OkHttp源码解析 (三)——代理和路由
Posted
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了OkHttp源码解析 (三)——代理和路由相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
参考技术A初看OkHttp源码,由于对Address、Route、Proxy、ProxySelector、RouteSelector等理解不够,读源码非常吃力,看了几遍依然对于寻找复用连接、创建连接、连接服务器、连接代理服务器、创建隧道连接等逻辑似懂非懂,本篇决定梳理一遍相关的概念及基本原理。
● HTTP/1.1(HTTPS)
● HTTP/2
● SPDY
一个http请求的流程(直连):
1、输入url及参数;
2、如果是url是域名则解析ip地址,可能对应多个ip,如果没有指定端口,则用默认端口,http请求用80;
3、创建socket,根据ip和端口连接服务器(socket内部会完成3次TCP握手);
4、socket成功连接后,发送http报文数据。
一个https请求的流程(直连):
1、输入url及参数;
2、如果是url是域名则解析ip地址,可能对应多个ip,如果没有指定端口,则用默认端口,https请求用443;
3、创建socket,根据ip和端口连接服务器(socket内部会完成3次TCP握手);
4、socket成功连接后进行TLS握手,可通过java标准款提供的SSLSocket完成;
5、握手成功后,发送https报文数据。
1、分类
● HTTP代理:普通代理、隧道代理
● SOCKS代理:SOCKS4、SOCKS5
2、HTTP代理分类及说明
普通代理
HTTP/1.1 协议的第一部分。其代理过程为:
● client 请求 proxy
● proxy 解析请求获取 origin server 地址
● proxy 向 origin server 转发请求
● proxy 接收 origin server 的响应
● proxy 向 client 转发响应
其中proxy获取目的服务器地址的标准方法是解析 request line 里的 request-URL。因为proxy需要解析报文,因此普通代理无法适用于https,因为报文都是加密的。
隧道代理
通过 Web 代理服务器用隧道方式传输基于 TCP 的协议。
请求包括两个阶段,一是连接(隧道)建立阶段,二是数据通信(请求响应)阶段,数据通信是基于 TCP packet ,代理服务器不会对请求及响应的报文作任何的处理,都是原封不动的转发,因此可以代理 HTTPS请求和响应。
代理过程为:
● client 向 proxy 发送 CONNET 请求(包含了 origin server 的地址)
● proxy 与 origin server 建立 TCP 连接
● proxy 向 client 发送响应
● client 向 proxy 发送请求,proxy 原封不动向 origin server 转发请求,请求数据不做任何封装,为原生 TCP packet.
3、SOCKS代理分类及说明
● SOCKS4:只支持TCP协议(即传输控制协议)
● SOCKS5: 既支持TCP协议又支持UDP协议(即用户数据包协议),还支持各种身份验证机制、服务器端域名解析等。
SOCK4能做到的SOCKS5都可得到,但反过来却不行,比如我们常用的聊天工具QQ在使用代理时就要求用SOCKS5代理,因为它需要使用UDP协议来传输数据。
有了上面的基础知识,下面分析结合源码分析OkHttp路由相关的逻辑。OkHttp用Address来描述与目标服务器建立连接的配置信息,但请求输入的可能是域名,一个域名可能对于多个ip,真正建立连接是其中一个ip,另外,如果设置了代理,客户端是与代理服务器建立直接连接,而不是目标服务器,代理又可能是域名,可能对应多个ip。因此,这里用Route来描述最终选择的路由,即客户端与哪个ip建立连接,是代理还是直连。下面对比下Address及Route的属性,及路由选择器RouteSelector。
描述与目标服务器建立连接所需要的配置信息,包括目标主机名、端口、dns,SocketFactory,如果是https请求,包括TLS相关的SSLSocketFactory 、HostnameVerifier 、CertificatePinner,代理服务器信息Proxy 、ProxySelector 。
Route提供了真正连接服务器所需要的动态信息,明确需要连接的服务器IP地址及代理服务器,一个Address可能会有很多个路由Route供选择(一个DNS对应对个IP)。
Address和Route都是数据对象,没有提供操作方法,OkHttp另外定义了RouteSelector来完成选择的路由的操作。
1、读取代理配置信息:resetNextProxy()
读取代理配置:
● 如果有指定代理(不读取系统配置,在OkHttpClient实例中指定),则只用1个该指定代理;
● 如果没有指定,则读取系统配置的,可能有多个。
2、获取需要尝试的socket地址(目标服务器或者代理服务器):resetNextInetSocketAddress()
结合Address的host和代理,解析要尝试的套接字地址(ip+端口)列表:
● 直连或者SOCK代理, 则用目标服务器的主机名和端口,如果是HTTP代理,则用代理服务器的主机名和端口;
● 如果是SOCK代理,根据目标服务器主机名和端口号创建未解析的套接字地址,列表只有1个地址;
● 如果是直连或HTTP代理,先DNS解析,得到InetAddress列表(没有端口),再创建InetSocketAddress列表(带上端口),InetSocketAddress与InetAddress的区别是前者带端口信息。
3、获取路由列表:next()
选择路由的流程解析:
● 遍历每个代理对象,可能多个,直连的代理对象为Proxy.DIRECT(实际是没有中间代理的);
● 对每个代理获取套接字地址列表;
● 遍历地址列表,创建Route,判断Route如果在路由黑名单中,则添加到失败路由列表,不在黑名单中则添加到待返回的Route列表;
● 如果最后待返回的Route列表为空,即可能所有路由都在黑名单中,实在没有新路由了,则将失败的路由集合返回;
● 传入Route列表创建Selection对象,对象比较简单,就是一个目标路由集合,及读取方法。
为了避免不必要的尝试,OkHttp会把连接失败的路由加入到黑名单中,由RouteDatabase管理,该类比较简单,就是一个失败路由集合。
1、创建Address
Address的创建在RetryAndFollowUpInteceptor里,每次请求会声明一个新的Address及StreamAllocation对象,而StreamAllocation使用Address创建RouteSelector对象,在连接时RouteSelector确定请求的路由。
每个Requst都会构造一个Address对象,构造好了Address对象只是有了与服务器连接的配置信息,但没有确定最终服务器的ip,也没有确定连接的路由。
2、创建RouteSelector
在StreamAllocation声明的同时会声明路由选择器RouteSelector,为一次请求寻找路由。
3、选择可用的路由Route
下面在测试过程跟踪实例对象来理解,分别测试直连和HTTP代理HTTP2请求路由的选择过程:
● 直连请求流程
● HTTP代理HTTPS流程
请求url: https://www.jianshu.com/p/63ba15d8877a
1、构造address对象
2、读取代理配置:resetNextProxy
3、解析目标服务器套接字地址:resetNextInetSocketAddress
4、选择Route创建RealConnection
5、确定协议
测试方法:
● 在PC端打开Charles,设置端口,如何设置代理,网上有教程,比较简单;
● 手机打开WIFI,选择连接的WIFI修改网络,在高级选项中设置中指定了代理服务器,ip为PC的ip,端口是Charles刚设置的端口;
● OkHttpClient不指定代理,发起请求。
1、构造address对象
2、读取代理配置:resetNextProxy
3、解析目标服务器套接字地址:resetNextInetSocketAddress
4、选择Route创建RealConnection
5、创建隧道
由于是代理https请求,需要用到隧道代理。
从图可以看出,建立隧道其实是发送CONNECT请求,header包括字段Proxy-Connection,目标主机名,请求内容类似:
6、确定协议,SSL握手
1、代理可分为HTTP代理和SOCK代理;
2、HTTP代理又分为普通代理和隧道代理;普通代理适合明文传输,即http请求;隧道代理仅转发TCP包,适合加密传输,即https/http2;
3、SOCK代理又分为SOCK4和SOCK5,区别是后者支持UDP传输,适合代理聊天工具如QQ;
4、没有设置代理(OkHttpClient没有指定同时系统也没有设置),客户端直接与目标服务器建立TCP连接;
5、设置了代理,代理http请求时,客户端与代理服务器建立TCP连接,如果代理服务器是域名,则解释代理服务器域名,而目标服务器的域名由代理服务器解析;
6、设置了代理,代理https/http2请求时,客户端与代理服务器建立TCP连接,发送CONNECT请求与代理服务器建立隧道,并进行SSL握手,代理服务器不解析数据,仅转发TCP数据包。
如何正确使用 HTTP proxy
OkHttp3中的代理与路由
HTTP 代理原理及实现(一)
ConnectInterceptor 解析——OkHttp 源码详解
前言
框架和流程——OkHttp 源码详解(一)
ConnectInterceptor 解析——OkHttp 源码详解(二)
OkHttp 主要的逻辑实现都在拦截器,拦截器中的重点,就是与服务端建立连接,这个过程包括了,dns,代理选择,tls连接,socket连接等,下面我们就从源码一步步分析
源码分析
下面从拦截器ConnectInterceptor 开始分析:
代码一
代码一:
/**
* Opens a connection to the target server and proceeds to the next interceptor. The network might
* be used for the returned response, or to validate a cached response with a conditional GET.
*/
object ConnectInterceptor : Interceptor
@Throws(IOException::class)
override fun intercept(chain: Interceptor.Chain): Response
//看过上篇文章的,应该很熟悉了,每一个Interceptor 都会被包裹为RealInterceptorChain,注意,这里的chain,是下一个Interceptor
val realChain = chain as RealInterceptorChain
//这里的call,就是RealCall,下面对initExchange 展开进行描述,见代码二
val exchange = realChain.call.initExchange(chain)
//使用参数,对下一个Interceptor 进行拷贝
val connectedChain = realChain.copy(exchange = exchange)
//执行下一个Interceptor
return connectedChain.proceed(realChain.request)
代码二
代码二:
在 RealCall.kt 中
/** Finds a new or pooled connection to carry a forthcoming request and response. */
internal fun initExchange(chain: RealInterceptorChain): Exchange
synchronized(this)
check(expectMoreExchanges) "released"
check(!responseBodyOpen)
check(!requestBodyOpen)
//exchangeFinder 对象是在RetryAndFollowUpInterceptor中创建的,见代码三
val exchangeFinder = this.exchangeFinder!!
//find 创建连接或者在连接池里找到一个可用链接
// codec ExchangeCodec 接口,它是一个socket 链接,用来传输request和response,
//有两种实现:Http1ExchangeCodec ,Http2ExchangeCodec
val codec = exchangeFinder.find(client, chain)
//创建了一个Exchange,它负责单个http 请求和响应对,真正的实现是在codec 中(实际的IO操作)
val result = Exchange(this, eventListener, exchangeFinder, codec)
//保存这个Exchange 对象,在RealCall对象的变量中
this.interceptorScopedExchange = result
this.exchange = result
synchronized(this)
this.requestBodyOpen = true
this.responseBodyOpen = true
if (canceled) throw IOException("Canceled")
return result
因为本篇文章,主要是研究,链接建立的过程,所以关于Exchange传输数据的就先不展开,下面来看一个 ExchangeFinder是在哪里 创建的
代码三
在RetryAndFollowUpInterceptor 的intercept 中,调用了下面的函数,为RealCall 对象,创建了一个ExchangeFinder
代码三:
在 RealCall.kt 中
fun enterNetworkInterceptorExchange(request: Request, newExchangeFinder: Boolean)
check(interceptorScopedExchange == null)
synchronized(this)
check(!responseBodyOpen)
"cannot make a new request because the previous response is still open: " +
"please call response.close()"
check(!requestBodyOpen)
if (newExchangeFinder)
//创建一个ExchangeFinder,在它里面实现了Dns,代理选择,路由选择,tls连接,socket连接
//具体每个功能的实现,也是有不同的类去完成,下面会一一详解RetryAndFollowUpInterceptor
this.exchangeFinder = ExchangeFinder(
connectionPool,
createAddress(request.url),
this,
eventListener
)
下面就看看代码二中的exchangeFinder.find(client, chain) 函数,看看链接建立的详细过程
代码四
代码四:
在ExchangeFinder.kt 中
fun find(
client: OkHttpClient,
chain: RealInterceptorChain
): ExchangeCodec
try
// 下面到findHealthyConnection函数中一看究竟
val resultConnection = findHealthyConnection(
connectTimeout = chain.connectTimeoutMillis,
readTimeout = chain.readTimeoutMillis,
writeTimeout = chain.writeTimeoutMillis,
pingIntervalMillis = client.pingIntervalMillis,
connectionRetryEnabled = client.retryOnConnectionFailure,
doExtensiveHealthChecks = chain.request.method != "GET"
)
//resultConnection 是 RealConnection 类型,它负责建立socket链接 ,建立tls链接,建立Tunnel(通过http代理,访问https 服务器)等操作
//面对http1和http2,又有各自不同的传输方式,所以使用newCodec() 抽象为ExchangeCodec,http1和http2 实现不同的接口功能(策略者模式)
return resultConnection.newCodec(client, chain)
catch (e: RouteException)
trackFailure(e.lastConnectException)
throw e
catch (e: IOException)
trackFailure(e)
throw RouteException(e)
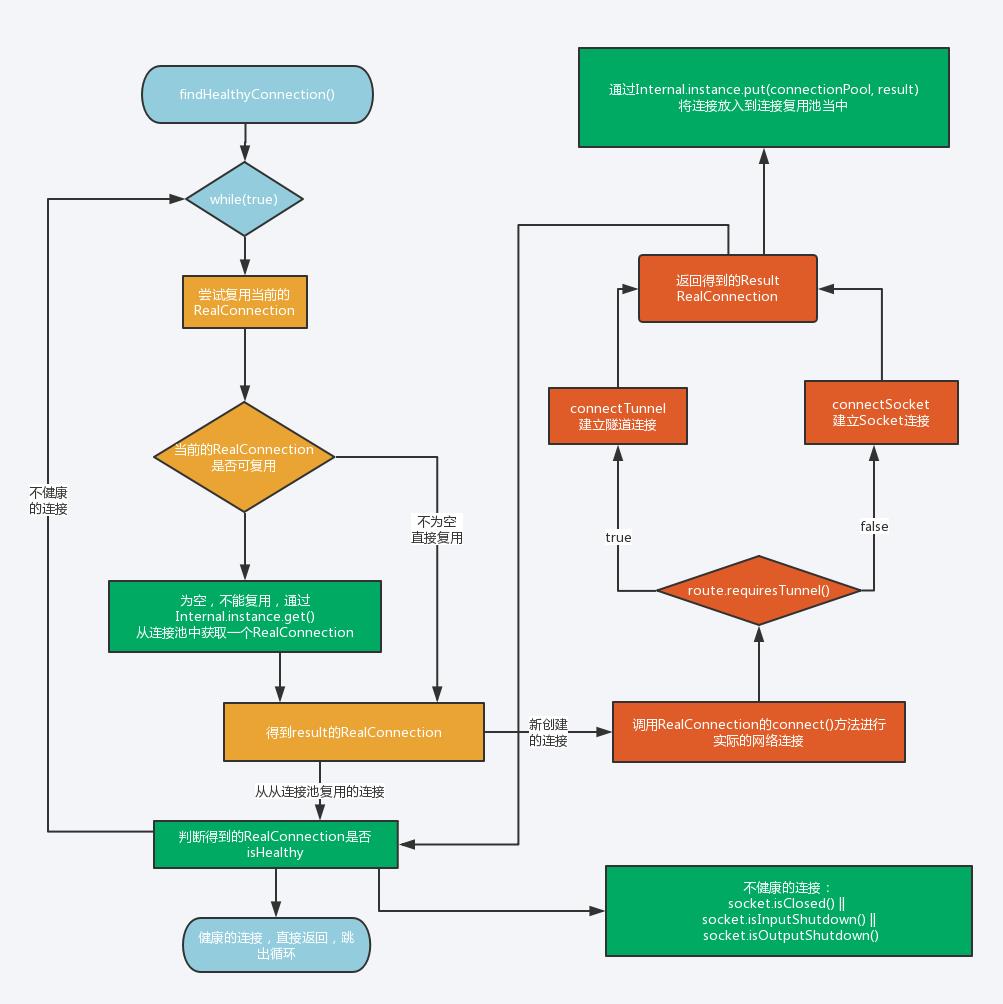
下面进入findHealthyConnection 函数中
代码五
代码五:
在ExchangeFinder.kt 中
/**
* Finds a connection and returns it if it is healthy. If it is unhealthy the process is repeated
* until a healthy connection is found.
*/
@Throws(IOException::class)
private fun findHealthyConnection(
connectTimeout: Int,
readTimeout: Int,
writeTimeout: Int,
pingIntervalMillis: Int,
connectionRetryEnabled: Boolean,
doExtensiveHealthChecks: Boolean
): RealConnection
//这里是一个死循环,退出循环的两种情况:1、得到一个健康的连接 2、抛出一个异常
while (true)
//得到一个连接,新建或者在连接池中,见代码六
val candidate = findConnection(
connectTimeout = connectTimeout,
readTimeout = readTimeout,
writeTimeout = writeTimeout,
pingIntervalMillis = pingIntervalMillis,
connectionRetryEnabled = connectionRetryEnabled
)
// Confirm that the connection is good.
if (candidate.isHealthy(doExtensiveHealthChecks))
return candidate
// 如果连接,不可用,就从连接池中删除
candidate.noNewExchanges()
// Make sure we have some routes left to try. One example where we may exhaust all the routes
// would happen if we made a new connection and it immediately is detected as unhealthy.
if (nextRouteToTry != null) continue
val routesLeft = routeSelection?.hasNext() ?: true
if (routesLeft) continue
val routesSelectionLeft = routeSelector?.hasNext() ?: true
if (routesSelectionLeft) continue
throw IOException("exhausted all routes")
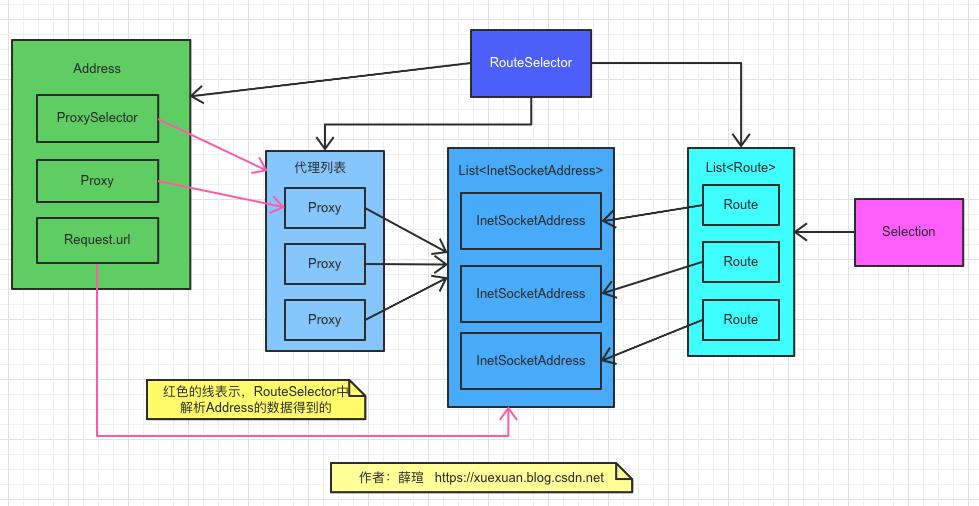
下面涉及的类比较多,来几张图,从总体的认识一下
RouteSelector 是用来根据代理创建Route, 然后封装到Selection
Selection 针对某一个代理的 一系列的Route,切换代理后,该对象也会跟着改变
Route 一个Url可能会对应多个IP地址(DNS负载均衡),每个socket 对应一个Route 对象
Address 包含 一个Url,指定的Proxy(可为空), ProxySelector (可能会有许多Proxy)
这几个类的关系图
下图是,建立连接的流程图:
代码六
代码六:
在ExchangeFinder.kt 类中
/**
* Returns a connection to host a new stream. This prefers the existing connection if it exists,
* then the pool, finally building a new connection.
*
* This checks for cancellation before each blocking operation.
*/
@Throws(IOException::class)
private fun findConnection(
connectTimeout: Int,
readTimeout: Int,
writeTimeout: Int,
pingIntervalMillis: Int,
connectionRetryEnabled: Boolean
): RealConnection
//如果当前的请求已经取消,就抛出异常
if (call.isCanceled()) throw IOException("Canceled")
//下面是使用RealCall 对象当前的连接
// Attempt to reuse the connection from the call.
val callConnection = call.connection // This may be mutated by releaseConnectionNoEvents()!
if (callConnection != null)
var toClose: Socket? = null
synchronized(callConnection)
if (callConnection.noNewExchanges || !sameHostAndPort(callConnection.route().address.url))
toClose = call.releaseConnectionNoEvents()
// If the call's connection wasn't released, reuse it. We don't call connectionAcquired() here
// because we already acquired it.
if (call.connection != null)
check(toClose == null)
return callConnection
// The call's connection was released.
toClose?.closeQuietly()
eventListener.connectionReleased(call, callConnection)
//2、上面RealCall 对象的连接不可用,We need a new connection. Give it fresh stats.
refusedStreamCount = 0
connectionShutdownCount = 0
otherFailureCount = 0
// Attempt to get a connection from the pool.
//callAcquirePooledConnection 函数,下面会详细分析
if (connectionPool.callAcquirePooledConnection(address, call, null, false))
val result = call.connection!!
eventListener.connectionAcquired(call, result)
return result
// 在连接池中也没有找到可用的,就去找Route,然后用Route创建一个连接
// 寻找Route 的步骤:
//1、先看nextRouteToTry 有没有值,(如果有值,就是上一次循环赋值的),拿出来使用
//2、nextRouteToTry 为空,去Selection 中去找(Selection 就是一些列Route的集合)
//3、如果Selection 中也没有,就去RouteSelector中,先找一个Selection,再在其中找Route
// 如果是第一次进来,那么会到第三种情况,先创建一个RouteSelector,next() 后Selection,Route 就都有了
// Nothing in the pool. Figure out what route we'll try next.
val routes: List<Route>?
val route: Route
if (nextRouteToTry != null)
// Use a route from a preceding coalesced connection.
routes = null
route = nextRouteToTry!!
nextRouteToTry = null
else if (routeSelection != null && routeSelection!!.hasNext())
// Use a route from an existing route selection.
routes = null
route = routeSelection!!.next()
else
// Compute a new route selection. This is a blocking operation!
var localRouteSelector = routeSelector
if (localRouteSelector == null)
//代码七 会详细介绍RouteSelector
localRouteSelector = RouteSelector(address, call.client.routeDatabase, call, eventListener)
this.routeSelector = localRouteSelector
val localRouteSelection = localRouteSelector.next()
routeSelection = localRouteSelection
routes = localRouteSelection.routes
if (call.isCanceled()) throw IOException("Canceled")
// Now that we have a set of IP addresses, make another attempt at getting a connection from
// the pool. We have a better chance of matching thanks to connection coalescing.
//注意这里参数,有传入routes 参数,
if (connectionPool.callAcquirePooledConnection(address, call, routes, false))
val result = call.connection!!
eventListener.connectionAcquired(call, result)
return result
route = localRouteSelection.next()
// 代码如果执行到这里,就说明还没有找到可用连接,但是找到了Route
// Connect. Tell the call about the connecting call so async cancels work.
val newConnection = RealConnection(connectionPool, route)
call.connectionToCancel = newConnection
try
// 建立socket 连接,建立tls连接,建立tunnel
// 见代码十:
newConnection.connect(
connectTimeout,
readTimeout,
writeTimeout,
pingIntervalMillis,
connectionRetryEnabled,
call,
eventListener
)
finally
call.connectionToCancel = null
call.client.routeDatabase.connected(newConnection.route())
// If we raced another call connecting to this host, coalesce the connections. This makes for 3
// different lookups in the connection pool!
// 最后一个参数是true,查找是否有多路复用(http2)的可用链接,如果有的话,就使用,并刚刚新创建的链接
if (connectionPool.callAcquirePooledConnection(address, call, routes, true))
val result = call.connection!!
//把上面找到的route 保存起来,如果当前返回的连接不健康,下次就尝试这个route
nextRouteToTry = route
newConnection.socket().closeQuietly()
//调用事件监听函数
eventListener.connectionAcquired(call, result)
return result
synchronized(newConnection)
//放入连接池中
connectionPool.put(newConnection)
//见代码九分析
call.acquireConnectionNoEvents(newConnection)
//调用事件监听函数
eventListener.connectionAcquired(call, newConnection)
return newConnection
下面来详细分析一下RouteSelector、然后在代码八分析 callAcquirePooledConnection 是如何在连接池中选择一个连接的。
来看看RouteSelector 类的完整代码
代码七
代码七:
在RouteSelector.kt 类中
/**
* Selects routes to connect to an origin server. Each connection requires a choice of proxy server,
* IP address, and TLS mode. Connections may also be recycled.
*/
class RouteSelector(
//在RealCall 中创建的address 对象,存放url,port,proxy,proxySelector(proxy 为空时 使用的)
private val address: Address,
private val routeDatabase: RouteDatabase,
private val call: Call,
private val eventListener: EventListener
)
/* State for negotiating the next proxy to use. */
private var proxies = emptyList<Proxy>()
private var nextProxyIndex: Int = 0
/* State for negotiating the next socket address to use. */
private var inetSocketAddresses = emptyList<InetSocketAddress>()
/* State for negotiating failed routes */
private val postponedRoutes = mutableListOf<Route>()
init
//首先会调用这里
resetNextProxy(address.url, address.proxy)
// 把设置的代理都找出来,如果没有设置代理,则使用proxySelector,
private fun resetNextProxy(url: HttpUrl, proxy: Proxy?)
fun selectProxies(): List<Proxy>
// If the user specifies a proxy, try that and only that.
if (proxy != null) return listOf(proxy)
// If the URI lacks a host (as in "http://</"), don't call the ProxySelector.
val uri = url.toUri()
if (uri.host == null) return immutableListOf(Proxy.NO_PROXY)
// Try each of the ProxySelector choices until one connection succeeds.
//注意这里的proxySelector( 类型是ProxySelector抽象类),对proxySelector 赋值 ,默认通过反射找到"sun.net.spi.DefaultProxySelector",如果为空,则使用NullProxySelector
val proxiesOrNull = address.proxySelector.select(uri)
//如果没有找到代理,就返回一个list,其中Proxy 的参数是直接相连,也就是没有代理
if (proxiesOrNull.isNullOrEmpty()) return immutableListOf(Proxy.NO_PROXY)
return proxiesOrNull.toImmutableList()
eventListener.proxySelectStart(call, url)
proxies = selectProxies()
//这里赋初值,后面会根据这个字段来判断,是否还有代理
nextProxyIndex = 0
eventListener.proxySelectEnd(call, url, proxies)
/**
* Returns true if there's another set of routes to attempt. Every address has at least one route.
*/
operator fun hasNext(): Boolean = hasNextProxy() || postponedRoutes.isNotEmpty()
/** Returns true if there's another proxy to try. */
private fun hasNextProxy(): Boolean = nextProxyIndex < proxies.size
//代码六中,调用了这里,来创建一个Selection(Route 的集合)
@Throws(IOException::class)
operator fun next(): Selection
if (!hasNext()) throw NoSuchElementException()
// Compute the next set of routes to attempt.
val routes = mutableListOf<Route>()
while (hasNextProxy())
//即使没有代理,proxies也会有一个Proxy,此时nextProxyIndex == 0,所以hasNextProxy()为true,进入到这里
// Postponed routes are always tried last. For example, if we have 2 proxies and all the
// routes for proxy1 should be postponed, we'll move to proxy2. Only after we've exhausted
// all the good routes will we attempt the postponed routes.
val proxy = nextProxy()
for (inetSocketAddress in inetSocketAddresses)
val route = Route(address, proxy, inetSocketAddress)
if (routeDatabase.shouldPostpone(route))
//如果这个路由之前失败过,就加入到postponedRoutes 中
postponedRoutes += route
else
// 直接把route 加入routes
routes += route
//如果有没有失败过得route,就终止循环
if (routes.isNotEmpty())
break
//所以的route都是失败过的,就把刚才postponedRoutes 加入到routes
if (routes.isEmpty())
// We've exhausted all Proxies so fallback to the postponed routes.
// 把postponedRoutes
routes += postponedRoutes
postponedRoutes.clear()
//用routes 创建Selection 对象
return Selection(routes)
/** Returns the next proxy to try. May be PROXY.NO_PROXY but never null. */
@Throws(IOException::class)
private fun nextProxy(): Proxy
if (!hasNextProxy())
throw SocketException(
"No route to $address.url.host; exhausted proxy configurations: $proxies")
val result = proxies[nextProxyIndex++]
resetNextInetSocketAddress(result)
return result
/** Prepares the socket addresses to attempt for the current proxy or host. */
@Throws(IOException::class)
private fun resetNextInetSocketAddress(proxy: Proxy)
// Clear the addresses. Necessary if getAllByName() below throws!
val mutableInetSocketAddresses = mutableListOf<InetSocketAddress>()
inetSocketAddresses = mutableInetSocketAddresses
val socketHost: String
val socketPort: Int
if (proxy.type() == Proxy.Type.DIRECT || proxy.type() == Proxy.Type.SOCKS)
//如果是直接相连,或者是SOCKS 直接通过ip 和端口,访问后台
socketHost = address.url.host
socketPort = address.url.port
else
// http 系列的代理
val proxyAddress = proxy.address()
require(proxyAddress is InetSocketAddress)
"Proxy.address() is not an InetSocketAddress: $proxyAddress.javaClass"
socketHost = proxyAddress.socketHost
socketPort = proxyAddress.port
if (socketPort !in 1..65535)
throw SocketException(以上是关于OkHttp源码解析 (三)——代理和路由的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章