nanjing");
System.out.println(aBoolean);
/*
* 操作Hash类型数据=>HashOperations:针对map类型的数据操作
* */
@Test
public void testHash()
HashOperations hashOperations = redisTemplate.opsForHash();
hashOperations.put("002", "name", "xiaoming");
hashOperations.put("002", "age", "20");
String age = (String) hashOperations.get("002", "age");
System.out.println(age);
// 获取所有字段
Set keys = hashOperations.keys("002");
for (Object key : keys)
System.out.println(key);
// 获取所有值
List values = hashOperations.values("002");
for (Object value : values)
System.out.println(value);
/*
* 操作List类型数据=>ListOperations:针对list类型的数据操作
* */
@Test
public void testList()
ListOperations listOperations = redisTemplate.opsForList();
//存值
listOperations.leftPush("mylist", "a");
listOperations.leftPushAll("mylist", "b", "c", "d");
//取值
List<String> mylist = listOperations.range("mylist", 0, -1);
for (String value : mylist)
System.out.println(value);
//获得列表长度
Long size = listOperations.size("mylist");
int lSize = size.intValue();
for (int i = 0; i < lSize; i++)
//出队列
Object element = listOperations.rightPop("mylist");
System.out.println("出队列:" + element);
/*
* 操作Set(无序集合)类型数据=>SetOperations:set类型数据操作
* */
@Test
public void testSet()
SetOperations setOperations = redisTemplate.opsForSet();
//存值
setOperations.add("myset", "a", "b", "c", "a");
//取值
Set<String> myset = setOperations.members("myset");
for (String o : myset)
System.out.println(o);
//删除成员
setOperations.remove("myset", "a", "b");
myset = setOperations.members("myset");
for (String o : myset)
System.out.println("删除后的数据:" + o);
/*
* 操作ZSet(有序集合)类型数据=>ZSetOperations:zset类型数据操作
* */
@Test
public void testZSet()
ZSetOperations zSetOperations = redisTemplate.opsForZSet();
//存值
zSetOperations.add("myZset", "a", 10.0);
zSetOperations.add("myZset", "b", 11.0);
zSetOperations.add("myZset", "c", 12.0);
zSetOperations.add("myZset", "a", 13.0);
//取值
Set<String> myZet = zSetOperations.range("myZset", 0, -1);
for (String s : myZet)
System.out.println(s);
//修改分数
zSetOperations.incrementScore("myZset", "b", 20.0);
myZet = zSetOperations.range("myZset", 0, -1);
for (String s : myZet)
System.out.println("修改分数: " + s);
//删除成员
zSetOperations.remove("myZset", "a", "b");
myZet = zSetOperations.range("myZset", 0, -1);
for (String s : myZet)
System.out.println("删除后的成员: " + s);
/*
* 通用操作
* */
@Test
public void testCommon()
//获取redis中所有的key
Set keys = redisTemplate.keys("*");
for (Object key : keys)
System.out.println(key);
//判断某个key是否存在
Boolean itcast = redisTemplate.hasKey("itcast");
System.out.println("判断某个key是否存在:"+itcast);
//删除指定key
redisTemplate.delete("myZset");
//获取指定key对应的value的数据类型
DataType dataType = redisTemplate.type("001");
System.out.println("获取指定key对应的value的数据类型:"+dataType.name());
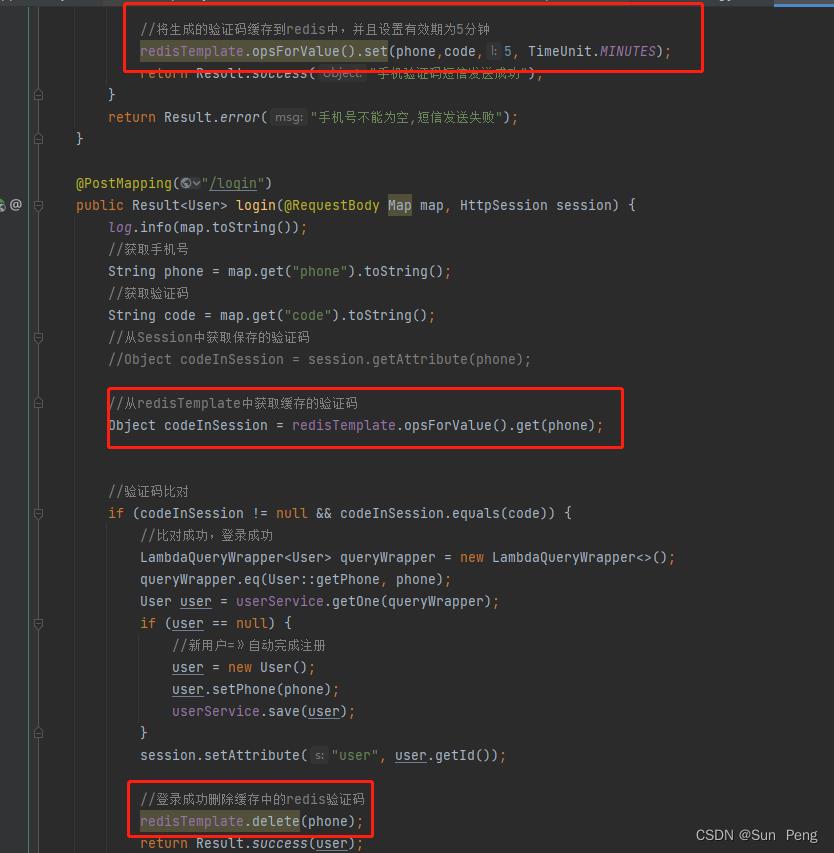
三、Spring Cache
【1】常用注解:
| 注解 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| @EnableCaching | 开启缓存注解功能 |
| @Cacheable | 判断是否有缓存数据,有=》返回缓存数据;没有=》放到缓存中 |
| @CachePut | 将方法的返回值放到缓存中 |
| @CacheEvict | 将一条或多条数据从缓存中删除 |
【2】使用案例
package com.itheima.controller;
import com.baomidou.mybatisplus.core.conditions.query.LambdaQueryWrapper;
import com.itheima.entity.User;
import com.itheima.service.UserService;
import lombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.cache.CacheManager;
import org.springframework.cache.annotation.CacheEvict;
import org.springframework.cache.annotation.CachePut;
import org.springframework.cache.annotation.Cacheable;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.*;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;
@RestController
@RequestMapping("/user")
@Slf4j
public class UserController
@Autowired
private CacheManager cacheManager;
@Autowired
private UserService userService;
/**
* CachePut:将方法返回值放入缓存
* value:缓存的名称,每个缓存名称下面可以有多个key
* key:缓存的key
*/
@CachePut(value = "userCache",key = "#user.id")
@PostMapping
public User save(User user)
userService.save(user);
return user;
/**
* CacheEvict:清理指定缓存
* value:缓存的名称,每个缓存名称下面可以有多个key
* key:缓存的key
*/
@CacheEvict(value = "userCache",key = "#p0")
//@CacheEvict(value = "userCache",key = "#root.args[0]")
//@CacheEvict(value = "userCache",key = "#id")
@DeleteMapping("/id")
public void delete(@PathVariable Long id)
userService.removeById(id);
//@CacheEvict(value = "userCache",key = "#p0.id")
//@CacheEvict(value = "userCache",key = "#user.id")
//@CacheEvict(value = "userCache",key = "#root.args[0].id")
@CacheEvict(value = "userCache",key = "#result.id")
@PutMapping
public User update(User user)
userService.updateById(user);
return user;
/**
* Cacheable:在方法执行前spring先查看缓存中是否有数据,如果有数据,则直接返回缓存数据;若没有数据,调用方法并将方法返回值放到缓存中
* value:缓存的名称,每个缓存名称下面可以有多个key
* key:缓存的key
* condition:条件,满足条件时才缓存数据
* unless:满足条件则不缓存
*/
@Cacheable(value = "userCache",key = "#id",unless = "#result == null")
@GetMapping("/id")
public User getById(@PathVariable Long id)
User user = userService.getById(id);
return user;
@Cacheable(value = "userCache",key = "#user.id + '_' + #user.name")
@GetMapping("/list")
public List<User> list(User user)
LambdaQueryWrapper<User> queryWrapper = new LambdaQueryWrapper<>();
queryWrapper.eq(user.getId() != null,User::getId,user.getId());
queryWrapper.eq(user.getName() != null,User::getName,user.getName());
List<User> list = userService.list(queryWrapper);
return list;
【3】底层不使用redis,重启服务,内存丢失=>解决:
pom.xml
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-data-redis</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-cache</artifactId>
</dependency>
application.yml
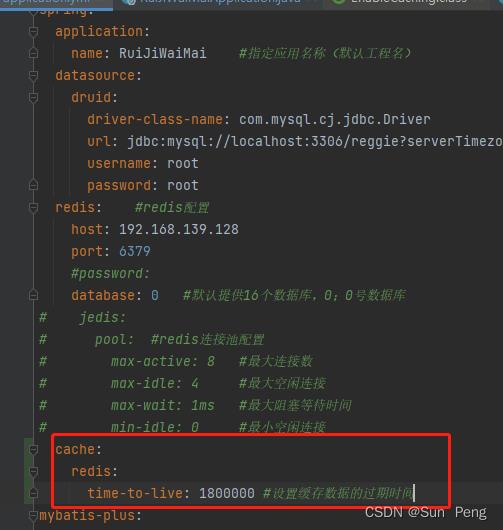
redis: #redis配置
host: 192.168.139.128
port: 6379
#password:
database: 0 #默认提供16个数据库,0;0号数据库
cache:
redis:
time-to-live: 1800000 #设置缓存数据的过期时间
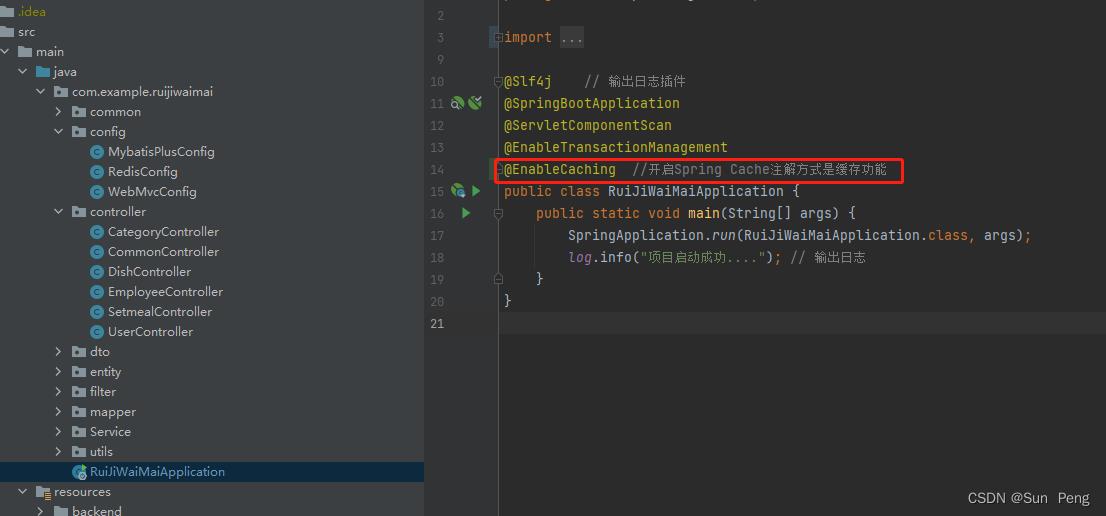
启动类:
Result:
注解使用:
@PostMapping()
@CacheEvict(value = "setmealCache",allEntries = true)
public Result<String> save(@RequestBody SetmealDto setmealDto关注“Java后端技术全栈”
回复“面试”获取全套大厂面试资料
缓存的简单认识
在项目中存在很多地方使用缓存,缓存是我们提高系统的一项必不可少的技术,无论是前端还是后端,都应用到了缓存技术,Mysql数据库也有使用缓存,所以认识缓存是非常有必要的。
前端使用缓存可以降低多次请求给服务端造成的压力。
后端使用缓存,可以降低数据库操作的压力,提升读取数据的性能。
前端缓存
本地缓存
网关缓存
服务端缓存
进程缓存
分布式缓存
其中我们可以使用Redis做分布式缓存。
Redis 简单认识
Redis是一个速度非常快的非关系型数据库(Non-Relational Database),Redis可以存储键值(key-value)数据。其中value可以用5种类型。可以将存储在内存的键值对数据持久化到硬盘上,可以使用复制特性来扩展读性能,还可以做客户端分片来扩展写性能。
为了满足Redis的高性能,它采用了(in-memory)数据集(Dataset),根据使用场景,可以通过每隔一段时间转存数据集到磁盘,或者追加没挑明了到日志来持久化。也可以禁用持久化,如果你只是需要一个功能丰富、网络传输化的内存缓存。
Redis数据模型
Redis数据模型不仅与关系型数据库不同,也不同于其他简单的NoSQL键值数据存储。
Redis数据类型类似于编程语言的基础类型数据,因此在对于咱们开发人员来说就更易于理解和使用。每个数据类型都支持适用于其类型的操作,受支持的数类型约束。
场景类型五种:
String字符串
Hash哈希
List列表
Set集合
ZSet有序集合
Spring Boot集成Redis
增加依赖
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-data-redis</artifactId>
</dependency>
<!-- 连接池-->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.apache.commons</groupId>
<artifactId>commons-pool2</artifactId>
</dependency>
添加配置
properties
# Redis数据库索引(默认为0)
spring.redis.database=0
# Redis服务器地址
spring.redis.host=127.0.0.1
# Redis服务器连接端口
spring.redis.port=6379
# Redis服务器连接密码(默认为空)
spring.redis.password=
# 连接池最大连接数(使用负值表示没有限制)
spring.redis.jedis.pool.max-active=20
# 连接池最大阻塞等待时间(使用负值表示没有限制)
spring.redis.jedis.pool.max-wait=-1
# 连接池中的最大空闲连接
spring.redis.jedis.pool.max-idle=10
# 连接池中的最小空闲连接
spring.redis.jedis.pool.min-idle=0
# 连接超时时间(毫秒)
spring.redis.timeout=1000
Redis使用
@RestController()
public class RedisController {
@Resource
private RedisTemplate redisTemplate;
/**
* 普通存储key-value
*/
@GetMapping("/setKeyAndValue")
public String setKeyAndValue() {
redisTemplate.opsForValue().set("name", "java后端技术全栈");
String value = (String) redisTemplate.opsForValue().get("name");
System.out.println("name value =" + value);
//设置有效期
redisTemplate.opsForValue().set("name1", "java后端技术栈", 100, TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS);
value = redisTemplate.opsForValue().get("name1") == null ? "" : (String)
redisTemplate.opsForValue().get("name1");
System.out.println("name1 value =" + value);
return "ok";
}
}
请求 http://localhost:8080/setKeyAndValue 输出
name value =java后端技术全栈
name1 value =java后端技术栈
OK,到此,Redis已经成功集成到Spring Boot项目中了。
集成进来后,我们就可以使用Redis来做很多事情了。
1,使用Redis来存储用户登录session
2,使用Redis的setnx和expire来做分布式锁
3,使用Redis的List来做队列
4,使用Redis的ZSet来做排行榜
5,使用自增inrc来确保不会超卖。
…..
上述这些使用场景是有前提条件的,因为没有绝对完美的技术,只能是选择相对能满足业务场景的就OK。
这里我们来做一个排行榜的场景。
Redis实现排行榜
需求是做一个用户购买理财产品金额的排行榜,相同的金额的以购买时间来排名。
public class UserAccount {
private Integer userId;
private String userName;
private BigDecimal amount;
private Date createTime;
//get set
}
写一个controller演示
@RestController()
public class RedisController {
@Resource
private RedisTemplate redisTemplate;
private static final String RANK_KEY_PRE = "user_amount_redis_key";
@GetMapping("/rank")
public String rank() {
List<UserAccount> userAccountList = new ArrayList<>();
UserAccount userAccount = new UserAccount();
userAccount.setAmount(new BigDecimal("100001"));
userAccount.setUserId(10001);
userAccount.setUserName("zhangsan");
userAccount.setCreateTime(new Date());
userAccountList.add(userAccount);
UserAccount userAccount1 = new UserAccount();
userAccount1.setAmount(new BigDecimal("100000"));
userAccount1.setUserId(10002);
userAccount1.setUserName("lisi");
userAccount1.setCreateTime(new Date());
userAccountList.add(userAccount1);
UserAccount userAccount2 = new UserAccount();
userAccount2.setAmount(new BigDecimal("100000"));
userAccount2.setUserId(10003);
userAccount2.setUserName("wangwu");
userAccount2.setCreateTime(DateUtil.parseDate("2020-08-15 10:10:10", DateUtil.DATE_TIME_FORMAT));
userAccountList.add(userAccount2);
UserAccount userAccount3 = new UserAccount();
userAccount3.setAmount(new BigDecimal("100002"));
userAccount3.setUserId(10004);
userAccount3.setUserName("laoliu");
userAccount3.setCreateTime(new Date());
userAccountList.add(userAccount3);
for (UserAccount ua : userAccountList) {
zadd(ua.getUserName(), RANK_KEY_PRE, ua.getAmount().longValue(), ua.getCreateTime().getTime());
}
List<ZSetOperations.TypedTuple> tuples = getRankCache(RANK_KEY_PRE, 0, 10);
for (int i =0; i <=tuples.size()-1; i++) {
ZSetOperations.TypedTuple tuple = tuples.get(i);
System.out.println(tuple.getValue() + " 第" +( i )+ "名,分数=" + tuple.getScore());
}
return "ok";
}
private void zadd(String userName, String key, long points, long updateTime) {
double timeRank = points + 1 - updateTime / Math.pow(10, (int) Math.log10(updateTime) + 1);
redisTemplate.opsForZSet().add(key, userName, timeRank);
}
private List<ZSetOperations.TypedTuple> getRankCache(String key, int start, int end) {
Set<ZSetOperations.TypedTuple> scoreSet = redisTemplate.opsForZSet().rangeWithScores(key, start, end);
if (CollectionUtils.isEmpty(scoreSet)) {
return new ArrayList<>();
}
List<ZSetOperations.TypedTuple> scoreList = new ArrayList<>();
for (ZSetOperations.TypedTuple item : scoreSet) {
scoreList.add(item);
}
return scoreList;
}
}
时间处理工具类
import java.text.DateFormat;
import java.text.ParseException;
import java.text.SimpleDateFormat;
import java.util.Date;
public class DateUtil {
public static final String DATE_TIME_FORMAT = "yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss";
/**
* 字符转Date类型
*
* @param dateString String 时间字符串
* @param formatString String 字符串格式;如:yyyy-MM-dd hh:mm:ss,年-月-日 时:分:秒
*/
public static Date parseDate(String dateString, String formatString) {
if (formatString == null) {
formatString = DATE_TIME_FORMAT;
}
DateFormat dd = new SimpleDateFormat(formatString);
try {
return dd.parse(dateString);
} catch (ParseException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
}
}
启动项目,然后请求
http://localhost:8080/rank
输出
lisi 第4名,分数=100000.84024399419
wangwu 第3名,分数=100000.840254259
zhangsan 第2名,分数=100001.84024399419
laoliu 第1名,分数=100002.84024399419
排名依据出来了。
redis的其他功能后面继续完善,本文就搞到这里。
码字不易,期待你们 点在看+分享。
推荐阅读
以上是关于spring boot在Java中操作缓存:的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章