JAVA:字符串详细
Posted 川川菜鸟
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了JAVA:字符串详细相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
一、字符串拼接
拼接a和b为c并输出:
package zifu;
public class zifu_1
public static void main(String[] args)
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
String a=new String("川川");
String b=new String("菜鸟");
String c=a+b;
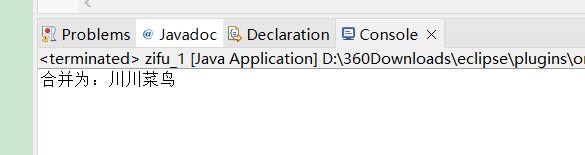
System.out.println("合并为:"+c);
演示:
二、字符与数字拼接
字符与数字拼接,数字会自动转换为字符:
package zifu;
public class zifu_2
public static void main(String[] args)
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
String a=new String("川川菜鸟");
int b=22;
float time=10000f;
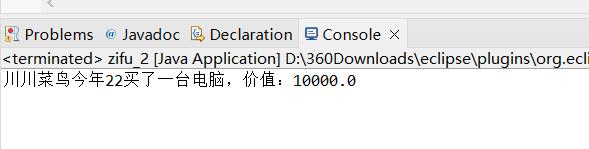
System.out.println(a+"今年"+b+"买了一台电脑,价值:"+time);
演示:
三、字符串相关信息获取
3.1长度获取
使用length函数:
package zifu;
public class zifu_3
public static void main(String[] args)
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
String a="川川菜鸟";
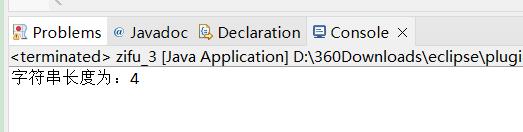
System.out.println("字符串长度为:"+a.length());
演示:
3.2索引位置获取
- 使用IndexOf方法,返回最先查找到的。
- lastIndexOf方法,返回最后查到的
例如以下的案例:
package zifu;
public class zifu_4
public static void main(String[] args)
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
String s=new String("川川菜鸟");
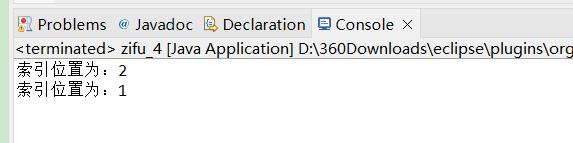
System.out.println("索引位置为:"+s.indexOf("菜"));
System.out.println("索引位置为:"+s.lastIndexOf("川"));
演示:
3.3索引位置的字符
- char.charAt(num),返回索引位置为num出的字符。
例如以下的案例:
package zifu;
public class zifu_4
public static void main(String[] args)
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
String s=new String("川川菜鸟");
// System.out.println("索引位置为:"+s.indexOf("菜"));
// System.out.println("索引位置为:"+s.lastIndexOf("川"));
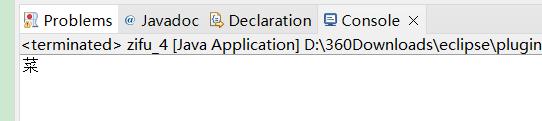
char a=s.charAt(2);
System.out.println(a);
演示:
3.4空格去除
trim()方法可以去除字符串的前面与后面的空格部分,不能去除中间。例如下面案例:
package zifu;
public class zifu_5
public static void main(String[] args)
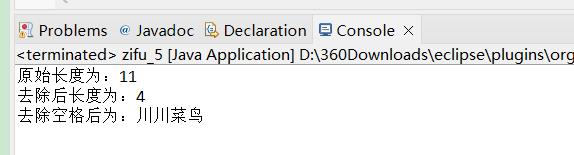
String s=new String(" 川川菜鸟 ");
String s2=s.trim();
System.out.println("原始长度为:"+s.length());
System.out.println("去除后长度为:"+s2.length());
System.out.println("去除空格后为:"+s2);
演示:
剔除全部的空格用replaceAll()方法,例如下面案例:
package zifu;
public class zifu_6
public static void main(String[] args)
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
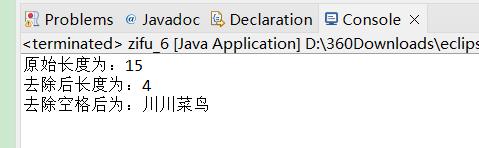
String s=new String(" 川川 菜鸟 ");
System.out.println("原始长度为:"+s.length());
s=s.replaceAll(" ","");
System.out.println("去除后长度为:"+s.length());
System.out.println("去除空格后为:"+s);
演示:
四、字符串替换
使用方法:replace()
语法:

例如:替换“菜鸟”为“帅哥”
package zifu;
public class zifu_7
public static void main(String[] args)
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
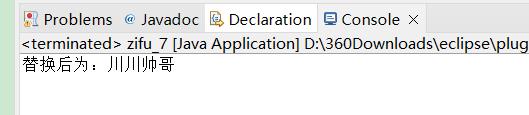
String s=new String("川川菜鸟");//创建原始字符串
String s2=s.replace("菜鸟", "帅哥");
System.out.println("替换后为:"+s2);
演示:
替换第一个出现的字符,使用方法replaceFirst,例如:替换第一个”菜“为”小”
package zifu;
public class zifu_8
public static void main(String[] args)
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
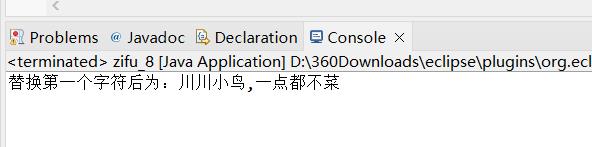
String s=new String("川川菜鸟,一点都不菜");//创建原始字符串
String s2=s.replaceFirst("菜", "小");
System.out.println("替换第一个字符后为:"+s2);
演示:
五、字符串判断
5.1是否相等
使用equals,语法:

案例如下:
package zifu;
public class zifu_9
public static void main(String[] args)
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
String a=new String("川川");
String b=new String("川川");
if(a.equals(b))
System.out.println("相等");
else
System.out.println("不相等");
5.2开始和结尾判断
- endWith,以什么结尾
- startsWith,以什么开始
案例:
package zifu;
public class zifu_10
public static void main(String[] args)
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
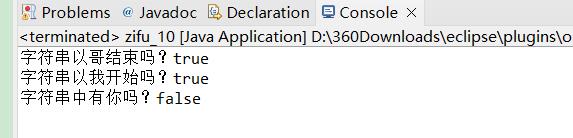
String a="我爱川川,川川帅哥";
System.out.println("字符串以哥结束吗?"+a.endsWith("哥"));
System.out.println("字符串以我开始吗?"+a.startsWith("我"));
System.out.println("字符串中有你吗?"+a.startsWith("你"));
演示:
六、大小写转换
案例:对变量a的字符串进行大小写转换
package zifu;
public class zifu_11
public static void main(String[] args)
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
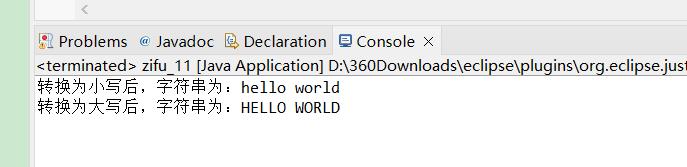
String a="Hello World";
a=a.toLowerCase();
String b=a.toUpperCase();
System.out.println("转换为小写后,字符串为:"+a);
System.out.println("转换为大写后,字符串为:"+b);
演示:
七、字符串分割
使用split()方法,内部传入分隔符。
案例如下:
package zifu;
public class zifu_12
public static void main(String[] args)
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
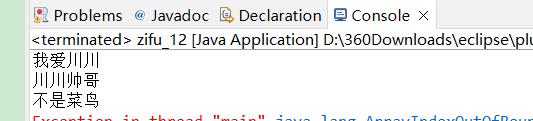
String s=new String("我爱川川,川川帅哥,不是菜鸟");
String[] s2=s.split(",");
for(int i=0;i<s.length();i++)
System.out.println(s2[i]);
演示:
 CSDN 社区图书馆,开张营业!
CSDN 社区图书馆,开张营业!
 深读计划,写书评领图书福利~
深读计划,写书评领图书福利~
以上是关于JAVA:字符串详细的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章