SSMMyBatis(九.查询语句专题)
Posted Beyong2019
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了SSMMyBatis(九.查询语句专题)相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
文章目录
1.返回Car
CarMapper.xml
<select id="selectById" resultType="Car">
select
id,
car_num as carNum,
brand,
guide_price as guidePrice,
produce_time as produceTime,
car_type as carType
from
t_car
where
id = #id
</select>
2.返回List< Car >
CarMapper.xml
<select id="selectAll" resultType="Car">
select
id,
car_num as carNum,
brand,
guide_price as guidePrice,
produce_time as produceTime,
car_type as carType
from
t_car
</select>
3.返回map集合
CarMapper.xml
<select id="selectByIdRetMap" resultType="map">
select * from t_car where id = #id
</select>
4.返回List< Map >
CarMapper.xml
<select id="selectAllRetListMap" resultType="map">
select * from t_car
</select>
CarMapper.java
List<Map<String, Object>> selectAllRetListMap();
5. 返回Map<String, Map>
CarMapper.xml
<select id="selectAllRetMap" resultType="map">
select * from t_car
</select>
CarMapper.java
/**
* 返回大Map集合,
* 大Map集合的key为每一条记录的主键值,
* value为每一条记录
* @return
*/
@MapKey("id") //将结果的id 作为大Map集合的key
Map<Long, Map<String, Object>> selectAllRetMap();
6.结果映射
查询结果的列名和java对象的属性名对应不上怎么办?
● 第一种方式:as 给列起别名
● 第二种方式:使用resultMap进行结果映射
● 第三种方式:是否开启驼峰命名自动映射(配置settings)
6.1 使用resultMap
CarMapper.xml
<!--
resultMap:
id:这个结果映射的标识,作为select标签的resultMap属性的值。
type:结果集要映射的类。可以使用别名。
-->
<resultMap id="carResultMap" type="Car">
<!--对象的唯一标识,官方解释是:为了提高mybatis的性能。建议写上。-->
<id property="id" column="id"/>
<result property="carNum" column="car_num"/>
<!--当属性名和数据库列名一致时,可以省略。但建议都写上。-->
<!--javaType用来指定属性类型。jdbcType用来指定列类型。一般可以省略。-->
<result property="brand" column="brand" javaType="string" jdbcType="VARCHAR"/>
<result property="guidePrice" column="guide_price"/>
<result property="produceTime" column="produce_time"/>
<result property="carType" column="car_type"/>
</resultMap>
<select id="selectAllByResultMap" resultMap="carResultMap">
select * from t_car
</select>
CarMapper.java
List<Car> selectAllByResultMap();
6.2 开启驼峰命名
在mybatis-config.xml文件中进行配置:
<!--放在properties标签后面-->
<settings>
<setting name="mapUnderscoreToCamelCase" value="true"/>
</settings>
7.返回总记录条数
CarMapper.xml
<select id="selectTotal" resultType="long">
select count(*) from t_car
</select>
SSMMybatis配置缓存
1.在没有配置的情况下,mybatis默认开启一级缓存。
1 Object object=mapper.getXxx(object); 2 Object object2=mapper.getXxx(object);
打个断点测试一下就知道了。
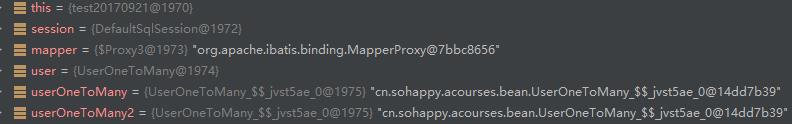
在同一个SqlSession中,第一次查询后,调用mapper相同方法,SqlSession会从一级缓存中取数据,而且得到的是相同的对象。不会发送SQL。
如果SqlSession进行了提交,那么一级缓存将会清除。
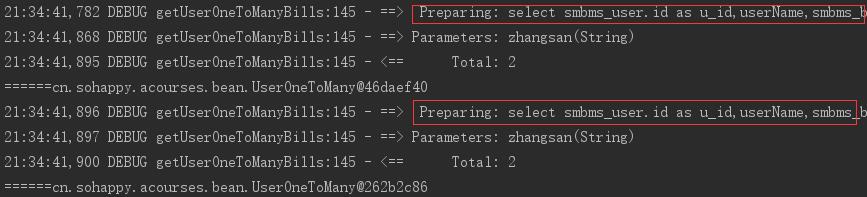
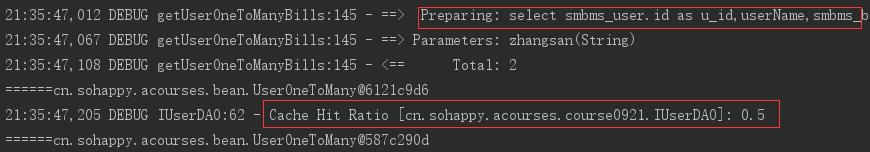
1 public void test(){ 2 SqlSession session = MyBatisUtil.getSession(); 3 IUserDAO mapper = session.getMapper(IUserDAO.class); 4 UserOneToMany user = new UserOneToMany(); 5 user.setUsercode("zhangsan"); 6 UserOneToMany userOneToMany = mapper.getUserOneToManyBills(user); 7 System.out.println("======"+userOneToMany); 8 session.commit(); 9 UserOneToMany userOneToMany2 = mapper.getUserOneToManyBills(user); 10 System.out.println("======"+userOneToMany2); 11 session.close(); 12 }
打印结果不同,且发送了两次SQL,获得了两个不同的对象:
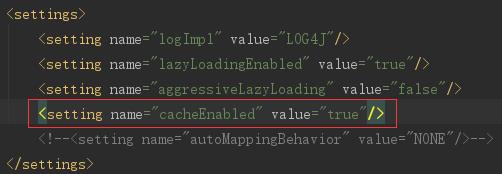
2.MyBatis开启二级缓存第一步:大配置中settings节点加入:<setting name="cacheEnabled" value="true"/>
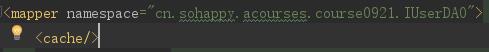
第二步:命名空间加入节点:<cache/>
这里<cache/>节点可以设置得更详细些,比如:
<cache eviction="LRU" flushInterval="100000" size="1024" readOnly="true"/>
其中eviction代表回收策略(LRU|FIFO|SOFT|WEAK);flushInterval代表刷新间隔时间,单位是毫秒;size是引用数目,就是缓存中可以存放多少个对象;readOnly只读,缓存只能读取不能修改。
简单说明下四个回收策略:
1.LRU(默认):最近最少使用,移除最长时间不用的对象。
2.FIFO:先进先出,按对象进入缓存的顺序移除它们。
3.SOFT:软引用,移除基于垃圾回收器状态和软引用规则的对象。
4.WEAK:弱引用,移除基于垃圾回收器状态和弱引用规则的对象。
第三步:相应实体类实现Serializable接口


测试方法不变,观察结果:

首先,程序只发送了一次SQL。其次,第二次取到的数据是从缓存中获得的,同样获取的是两个不同的对象。
以上是关于SSMMyBatis(九.查询语句专题)的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章