scikit-opt的使用
Posted Harris-H
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了scikit-opt的使用相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
scikit-opt的使用
一个封装了7种启发式算法的 Python 代码库
(差分进化算法、遗传算法、粒子群算法、模拟退火算法、蚁群算法、鱼群算法、免疫优化算法)
0.安装
pip install scikit-opt
或者直接把源代码中的 sko 文件夹下载下来放本地也调用可以
1.差分进化算法(DE)
(Differential Evolution Algorithm,DE)
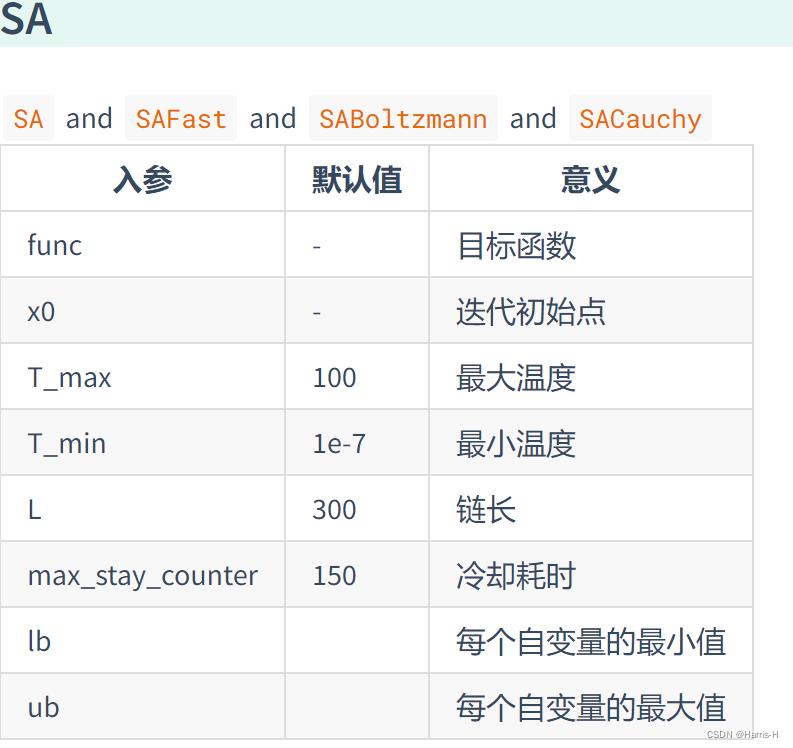
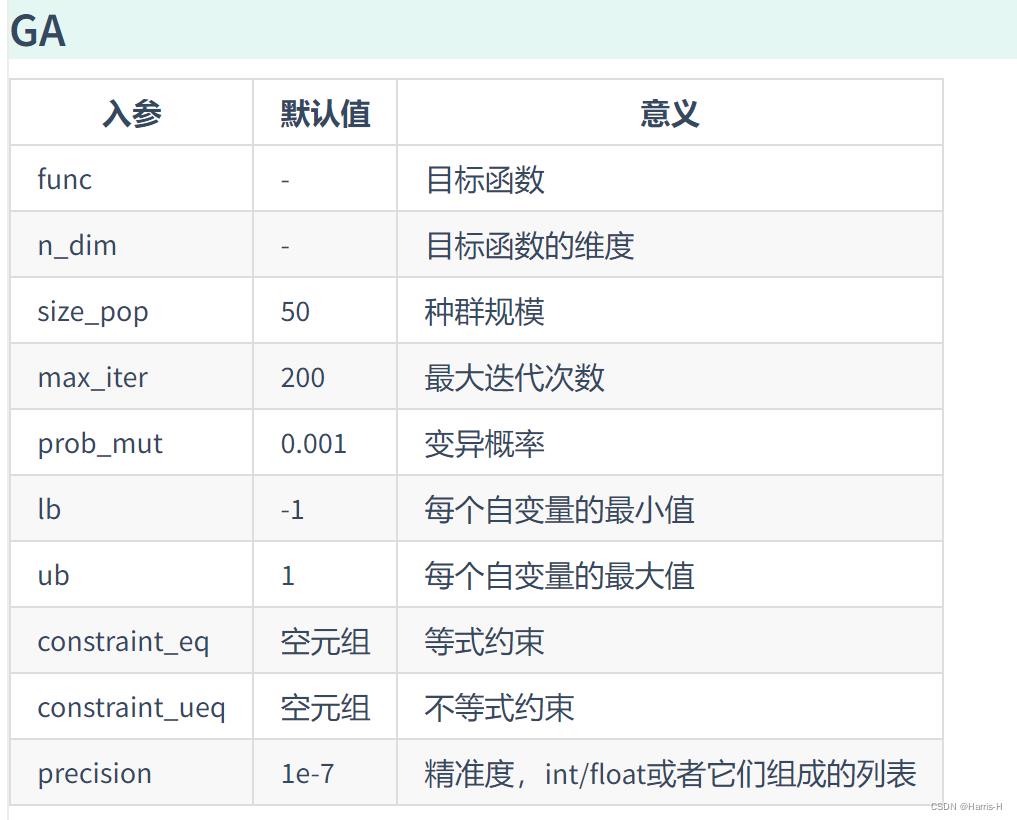
参数说明
| 入参 | 默认值 | 意义 |
|---|---|---|
| func | - | 目标函数 |
| n_dim | - | 目标函数的维度 |
| size_pop | 50 | 种群规模 |
| max_iter | 200 | 最大迭代次数 |
| prob_mut | 0.001 | 变异概率 |
| F | 0.5 | 变异系数 |
| lb | -1 | 每个自变量的最小值 |
| ub | 1 | 每个自变量的最大值 |
| constraint_eq | 空元组 | 等式约束 |
| constraint_ueq | 空元组 | 不等式约束(<=0) |
'''
min f(x1, x2, x3) = x1^2 + x2^2 + x3^2
s.t.
x1*x2 >= 1
x1*x2 <= 5
x2 + x3 = 1
0 <= x1, x2, x3 <= 5
'''
def obj_func(p):
x1, x2, x3 = p
return x1 ** 2 + x2 ** 2 + x3 ** 2
constraint_eq = [
lambda x: 1 - x[1] - x[2]
]
constraint_ueq = [
lambda x: 1 - x[0] * x[1],
lambda x: x[0] * x[1] - 5
]
# %% Do DifferentialEvolution
from sko.DE import DE
de = DE(func=obj_func, n_dim=3, size_pop=50, max_iter=800, lb=[0, 0, 0], ub=[5, 5, 5],
constraint_eq=constraint_eq, constraint_ueq=constraint_ueq)
best_x, best_y = de.run()
print('best_x:', best_x, '\\n', 'best_y:', best_y)
结果
best_x: [1.02276678 0.9785311 0.02146889]
best_y: [2.00403592]
2.粒子群算法(PSO)
def demo_func(x):
x1, x2, x3 = x
return x1 ** 2 + (x2 - 0.05) ** 2 + x3 ** 2
# %% Do PSO
from sko.PSO import PSO
pso = PSO(func=demo_func, n_dim=3, pop=40, max_iter=150, lb=[0, -1, 0.5], ub=[1, 1, 1], w=0.8, c1=0.5, c2=0.5)
pso.run()
print('best_x is ', pso.gbest_x, 'best_y is', pso.gbest_y)
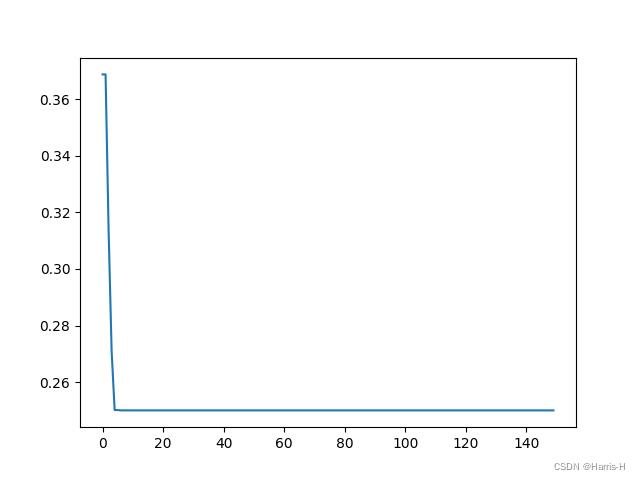
# %% Plot the result
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
plt.plot(pso.gbest_y_hist)
plt.show()
best_x is [0. 0.05 0.5 ] best_y is [0.25]
3.模拟退火(SA)
demo_func = lambda x: x[0] ** 2 + (x[1] - 0.05) ** 2 + x[2] ** 2
# %% Do SA
from sko.SA import SA
sa = SA(func=demo_func, x0=[1, 1, 1], T_max=1, T_min=1e-9, L=300, max_stay_counter=150)
best_x, best_y = sa.run()
print('best_x:', best_x, 'best_y', best_y)
# %% Plot the result
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import pandas as pd
plt.plot(pd.DataFrame(sa.best_y_history).cummin(axis=0))
plt.show()
# %%
from sko.SA import SAFast
sa_fast = SAFast(func=demo_func, x0=[1, 1, 1], T_max=1, T_min=1e-9, q=0.99, L=300, max_stay_counter=150)
sa_fast.run()
print('Fast Simulated Annealing: best_x is ', sa_fast.best_x, 'best_y is ', sa_fast.best_y)
# %%
from sko.SA import SAFast
sa_fast = SAFast(func=demo_func, x0=[1, 1, 1], T_max=1, T_min=1e-9, q=0.99, L=300, max_stay_counter=150,
lb=[-1, 1, -1], ub=[2, 3, 4])
sa_fast.run()
print('Fast Simulated Annealing with bounds: best_x is ', sa_fast.best_x, 'best_y is ', sa_fast.best_y)
# %%
from sko.SA import SABoltzmann
sa_boltzmann = SABoltzmann(func=demo_func, x0=[1, 1, 1], T_max=1, T_min=1e-9, q=0.99, L=300, max_stay_counter=150)
sa_boltzmann.run()
print('Boltzmann Simulated Annealing: best_x is ', sa_boltzmann.best_x, 'best_y is ', sa_fast.best_y)
# %%
from sko.SA import SABoltzmann
sa_boltzmann = SABoltzmann(func=demo_func, x0=[1, 1, 1], T_max=1, T_min=1e-9, q=0.99, L=300, max_stay_counter=150,
lb=-1, ub=[2, 3, 4])
sa_boltzmann.run()
print('Boltzmann Simulated Annealing with bounds: best_x is ', sa_boltzmann.best_x, 'best_y is ', sa_fast.best_y)
# %%
from sko.SA import SACauchy
sa_cauchy = SACauchy(func=demo_func, x0=[1, 1, 1], T_max=1, T_min=1e-9, q=0.99, L=300, max_stay_counter=150)
sa_cauchy.run()
print('Cauchy Simulated Annealing: best_x is ', sa_cauchy.best_x, 'best_y is ', sa_cauchy.best_y)
# %%
from sko.SA import SACauchy
sa_cauchy = SACauchy(func=demo_func, x0=[1, 1, 1], T_max=1, T_min=1e-9, q=0.99, L=300, max_stay_counter=150,
lb=[-1, 1, -1], ub=[2, 3, 4])
sa_cauchy.run()
print('Cauchy Simulated Annealing with bounds: best_x is ', sa_cauchy.best_x, 'best_y is ', sa_cauchy.best_y)
参数说明
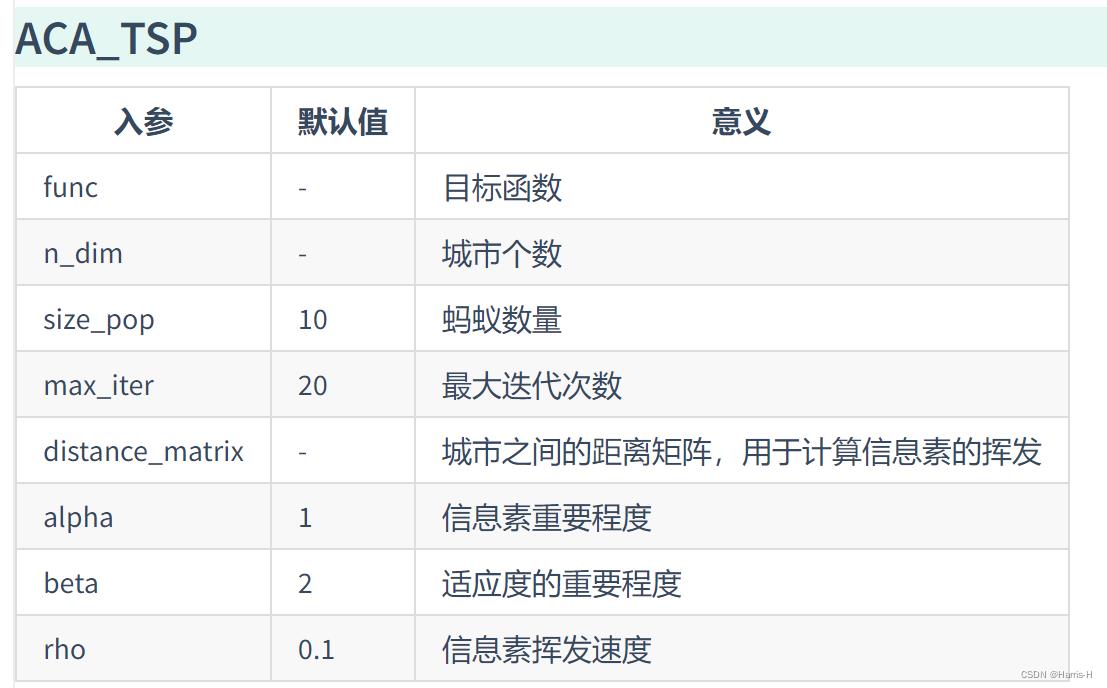
4.蚁群算法(ACA)
import numpy as np
from scipy import spatial
import pandas as pd
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
num_points = 25
points_coordinate = np.random.rand(num_points, 2) # generate coordinate of points
distance_matrix = spatial.distance.cdist(points_coordinate, points_coordinate, metric='euclidean')
def cal_total_distance(routine):
num_points, = routine.shape
return sum([distance_matrix[routine[i % num_points], routine[(i + 1) % num_points]] for i in range(num_points)])
# %% Do ACA
from sko.ACA import ACA_TSP
aca = ACA_TSP(func=cal_total_distance, n_dim=num_points,
size_pop=50, max_iter=200,
distance_matrix=distance_matrix)
best_x, best_y = aca.run()
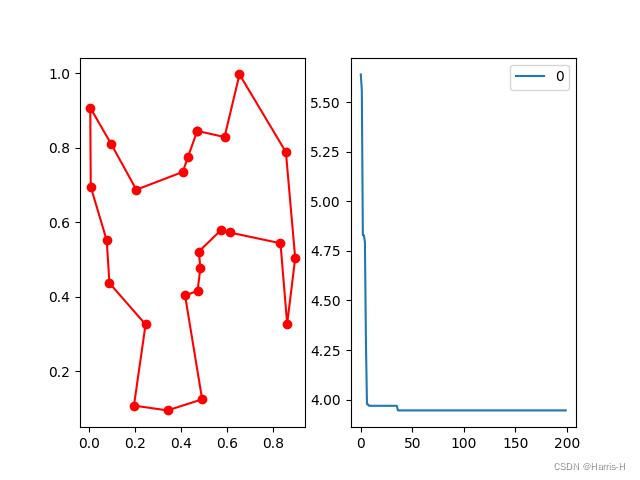
# %% Plot
fig, ax = plt.subplots(1, 2)
best_points_ = np.concatenate([best_x, [best_x[0]]])
print(best_x) # 结果序列
print(best_points_) # 添加起点形成环
best_points_coordinate = points_coordinate[best_points_, :] # 找到点序列对应的坐标序列
ax[0].plot(best_points_coordinate[:, 0], best_points_coordinate[:, 1], 'o-r') # 连接
pd.DataFrame(aca.y_best_history).cummin().plot(ax=ax[1])
plt.show()
5.遗传算法(GA)
import numpy as np
def schaffer(p):
'''
This function has plenty of local minimum, with strong shocks
global minimum at (0,0) with value 0
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Test_functions_for_optimization
'''
x1, x2 = p
part1 = np.square(x1) - np.square(x2)
part2 = np.square(x1) + np.square(x2)
return 0.5 + (np.square(np.sin(part1)) - 0.5) / np.square(1 + 0.001 * part2)
# %%
from sko.GA import GA
ga = GA(func=schaffer, n_dim=2, size_pop=50, max_iter=800, prob_mut=0.001, lb=[-1, -1], ub=[1, 1], precision=1e-7)
best_x, best_y = ga.run()
print('best_x:', best_x, '\\n', 'best_y:', best_y)
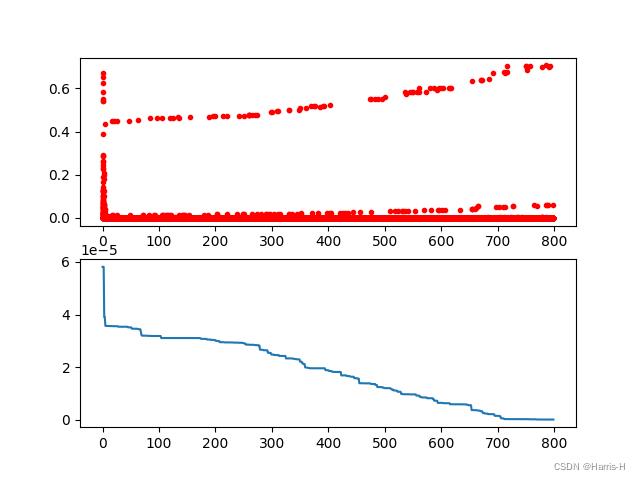
# %% Plot the result
import pandas as pd
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
Y_history = pd.DataFrame(ga.all_history_Y)
print(Y_history)
fig, ax = plt.subplots(2, 1)
ax[0].plot(Y_history.index, Y_history.values, '.', color='red')
Y_history.min(axis=1).cummin().plot(kind='line')
plt.show()
结果
best_x: [0.00294498 0.00016674]
best_y: [8.77542544e-09]
0 1 ... 48 49
0 2.432570e-01 8.702831e-02 ... 3.420108e-04 1.928273e-02
1 6.365298e-02 4.969987e-02 ... 1.994070e-02 3.016882e-02
2 8.110868e-04 5.950608e-04 ... 1.694919e-03 2.924401e-02
3 9.968317e-04 1.167487e-04 ... 1.288323e-03 2.983435e-04
4 2.318954e-03 2.191508e-04 ... 1.501895e-04 1.733578e-03
.. ... ... ... ... ...
795 9.406647e-09 8.849707e-09 ... 9.312904e-09 9.406647e-09
796 8.849707e-09 8.849707e-09 ... 8.830077e-09 8.849707e-09
797 8.849707e-09 8.849707e-09 ... 8.849707e-09 8.849707e-09
798 8.830077e-09 8.849707e-09 ... 8.849707e-09 8.849707e-09
799 8.830077e-09 8.849707e-09 ... 8.958900e-09 8.849707e-09
[800 rows x 50 columns]
以上是关于scikit-opt的使用的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章