Tree-LSTM的一些理解以及DGL代码实现
Posted Icy Hunter
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了Tree-LSTM的一些理解以及DGL代码实现相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
文章目录
前言
Tree-LSTM其实在好久之前就研究过了,那也应该是我第一次学DGL的时候。因为树就是一种特殊的图,也算是我入门图神经网络的基础操作,依稀记得当时搞着模型也是弄了蛮久的…
Tree-LSTM
Tree-LSTM是一种树形结构的LSTM,能够提高LSTM计算的并行速度,同时能够融入依存树或者句法树的相关信息,从而达到比较好的句子建模的效果。
Tree-LSTM有两种形式,一种是N-ary Tree-LSTM还有一种是Child-sum Tree-LSTM,前者能够记录时序信息但对孩子节点的个数有特点限制,后者会失去位置信息,但是对孩子节点的个数没有要求。
LSTM
在理解两种Tree-LSTM前,可以回顾一下我们经典的LSTM:

其中:
σ()、tanh()是激活函数
it是输入们得到的信息,xt 是输入的特征,W(i) 是对应输入门输入特征的变换矩阵,ht-1是前一个状态的隐藏层 U(i) 是输入门隐藏层的变换矩阵,b(i) 为输入门的偏置
ft是遗忘门得到的信息,xt 是输入的特征,W(f) 是对应遗忘门输入特征的变换矩阵,ht-1是前一个状态的隐藏层 U(f) 是遗忘门隐藏层的变换矩阵,b(f) 为遗忘门的偏置
ot是输出门得到的信息,xt 是输入的特征,W(o) 是对应输出门输入特征的变换矩阵,ht-1是前一个状态的隐藏层 U(o) 是输出门隐藏层的变换矩阵,b(o) 为遗忘门的偏置
ct为当前的细胞状态,⨀代表点积,即矩阵对应元素相乘
ht则是更新后的隐藏层
总的来说,公式还是比较简单的,因为没有Σ求和符号什么的,读懂公式的计算过程还是很容易的。
N-ary Tree-LSTM
N-ary Tree-LSTM即有N个孩子节点的Tree-LSTM,特点是能够较好的保留时序信息,不过对孩子节点的个数有限制要求,因此这种一般都为二叉树结构的输入,因为计算起来比较简单。

N-ary Tree-LSTM和经典的LSTM就是多了几个Σ求和符号。
如果N=2,那么意味着每个父节点的孩子节点数都为2,那么输入门、输出门、遗忘门中各自有两个U来对前一时刻对应两个孩子节点的隐藏层进行线性变换,然后求和,因为这操作分别对应左右两个孩子,因此是能够记录时序信息的。因为N=2是事先设定的,如果你的数据里出现了三个孩子节点的情况,那么就要报错了。
还是举个例子比较形象

例如N=2,0为父节点,那么N-ary Tree-LSTM会在子节点1和2的位置中的三种门中分别设置一个隐藏层变换矩阵U1和U2,左节点就和U1计算,右节点就和U2计算,这样就保证位置信息能够得以保留,但是不能够解决数据中含有三叉及以上的情况。
Child-sum Tree-LSTM
Child-sum Tree-LSTM就比较简单了,顾名思义,他就是将子节点的隐藏层都求和然后再去更新父节点的隐藏层。

对比N-ary Tree-LSTM可以发现三个门中的Σ求和符号没了,因为(2)中将孩子节点的隐藏层直接求和,记为
h
~
\\widetildeh
h
j,然后用它进去三门进行计算即可。因为这里是求和操作,那么孩子节点的个数就不受限制了,因为求和之后就相当于只有一个了,三门中只需要设置一个对应的U即可,但是缺点就是,求和之后,孩子节点的位置信息就失去了。
以及这里遗忘门是对每个孩子节点各自求一个遗忘信息,不过是共享参数U(f)
同样可以举个例子,例如此时N=3
如果是N-ary Tree-LSTM:
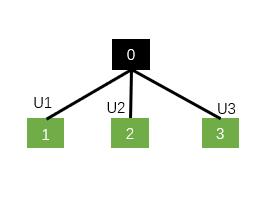
就要对应分别三组。
如果是Child-sum Tree-LSTM:

只需要一个就可以了,因为子节点都求和了。
DGL代码实现
N-ary Tree-LSTM
这个代码完全来自DGL官网。这里是一个对每个节点做预测的情感分类任务。
from collections import namedtuple
import dgl
from dgl.data.tree import SSTDataset
SSTBatch = namedtuple('SSTBatch', ['graph', 'mask', 'wordid', 'label'])
# Each sample in the dataset is a constituency tree. The leaf nodes
# represent words. The word is an int value stored in the "x" field.
# The non-leaf nodes have a special word PAD_WORD. The sentiment
# label is stored in the "y" feature field.
trainset = SSTDataset(mode='tiny') # the "tiny" set has only five trees
tiny_sst = trainset.trees
num_vocabs = trainset.num_vocabs
num_classes = trainset.num_classes
vocab = trainset.vocab # vocabulary dict: key -> id
inv_vocab = v: k for k, v in vocab.items() # inverted vocabulary dict: id -> word
a_tree = tiny_sst[0]
for token in a_tree.ndata['x'].tolist():
if token != trainset.PAD_WORD:
print(inv_vocab[token], end=" ")
import torch as th
import torch.nn as nn
class TreeLSTMCell(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, x_size, h_size):
super(TreeLSTMCell, self).__init__()
self.W_iou = nn.Linear(x_size, 3 * h_size, bias=False)
self.U_iou = nn.Linear(2 * h_size, 3 * h_size, bias=False)
self.b_iou = nn.Parameter(th.zeros(1, 3 * h_size))
self.U_f = nn.Linear(2 * h_size, 2 * h_size)
def message_func(self, edges):
return 'h': edges.src['h'], 'c': edges.src['c']
def reduce_func(self, nodes):
# concatenate h_jl for equation (1), (2), (3), (4)
h_cat = nodes.mailbox['h'].view(nodes.mailbox['h'].size(0), -1)
# equation (2)
f = th.sigmoid(self.U_f(h_cat)).view(*nodes.mailbox['h'].size())
# second term of equation (5)
c = th.sum(f * nodes.mailbox['c'], 1)
return 'iou': self.U_iou(h_cat), 'c': c
def apply_node_func(self, nodes):
# equation (1), (3), (4)
iou = nodes.data['iou'] + self.b_iou
i, o, u = th.chunk(iou, 3, 1)
i, o, u = th.sigmoid(i), th.sigmoid(o), th.tanh(u)
# equation (5)
c = i * u + nodes.data['c']
# equation (6)
h = o * th.tanh(c)
return 'h' : h, 'c' : c
class TreeLSTM(nn.Module):
def __init__(self,
num_vocabs,
x_size,
h_size,
num_classes,
dropout,
pretrained_emb=None):
super(TreeLSTM, self).__init__()
self.x_size = x_size
self.embedding = nn.Embedding(num_vocabs, x_size)
if pretrained_emb is not None:
print('Using glove')
self.embedding.weight.data.copy_(pretrained_emb)
self.embedding.weight.requires_grad = True
self.dropout = nn.Dropout(dropout)
self.linear = nn.Linear(h_size, num_classes)
self.cell = TreeLSTMCell(x_size, h_size)
def forward(self, batch, h, c):
"""Compute tree-lstm prediction given a batch.
Parameters
----------
batch : dgl.data.SSTBatch
The data batch.
h : Tensor
Initial hidden state.
c : Tensor
Initial cell state.
Returns
-------
logits : Tensor
The prediction of each node.
"""
g = batch.graph
# to heterogenous graph
g = dgl.graph(g.edges())
# feed embedding
embeds = self.embedding(batch.wordid * batch.mask)
g.ndata['iou'] = self.cell.W_iou(self.dropout(embeds)) * batch.mask.float().unsqueeze(-1)
g.ndata['h'] = h
g.ndata['c'] = c
# propagate
dgl.prop_nodes_topo(g,
message_func=self.cell.message_func,
reduce_func=self.cell.reduce_func,
apply_node_func=self.cell.apply_node_func)
# compute logits
h = self.dropout(g.ndata.pop('h'))
logits = self.linear(h)
return logits
from torch.utils.data import DataLoader
import torch.nn.functional as F
device = th.device('cpu')
# hyper parameters
x_size = 256
h_size = 256
dropout = 0.5
lr = 0.05
weight_decay = 1e-4
epochs = 10
# create the model
model = TreeLSTM(trainset.num_vocabs,
x_size,
h_size,
trainset.num_classes,
dropout)
print(model)
# create the optimizer
optimizer = th.optim.Adagrad(model.parameters(),
lr=lr,
weight_decay=weight_decay)
def batcher(dev):
def batcher_dev(batch):
batch_trees = dgl.batch(batch)
return SSTBatch(graph=batch_trees,
mask=batch_trees.ndata['mask'].to(device),
wordid=batch_trees.ndata['x'].to(device),
label=batch_trees.ndata['y'].to(device))
return batcher_dev
train_loader = DataLoader(dataset=tiny_sst,
batch_size=5,
collate_fn=batcher(device),
shuffle=False,
num_workers=0)
# training loop
for epoch in range(epochs):
for step, batch in enumerate(train_loader):
g = batch.graph
n = g.number_of_nodes()
h = th.zeros((n, h_size))
c = th.zeros((n, h_size))
logits = model(batch, h, c)
logp = F.log_softmax(logits, 1)
loss = F.nll_loss(logp, batch.label, reduction='sum')
optimizer.zero_grad()
loss.backward()
optimizer.step()
pred = th.argmax(logits, 1)
acc = float(th.sum(th.eq(batch.label, pred))) / len(batch.label)
print("Epoch :05d | Step :05d | Loss :.4f | Acc :.4f |".format(
epoch, step, loss.item(), acc))
Child-sum Tree-LSTM
可以看懂了N-ary再来看Child-sum的,差不太多。
import torch as th
import torch.nn as nn
class ChildSumTreeLSTMCell(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, x_size, h_size):
super(ChildSumTreeLSTMCell, self).__init__()
self.W_iou = nn.Linear(x_size, 3 * h_size, bias=False)
self.U_iou = nn.Linear(h_size, 3 * h_size, bias=False)
self.b_iou = nn.Parameter(th.zeros(1, 3 * h_size))
self.U_f = nn.Linear(h_size, h_size)
def message_func(self, edges):
return 'h': edges.src['h'], 'c': edges.src['c']
def reduce_func(self, nodes):
h_tild = th.sum(nodes.mailbox['h'], 1)
f = th.sigmoid(self.U_f(nodes.mailbox['h']))
c = th.sum(f * nodes.mailbox['c'], 1)
return 'iou': self.U_iou(h_tild), 'c': c
def apply_node_func(self, nodes):
iou = nodes.data['iou'] + self.b_iou
i, o, u = th.chunk(iou, 3, 1)
i, o, u = th.sigmoid(i), th.sigmoid(o), th.tanh(u)
c = i * u + nodes.data['c']
h = o * th.tanh(c)
return 'h': h, 'c': c
class TreeLSTM(nn.Module):
def __init__(self,
num_vocabs,
x_size,
h_size,
num_classes,
dropout,
pretrained_emb=None):
super(TreeLSTM, self).__init__()
self.x_size = x_size
self.embedding = nn.Embedding(num_vocabs, x_size)
if pretrained_emb is not None:#这里可以使用预训练词向量
print('Using glove')
self.embedding.weight.data.copy_(pretrained_emb)
self.embedding.weight.requires_grad = True
self.dropout = nn.Dropout(dropout)
self.linear = nn.Linear(h_size, num_classes)
self.cell = ChildSumTreeLSTMCell(x_size, h_size)
def forward(self, batch, h, c):
"""Compute tree-lstm prediction given a batch.
Parameters
----------
batch : dgl.data.SSTBatch
The data batch.
h : Tensor
Initial hidden state.
c : Tensor
Initial cell state.
Returns
-------
logits : Tensor
The prediction of each node.
"""
# print("batch", batch)
g = batch.graph
# print("g", g)
# to heterogenous graph
g = dgl.graph(g.edges())
# feed embedding
embeds = self.embedding(batch.wordid * batch.mask)
#叶子节点没有入度,因此message_func和reduce_func都可以忽略,直接apply_node_func
g.ndata['iou'] = self.cell.W_iou(self.dropout(embeds)) * batch.mask.float().unsqueeze(-1)
g.ndata['h'] = h
g.ndata['c'] = c
g.ndata['node_pos'] = batch.node_pos
# print(type(batch.wordid))
# prop_nodes_topo是根据我们指定的拓扑顺序来进行消息传递
dgl.prop_nodes_topo(g,
message_func=self.cell.message_func,
reduce_func=self.cell.reduce_func,
apply_node_func=self.cell.apply_node_func)
# compute logits
# print("after_prop_nodes_topo", g)
h = self.dropout(g.ndata.pop('h'))
pos = g.ndata["node_pos"]
pos_sen = torch.nonzero(pos==0).squeeze() # 0的位置为根节点
sen_hidden = h[pos_sen]
logits = self.linear(sen_hidden)
return logits
child_sum_Tree_LSTM = TreeLSTM(100, 50, 50, 2, 0.2)
print(child_sum_Tree_LSTM)
参考
2015-Tree-LSTM-Improved Semantic Representations From Tree-Structured Long Short-Term Memory Networks
https://docs.dgl.ai/tutorials/models/2_small_graph/3_tree-lstm.html#sphx-glr-tutorials-models-2-small-graph-3-tree-lstm-py
以上是关于Tree-LSTM的一些理解以及DGL代码实现的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章