运筹系列17:routing模型之CVRP问题
Posted IE06
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了运筹系列17:routing模型之CVRP问题相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
1. CVRP模型
CVRP指的是有容量(capacity)限制的VRP模型,是最常见的VRP模型。
2. 示例
依旧用上一章节的点,不同的是每个点多了一个送货需求。每辆车的最大容量是15,最小化总运输距离。
dimension可以使用AddDimensionWithVehicleCapacity方法,和AddDimension唯一的区别就是,第三个参数从一个固定值变成了一个列表,表示每一辆车有自己单独的最大容量限制。

from __future__ import print_function
from ortools.constraint_solver import pywrapcp
from ortools.constraint_solver import routing_enums_pb2
###########################
# Problem Data Definition #
###########################
def create_data_model():
"""Stores the data for the problem"""
data =
# Locations in block units
_locations = \\
[(4, 4), # depot
(2, 0), (8, 0), # locations to visit
(0, 1), (1, 1),
(5, 2), (7, 2),
(3, 3), (6, 3),
(5, 5), (8, 5),
(1, 6), (2, 6),
(3, 7), (6, 7),
(0, 8), (7, 8)]
demands = [0, # depot
1, 1, # row 0
2, 4,
2, 4,
8, 8,
1, 2,
1, 2,
4, 4,
8, 8]
capacities = [15, 15, 15, 15]
# Multiply coordinates in block units by the dimensions of an average city block, 114m x 80m,
# to get location coordinates.
data["locations"] = [(l[0] * 114, l[1] * 80) for l in _locations]
data["num_locations"] = len(data["locations"])
data["num_vehicles"] = 4
data["depot"] = 0
data["demands"] = demands
data["vehicle_capacities"] = capacities
return data
#######################
# Problem Constraints #
#######################
def manhattan_distance(position_1, position_2):
"""Computes the Manhattan distance between two points"""
return (
abs(position_1[0] - position_2[0]) + abs(position_1[1] - position_2[1]))
def create_distance_callback(data):
"""Creates callback to return distance between points."""
_distances =
for from_node in range(data["num_locations"]):
_distances[from_node] =
for to_node in range(data["num_locations"]):
if from_node == to_node:
_distances[from_node][to_node] = 0
else:
_distances[from_node][to_node] = (
manhattan_distance(data["locations"][from_node],
data["locations"][to_node]))
def distance_callback(from_node, to_node):
"""Returns the manhattan distance between the two nodes"""
return _distances[from_node][to_node]
return distance_callback
def create_demand_callback(data):
"""Creates callback to get demands at each location."""
def demand_callback(from_node, to_node):
return data["demands"][from_node]
return demand_callback
def add_capacity_constraints(routing, data, demand_callback):
"""Adds capacity constraint"""
capacity = "Capacity"
routing.AddDimensionWithVehicleCapacity(
demand_callback,
0, # null capacity slack
data["vehicle_capacities"], # vehicle maximum capacities
True, # start cumul to zero
capacity)
###########
# Printer #
###########
def print_solution(data, routing, assignment):
"""Print routes on console."""
total_dist = 0
for vehicle_id in range(data["num_vehicles"]):
index = routing.Start(vehicle_id)
plan_output = 'Route for vehicle 0:\\n'.format(vehicle_id)
route_dist = 0
route_load = 0
while not routing.IsEnd(index):
node_index = routing.IndexToNode(index)
next_node_index = routing.IndexToNode(assignment.Value(routing.NextVar(index)))
route_dist += manhattan_distance(
data["locations"][node_index],
data["locations"][next_node_index])
route_load += data["demands"][node_index]
plan_output += ' 0 Load(1) -> '.format(node_index, route_load)
index = assignment.Value(routing.NextVar(index))
node_index = routing.IndexToNode(index)
total_dist += route_dist
plan_output += ' 0 Load(1)\\n'.format(node_index, route_load)
plan_output += 'Distance of the route: 0m\\n'.format(route_dist)
plan_output += 'Load of the route: 0\\n'.format(route_load)
print(plan_output)
print('Total Distance of all routes: 0m'.format(total_dist))
########
# Main #
########
def main():
"""Entry point of the program"""
# Instantiate the data problem.
data = create_data_model()
# Create Routing Model
routing = pywrapcp.RoutingModel(
data["num_locations"],
data["num_vehicles"],
data["depot"])
# Define weight of each edge
distance_callback = create_distance_callback(data)
routing.SetArcCostEvaluatorOfAllVehicles(distance_callback)
# Add Capacity constraint
demand_callback = create_demand_callback(data)
add_capacity_constraints(routing, data, demand_callback)
# Setting first solution heuristic (cheapest addition).
search_parameters = pywrapcp.RoutingModel.DefaultSearchParameters()
search_parameters.first_solution_strategy = (
routing_enums_pb2.FirstSolutionStrategy.PATH_CHEAPEST_ARC)
# Solve the problem.
assignment = routing.SolveWithParameters(search_parameters)
if assignment:
print_solution(data, routing, assignment)
if __name__ == '__main__':
main()
输出为:

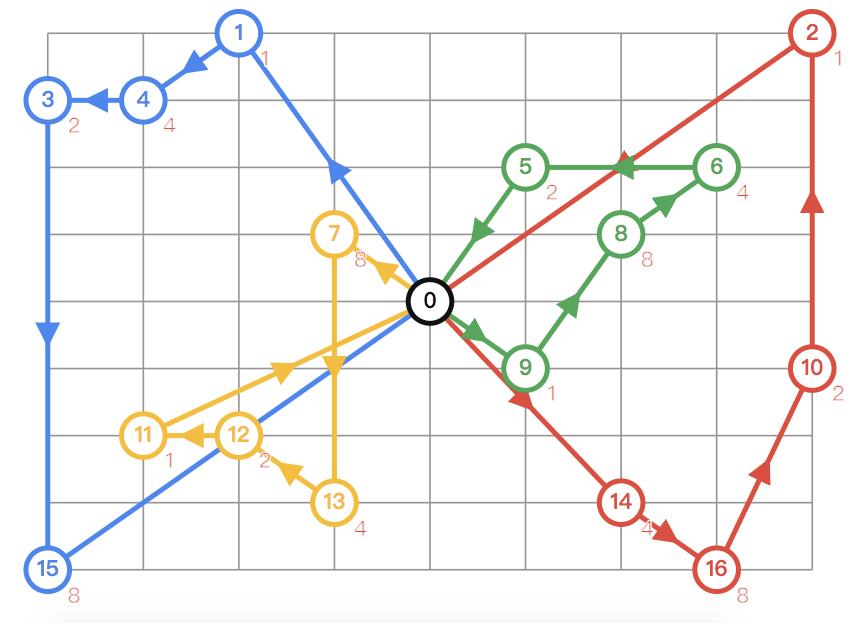
结果如下图:
 开发者涨薪指南
开发者涨薪指南
 48位大咖的思考法则、工作方式、逻辑体系
48位大咖的思考法则、工作方式、逻辑体系
以上是关于运筹系列17:routing模型之CVRP问题的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章