线程池的使用(7种创建方法)
Posted Youcan.
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了线程池的使用(7种创建方法)相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
目录
c. scheduleAtFixedRate VS scheduleWithFixedDelay
线程池的创建⽅法总共有 7 种,但总体来说可分为 2 类:
1. 通过 ThreadPoolExecutor 创建的线程池; 2. 通过 Executors 创建的线程池。线程池的创建⽅式总共包含以下 7 种(其中 6 种是通过 Executors 创建的, 1 种是通过 ThreadPoolExecutor 创建的):
1. Executors.newFixedThreadPool:创建⼀个固定⼤⼩的线程池,可控制并发的线程数,超出的线程会在队列中等待; 2. Executors.newCachedThreadPool:创建⼀个可缓存的线程池,若线程数超过处理所需,缓存⼀段时间后会回收,若线程数不够,则新建线程; 3. Executors.newSingleThreadExecutor:创建单个线程数的线程池,它可以保证先进先出的执⾏顺序; 4. Executors.newScheduledThreadPool:创建⼀个可以执⾏延迟任务的线程池; 5. Executors.newSingleThreadScheduledExecutor:创建⼀个单线程的可以执⾏延迟任务的线程池; 6. Executors.newWorkStealingPool:创建⼀个抢占式执⾏的线程池(任务执⾏顺序不确定)【JDK1.8 添加】。 7. ThreadPoolExecutor:最原始的创建线程池的⽅式,它包含了 7 个参数可供设置,后⾯会详细讲。
1. 固定数量的线程池
public class ThreadPoolDemo3
public static void main(String[] args)
ExecutorService threadPool = Executors.newFixedThreadPool(2);
//添加任务方式 1
threadPool.submit(new Runnable()
@Override
public void run()
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName());
);
//添加任务方式2
threadPool.execute(new Runnable()
@Override
public void run()
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName());
);
输出:
pool-1-thread-1
pool-1-thread-2a. 线程池返回结果
public class ThreadPoolDemo4
public static void main(String[] args) throws ExecutionException, InterruptedException
ExecutorService threadPool = Executors.newFixedThreadPool(2);
//执行任务
Future<Integer> result = threadPool.submit(new Callable<Integer>()
@Override
public Integer call() throws Exception
int num = new Random().nextInt(10);
System.out.println("随机数" + num);
return num;
);
//打印线程池返回方式
System.out.println("返回结果:" + result.get());
输出
随机数8
返回结果:8使用submit可以执行有返回值的任务或者是无返回值的任务;而execute只能执行不带返回值的任务。
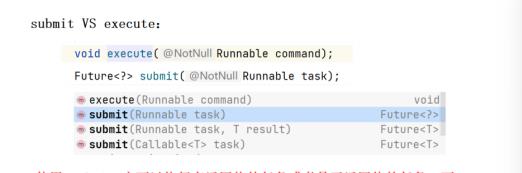
b. ⾃定义线程池名称或优先级
public class ThreadPoolDemo5
public static void main(String[] args) throws ExecutionException, InterruptedException
// 创建线程工厂
ThreadFactory threadFactory = new ThreadFactory()
@Override
public Thread newThread(Runnable r)
//!!!!!!!一定要注意:要把任务Runnable设置给新创建的线程
Thread thread = new Thread(r);
//设置线程的命名规则
thread.setName("我的线程" + r.hashCode());
//设置线程的优先级
thread.setPriority(Thread.MAX_PRIORITY);
return thread;
;
ExecutorService threadPool = Executors.newFixedThreadPool(2,threadFactory);
//执行任务1
Future<Integer> result = threadPool.submit(new Callable<Integer>()
@Override
public Integer call() throws Exception
int num = new Random().nextInt(10);
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getPriority() + ", 随机数:" + num);
return num;
);
//打印线程池返回结果
System.out.println("返回结果:" + result.get());
提供的功能:
1. 设置(线程池中)线程的命名规则。
2. 设置线程的优先级。
3. 设置线程分组。
4. 设置线程类型(用户线程、守护线程)。
2. 带缓存的线程池
public class ThreadPoolDemo6
public static void main(String[] args)
//创建线程池
ExecutorService service = Executors.newCachedThreadPool();
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++)
int finalI = i;
service.submit(() ->
System.out.println("i : " + finalI + "|线程名称:" + Thread.currentThread().getName());
);
输出
i : 1|线程名称:pool-1-thread-2
i : 4|线程名称:pool-1-thread-5
i : 3|线程名称:pool-1-thread-4
i : 5|线程名称:pool-1-thread-6
i : 0|线程名称:pool-1-thread-1
i : 2|线程名称:pool-1-thread-3
i : 6|线程名称:pool-1-thread-7
i : 7|线程名称:pool-1-thread-8
i : 8|线程名称:pool-1-thread-9
i : 9|线程名称:pool-1-thread-1优点:线程池会根据任务数量创建线程池,并且在一定时间内可以重复使用这些线程,产生相应的线程池。
缺点:适用于短时间有大量任务的场景,它的缺点是可能会占用很多的资源。
3. 执⾏定时任务
a. 延迟执⾏(⼀次)
public class ThreadPoolDemo7
public static void main(String[] args)
//创建线程池
ScheduledExecutorService service = Executors.newScheduledThreadPool(5);
System.out.println("添加任务的时间:" + LocalDateTime.now());
//执行定时任务(延迟3s执行)只执行一次
service.schedule(new Runnable()
@Override
public void run()
System.out.println("执行子任务:" + LocalDateTime.now());
,3, TimeUnit.SECONDS);
输出
添加任务的时间:2022-04-13T14:19:39.983
执行子任务:2022-04-13T14:19:42.987
b. 固定频率执⾏
public class ThreadPoolDemo8
public static void main(String[] args)
//创建线程池
ScheduledExecutorService service = Executors.newScheduledThreadPool(5);
System.out.println("添加任务时间:" + LocalDateTime.now());
//2s之后开始执行定时任务,定时任务每隔4s执行一次
service.scheduleAtFixedRate(new Runnable()
@Override
public void run()
System.out.println("执行任务:" + LocalDateTime.now());
,2,4, TimeUnit.SECONDS);
输出
添加任务时间:2022-04-13T14:24:38.810
执行任务:2022-04-13T14:24:40.814
执行任务:2022-04-13T14:24:44.814
执行任务:2022-04-13T14:24:48.813
执行任务:2022-04-13T14:24:52.815
执行任务:2022-04-13T14:24:56.813
执行任务:2022-04-13T14:25:00.813
执行任务:2022-04-13T14:25:04.814
执行任务:2022-04-13T14:25:08.813
... ...
... ...
执行任务:2022-04-13T14:26:44.814
执行任务:2022-04-13T14:26:48.813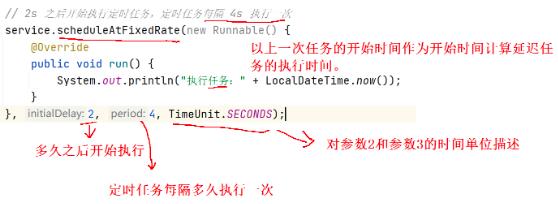
注意事项:
public class ThreadPoolDemo9
public static void main(String[] args)
//创建线程池
ScheduledExecutorService service = Executors.newScheduledThreadPool(5);
System.out.println("添加任务时间:" + LocalDateTime.now());
service.scheduleAtFixedRate(new Runnable()
@Override
public void run()
System.out.println("执行任务: " + LocalDateTime.now());
try
Thread.sleep(5 * 1000);
catch (InterruptedException e)
e.printStackTrace();
,2,4, TimeUnit.SECONDS);
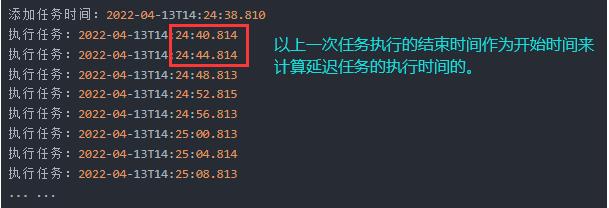
输出
添加任务时间:2022-04-13T14:33:34.551
执行任务: 2022-04-13T14:33:36.556
执行任务: 2022-04-13T14:33:41.557
执行任务: 2022-04-13T14:33:46.559
执行任务: 2022-04-13T14:33:51.561
执行任务: 2022-04-13T14:33:56.562
执行任务: 2022-04-13T14:34:01.564
执行任务: 2022-04-13T14:34:06.566
执行任务: 2022-04-13T14:34:11.566
执行任务: 2022-04-13T14:34:16.567
执行任务: 2022-04-13T14:34:21.570
执行任务: 2022-04-13T14:34:26.570
... ....

c. scheduleAtFixedRate VS scheduleWithFixedDelay
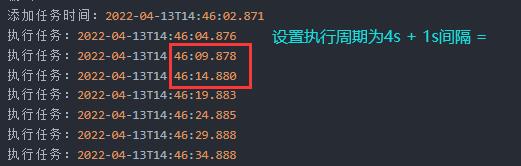
scheduleAtFixedRate 是以上⼀次任务的开始时间,作为下次定时任务的参考时间的(参考时间+延迟任务=任务执⾏)。 scheduleWithFixedDelay 是以上⼀次任务的结束时间,作为下次定时任务的参考时间的。
public class ThreadPoolDemo10
public static void main(String[] args)
//创建线程池
ScheduledExecutorService service = Executors.newScheduledThreadPool(5);
System.out.println("添加任务时间:" + LocalDateTime.now());
//2s之后开始执行定时任务,定时任务每隔4s执行一次
service.scheduleWithFixedDelay(new Runnable()
@Override
public void run()
System.out.println("执行任务:" + LocalDateTime.now());
try
Thread.sleep(1000);
catch (InterruptedException e)
e.printStackTrace();
, 2, 4, TimeUnit.SECONDS);
输出
添加任务时间:2022-04-13T14:46:02.871
执行任务:2022-04-13T14:46:04.876
执行任务:2022-04-13T14:46:09.878
执行任务:2022-04-13T14:46:14.880
执行任务:2022-04-13T14:46:19.883
执行任务:2022-04-13T14:46:24.885
执行任务:2022-04-13T14:46:29.888
执行任务:2022-04-13T14:46:34.888
执行任务:2022-04-13T14:46:39.891
执行任务:2022-04-13T14:46:44.893
执行任务:2022-04-13T14:46:49.895
执行任务:2022-04-13T14:46:54.897
执行任务:2022-04-13T14:46:59.900
执行任务:2022-04-13T14:47:04.901
... ...
4. 定时任务单线程
public class ThreadPoolDemo11
public static void main(String[] args)
ScheduledExecutorService service = Executors.newSingleThreadScheduledExecutor();
System.out.println("添加任务的时间:" + LocalDateTime.now());
service.schedule(new Runnable()
@Override
public void run()
System.out.println("执行时间:" + LocalDateTime.now());
,2, TimeUnit.SECONDS );
输出
添加任务的时间:2022-04-13T15:06:38.100
执行时间:2022-04-13T15:06:40.1065. 单线程线程池
public class ThreadPoolDemo12
public static void main(String[] args)
ExecutorService service = Executors.newSingleThreadScheduledExecutor();
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++)
service.submit(new Runnable()
@Override
public void run()
System.out.println("线程名:" + Thread.currentThread().getName());
);
输出
线程名:pool-1-thread-1
线程名:pool-1-thread-1
线程名:pool-1-thread-1
线程名:pool-1-thread-1
线程名:pool-1-thread-1
线程名:pool-1-thread-1
线程名:pool-1-thread-1
线程名:pool-1-thread-1
线程名:pool-1-thread-1
线程名:pool-1-thread-1
(MS) 为什么不直接用线程?
单线程的线程池又什么意义?
1. 复用线程。
2. 单线程的线程池提供了任务队列和拒绝策略(当任务队列满了之后(Integer.MAX_VALUE),新来的任务就会拒绝策略)
6. 根据当前CPU⽣成线程池
public class ThreadPoolDemo13
public static void main(String[] args)
ExecutorService service = Executors.newWorkStealingPool();
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++)
service.submit(() ->
System.out.println("线程名" + Thread.currentThread().getName());
);
while(!service.isTerminated())
输出
线程名ForkJoinPool-1-worker-17. ThreadPoolExecutor
线程池的使用(7种创建方法)_Youcan.的博客-CSDN博客 https://blog.csdn.net/m0_48273471/article/details/124171220
https://blog.csdn.net/m0_48273471/article/details/124171220
java线程池之一:创建线程池的方法
在Java开发过程中经常需要用到线程,为了减少资源的开销,提高系统性能,Java提供了线程池,即事先创建好线程,如果需要使用从池中取即可,Java中创建线程池有以下的方式,
1、使用ThreadPoolExecutor类
2、使用Executors类
其实这两种方式在本质上是一种方式,都是通过ThreadPoolExecutor类的方式,下面分析其使用方式。
一、ThreadPoolExecutor的方式
1、使用方法
查看JDK的源码,ThreadPoolExecutor类提供了以下构造方法,
可以看到有四个构造方法,先看第一个构造方法,其代码如下,
public ThreadPoolExecutor(int corePoolSize,int maximumPoolSize,long keepAliveTime,TimeUnit unit,BlockingQueue<Runnable> workQueue) {this(corePoolSize, maximumPoolSize, keepAliveTime, unit, workQueue,Executors.defaultThreadFactory(), defaultHandler);}
从上面的代码中可以确定,我们需要传的参数有corePoolSize、maximumPoolSize、keepAliveTime、unit、workQueue
下面对这几个参数进行说明
corePoolSize:线程池的核心线程数;
maximumPoolSize:线程池的最大线程数;
keepAliveTime:线程池空闲时线程的存活时长;
unit:线程存活时长大单位,结合上个参数使用;
workQueue:存放任务的队列,使用的是阻塞队列;
在这个方法中调用了另外的一个构造方法,即上图中四个构造方法中的第四个,从源码中得知,一个线程池包含的属性共有corePoolSize、maximumPoolSize、keepAliveTime、unit、workQueue、threadFactory、handler七个,上面说到了五个,下面是其他两个的含义,
threadFactory:线程池创建线程的工厂;
handler:在队列(workQueue)和线程池达到最大线程数(maximumPoolSize)均满时仍有任务的情况下的处理方式;
上面的七个参数,也即ThreadPoolExecutor的第四个构造方法需要的参数。
我们再来看中间的两个构造方法,和第一个的区别在于,第二个和第三个指定了创建线程的工厂和线程池满时的处理策略。
通过上面的方式便创建了线程池
二、Executors的方式
1、使用方法
Executors类提供了下面的构造方法,
可以看到提供了约10个的构造方法,但是发现其方法返回值为ExecutorService,这不是我们要的ThreadPoolExecutor那,别急,看下ExecutorService这个类是什么,
其源码如下,

其是一个接口,和ThreadPoolExecutor没什么关系那,不对,可以大胆猜想下,ThreaPoolExecutor可以实现接口,验证下我们的猜想,
ThreadPoolExecutor继承了AbstractExecutorService
AbstractExecutorService抽象类实现了ExecutorService接口,那么ThreadPoolExcutor和ExecutorService就有了关系。
我们再挑选ExecutorService中的方法看下其具体实现,
public static ExecutorService newFixedThreadPool(int nThreads) {return new ThreadPoolExecutor(nThreads, nThreads,0L, TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS,new LinkedBlockingQueue<Runnable>());}
从上面的代码中可以看出,其返回的是ThreaPoolExecutor对象,调用的是ThreaPoolExecutor类四个构造方法中的第一个。
总结,上面两种创建线程池的方式,其本质都是通过ThreaPoolExecutor类的构造方法的方式,所以ThreaPoolExecutor是重点。
以上是关于线程池的使用(7种创建方法)的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章