LinuxLinux和Window下 与 的区别git命令行的使用
Posted 学IT的小卢
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了LinuxLinux和Window下 与 的区别git命令行的使用相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
作者:小卢
专栏:《Linux》、《Git》
喜欢的话:世间因为少年的挺身而出,而更加瑰丽。 ——《人民日报》
目录
1. 回车换行符在Window下和在Linux下的区别:
1.1回车换行符:
- 在Window下:回车换行符为\\r\\n
- 在Linux下:回车换行符为\\n
因此当shell文件是在Windows下编写的时候,所有的换行符都是“\\r\\n”,shell下是没办法执行这个文件的
\\n为换行符,换行相当于光标跳转到下一行的这个位置
\\r为回车符,回车相当于光标跳转到当前行的最左边的位置
1. 2.行缓冲区打印:
test.c文件和Makefile文件内容:
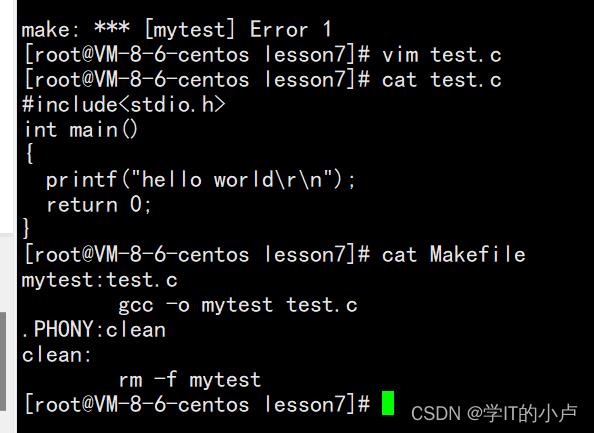
此时test.c文件有\\n(行缓冲区内容打印)
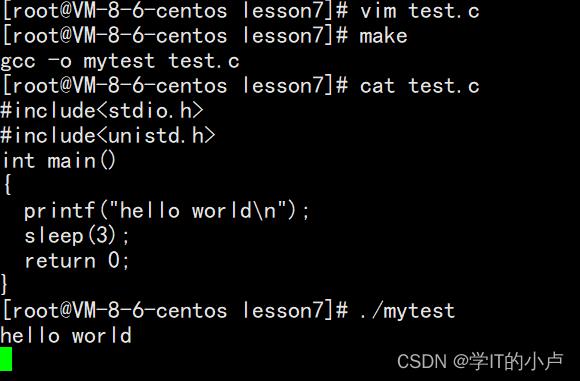
此时运行,打印出hello world 这时光标会停3秒
如果没有\\n,会先停3秒然后再打印出hello world
无论是否有\\n时,都是先走printf再sleep的,当有\\n时如果读到了\\n的位置就会先将行缓冲区的内容马上打印出来再往下走。
fflush函数可以立马刷新行缓冲区
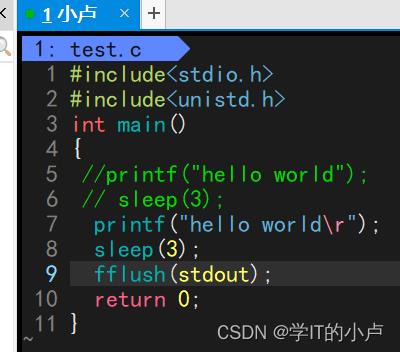
1.3进度条小程序 :
proc.c文件:
#include"proc.h"
#include<string.h>
#include<unistd.h>
#define SIZE 102
#define STYLE '='
#define ARR '>'
void proc()
const char *lable="|/-\\\\";
char bar[SIZE];
memset(bar,'\\0',sizeof(bar));
int i=0;
while(i<=100)
printf("[%-100s][%d%%][%c]\\r",bar,i,lable[i%4]);
fflush(stdout);
bar[i++]=STYLE;
if(i!=100)
bar[i]=ARR;
usleep(100000);
printf("\\n");
proc.h文件:
#include<stdio.h>
#pragma once
extern void proc();2.git命令行的使用:
2.1git仓库的创建:
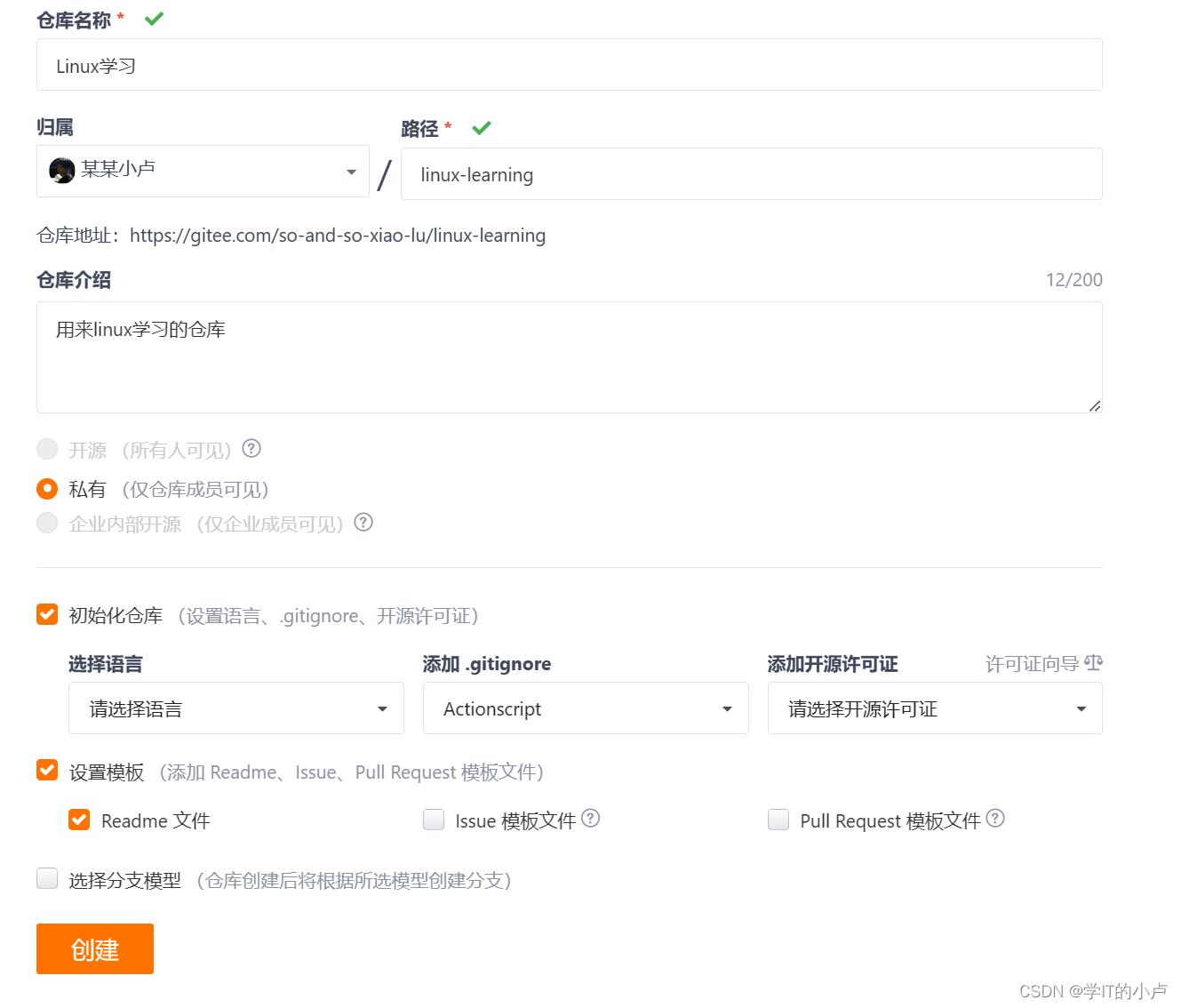
2.1.1创建仓库:
首先在git网站创建一个仓库:
我这里是举例,不用跟我创建的一模一样
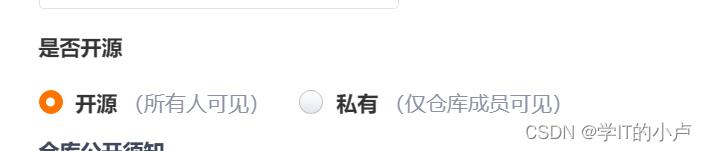
- 初始化仓库和设置模板尽量跟我一致,其他随意
2.1.2将仓库开源:
先点击仓库,然后点击管理设为开源就好了
2.2检查Linux是否安装Git:
检查是否安装了git
git --version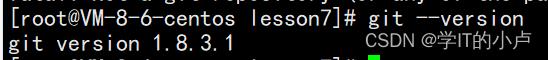
安装指令
sudo yum install -y git 2.3clone一个远端仓库:
复制仓库的链接
Linux中弄个远端仓库:
git clone 链接 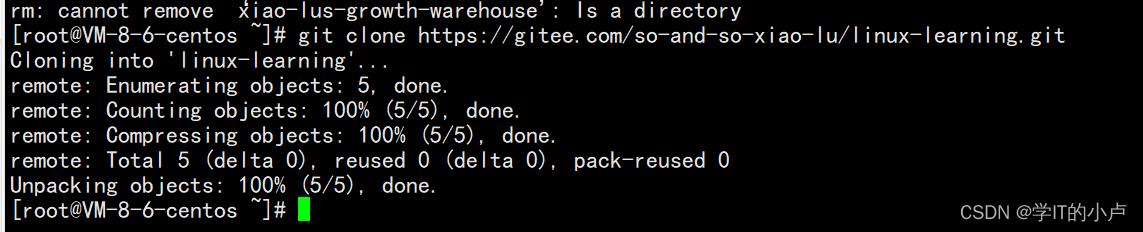
2.4提交代码带Git:
git add 文件名 提交当前目录下的所有代码
git commit -m “文字描述”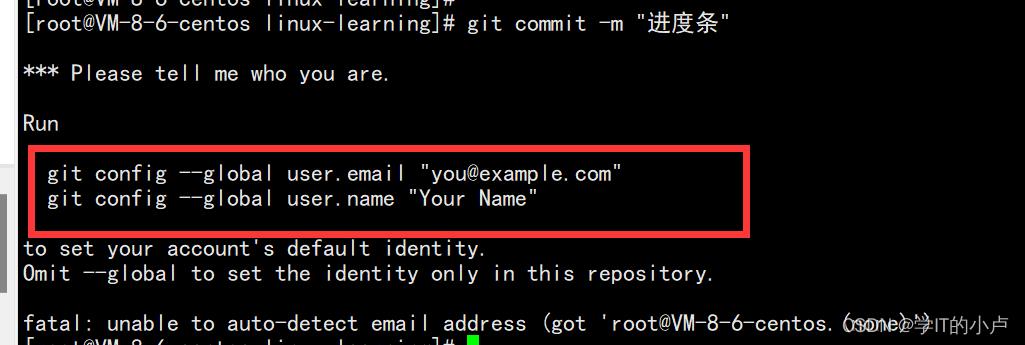
第一次在Linux提交代码的会出现这个情况:
这里需要你设置邮箱和名字
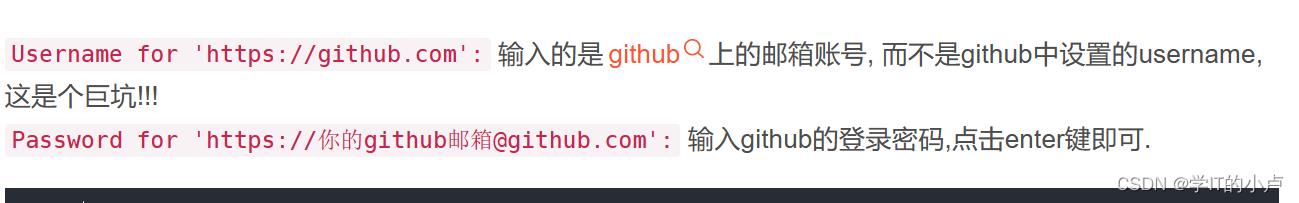
- 这里的邮箱是你git账号的邮箱,名字自己取,密码也是git账号的密码

git push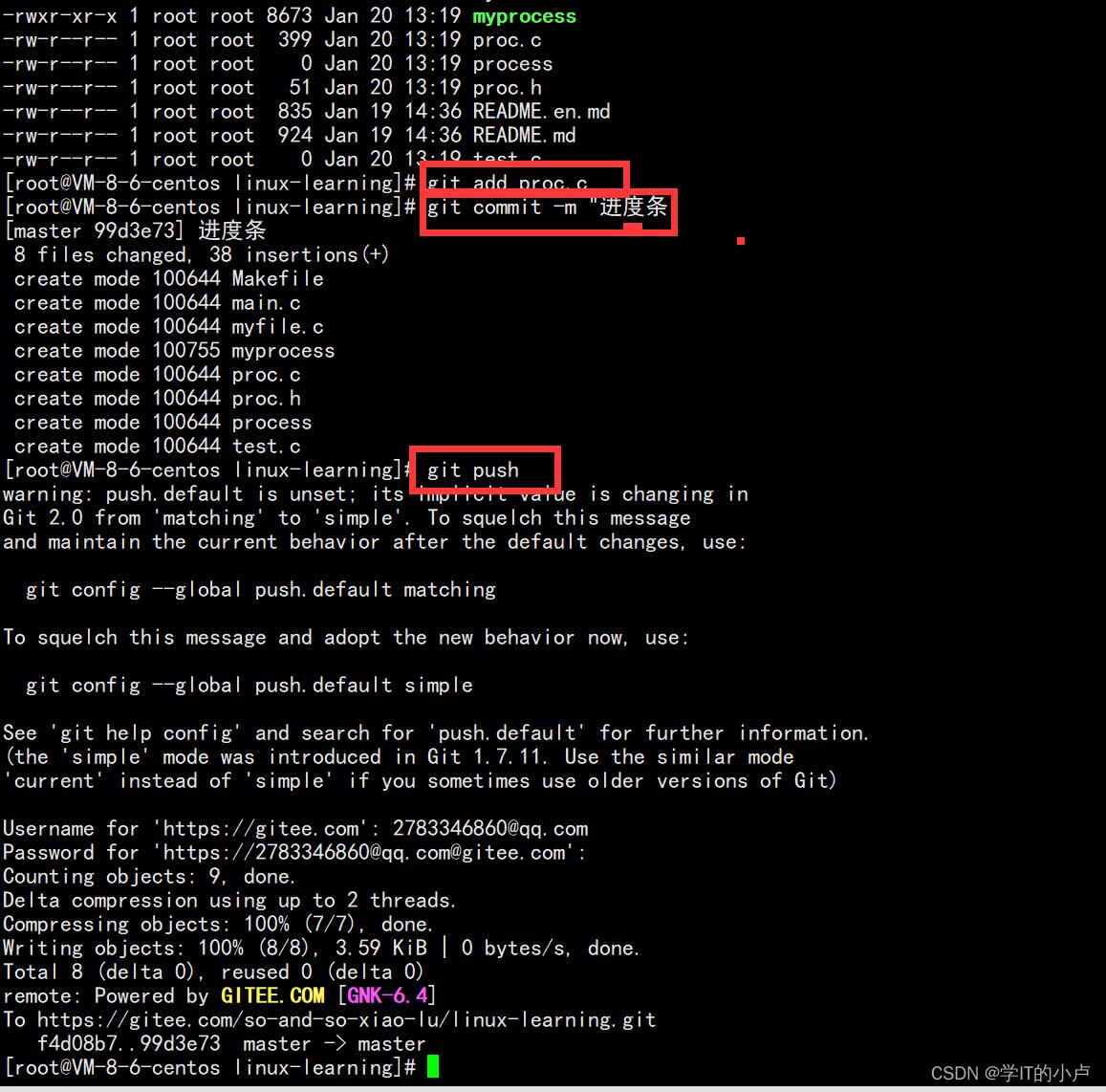
然后去git网站看看有没有上传上去就好啦
LinuxLinux下 环境变量/etc/profile/etc/bashrc~/.bashrc的区别
转自:http://blog.csdn.net/qiao1245/article/details/44650929
------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
==========================================================================================
最近配置了JAVA和Scala的环境变量,发现自己对Linux下 /etc/profile、/etc/bashrc、~/.bashrc的区别不是特别清楚,特此查阅了相关资料,整理下来,供以后查阅。如有错误之处,还望各位朋友批评指正。
①/etc/profile:
该文件登录操作系统时,为每个用户设置环境信息,当用户第一次登录时,该文件被执行。也就是说这个文件对每个shell都有效,用于获取系统的环境信息。
# /etc/profile
# System wide environment and startup programs, for login setup
# Functions and aliases go in /etc/bashrc
# It‘s NOT a good idea to change this file unless you know what you
# are doing. It‘s much better to create a custom.sh shell script in
# /etc/profile.d/ to make custom changes to your environment, as this
# will prevent the need for merging in future updates.
②/etc/bashrc:
为每一个运行bash shell的用户执行此文件,当bash shell被打开时,该文件被读取。也就是说,当用户shell执行了bash时,运行这个文件。
# /etc/bashrc
# System wide functions and aliases
# Environment stuff goes in /etc/profile
# It‘s NOT a good idea to change this file unless you know what you
# are doing. It‘s much better to create a custom.sh shell script in
# /etc/profile.d/ to make custom changes to your environment, as this
# will prevent the need for merging in future updates.
③~/.bashrc
该文件存储的是专属于个人bash shell的信息,当登录时以及每次打开一个新的shell时,执行这个文件。在这个文件里可以自定义用户专属的个人信息。
那么在用户登录系统时候,相关的文件执行顺序是什么呢。
在刚登录Linux时,首先启动 /etc/profile 文件,然后再启动用户目录下的 ~/.bash_profile、 ~/.bash_login或 ~/.profile文件中的其中一个,执行的顺序为:~/.bash_profile、 ~/.bash_login、 ~/.profile。如果 ~/.bash_profile文件存在的话,一般还会执行 ~/.bashrc文件。
以上是关于LinuxLinux和Window下 与 的区别git命令行的使用的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章
