组件篇值RPC(上)
Posted L@wang
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了组件篇值RPC(上)相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
- 组件篇值RPC(上)
基础架构
暂时无法在文档外展示此内容
基础架构之组件篇
组件篇
- RPC
- 注册中心
- Zookeeper
- 配置中心
- Nacos
- 消息队列
- 事务消息
- 延时消息
- Spring
组件篇之RPC(上)
01.RPC原理分析
理解RPC - Remote Procedure Call
- 远程过程调用
- 基于网络表达语义和传达数据
- 通信协议
- 像调用本地方法调用远程服务
- 扩展了算力
- 服务治理的基础
RPC作用 - 屏蔽组包/解包
- 屏蔽数据发送/接收
- 提高开发效率
- 业务发展的必然产物
RPC核心组成 - 远程方法对象代理
- 连接管理
- 序列化/反序列化
- 寻址与负载均衡
RPC调用方式 - 同步调用
- 异步调用
RPC调用过程
暂时无法在文档外展示此内容
02.精简版RPC实现
假如没有RPC : 如果没有RPC框架支持,实现远程调用需要做哪些事情?
Client 端
建立与Server的连接
组装数据
发送数据包
接收处理结果数据包
解析返回数据包
Server 端
监听端口
响应连接请求
接收数据包
解析数据包,调用相应方法
组装请求处理结果数据包
发送结果数据包
设计“用户”服务
功能需求:用户信息管理—CRUD
调用方式:TCP长连接同步交互
协议:自定义协议
接口设计
注册: bool addUser(User user)
更新: bool updateUser(long uid, User user)
注销: bool deleteUser(long uid)
查询: User Info getUser(long ui)
序列化协议
远程调用涉及数据的传输,就会涉及组包和解包,需要调用方和服务方约定数据格式——序列化协议
暂时无法在文档外展示此内容
package com.naixue.client.protocol;
import com.naixue.client.entity.User;
import com.naixue.util.ByteConverter;
import java.io.*;
public class RpcProtocol implements Serializable
public static int CMD_CREATE_USER = 1;
private int version;
private int cmd;
private int magicNum;
private int bodyLen = 0;
private byte[] body;
final public static int HEAD_LEN = 16;
public byte[] getBody()
return body;
public RpcProtocol setBody(byte[] body)
this.body = body;
return this;
public int getVersion()
return version;
public RpcProtocol setVersion(int version)
this.version = version;
return this;
public int getCmd()
return cmd;
public RpcProtocol setCmd(int cmd)
this.cmd = cmd;
return this;
public int getMagicNum()
return magicNum;
public RpcProtocol setMagicNum(int magicNum)
this.magicNum = magicNum;
return this;
public int getBodyLen()
return bodyLen;
public RpcProtocol setBodyLen(int bodyLen)
this.bodyLen = bodyLen;
return this;
public byte[] generateByteArray()
byte[] data = new byte[HEAD_LEN + bodyLen];
int index = 0;
System.arraycopy(ByteConverter.intToBytes(version), 0, data, index,
Integer.BYTES);
index += Integer.BYTES;
System.arraycopy(ByteConverter.intToBytes(cmd), 0, data, index,
Integer.BYTES);
index += Integer.BYTES;
System.arraycopy(ByteConverter.intToBytes(magicNum), 0, data, index,
Integer.BYTES);
index += Integer.BYTES;
System.arraycopy(ByteConverter.intToBytes(bodyLen), 0, data, index,
Integer.BYTES);
index += Integer.BYTES;
System.arraycopy(body, 0, data, index, body.length);
return data;
public RpcProtocol byteArrayToRpcHeader(byte[] data)
int index = 0;
this.setVersion(ByteConverter.bytesToInt(data, index));
index += Integer.BYTES;
this.setCmd(ByteConverter.bytesToInt(data, index));
index += Integer.BYTES;
this.setMagicNum(ByteConverter.bytesToInt(data, index));
index += Integer.BYTES;
this.setBodyLen(ByteConverter.bytesToInt(data, index));
index += Integer.BYTES;
this.body = new byte[this.bodyLen];
System.arraycopy(data, index, this.body, 0, this.bodyLen);
return this;
public User byteArrayToUserInfo(byte[] data)
User user = new User();
int index = 0;
user.setUid(ByteConverter.bytesToLong(data, index));
index += Long.BYTES;
user.setAge(ByteConverter.bytesToShort(data, index));
index += Short.BYTES;
user.setSex(ByteConverter.bytesToShort(data, index));
index += Short.BYTES;
return user;
public byte[] userInfoTobyteArray(User info)
byte[] data = new byte[Long.BYTES + Short.BYTES + Short.BYTES];
int index = 0;
System.arraycopy(ByteConverter.longToBytes(info.getUid()), 0, data,
index, Long.BYTES);
index += Long.BYTES;
System.arraycopy(ByteConverter.shortToBytes(info.getAge()), 0, data,
index, Short.BYTES);
index += Short.BYTES;
System.arraycopy(ByteConverter.shortToBytes(info.getSex()), 0, data,
index, Short.BYTES);
return data;
public static Object bytes2Object(byte[] objBytes) throws Exception
if (objBytes == null || objBytes.length == 0)
return null;
ByteArrayInputStream bi = new ByteArrayInputStream(objBytes);
ObjectInputStream oi = new ObjectInputStream(bi);
Object obj = oi.readObject();
bi.close();
oi.close();
return obj;
public static byte[] object2Bytes(Serializable obj) throws Exception
if (obj == null)
return null;
ByteArrayOutputStream bo = new ByteArrayOutputStream();
ObjectOutputStream oo = new ObjectOutputStream(bo);
oo.writeObject(obj);
bo.close();
oo.close();
return bo.toByteArray();
public byte[] createUserRespTobyteArray(int result)
byte[] data = new byte[Integer.BYTES];
int index = 0;
System.arraycopy(ByteConverter.intToBytes(result), 0, data, index,
Integer.BYTES);
return data;
暂时无法在文档外展示此内容
public static int CMD_CREATE_USER = 1;
private int version;// = 1
private int cmd;// = 0
private int magicNum; // = 0x20191009
private int bodyLen = 0;// = 12
private byte[] body;
final public static int HEAD_LEN = 16;
暂时无法在文档外展示此内容
Consumer代码实现
- 创建代理类
- 构造请求数据
- 执行远程调用
package com.naixue;
import com.naixue.client.entity.User;
import com.naixue.client.service.UserService;
/**
-
Created by chendong on 2019/9/3.
*/
public class RpcClient
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception
UserService proxyUserService = new UserService();User user = new User(); user.setAge((short) 26); user.setSex((short) 1); int ret = proxyUserService.addUser(user); if(ret == 0) System.out.println("调用远程服务创建用户成功!!!"); else System.out.println("调用远程服务创建用户失败!!!");
addUser :
package com.naixue.client.entity;
import java.io.Serializable;
/**
-
Created by chendong on 2019/9/3.
*/
public class User implements Serializable
private long uid;
private short age;
private short sex;public long getUid()
return uid;
public User setUid(long uid)
this.uid = uid;
return this;
public short getAge()
return age;
public User setAge(short age)
this.age = age;
return this;
public short getSex()
return sex;
public User setSex(short sex)
this.sex = sex;
return this;
package com.naixue.client.connect;
import org.slf4j.Logger;
import org.slf4j.LoggerFactory;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.net.InetSocketAddress;
import java.nio.ByteBuffer;
import java.nio.channels.SocketChannel;
public class TcpClient
private Logger logger = LoggerFactory.getLogger(this.getClass());
private static int MAX_PACKAGE_SIZE = 1024 * 4;
private static String SERVER_IP = “127.0.0.1”;
private static int SERVER_PORT = 58885;
private static TcpClient instance = null;
private boolean isInit = false;
//private ChannelFuture channelFuture = null;
SocketChannel client = null;
private final static int CONNECT_TIMEOUT_MILLIS = 2000;
//private Bootstrap bootstrap = new Bootstrap();
public TcpClient()
public static TcpClient GetInstance()
if (instance == null)
instance = new TcpClient();
return instance;
public void init() throws Exception
if(!isInit)
client = SocketChannel.open(new InetSocketAddress(SERVER_IP, SERVER_PORT));
client.configureBlocking(true);
isInit = true;
public boolean sendData(byte[] data)
ByteBuffer byteBuffer = ByteBuffer.wrap(data);
byteBuffer.put(data);
byteBuffer.flip();
int ret = 0;
try
ret = client.write(byteBuffer);
catch (IOException e)
e.printStackTrace();
return false;
return true;
public byte[] recvData()
ByteBuffer byteBuffer = ByteBuffer.allocate(MAX_PACKAGE_SIZE);
try
int rs = client.read(byteBuffer);
byte[] bytes = new byte[rs];
byteBuffer.flip();
byteBuffer.get(bytes);
return bytes;
catch (IOException e)
e.printStackTrace();
return null;
package com.naixue.client.service;
import com.naixue.client.connect.TcpClient;
import com.naixue.client.entity.User;
import com.naixue.client.protocol.RpcProtocol;
import com.naixue.util.ByteConverter;
import org.slf4j.Logger;
import org.slf4j.LoggerFactory;
public class UserService
private Logger logger = LoggerFactory.getLogger(this.getClass());
public int addUser (User userinfo) throws Exception
//初始化客户端连接
TcpClient client = TcpClient.GetInstance();
try
client.init();
catch (Exception e)
e.printStackTrace();
logger.error("init rpc client error");
//构造请求数据 组装协议数据
RpcProtocol rpcReq = new RpcProtocol();
rpcReq.setCmd(RpcProtocol.CMD_CREATE_USER);
rpcReq.setVersion(0x01);
rpcReq.setMagicNum(0x20110711);
byte[] body = rpcReq.userInfoTobyteArray(userinfo);
rpcReq.setBodyLen(body.length);
rpcReq.setBody(body);
//序列化 序列化数据
byte[] reqData = rpcReq.generateByteArray();
//发送请求 发送请求等待返回
client.sendData(reqData);
//接收请求结果
byte[] recvData = client.recvData();
//反序列化结果 反序列化返回数据
RpcProtocol rpcResp = new RpcProtocol();
rpcResp.byteArrayToRpcHeader(recvData);
int ret = ByteConverter.bytesToInt(rpcResp.getBody(), 0);
return ret;
序列化/反序列化
/**
- @ClassName: $ByteConverter
- @Description: $
- @author $wangzongsheng
- @version V1.0
- @Date $2019-01-14
*/
package com.naixue.util;
public class ByteConverter
/**
* @param buf
* @return
*/
public static short bytesToShort(byte[] buf)
return (short) (buf[0] & 0xff | ((buf[1] << 8) & 0xff00));
/**
* @param buf
* @return
*/
public static int bytesToIntBigEndian(byte[] buf)
return buf[0] & 0xff | ((buf[1] << 8) & 0xff00)
| ((buf[2] << 16) & 0xff0000) | ((buf[3] << 24) & 0xff000000);
/**
* byte array to int
*
* @param buf
* @return
*/
public static long bytesToLong(byte[] buf)
return (long) buf[0] & 0xffl
| (((long) buf[1] << 8) & 0xff00l)
| (((long) buf[2] << 16) & 0xff0000l)
| (((long) buf[3] << 24) & 0xff000000l)
| (((long) buf[4] << 32) & 0xff00000000l)
| (((long) buf[5] << 40) & 0xff0000000000l)
| (((long) buf[6] << 48) & 0xff000000000000l)
| (((long) buf[7] << 56) & 0xff00000000000000l);
public static byte[] shortToBytes(short n)
byte[] buf = new byte[2];
for (int i = 0; i < buf.length; i++)
buf[i] = (byte) (n >> (8 * i));
return buf;
/**
* int to byte array
*
* @param n
* @return
*/
public static byte[] intToBytes(int n)
byte[] buf = new byte[4];
for (int i = 0; i < buf.length; i++)
buf[i] = (byte) (n >> (8 * i));
return buf;
public static byte[] longToBytes(long n)
byte[] buf = new byte[8];
for (int i = 0; i < buf.length; i++)
buf[i] = (byte) (n >> (8 * i));
return buf;
public static short bytesToShort(byte[] buf, int offset)
return (short) (buf[offset] & 0xff | ((buf[offset + 1] << 8) & 0xff00));
public static int bytesToInt(byte[] buf, int offset)
return buf[offset] & 0xff
| ((buf[offset + 1] << 8) & 0xff00)
| ((buf[offset + 2] << 16) & 0xff0000)
| ((buf[offset + 3] << 24) & 0xff000000);
public static long bytesToLong(byte[] buf, int offset)
return (long) buf[offset] & 0xffl
| (((long) buf[offset + 1] << 8) & 0xff00l)
| (((long) buf[offset + 2] << 16) & 0xff0000l)
| (((long) buf[offset + 3] << 24) & 0xff000000l)
| (((long) buf[offset + 4] << 32) & 0xff00000000l)
| (((long) buf[offset + 5] << 40) & 0xff0000000000l)
| (((long) buf[offset + 6] << 48) & 0xff000000000000l)
| (((long) buf[offset + 7] << 56) & 0xff00000000000000l);
序列化过程
- 序列化请求参数到body
- 序列化RpcProtocol
反序列化过程 - 反序列化RpcProtocol
- 反序列化body
package com.naixue.util;
import com.naixue.client.protocol.RpcProtocol;
import io.netty.buffer.ByteBuf;
import io.netty.channel.ChannelHandlerContext;
import io.netty.handler.codec.ByteToMessageDecoder;
import org.slf4j.Logger;
import org.slf4j.LoggerFactory;
import java.util.List;
public class PkgDecoder extends ByteToMessageDecoder
private Logger logger = LoggerFactory.getLogger(PkgDecoder.class);
public PkgDecoder()
@Override
protected void decode(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, ByteBuf buffer, List<Object> out) throws Exception
if (buffer.readableBytes() < RpcProtocol.HEAD_LEN)
return; //未读完足够的字节流,缓存后继续读
byte[] intBuf = new byte[4];
buffer.getBytes(buffer.readerIndex() + RpcProtocol.HEAD_LEN - 4, intBuf); // ImHeader的bodyLen在第68位到71为, int类型
int bodyLen = ByteConverter.bytesToIntBigEndian(intBuf);
if (buffer.readableBytes() < RpcProtocol.HEAD_LEN + bodyLen)
return; //未读完足够的字节流,缓存后继续读
byte[] bytesReady = new byte[RpcProtocol.HEAD_LEN + bodyLen];
buffer.readBytes(bytesReady);
out.add(bytesReady);
/**
- @ClassName: $PkgEncoder
- @Description: $tcp编码器
- @author $wangzongsheng
- @version V1.0
- @Date $2019-01-14
*/
package com.naixue.util;
import io.netty.buffer.ByteBuf;
import io.netty.channel.ChannelHandlerContext;
import io.netty.handler.codec.MessageToByteEncoder;
public class PkgEncoder extends MessageToByteEncoder
public PkgEncoder()
@Override
protected void encode(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, Object msg, ByteBuf out) throws Exception
try
//在这之前可以实现编码工作。
out.writeBytes((byte[])msg);
finally
03.RPC服务消费方核心设计
RPC功能
- RPC基础功能
- 数据传输
- 序列化/反序列化
- 客户端代理类
- 请求映射分发
- RPC产品功能
Consumer
连接管理
负载均衡
请求路由
超时处理
Provider
队列/线程池
超时丢弃
优雅关闭
过载保护
连接管理
保持与服务提供方长连接,用于传输请求数据和返回结果。
暂时无法在文档外展示此内容
初始化时机
饿汉模式
懒汉模式
连接数维护
服务连接池
数据库连接池
思考:两类连接有什么本质区别?
心跳/断线重连
客户端线程模型
package com.naixue.server.connect;
import java.net.InetSocketAddress;
import com.naixue.server.entity.User;
import com.naixue.server.protocol.RpcProtocol;
import com.naixue.server.server.UserService;
import io.netty.buffer.ByteBuf;
import io.netty.buffer.Unpooled;
import io.netty.channel.Channel;
import io.netty.channel.ChannelHandlerContext;
import io.netty.channel.ChannelInboundHandlerAdapter;
import org.slf4j.Logger;
import org.slf4j.LoggerFactory;
public class ServerHandler extends ChannelInboundHandlerAdapter
private Logger logger = LoggerFactory.getLogger(ServerHandler.class);
private static int CMD_CREATE_USER = 1;
private static int CMD_FIND_USER = 2;
@Override
public void channelActive(ChannelHandlerContext ctx) throws Exception
Channel ch = ctx.channel();
InetSocketAddress socketAddress = (InetSocketAddress) ch.remoteAddress();
String clientIp = socketAddress.getAddress().getHostAddress();
logger.info("client connect to rpc server, client's ip is: " + clientIp);
@Override
public void channelInactive(ChannelHandlerContext ctx) throws Exception
Channel ch = ctx.channel();
InetSocketAddress socketAddress = (InetSocketAddress) ch.remoteAddress();
String clientIp = socketAddress.getAddress().getHostAddress();
logger.info("client close the connection to rpc server, client's ip is: " + clientIp);
@Override
public void channelRead(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, Object msg) throws Exception
byte[] recvData = (byte[]) msg;
if (recvData.length == 0)
logger.warn("receive request from client, but the data length is 0");
return;
logger.info("receive request from client, the data length is: " + recvData.length);
//反序列化请求数据
RpcProtocol rpcReq = new RpcProtocol();
rpcReq.byteArrayToRpcHeader(recvData);
if(rpcReq.getMagicNum() != RpcProtocol.CONST_CMD_MAGIC)
logger.warn("request msgic code error");
return;
//解析请求,并调用处理方法
int ret = -1;
if(rpcReq.getCmd() == CMD_CREATE_USER)
User user = rpcReq.byteArrayToUserInfo(rpcReq.getBody());
UserService userService = new UserService();
ret = userService.addUser(user);
//构造返回数据
RpcProtocol rpcResp = new RpcProtocol();
rpcResp.setCmd(rpcReq.getCmd());
rpcResp.setVersion(rpcReq.getVersion());
rpcResp.setMagicNum(rpcReq.getMagicNum());
rpcResp.setBodyLen(Integer.BYTES);
byte[] body = rpcResp.createUserRespTobyteArray(ret);
rpcResp.setBody(body);
ByteBuf respData = Unpooled.copiedBuffer(rpcResp.generateByteArray());
ctx.channel().writeAndFlush(respData);
package com.naixue.server.connect;
import com.naixue.util.PkgDecoder;
import io.netty.bootstrap.ServerBootstrap;
import io.netty.channel.*;
import io.netty.channel.nio.NioEventLoopGroup;
import io.netty.channel.socket.SocketChannel;
import io.netty.channel.socket.nio.NioserverSocketChannel;
import io.netty.channel.ChannelInitializer;
import org.slf4j.LoggerFactory;
import org.slf4j.Logger;
public class TcpServer
private Logger logger = LoggerFactory.getLogger(this.getClass());
private int port;
private final EventLoopGroup bossGroup; //处理Accept连接事件的线程
private final EventLoopGroup workerGroup; //处理handler的工作线程
public TcpServer(int port)
this.port = port;
this.bossGroup = new NioEventLoopGroup(1);
int cores = Runtime.getRuntime().availableProcessors();
this.workerGroup = new NioEventLoopGroup(cores);
public void start() throws Exception
try
ServerBootstrap serverBootstrap = new ServerBootstrap();
serverBootstrap.group(bossGroup, workerGroup);
serverBootstrap.channel(NioServerSocketChannel.class);
serverBootstrap.option(ChannelOption.SO_BACKLOG, 1024); //连接数
serverBootstrap.localAddress(this.port);
serverBootstrap.childOption(ChannelOption.SO_KEEPALIVE, true);
serverBootstrap.childHandler(new ChannelInitializer<SocketChannel>()
@Override
protected void initChannel(SocketChannel socketChannel) throws Exception
ChannelPipeline pipeline = socketChannel.pipeline();
pipeline.addLast(new PkgDecoder());
pipeline.addLast(new ServerHandler());
);
ChannelFuture channelFuture = serverBootstrap.bind().sync();
if (channelFuture.isSuccess())
logger.info("rpc server start success!");
else
logger.info("rpc server start fail!");
channelFuture.channel().closeFuture().sync();
catch (Exception ex)
logger.error("exception occurred exception=" + ex.getMessage());
finally
bossGroup.shutdownGracefully().sync(); // 释放线程池资源
workerGroup.shutdownGracefully().sync();
package com.naixue.server.entity;
/**
-
Created by zhuanzhuan on 2019/9/3.
*/
public class User
private long uid;
private short age;
private short sex;public long getUid()
return uid;
public User setUid(long uid)
this.uid = uid;
return this;
public short getAge()
return age;
public User setAge(short age)
this.age = age;
return this;
public short getSex()
return sex;
public User setSex(short sex)
this.sex = sex;
return this;
package com.naixue.server.protocol;
import com.naixue.server.entity.User;
import com.naixue.util.ByteConverter;
import java.io.*;
public class RpcProtocol
static public int CONST_CMD_MAGIC = 0x20110711;
private int version;
private int cmd;
public int magicNum;
private int bodyLen;
private byte[] body;
final public static int HEAD_LEN = 16;
public byte[] getBody()
return body;
public RpcProtocol setBody(byte[] body)
this.body = body;
return this;
public int getVersion()
return version;
public RpcProtocol setVersion(int version)
this.version = version;
return this;
public int getCmd()
return cmd;
public RpcProtocol setCmd(int cmd)
this.cmd = cmd;
return this;
public int getMagicNum()
return magicNum;
public RpcProtocol setMagicNum(int magicNum)
this.magicNum = magicNum;
return this;
public int getBodyLen()
return bodyLen;
public RpcProtocol setBodyLen(int bodyLen)
this.bodyLen = bodyLen;
return this;
public byte[] generateByteArray()
byte[] data = new byte[HEAD_LEN + bodyLen];
int index = 0;
System.arraycopy(ByteConverter.intToBytes(version), 0, data, index, Integer.BYTES);
index += Integer.BYTES;
System.arraycopy(ByteConverter.intToBytes(cmd), 0, data, index, Integer.BYTES);
index += Integer.BYTES;
System.arraycopy(ByteConverter.intToBytes(magicNum), 0, data, index, Integer.BYTES);
index += Integer.BYTES;
System.arraycopy(ByteConverter.intToBytes(bodyLen), 0, data, index, Integer.BYTES);
index += Integer.BYTES;
System.arraycopy(body, 0, data, index, body.length);
return data;
public RpcProtocol byteArrayToRpcHeader(byte[] data) throws IOException, ClassNotFoundException
if (data == null || data.length == 0)
return null;
int index = 0;
this.setVersion(ByteConverter.bytesToInt(data, index));
index += Integer.BYTES;
this.setCmd(ByteConverter.bytesToInt(data, index));
index += Integer.BYTES;
this.setMagicNum(ByteConverter.bytesToInt(data, index));
index += Integer.BYTES;
this.setBodyLen(ByteConverter.bytesToInt(data, index));
index += Integer.BYTES;
this.body = new byte[this.bodyLen];
System.arraycopy(data, index, this.body, 0, this.bodyLen);
return this;
public User byteArrayToUserInfo(byte[] data)
User user = new User();
int index = 0;
user.setUid(ByteConverter.bytesToLong(data, index));
index += Long.BYTES;
user.setAge(ByteConverter.bytesToShort(data, index));
index += Short.BYTES;
user.setSex(ByteConverter.bytesToShort(data, index));
index += Short.BYTES;
return user;
public byte[] userInfoTobyteArray(User info)
byte[] data = new byte[Long.BYTES + Short.BYTES + Short.BYTES];
int index = 0;
System.arraycopy(ByteConverter.longToBytes(info.getUid()), 0, data, index, Long.BYTES);
index += Long.BYTES;
System.arraycopy(ByteConverter.shortToBytes(info.getAge()), 0, data, index, Short.BYTES);
index += Short.BYTES;
System.arraycopy(ByteConverter.shortToBytes(info.getSex()), 0, data, index, Short.BYTES);
return data;
public static Object bytes2Object(byte[] objBytes) throws Exception
if (objBytes == null || objBytes.length == 0)
return null;
ByteArrayInputStream bi = new ByteArrayInputStream(objBytes);
ObjectInputStream oi = new ObjectInputStream(bi);
Object obj = oi.readObject();
bi.close();
oi.close();
return obj;
public static byte[] object2Bytes(Serializable obj) throws Exception
if (obj == null)
return null;
ByteArrayOutputStream bo = new ByteArrayOutputStream();
ObjectOutputStream oo = new ObjectOutputStream(bo);
oo.writeObject(obj);
bo.close();
oo.close();
return bo.toByteArray();
public byte[] createUserRespTobyteArray(int result)
byte[] data = new byte[Integer.BYTES];
int index = 0;
System.arraycopy(ByteConverter.intToBytes(result), 0, data, index, Integer.BYTES);
return data;
package com.naixue.server.server;
import com.naixue.server.entity.User;
import org.slf4j.Logger;
import org.slf4j.LoggerFactory;
/**
-
Created by chendong on 2019/9/3.
*/
public class UserService
private Logger logger = LoggerFactory.getLogger(this.getClass());public int addUser(User userinfo)
logger.debug(“create user success, uid=” + userinfo.getUid());
return 0;
package com.naixue;
import com.naixue.server.connect.TcpServer;
import org.slf4j.Logger;
import org.slf4j.LoggerFactory;
public class RpcServer
private static Logger logger = LoggerFactory.getLogger(RpcServer.class);
private static int SERVER_LISTEN_PORT = 58885;
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception
Thread tcpServerThread = new Thread("tcpServer")
public void run()
TcpServer tcpServer = new TcpServer(SERVER_LISTEN_PORT);
try
tcpServer.start();
catch (Exception e)
logger.info("TcpServer start exception: " + e.getMessage());
;
tcpServerThread.start();
tcpServerThread.join();
Flink内核原理学习组件通信RPC
Flink内核原理学习之 RPC
文章目录
一、Akka与Actor模型
Akka是用于开发并发、容错和可伸缩应用的框架(常用于RPC通信框架),是Actor模型的实现。每个Actor都是独立的,相互间通过发送异步消息进行通信(其强大之处就在于异步)。多个Actor构成一个ActorSystem,每个Actor顺序处理消息队列中的消息,ActorSystem中共享一个线程池(这也就是为什么不建议用同步调用的原因)。
ActorSystem能过识别消息发送给本地还是远程ActorSystem(路径)。Actor还有继承关系,父Actor可以创建子Actor(第一个Actor由ActorSystem创建),父Actor监督子Actor进行容错。
如上文所说,第一个Actor是ActorSystem创建的,另外,我们只能通过ActorRef(Actor的引用,对原生的Actor实例进行了封装,外界不能改变内部Actor状态)来于Actor进行通信。获取Actor需要通过其路径获得其ActorRef(显然远程通信需要在路径提供ip+端口号)。Actor的两种异步通信方法为tell和ack,tell是异步给某个Actor发送消息而不需要返回值;ack则是异步发送消息后,通过Future对象异步回调获取返回结果。
二、RPC消息类型
- 握手消息
RemoteHandshakeMessage: 与 Actor 握手消息
HandshakeSuccessMessage: 与 Actor 握手成功消息
- Fenced消息
LocalFencedMessage: 本地 Fence Token 消息,在同一个JVM中的调用
RemoteFencedMessage: 远程 Fence Token 消息,包括本地不同JVM和跨节点JVM调用
ps:Fenced消息用来防止JobManager内组件在HA模式下的集群脑裂问题,思想fencing机制在选举时维护一个ID,过期ID无效化。
- 调用消息(非Fenced):
LocalRpcInvocation: 本地RpcEndpoint 调用消息,同一个JVM内的调用
RemoteRpcInvocation: 远程RpcEndpoint 调用消息,包括本地不同JVM和跨节点JVM调用
- 执行消息(消息体中带有Runnable或Callable对象,让Actor执行)
三、Flink通信组件
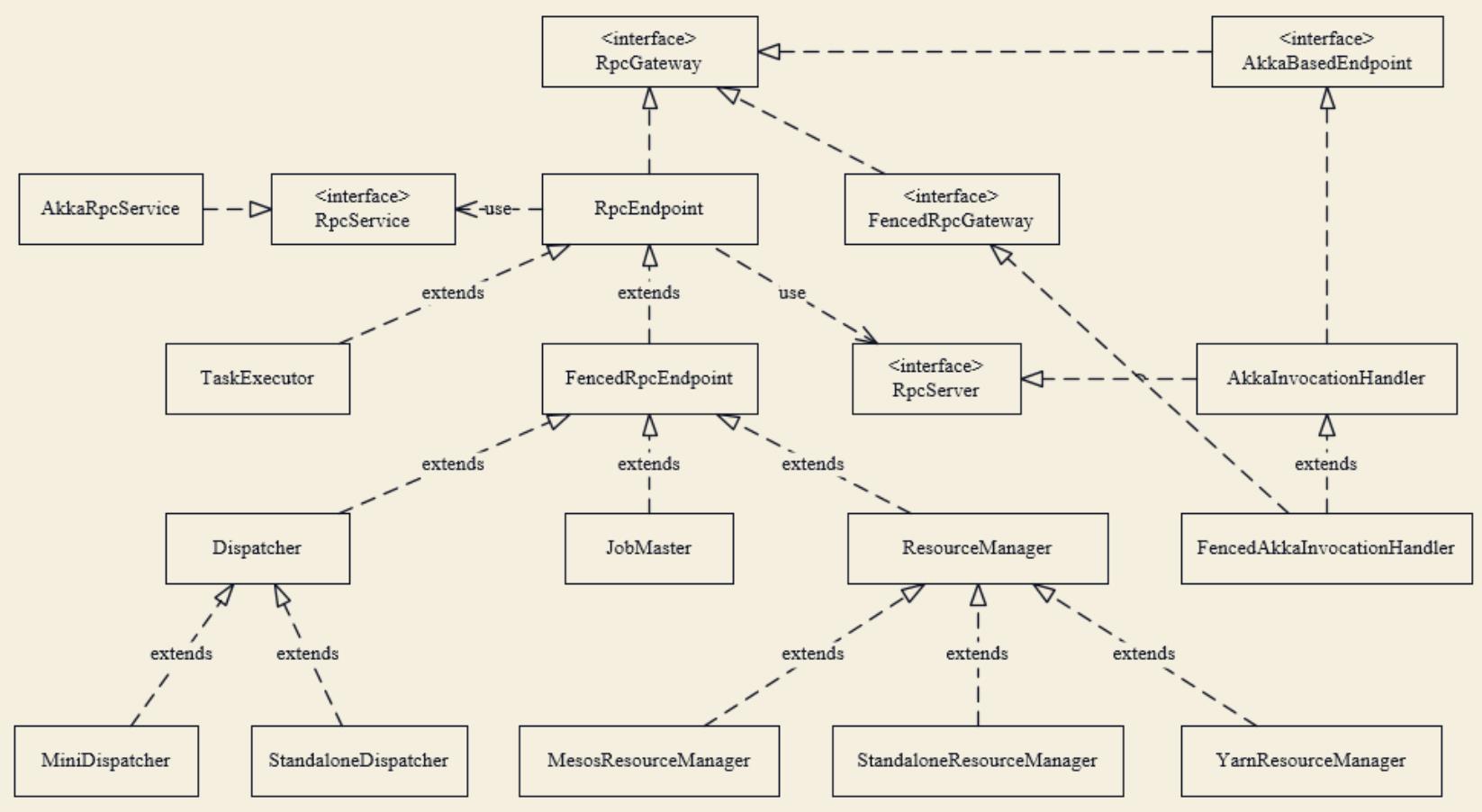
3.1 RpcGateway
Flink 的 RPC 协议通过 RpcGateway 来定义,主要定义通信行为(用于远程调用 RpcEndpoint 的某些方法),可以理解为对方的客服端代理。远程调用远端的Actor,则必须提供ip和端口号,这点在RpcGateway接口中也能看到。
3.2 RpcEndpoint
RpcEndpoint 是通信终端,提供 RPC 服务组件的生命周期管理(start、stop)。每个 RpcEndpoint 对应了一个路径(endpointId 和 actorSystem 共同确定),每个路径对应一个 Actor, 其实现了 RpcGateway 接口,其构造函数如下:
protected RpcEndpoint(final RpcService rpcService, final String endpointId)
// 保存 rpcService 和 endpointId
this.rpcService = checkNotNull(rpcService, "rpcService");
this.endpointId = checkNotNull(endpointId, "endpointId");
// 通过 RpcService 启动 RpcServer
this.rpcServer = rpcService.startServer(this);
// 主线程执行器,所有调用在主线程中串行执行
this.mainThreadExecutor = new MainThreadExecutor(rpcServer,
this::validateRunsInMainThread);
构造的时候调用 rpcService.startServer()启动 RpcServer,进入可以接收处理请求的状态, 最后将 RpcServer 绑定到主线程上真正执行起来。
值得注意的是在 Flink 的设计中,对于同一个 Endpoint,所有的调用都运行在主线程,因此不会有并发问题,当启动 RpcEndpoint进行 Rpc 调用时,其会委托 RcpServer 进行处理。
3.3 RpcService与RpcServer
RpcService 和 RpcServer 是 RpcEndPoint 的成员变量。
(1) RpcService 是 Rpc 服务的接口,其主要作用如下:
- 根据提供的RpcEndpoint来启动和停止RpcServer(Actor);
- 根据提供的地址连接到(对方的)RpcServer,并返回一个RpcGateway;
- 延迟/立刻调度Runnable、Callable;
在 Flink 中实现类为 AkkaRpcService,是 Akka 的 ActorSystem 的封装,基本可以理解成 ActorSystem 的一个适配器。在 ClusterEntrypoint(JobMaster)和 TaskManagerRunner (TaskExecutor)启动的过程中初始化并启动。
AkkaRpcService 中封装了 ActorSystem,并保存了 ActorRef 到 RpcEndpoint 的映射关系。 RpcService 跟 RpcGateway 类似,也提供了获取地址和端口的方法。
RpcService会根据 RpcEndpoint 类型(FencedRpcEndpoint 或其他)来创建不同的 AkkaRpcActor(FencedAkkaRpcActor 或 AkkaRpcActor),并将 RpcEndpoint 和 AkkaRpcActor 对应的 ActorRef 保存起来,AkkaRpcActor 是底层 Akka 调用的实际接收者,RPC 的请求在客户端被封装成 RpcInvocation 对象,以 Akka消息的形式发送。
(2) RpcServer 负责接收响应远端 RPC 消息请求,自身的代理对象。有两个实现:
- AkkaInvocationHandler
- FencedAkkaInvocationHandler
RpcServer 的启动是通知底层的 AkkaRpcActor 切换为 START 状态,开始处理远程调用请求:
class AkkaInvocationHandler implements InvocationHandler, AkkaBasedEndpoint, RpcServer @Override
public void start()
rpcEndpoint.tell(ControlMessages.START, ActorRef.noSender());
远程RPC请求最终使用动态代理将所有的消息转发到 InvocationHandler,具体代码如下:
public <C extends RpcEndpoint & RpcGateway> RpcServer startServer(C rpcEndpoint)
... ...
// 生成 RpcServer 对象,
//而后对该server的调用都会进入Handler的invoke方法处理,Handler实现了多个接口的方法
// 生成一个包含这些接口的代理,将调用转发到 InvocationHandler
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
RpcServer server = (RpcServer) Proxy.newProxyInstance(
classLoader,
implementedRpcGateways.toArray(new Class<?> [implementedRpcGateways.size()]),
akkaInvocationHandler);
return server;
3.4 AkkaRpcActor
AkkaRpcActor 是 Akka 的具体实现,主要负责处理如下类型消息:
- 本地 Rpc 调用 LocalRpcInvocation:
会指派给 RpcEndpoint 进行处理,如果有响应结果,则将响应结果返还给 Sender(发消息的Actor)。 - RunAsync & CallAsync:
这类消息带有可执行的代码,直接在 Actor 的线程中执行。 - 控制消息 ControlMessages:
用来控制 Actor 行为,START 启动,STOP 停止,停止后收到的消息会丢弃掉。
四、PRC交互过程
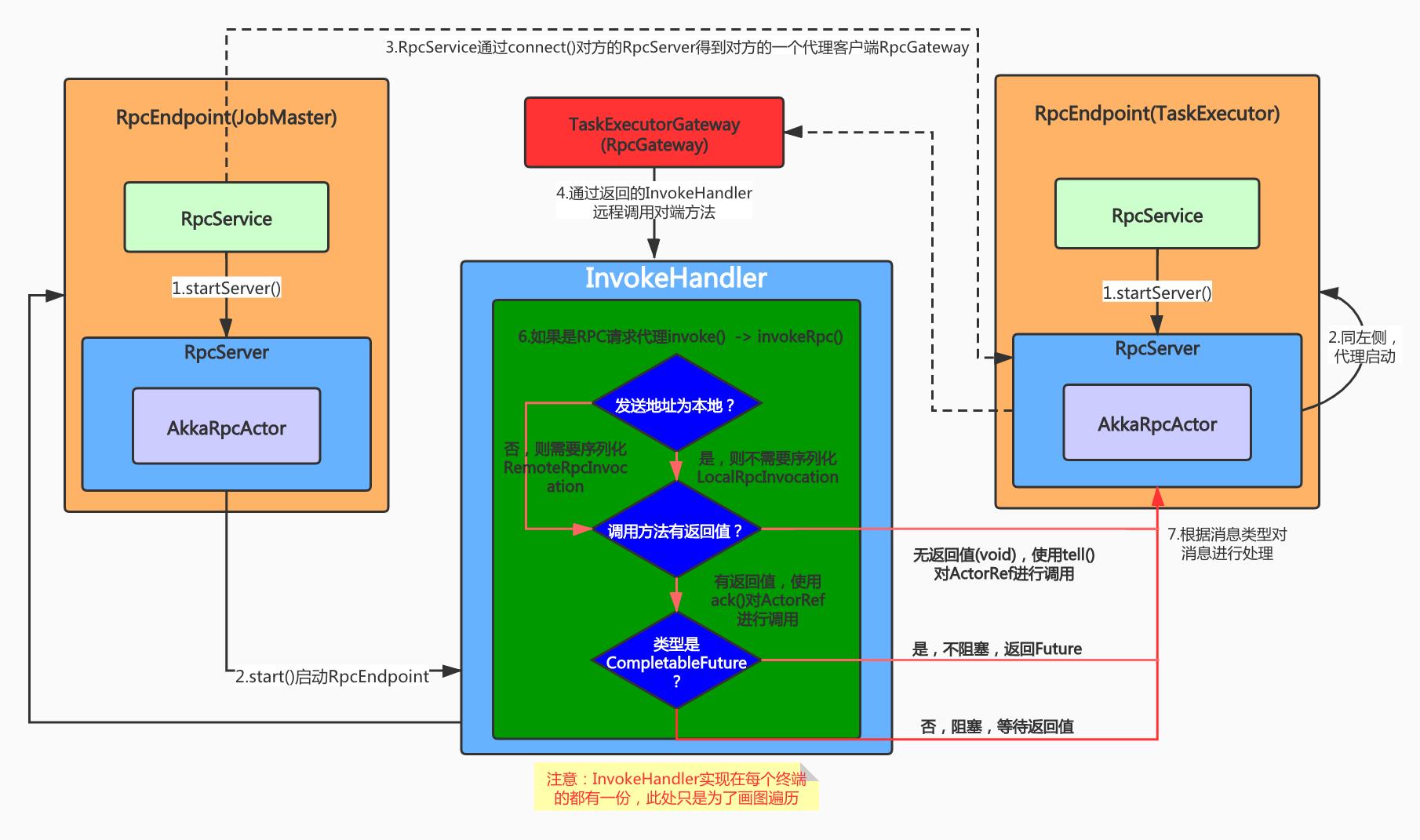
具体流程如下:
首先强调几点,第一,RpcService是在ClusterEntrypoint(JobMaster)、TaskManagerRunner(TaskExecutor)启动过程中就被初始化和启动了的;第二,在RpcEndpoint初始化时传入参数RpcService并由其启动RpcServer进而启动整个RpcEndpoint(实际是自己给自己发消息使得内部封装的Actor收到了START消息)。这个启动过程在上图中也有体现。
- 启动过程见强调的两点,主要就是RpcService是对ActorSystem的底层封装。RpcEndpoint封装了RpcService和RpcServer,提供Actor执行的单一线程。而RpcServer是Endpoint处理RPC请求的代理(代理的各种本地、远端消息请求),其代理实现类承接了消息解析和对底层Actor的消息通知的任务。
- 在组件的Endpoint启动后,发送RPC请求的Endpoint由RpcService向对端的RpcServer发送请求。对端RpcServer并不会直接处理请求消息而是返回一个Gateway(自身的一个客户端)。发送端通过此Gateway向对端RpcServer请求远程调用方法。
- 而Gateway中会有一个InvocationHandler(也就是对方的代理),其中的invoke()会对调用请求进行分析、对应的封装和处理。比如,首先判断是否为PRC方法调用,是则调用invokeRpc(),此方法将消息封装为RPCInvocation消息(本地就为LocalRPCInvocation,远程则为RemoteRpcInvocation);然后判断方法调用是否需要等待结果,如果无需等待(void)则向Actor发送tell类型的消息,如果需要返回结果则发送ack类型消息。
- 消息代理后正式通过RpcEndpoint绑定的ActorRef发送给AkkaRpcActor,内部封装的Actor根据不同消息类型进行相应的处理(第二节所提到的4种消息类型)。
以上是关于组件篇值RPC(上)的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章